Page 528 of 1395
Description
Power Flow (cont'd)
3rd Gear {8. @, or @ position)
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 3rd clutch. Power from the mainshaft 3rd gear is transmitted to the countershaft
3rd gear.
2. Power is transm ifted to the final d rive gear, wh ich d rives the f inal driven gear and the transfer shaft drive gear (4WD).
3, The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transter shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft (4WD).
NOTE:
. Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch, but since the rotation speed of 3rd gear exceeds that of 1st gear,
power from lst gear is cut off at the one-way clutch.
. The illustration shows the 4WD automatic transmission; Dower flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identical
to the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
CONVERTEF
MAINSHAFT 3RD GEAR
COUNTERSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT3RO GEAR
3RD CLUTCH
DRIVEN GEAR
SHAFT DRIVE GEAR (4WO)
TRANSFER SHAFT (,lwDl
TRANSFER ORIVEN GEAN SHAFT (4WD)
14-12
www.emanualpro.com
Page 529 of 1395

4th Goar (E or D positionl
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 4th clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, and the mainshaft 4th gear
rotates,
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 4th gear, which drives the countershaft.
3. Power is transm ifted to the f inal d rive gear, which drives the fina I driven gear and the transfer shaft drive gear (4WD).
4. The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transfer shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft {4WD).
NOTE:
. Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch, but since the rotation speed of 4th gear exceeds that of 1st gear,
power from 1st gear is cut off at the one-way clutch,
. The illustration shows the 4WO automatic transmission; power flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identical
to the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
ilTH GEAR
TOROUE CONVERTER
.TH CLUTCH
COU'{TERSHAFT
REVERSE SELECTOR HUB
REVERSE SELECTOR
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
TRANSFEB SHAFT DRIVE GEAB I'WD)
TNANSFER SHAFT I4WDI{cont'd)
14-13
TMNSFER DRIVEN GEAR SHAFT (4WDI
www.emanualpro.com
Page 530 of 1395
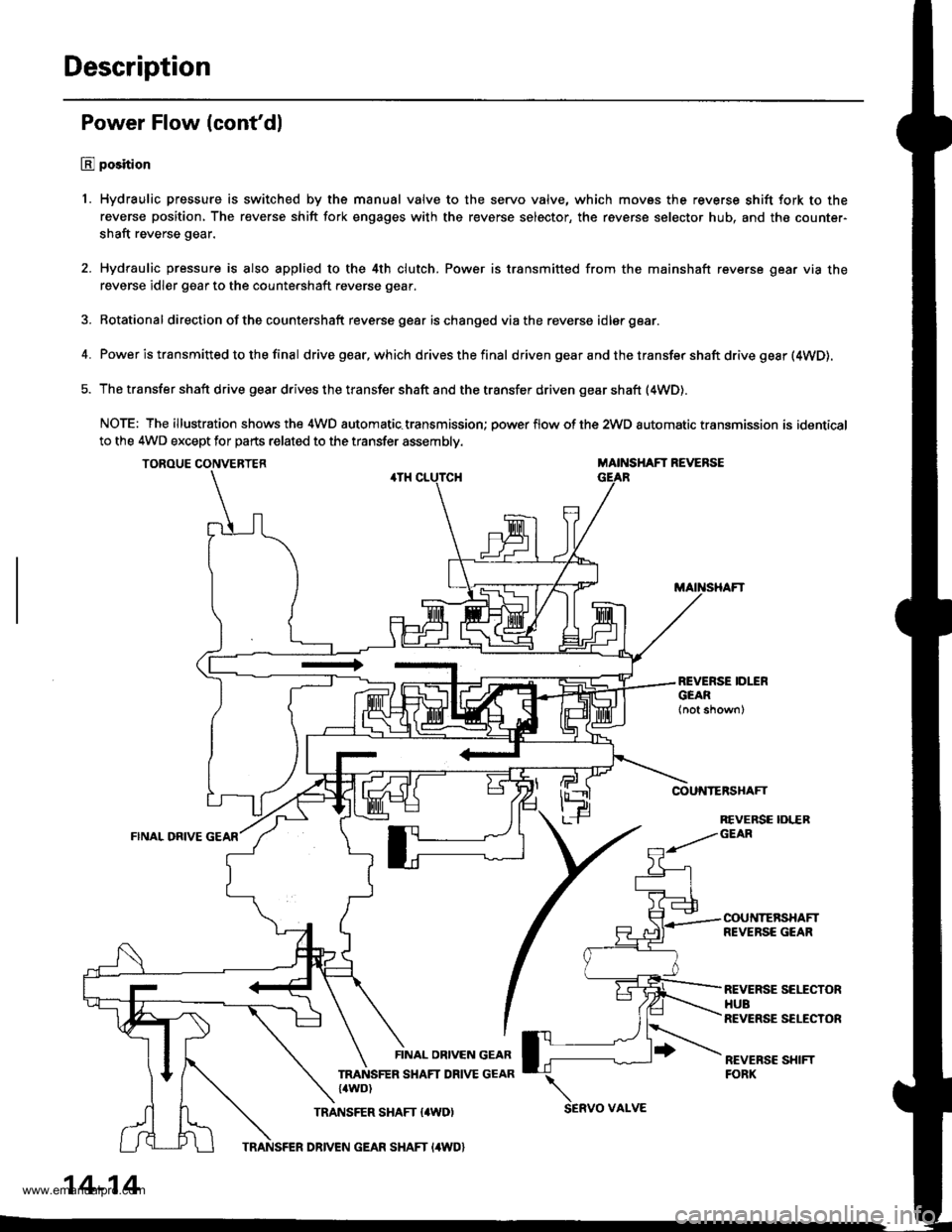
Description
Power Flow (cont'dl
E position
1. Hydraulic pressure is switched by the manual valve to the servo valve, which movss the reverse shift fork to the
reverse position, The reverse shift fork engages with the reverse selector, the reverse selector hub, and the counter-
shaft reverse gear.
2. Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 4th clutch. Power is transmitted from the mainshaft reverse gear via the
reverse idler gear to the countershaft reverse gear.
3. Rotational direction ofthe countershaft reverse gear ischanged viathe reverse idlergear.
4. Power is transmitted to the final drivegear,which drivesthefinal d riven gear a nd the transfer shaft drive gesr (4WD).
5. The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transfer shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft (4WD).
NOTE: The illustration shows the 4WD automatic.transmission; power flow of the 2wD automatic transmission is identical
to the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
TOROUE CONVERTERMAINSHAFT REVERSE
COUNTERSHAFT
FINAL ORIVE
REVERSE IDLERGEAR
COUNTERSHAFTREVERSE GEAR
REVERSE SEITCTORHUBREVERSE SELECTOR
REVEBSC SHIFTFORK
FINAL OBIVEN GEAR
TRANSFER SHAFT DRIVE GEAR{4WD)
TRANSFER SHAFT {4WD)SERVO VAI-VE
14-14
TRANSFER DRIVEN GEAR SHAFT I4WD}
www.emanualpro.com
Page 540 of 1395
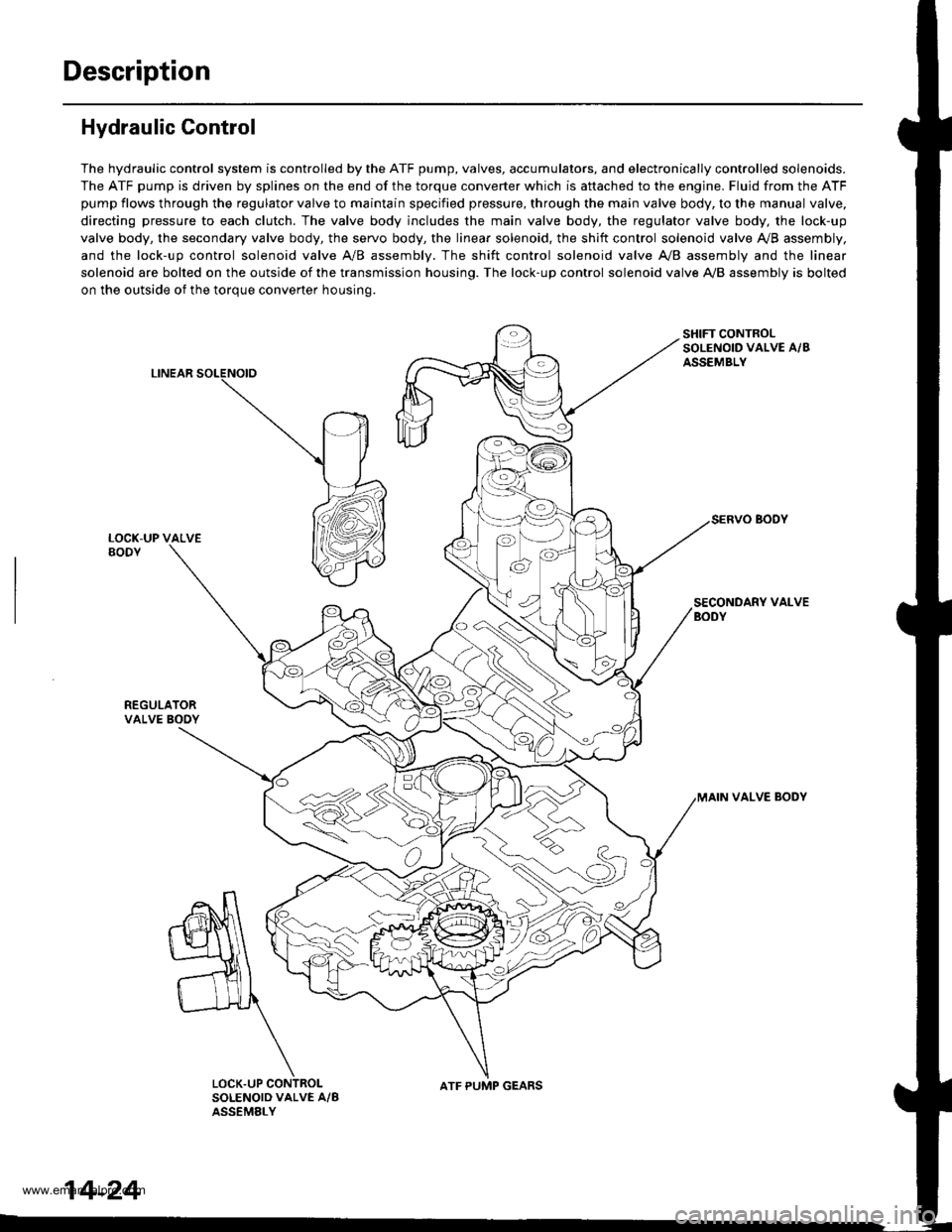
Description
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, accumulators, and electronically controlled solenoids.
The ATF pump is driven by splines on the end of the torque converter which is aftached to the engine. Fluid from the ATF
pump flows through the regulator valve to maintain specified pressure, through the main valve body, to the manual valve,
directing pressure to each clutch. The valve body includes the main valve body, the regulator valve body, the lock-up
valve body, the secondary valve body, the servo body, the linear solenoid, the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B assembly,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve A/B assembly. The shift control solenoid valve A,/B assembly and the linear
solenoid are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing. The lock-up control solenoid valve A,/B assembly is bolted
on the outside of the torque converter housing.
LINEAR
SHIFT CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMBLY
SECONDARY VALVEBODY
REGULATORVALVE BOOY
VALVE BODY
SOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMELY
N
ATF PUMP GEARS
14-24
www.emanualpro.com
Page 541 of 1395
Main Valve Sody
The main valve body houses the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve. the 2nd orifice control valve. the CPB valve, the modu-
lator valve. the servo control valve. and the relief valve. The primary functions of the main valve body are to switch fluid
pressure on and off, and to control the hydraulic pressure going to the hydraulic control system.
CP8 VALVE2ND ORIFICE CONTROLVALVE
MODULATOR VALVE
RELIEF VALVE
1-2 SHIFT VALVE
MANUAL VALVE
MAIN VALVEBOOY
SERVO CONTROI-VALVE
Secondary valve Body
The secondary valve body is located on the main valve body, The secondary valve body houses the 2-3 shift valve, the 3-4
shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve, and the CPC valve'
3.' SHIFT VALVE
.TH EXHAUST VALVE
CPC VAL
(cont'd)
14-25
2.3 SHIFT VALVE
3na ORIFICE CONTROLVALVE
VALVE
www.emanualpro.com
Page 542 of 1395
Description
Hydraulic Control (cont'd)
Regulator Valve Body
The regulator valve body is located on the main valve body. The regulator valve body consists of the regulator vatve, thetorque converter check valve. the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up control valve.
Lock-up Valve Body
The lock-up valve body, with lock-up shift valve and lock-up timing valve, is located on the regulator valve body.
LOCK.UP SHIFT
NMING VALVE
COOLER RELIEF VALVE
VALVE
14-26
www.emanualpro.com
Page 543 of 1395
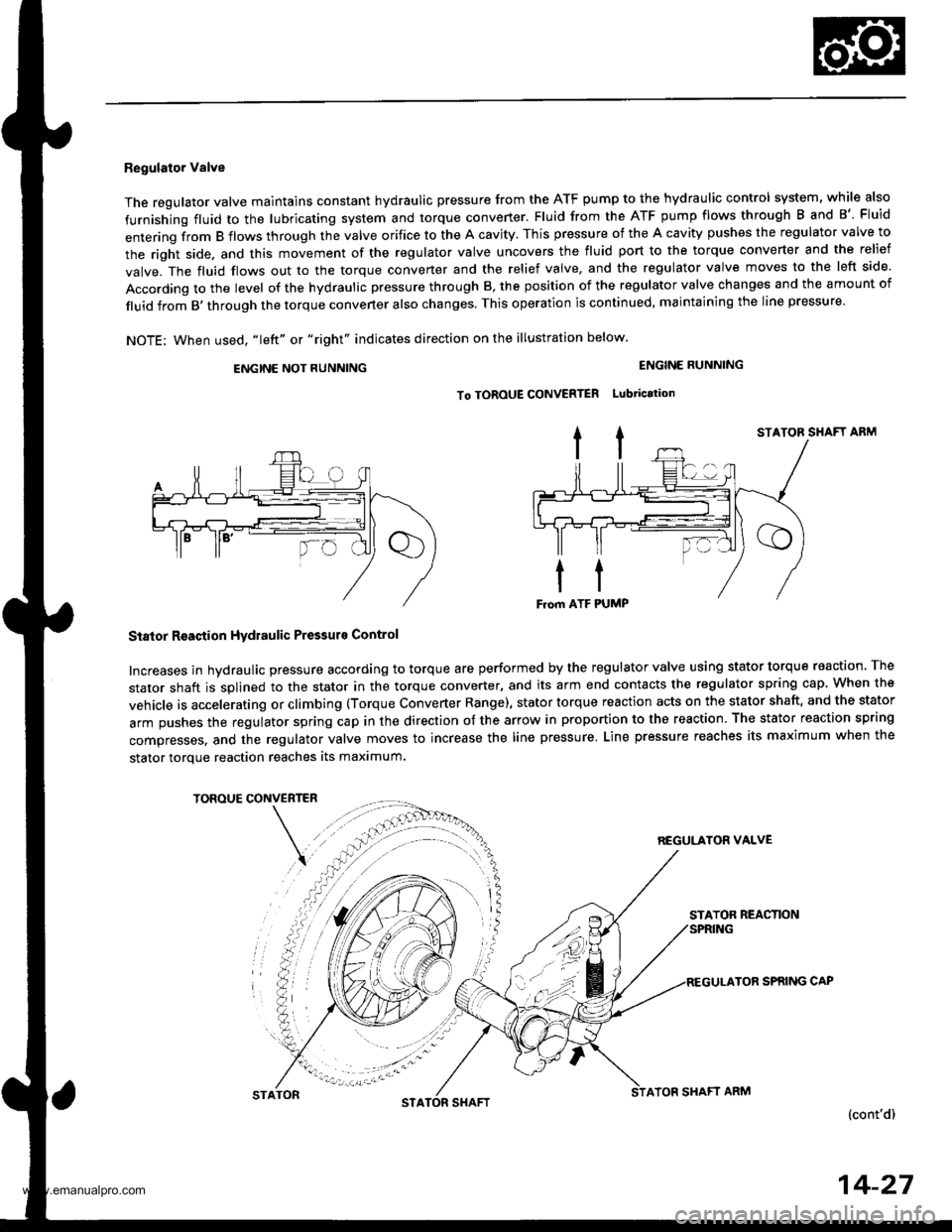
Regulator Valve
The regulator valve maintains constant hydraulic pressure from the ATF pump to the hydraullc control system, while also
furnishing fluid to the lubricating system and torque converter. Fluid from the ATF pump flows through B and B'. Fluid
entering from B flows through the valve orifice to the A cavity. This pressure of the A cavity pushes the regulator valve to
the right side. and this movement of the regulator valve uncovers the fluid port to the torque converter and the relief
valve. The fluid flows out to the torque converter and the relief valve, and the regulator valve moves to the left side.
According to the level of the hydraulic pressure through B, the position of the regulator valve changes and the amount of
fluid from B,through the torque converter also changes. This operation is continued, maintaining the line pressure.
NOTE; When used, "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on the illustration below.
ENGINE NOT RUNNING
STATOR SHAFT ABM
Stator Reaction Hydraulic Pressurs Control
Increases in hydraulic pressure according to torque are performed by the regulator valve using stator torque reaction. The
stator shaft is splined to the stator in the torque converter, and its arm end contacts the regulator spring cap When the
vehicle is accelerating or climbing (Torque Converter Range), stator torque reaction acts on the stator shaft, and the stator
arm pushes the regulator spring cap in the direction of the arrow in proportion to the reaction. The stator reaction spring
compresses, and the regulator valve moves to increase the line pressure. Line pressure reaches its maximum when the
stator torque reaction reaches its maximum.
TOROUE CONVERTER
REGULATON VALVE
STATOR REACTION
TOR SPRING CAP
(cont'd)
ENGINE RUNNING
To TOROUE CONVERTER Lubtication
STATONSTASHAFTATOF SHAFT ARM
14-27
www.emanualpro.com
Page 544 of 1395
Description
Hydraulic Control (cont'd)
Servo Body
The servo body is located on the secondary valve body. The servo body contains the servo valve (which is integrated withthe reverse shift fork), and the accumulators.
2ND ACCUMULATOR
3RD SUBACCUMULATOR
SERVO BODY
1ST ACCUMULATOR
SERVO VALVE/SHIFTFORK SHAFT
14-28
www.emanualpro.com