Page 696 of 2189
Description
Electronic Control System (cont'dl
Circuit Diagram and Terminal Locations -'99 - O0 Models
GNTONSWICH,,--b. rcj
LI
LOCK.UPCONIFOLSOLEI\Q D VALVE A
LOCK UP CON'IROLSOLENODVALVEB
SH FI CONTROL
SHIFTCONTFOLSOLENOIDVALVEE
L NEAF SOLEIOIO
PG2
IGP2
v3u
vcc2
sc2
6NII ON SWICH
14-18
Page 697 of 2189
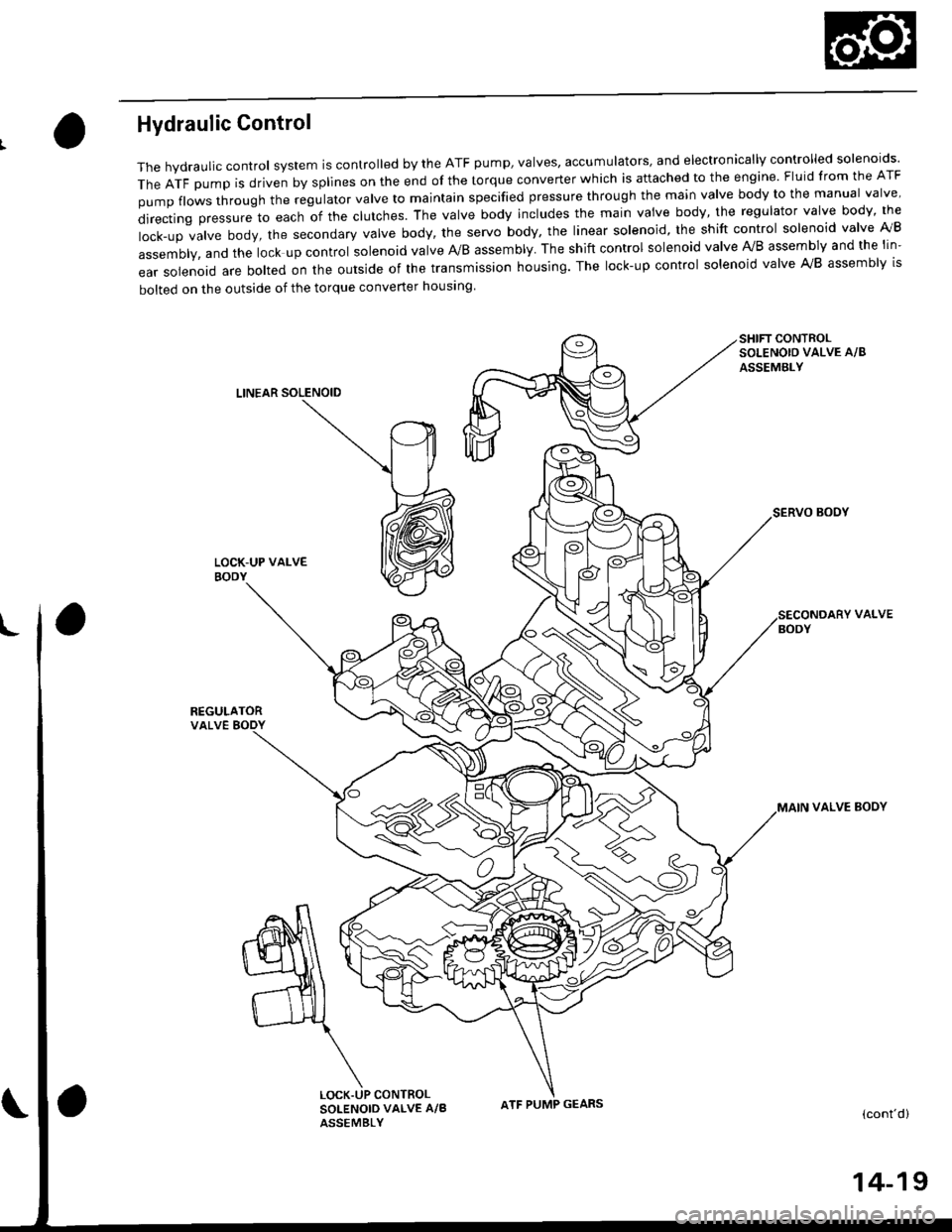
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, accumulators, and electronically controlled solenoids'
TheATFpUmpisdrivenbysp||nesontheendofthetorqueconverterWhichisattachedtotheengine.F|uidfromtheATF
pumpf|owsthroughtheregu|atorva|vetomajntainspecifiedpressurethroughthemainva|vebodytothemanuaIva|ve'
directingpressuretoeachofthec|utches.Theva|vebodyinc|udesthemainvaivebody,theregu|atorvalvebody,the
|ock-upva|vebody,thesecondaryVa|vebody,theservobody,theIinearso|enoid,theshiftcontro|so|enoidva|velVB
assembly, and the lock up control solenoid valve A/B assembly. The shift control solenoid valve Ay'B assembly and the lin-
ear solenoid are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing. The lock-up control solenoid valve A,/B assembly is
bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing
SHIFT CONTROLSOLENOIO VALVE A/8
ASSEMBLY
LINEAR SOLENOID
SERVO BOOY
REGULATORVALVE BODY
VALVE
VALVE BOOY
(cont'd)
CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMBLY
ATF PUMP GEARS
14-19
Page 698 of 2189
Description
Hydraulic Control (cont'dl
Msin Valve Body
The main valve body houses the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve, the 2nd orifice control valve, the cpB valve, the modu-lator valve' the servo control valve, and the relief valve. The primary functions of the main valve body are to swatch fluidpressure on and off and to control the hydraulic pressure going to the hydraulic control svstem.
2ND ORIFICE CONTROTVALVE
1-2 SHIFT VALVE
RELIEF VALVE
CPC VAL
3-4 SHTFT V
VALVE
Socondary Valve Body
The secondary valve body is located on the main valve body. The secondary valve body houses the 2-3 shift vatve, the 3-4shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve, and the CpC valve.
CONTROL
2.3 SHIFT VALVE
4TH EXHAUST VALV€
VALVE
14-20
VALVE
Page 700 of 2189

Description
Hydraulic Control (cont'dl
Regulator Valve
The regulator valve maintains a constant hydraulic pressure from the ATF pump to the hydraulic control system, whitealso furnishing fluid to the lubricating system and torque converter. The fluid from the ATF pump flows through B and 8,.The regulator valve has a valve orifice. The fluid entering from B flows through the orifice to the A cavity. This pressure ofthe A cavity pushes the regulator valve to the right side, and this movement of the regulator valve uncovers the fluid portto the torque converter and the relief valve. The fluid flows out to the torque converter, and the relief valve and regulatorvalve moves to the left side. According to the level of the hydraulic pressure through B, the position of the regutator vatvechanges and the amount of the fluid from B' through D and c also changes. This operation is continued. maantaining theline pressure,
NOTE: When used. "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on the illustration betow.
ENGINE NOT RUNNING
TOROUE CONVERTER
ENGINE RUNNING
To TOROUE CONVERTER Lubrication
Stator Roaction Hydraulic Prossur6 Control
Hydraulic pressure increases according to torque, are performed by the regulator valve using the stator torque reaction.The stator shaft is splined with the stator in the torque converter, and its arm end contacts the regulator sprang cap. whenthe vehicle is accelerating or climbing (Torque Convert€r Range), the stator torque reaction acts on the stator shaft, andthe stator arm pushes the regulator spring cap in the direction of the arrow in proponion to the reaction. Jne stator reac-tion spring compresses, and th€ reoulator valve moves to increase the line pressure which is regulated by the regulatorvalve. The line pressure reaches its maximum when the stator torque reaction reaches its maximum.
STATOR SHAFT ARM
REGULATOR VALVE
14-22
STATORATOR SHAFT ARM
SPRING CAP
Page 712 of 2189

Description
Lock-up System (cont'd)
TOROUE CONVERTER
In B.rl position, in 3rd and 4th, and lDl_- position in 3rd.pressurized fluid is drajned from the back of the torqueconverter through a fluid passage. causing the lock-uppiston to be held against the torque convener cover. Asthis takes place, the mainshaft rotates at the same speedas the engine crankshaft, Together with the hydrauliccontrol, the PCM optimized the timing of the lock_upsystem. Under certain conditions, the lock_up clutch isapplied during deceleration, in 3rd and 4th gear.
The lock-up system controls the range of lock_up accord_ing to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B. and thelinear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves Aand B activate, modulator pressure changes. Lock_upcontrol solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoidare mounted on the outside of the torque converterhousing. and are controlled by the pclvl.
Lock-up Conditions/Lock-up Control Solenoid Valves/Linear Solenoid Pressure
MODULATOR PRESSURE
.-- LINEAR SOLENOID PRESSURE
LOCK.UP CONTROL. VALVE
LOCK.UP CONTROLSOLENOID VALVELock-up
Conditions
Lock-up Control
Solenoid ValveLineal
Solenoid
PressureAB
Lock-up OFFOFFOFFHig h
Lock-up. HalfONDuty operation
OFF - ON
Lock-up. FullONONHigh
Lock-up
during
decelerationONDuty operation
OFF * ONLowTOROUE CONVERTERCHECI( VALVE
RELIEF VAI-VE
LOCK.UP TIMINGVALVE
^ r______rr r cooLER RELTEF VALVE
t'-
14-34
ATF PUMP
Page 714 of 2189
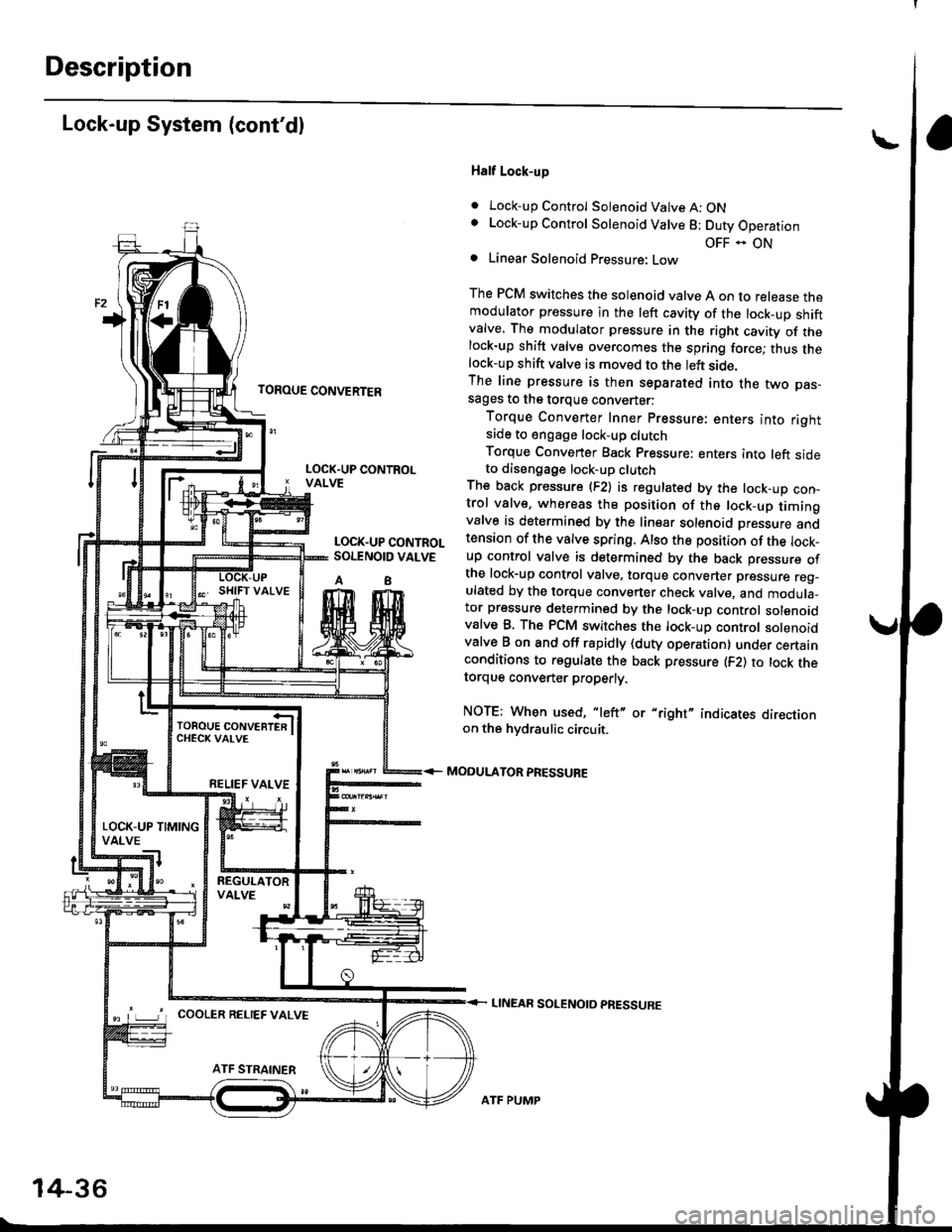
Description
Lock-up System (cont'dl
TOROUE CONVERTER
Half Lock-up
. Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve A: ONLock-up Control Solenoid Valve 8: Duty Operation
OFF - ONLinear Solenoid Pressure: Low
The PCM switches the solenoid valve A on to release themodulator pressure in the left cavity of the lock_up shiftvalve. The modulator pressure in the right cavity of thelock-up shift valve overcomes the spring force; thus thelock-up shift valve is moved to the left side.The line pressure is then separated into the two pas-sages to the torque converter:
Torque Converter Inner pressure: enters into rightsade to engage lock-up clutch
Torque Converter Back pressure: enters into left sideto diseogage lock-up clutchThe back pressure (F2) is regulated by the lock-up con-trol valve, whereas the position of the lock-up timingvalve is determined by the linear solenoid Dressure andtension of the valve spring. Also the position of the lock_up control valve is determined by the back pressure ofthe lock-up control valve, torque converter pressure reg_ulated by the torque converter check valve, and modula_tor pressure determined by the lock-up control solenoidvalve B. The PCM switches the lock-up control solenoidvalve B on and off rapidly {duty operation} under certainconditions to regulate the back pressure (F2) to lock thetorque convener properly.
NOTE: When used, "left" or "right" indicates directionon the hvdraulic circuit.
MODULATOR PRESSURE
LINEAR SOLENOTD PRESSURE
LOCK.UP CONTROLVALVE
LOCK.UP CONTROLSOI.TNOID VALVE
A8
TOROUE CONVERTERCHECK VAI-VE
RELIEF VALVE
LOCK-UP TIMINGVALVE
^ L____J'r cooLER RELTEF valvE
14-36
ATF PUMP
Page 716 of 2189
Description
Lock-up System (cont'dl
TOROUE CONVERTER
Deceleration Lock-up
. Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve A: ON. Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve B: Duty Operation
OFF - ONa Linear Solenoid Pressure: Low
The PCM switches solenoid valve B on and off rapidly
under certain conditions. The slight lock-up and half
lock-up regions are maintained so as to lock the torque
converter properly.
NOTE: When used, "left" or "right" indicates direction
on the hydraulic circuit,
MOOULATOR PRESSURE
LINEAR SOLENOID PRESSURE
LOCK-UP CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE
RELIEF VALVE
LOCK.UP TIMINGVALVE
COOLER RELIEF VALVE
ATF STRAINER
1434
ATF PUMP
Page 720 of 2189
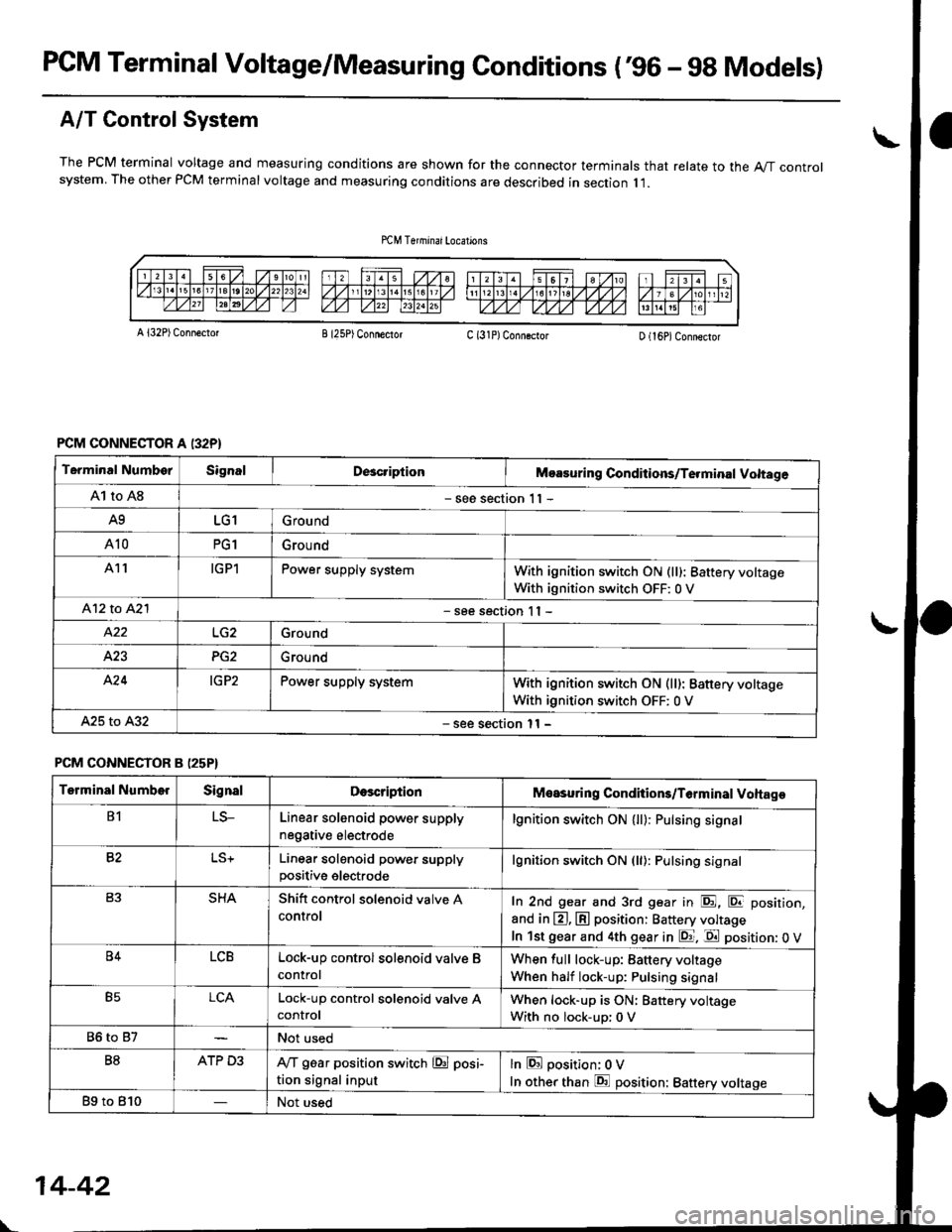
PCM Terminal Voltage/Measuring Gonditions ('96 - 9g Models)
A/T Control System
The PCM terminal voltage and measuring conditions are shown for the connector terminals that relate to the A"/T controlsystem. The other PCM terminal voltage and measuring conditions are described in section I l.
A l32P) Conn€ctotB I25P) ConnectorC (31P)ConngctorD (16P)Connector
PCM CONNECTOR A I32P}
Terminal NumborSignalDcacriptionMoasuring Conditions/Te.minal Voltage
A1 to A8- see section 1 I -
A9LG1Ground
A10PG1Grou nd
A11IGPlPower supply systemWith ignition switch ON (ll): 8attery voltage
With ignition switch OFF: 0 V
412 to A2l- see section I I -
Ground
423PG2Ground
A'24IG P2Power supply systemWith ignition switch ON (ll): Battery voltage
With ignition switch OFF: 0 V
A25 to A32- see section l1 -
PCM CONNECTOR B (25P}
Terminal NumberSignalDescriptionMeasuring Conditions/T6rminal Voltage
B1LS-Linear solenoid power supply
negative electrode
lgnition switch ON (ll): Pulsing signa.
82Linear solenoid power supplypositive electrode
lgnition switch ON (ll): Pulsing signal
SHAShitt control solenoid valve A
controlIn 2nd gear and 3rd gear in E, E position,
and in @, @ position: Battery voltage
In lst gear and 4th gear in E. E position: 0 V
B4LCBLock-up control solenoid valve B
control
When full lock-up: Battery voltage
When half lock-up: Pulsing signal
B5LCALock-up control sol€noid valve AcontrolWhen lock-up is ON: Battery voltage
With no lock-up: 0 V
86 to 87Not used
B8ATP D3IVT g6ar position switch @ posi-
tion signal input
lnEposition; OV
In other than E position: Battery voltage
Bg to 810Not used
\-
14-42