1998 HONDA CIVIC crank
[x] Cancel search: crankPage 472 of 2189

\
Starter Switch Signal ('99 - 00 Models except Dl6Y5 engine with M/T)
NOTE:. M/f: Clutch pedal must be depressed.. A,/T: Transmission in E or E position
ECM,/PCM CONNECTORS
I
This signals the ECM/PCM when the engine is cranking
Ch€ck for an open or short in the
wire {STS linel:Measure voltage between ECM/PC[/| connector terminals A24
and 820 with the ignition switch
in the start position (lll).
Inspect the No.31 STARTER SIG-NAL (7.5 Alluse in the under-dash
- Repair 3hort in tho wire be'
tween tho ECM/PCM lA24)and tho No. 31 STARTER SIG-NAL 17.5 Al fuse or the PGM-FImein relay.- ReDlaco the No. 31 STARTERSIGNAL 17.5 Al fuse.
Staner 3witch signal is OK.
Repair open in the wirc betwean
the ECM/PCM lA24) and the No.
31 STARTER SIGNAL {7.5 Alfuse.
W;re side of female terminals
Page 521 of 2189
Emission Gontrol System
System Description
The emission control system includes a Three Way Cata-lytic Convener (TWC), Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
system,. Positive Crankcase Ventilation (pCV) system andEvaporative Emission (EVAP) Control system. The emis-sion control system is designed to meet federal and stateemission standards.*: D16Y5 engine
Tailpipe Emission
Inspestion
@@ Do not smoke during ihis procedure. Keepany open flame away from your work area.
1. Start the engine. Hold the engine at 3,000 rpm withno load (in Park or neutral) until the radiator fancomes on. then let it idle.
2. Connect a tachometer.
Check and, if necessary, adjust the idle speed (see
page 11-220 - 223).
Warm up and calibrate the CO meter according to themeter manufacturer's instructions.
Check idle CO with the headlights, heater blower,rear window defogger, cooling fan, and air condition-er off.
NOTE: (Canada) Pull the parking brake lever up.Start the engine, then check that the headlights areoff.
CO mete. should indicate 0.1% maximum.
NOTE: '98 Dl6Y5 engine - lf the idle speed incress-es to 8101 50 rpm, this means the EVAp system ispurging the canister. To stop the purging temporari-ly. raise the engine speed above 1,000 rpm with theaccelerator pedal, then slowly release the pedal.
11-252
eFORWARD -
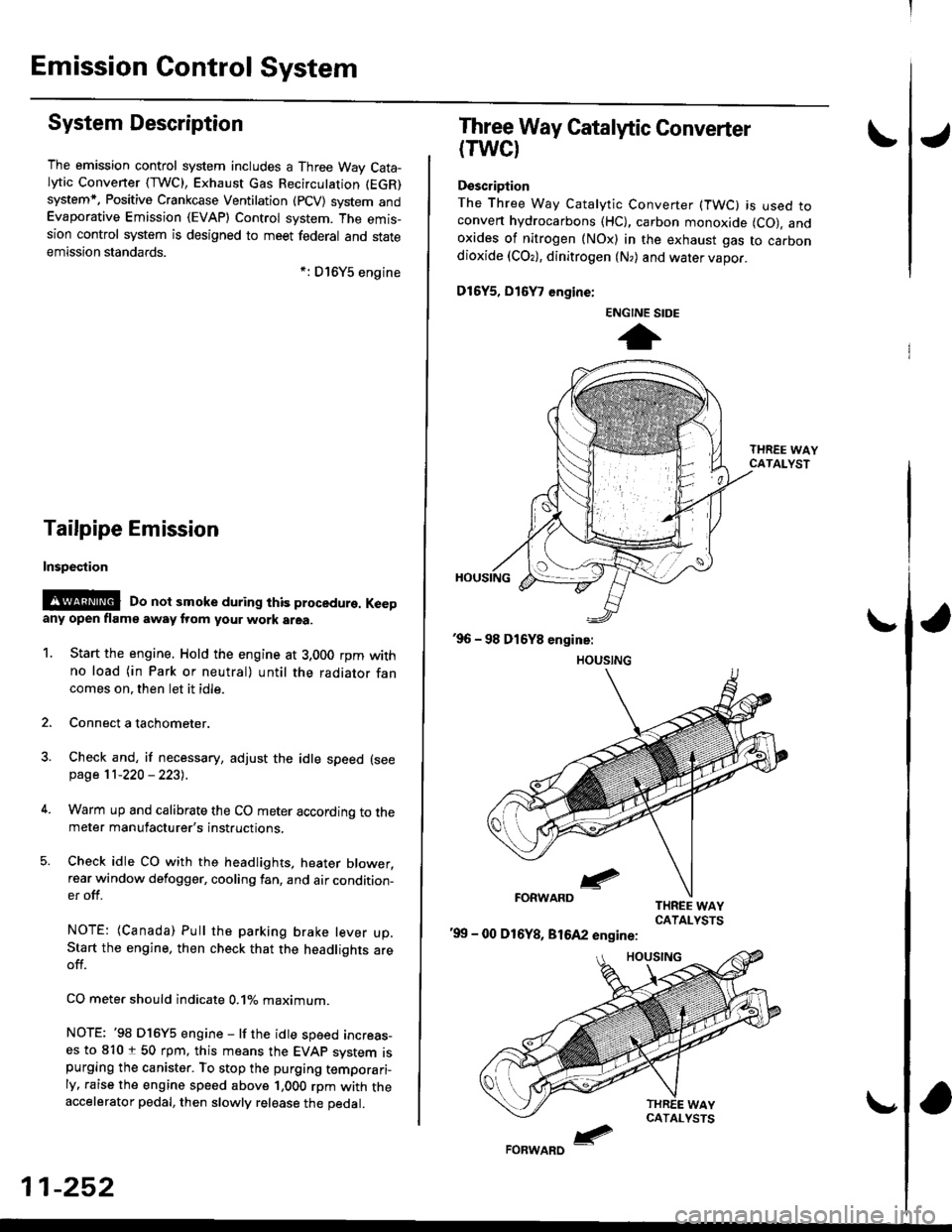
Three Way Catalytic Converter
(TWCI
Doscription
The Three Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) is used toconven hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), andoxides of nitrogen (NOx) in the exhaust gas to carbondioxide (COr), dinitrogen (N,) and water vapor.
D15Y5, D16
, engine:
'99 - 00 D16Y8, 81642 engine:
ENGINE SIDE
t
Page 535 of 2189

Emission Control System
Positive Crankcase Ventilation IPCVI System
Descripiion
The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system is
designed to prevent blow-by gas from escaping to the
atmosphere. The PCV valve contains a spring-loaded
plunger. When the engine starts, the plunger in the PCV
valve is lifted in proportion to intake manifold vacuum
and the blow-by gas is drawn directly into the intake
manifold.
D15Y5, D16Y8, 816A2 ongins:
BREATHERHOSE
Dl6'|11 6ngin6:
-: aLOW-BY VAPOR-: FnESH AIF
11-266
tJ
lrcpection
1. Check the PCV hoses and connections for leaks and
clogging.
2. At idle, make sure there is a clicking sound from the
PCV valve when the hose between the PCV valve
and the intake manifold is lightly pinched with your
fingers or pliers,
D16Y5, D16Y8 ongins:
BREATHERHOSE
PCV VALVE
Gently pinch here.
Bl6A2 engins:VALVE
lf there is no clicking sound, check the PCV valve
grommet for cracks and damage. If the grommet is
OK, replace the PCV valve and recheck.
PCV
Page 576 of 2189
Flywheel
\Inspection
1.
2.
3.
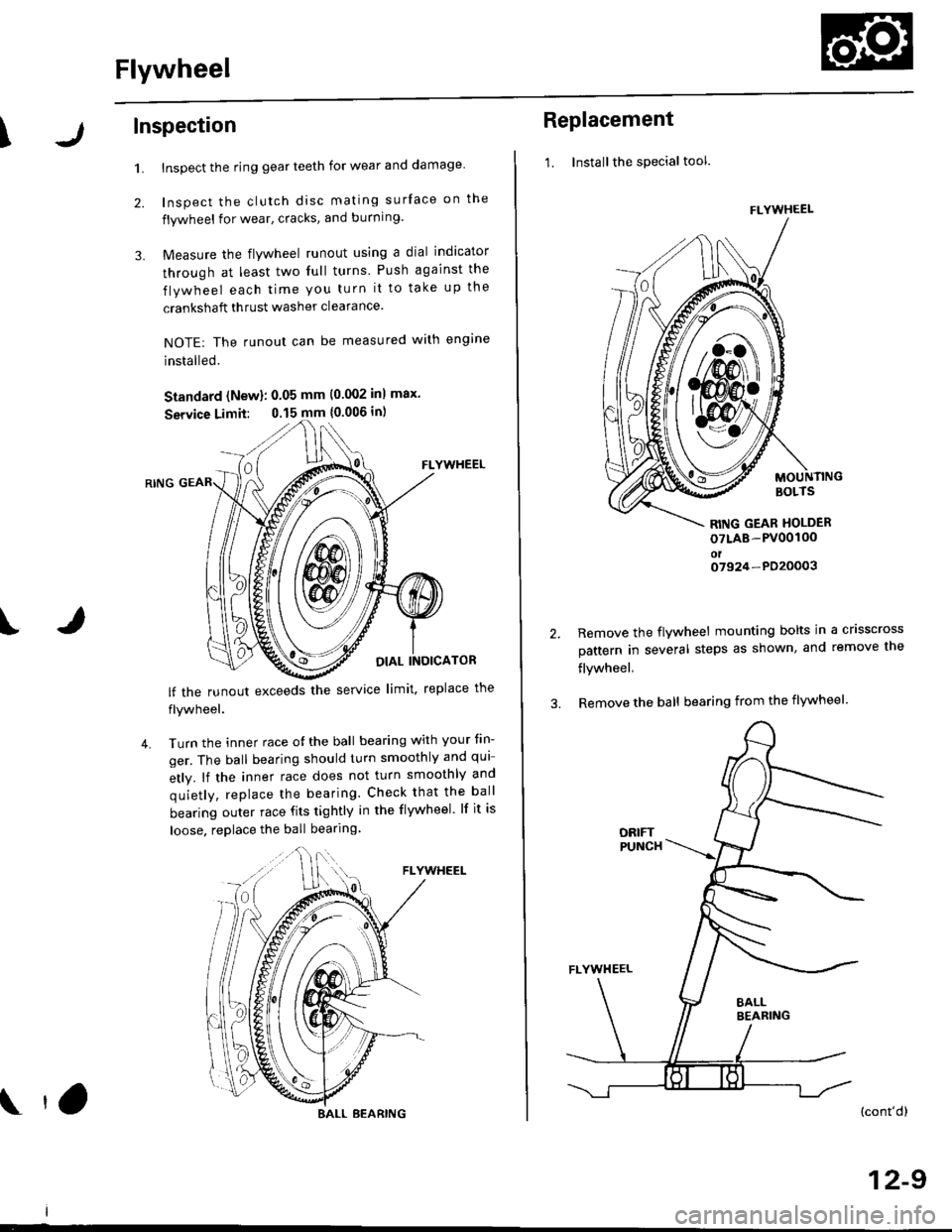
Inspect the ring gear teeth for wear and damage
Inspect the clutch disc mating surface on the
flywheel for wear, cracks, and burning.
Measure the flywheel runout using a dial indicator
through at least two full turns Push against the
flywheel each time you turn it to take up the
crankshaft thrust washer clearance.
NOTE: The runout can be measured with engine
installed.
Standard (New): 0.05 mm (0.002 inl max.
Service Limit: 0.15 mm {0.006 in)
FLYWHEEL
OIAL INOICATOR
FLYWHEEL
lf the runout exceeds the service limit. replace the
flywheel.
Turn the inner race o{ the ball bearing with your tin-
ger. The ball bearing should turn smoothly and qui
etly. lf the inner race does not turn smoothly and
quietly, replace the bearing. Check that the ball
bearing outer race fits tightly in the flywheel. lf it is
loose. replace the ball bearing
IJ
4.
BALL BEARING tO
Replacement
1. Installthe special tool.
MOUNTINGBOLTS
RITIG GEAR HOLDER
oTLAB-PV00100oto7924-PD20003
2.Remove the flywheel mounting bolts in a crisscross
pattern in several steps as shown, and remove the
flywheel,
Remove the ball bearing from the flywheel
(cont'dl
12-9
FLYWHEEL
t\
m\J
Page 577 of 2189

FlywheelClutch Disc, Pressure Plate
Replacement (cont'dl
4. Drive the new ball bearing into the flywheel using
the special tools as shown.
DRIVER07749-0010000
ATTACHMENT,32x35mm07746-OOIOTOO
FLYWHEEL
BEARING
Align the hole in the flywheel with the crankshaft
dowel pin and install the flywheel. Install the
mounting bolts finger-ti9ht.
Install special tool, then torque the flywheel mount-
ing bolts in a crisscross pattern in several steps as
snown.
5.
6.
MOUNTING BOLTS118 N.m (12.0 kgl.m,87 tbf.ft)
RING GEAR HOLDER07LAB-PV00100ol07924 -PO20003
WVa// ,
12-10
Installation
1. Install the special tool.
Y
07936-3710r00
{P/N 08798-90021
RING GEAR HOLDER07LAB-PVOO100ot07924-PD20003
CLUTCH ALIGNMENT SHAFTOTJAF_PM7012A
2.
3.
Installthe clutch disc using the special tools.
Install the pressure plate.
RING GEAR HOLDERoTLAB PV00'l OO
07924 PD20003
OTJAF_PM70124HANOLE07936-3710100
CLUTCH DISC
Page 681 of 2189

Description
The automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides
4 soeeds forward and 1 reverse.
Torque Convertel, Geats, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator, assembled in a single unit. They are connected to the engine
crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is a ring gear
which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started. The entire torque converter assembly seryes as a
flywheel while transmiuing power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in Iine with the engine
crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd and 4th clutches, gears tor 2nd, 4th, reverse and lst (3rd gear is integral
with the mainshaft, while the reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch, and
gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse. 1st and park. The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the counter-
shaft. When certain combinations of gears in transmission are engaged by clutches. power is transmitted from the main-
shaft to the countershaft to provide E, ld, E, and E positions.
Electronic Control
The electronic control svstem consists of the Powertrain Control Module {PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four
solenojd valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comtonable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main vatve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body and the
lock-up valve body through the respective separator plates, They are bolted on the torque converter housang
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve. the 2nd orifice control valve, the CPB {Clutch Pressure
Back-up) valve, the modulator valve. the servo control valve, the relief valve, and ATF pump gears The secondary valve
body contains the 2-3 shift valve. the 3-4 shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch
pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve,
the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up control valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the
reverse shift fork, and the accumulators. The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing
valve. The linear solenoid and the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid from regulator
passes through the manual valve to the various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective teed pipes
or internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will activate
Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes a line
to one of the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear, The shift control solenoid valves A and B are con-
trolled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
In ,Dt1 position, in 3rd and 4th. and in E position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter
through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the PCM optimizes the timing of
the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and
B, and linear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes The lock-
up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
(cont'd)
14-3
Page 712 of 2189

Description
Lock-up System (cont'd)
TOROUE CONVERTER
In B.rl position, in 3rd and 4th, and lDl_- position in 3rd.pressurized fluid is drajned from the back of the torqueconverter through a fluid passage. causing the lock-uppiston to be held against the torque convener cover. Asthis takes place, the mainshaft rotates at the same speedas the engine crankshaft, Together with the hydrauliccontrol, the PCM optimized the timing of the lock_upsystem. Under certain conditions, the lock_up clutch isapplied during deceleration, in 3rd and 4th gear.
The lock-up system controls the range of lock_up accord_ing to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B. and thelinear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves Aand B activate, modulator pressure changes. Lock_upcontrol solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoidare mounted on the outside of the torque converterhousing. and are controlled by the pclvl.
Lock-up Conditions/Lock-up Control Solenoid Valves/Linear Solenoid Pressure
MODULATOR PRESSURE
.-- LINEAR SOLENOID PRESSURE
LOCK.UP CONTROL. VALVE
LOCK.UP CONTROLSOLENOID VALVELock-up
Conditions
Lock-up Control
Solenoid ValveLineal
Solenoid
PressureAB
Lock-up OFFOFFOFFHig h
Lock-up. HalfONDuty operation
OFF - ON
Lock-up. FullONONHigh
Lock-up
during
decelerationONDuty operation
OFF * ONLowTOROUE CONVERTERCHECI( VALVE
RELIEF VAI-VE
LOCK.UP TIMINGVALVE
^ r______rr r cooLER RELTEF VALVE
t'-
14-34
ATF PUMP
Page 803 of 2189

19. Remove the engine stiffener and the torque con-
verter cover.
Remove the eight drive plate bolts one at a tlme
while rotating the crankshaft pulley.
Remove the distributor.
Attach a hoisting bracket to the engine, then lift the
engine slightly.
HOISTBRACKET
20.
21.
COVER
23. Place a jack under the transmission. and ra6a :'.
transmission iust enough to take weight otf ol tF.
mounts. then remove the transmission mounl
TRANSMISSIONMOUNT BRACKET
Remove the transmission housing mounting bolts
and the rear engine mounting bolts.
Pull the transmission away from the engine until it
clears the 14 mm dowel pins, then lower it on the
transmission jack.
TRANSMISSION HOUSING
lf necessary, remove the torque converter anc:"
starter motor.
24.
25.
1+16