1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Temperature sensor 5.9
[x] Cancel search: Temperature sensor 5.9Page 345 of 2627

ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLANT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLANT.......31
DESCRIPTION - HOAT COOLANT.........32
OPERATION...........................33
COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER- GAS
ENGINES
DESCRIPTION.........................33
OPERATION...........................33
REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................33
RADIATOR FAN - GAS ENGINES
REMOVAL.............................33
CLEANING............................34
INSPECTION..........................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
RADIATOR FAN - 5.9L DIESEL
REMOVAL.............................35
CLEANING............................35
INSPECTION..........................35
INSTALLATION.........................36
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
DESCRIPTION.........................36
OPERATION...........................36
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE BLOCK
HEATER ............................36
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................37
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER - 5.9L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION.........................37
OPERATION...........................38
REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................38
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................38
OPERATION...........................38
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................41
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT- 5.7L
DESCRIPTION.........................41
OPERATION...........................41
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐTHERMOSTAT . . . 42
REMOVAL.............................42
INSTALLATION.........................43
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - 3.7L/4.7L
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐTHERMOSTAT . . . 44
REMOVAL.............................45INSTALLATION.........................45
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - 5.9L
DIESEL
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - THERMOSTAT . . . 47
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - 8.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................48
OPERATION...........................48
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - THERMOSTAT . . . 48
REMOVAL.............................49
INSTALLATION.........................49
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH-GAS ENGINES
DESCRIPTION.........................50
OPERATION...........................50
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VISCOUS FAN
DRIVE..............................50
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH - 5.9L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION.........................52
OPERATION...........................52
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED VISCOUS
FAN DRIVE..........................52
RADIATOR-3.7L/4.7L/5.7L
DESCRIPTION.........................54
OPERATION...........................54
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RADIATOR
COOLANT FLOW......................54
REMOVAL.............................54
CLEANING............................55
INSPECTION..........................55
INSTALLATION.........................55
RADIATOR - 5.9L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION.........................56
OPERATION...........................56
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RADIATOR
COOLANT FLOW......................56
REMOVAL.............................56
CLEANING............................56
INSPECTION..........................56
INSTALLATION.........................57
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
DESCRIPTION.........................57
OPERATION...........................58
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RADIATOR
CAP-TO-FILLER NECK SEAL.............58
7 - 30 ENGINEDR
Page 353 of 2627

OPERATION
The heater warms the engine coolant providing
easier engine starting and faster warm-up in low
temperatures. Connecting the power cord to a
grounded 110-120 volt AC electrical outlet with a
grounded three wire extension cord provides the elec-
tricity needed to heat the element.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Drain coolant from radiator and cylinder block
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(3) Unscrew the power cord retaining cap and dis-
connect cord from heater element.
(4) Using a suitable size socket, loosen and remove
the block heater element (Fig. 9).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean and inspect the threads in the cylinder
block.
(2) Coat heater element threads with Mopart
Thread Sealer with Teflon.
(3) Screw block heater into cylinder block and
tighten to 55 N´m (41 ft. lbs.).
(4) Connect block heater cord and tighten retain-
ing cap.
(5) Fill cooling system with recommended coolant
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(6) Start and warm the engine.
(7) Check block heater for leaks.
ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is
used to sense engine coolant temperature. The sensor
protrudes into an engine water jacket.
The ECT sensor is a two-wire Negative Thermal
Coefficient (NTC) sensor. Meaning, as engine coolant
temperature increases, resistance (voltage) in the
sensor decreases. As temperature decreases, resis-
tance (voltage) in the sensor increases.
OPERATION
At key-on, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
sends out a regulated 5 volt signal to the ECT sensor.
The PCM then monitors the signal as it passes
through the ECT sensor to the sensor ground (sensor
return).
When the engine is cold, the PCM will operate in
Open Loop cycle. It will demand slightly richer air-
fuel mixtures and higher idle speeds. This is done
until normal operating temperatures are reached.
The PCM uses inputs from the ECT sensor for the
following calculations:
²for engine coolant temperature gauge operation
through CCD or PCI (J1850) communications
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance curves
²ASD relay shut-down times
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor key-on steps
²Pulse-width prime-shot during cranking
²O2 sensor closed loop times
²Purge solenoid on/off times
²EGR solenoid on/off times (if equipped)
²Leak Detection Pump operation (if equipped)
²Radiator fan relay on/off times (if equipped)
²Target idle speed
Fig. 8 Engine Block Heater ± 5.9L Diesel Engine
1 - BLOCK HEATER
Fig. 9 Block Heater - 5.9L Diesel Engine
1 - BLOCK HEATER
7 - 38 ENGINEDR
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 355 of 2627

5.9L Diesel
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor on
the 5.9L diesel engine is located near the thermostat
housing (Fig. 14).WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. COOLING SYSTEM
MUST BE PARTIALLY DRAINED BEFORE REMOV-
ING THE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR.
(1) Partially drain the cooling system.
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
sensor.
(3) Remove the sensor from the cylinder head.
8.0L V-10
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor on
the 8.0L V-10 engine is threaded into the thermostat
housing (Fig. 15).
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. COOLING SYSTEM
MUST BE PARTIALLY DRAINED BEFORE REMOV-
ING THE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR.
(1) Partially drain the cooling system.
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
sensor.
(3) Remove the sensor from the cylinder head.
Fig. 12 ECT LOCATION - 5.7L V-8
1 - TOP OF AIR CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR
2 - ECT SENSOR LOCATION
Fig. 13 ECT REMOVE / INSTALL 5.7L V-8
1 - FRONT OF INTAKE MANIFOLD
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - ECT SENSOR
Fig. 14 ECT LOCATION - 5.9L DIESEL
1 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - ECT SENSOR
7 - 40 ENGINEDR
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 356 of 2627

INSTALLATION
3.7L V-6
(1) Apply thread sealant to sensor threads.
(2) Install sensor to engine.
(3) Tighten sensor to 11 N´m (8 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
(5) Replace any lost engine coolant. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
4.7L V-8
(1) Apply thread sealant to sensor threads.
(2) Install sensor to engine.
(3) Tighten sensor to 11 N´m (8 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
(5) Replace any lost engine coolant. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
5.7L V-8
(1) Apply thread sealant to sensor threads.
(2) Install sensor to engine.
(3) Tighten sensor to 11 N´m (8 ft. lbs.) torque.(4) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
(5) Replace any lost engine coolant. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
5.9L Diesel
(1) Install sensor to engine.
(2) Tighten sensor to 18 N´m (13 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
(4) Replace any lost engine coolant. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
8.0L V-10
(1) Apply thread sealant to sensor threads.
(2) Install sensor to engine.
(3) Tighten sensor to 11 N´m (8 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
(5) Replace any lost engine coolant. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT- 5.7L
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: Do not operate an engine without a ther-
mostat, except for servicing or testing.
The thermostat on the 5.7L gas powered engine is
located behind the thermostat housing at the front of
the intake manifold (Fig. 16).
The thermostat is a wax pellet driven, reverse pop-
pet choke type.
Coolant leakage into the pellet container will cause
the thermostat to fail in the open position. Thermo-
stats very rarely stick. Do not attempt to free a ther-
mostat with a prying device.
The same thermostat is used for winter and sum-
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with-
out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes longer engine
warmup time, unreliable warmup performance,
increased exhaust emissions and crankcase condensa-
tion that can result in sludge formation.
OPERATION
The wax pellet is located in a sealed container at
the spring end of the thermostat. When heated, the
pellet expands, overcoming closing spring tension
and water pump pressure to force the valve to open.
Fig. 15 ECT SENSOR - 8.0L V-10
1 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMP. SENSOR (FOR PCM)
2 - HEATER SUPPLY FITTING
3 - BOLTS (6)
4 - HOUSING WITH INTEGRAL SEAL
5 - THERMOSTAT
6 - RUBBER LIP SEAL
7 - TEMP. GAUGE SENDING UNIT
DRENGINE 7 - 41
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 363 of 2627

(7) Start the engine and check for coolant leaks.
Run engine to check for proper thermostat operation.
ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT - 8.0L
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: Do not operate an engine without a ther-
mostat, except for servicing or testing.
The thermostat on all gas powered engines is
located beneath the thermostat housing at the front
of the intake manifold (Fig. 27).
The thermostat is a moveable sleeve type.
Coolant leakage into the pellet container will cause
the thermostat to fail in the open position. Thermo-
stats very rarely stick. Do not attempt to free a ther-
mostat with a prying device.
The same thermostat is used for winter and sum-
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with-
out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes longer engine
warmup time, unreliable warmup performance,
increased exhaust emissions and crankcase condensa-
tion that can result in sludge formation.
OPERATION
The wax pellet is located in a sealed container at
the spring end of the thermostat. When heated, the
pellet expands, overcoming closing spring tension
and water pump pressure to force the valve to open.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - THERMOSTAT
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
Allgasoline powered modelsare equipped with
On-Board Diagnostics for certain cooling system com-
ponents. Refer to On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) in the
Diagnosis section of this group for additional infor-
mation. If the powertrain control module (PCM)
detects low engine coolant temperature, it will record
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in the PCM mem-
ory. Do not change a thermostat for lack of heat as
indicated by the instrument panel gauge or by poor
heater performance unless a DTC is present. Refer to
the Diagnosis section of this group for other probable
causes. For other DTC numbers, (Refer to 25 - EMIS-
SIONS CONTROL - DESCRIPTION).
Fig. 26 Thermostat Removal/Installation
1 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
2 - CYLINDER HEAD
3 - THERMOSTAT
Fig. 27 Thermostat - 8.0L V-10 Engine
1 - COOLANT TEMP. SENSOR (FOR PCM)
2 - HEATER SUPPLY FITTING
3 - BOLTS (6)
4 - HOUSING WITH INTEGRAL SEAL
5 - THERMOSTAT
6 - RUBBER LIP SEAL
7 - TEMP. GAUGE SENDING UNIT
7 - 48 ENGINEDR
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 368 of 2627

LEAKS
Viscous fan drive operation is not affected by small
oil stains near the drive bearing. If leakage appears
excessive, replace the fan drive unit.
ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED VISCOUS DRIVE
If the fan assembly free-wheels without drag (the
fan blades will revolve more than five turns when
spun by hand), do not replace the fan drive. This
spin test must be performed when the engine is cool.
If the fan assembly does not free-wheel and a
metallic grinding sound exists, replace the electroni-
cally controlled fan drive (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
NOTE: The following test may take up to 15 minutes
to perform.
The engine should be at normal operating temper-
ature.
(1) Set the parking brake and verify the transmis-
sion is in park or neutral.
(2) Set air conditioner (if equipped) and blower fan
to OFF.
(3) Start and allow engine to reach normal operat-
ing temperatures.
(4) Stop engine, connect the DRB III and select
appropriate model year and engine option.
(5) Check for and correct existing DTC's
(6) Using Tool 6801, connect pin 1 of the electron-
ically controlled viscous fan drive connector, located
at the lower fan shroud to battery ground (Fig. 35).
(7) Using the DRB III, verify that DTC 0480 set.
(8) Start the engine.
(9) Go to the SENSOR screen and observe the fan
speed.
(10) Run the engine at 2500 rpm.
NOTE: It maybe take 15 minutes before fan speed
increases.
(11) The fan speed should increase according to
the table below.
(12) If fan speed does not increase, replace the
electronically control viscous fan drive.
ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED VISCOUS FAN
DRIVE SPEEDS
ENGINE RPM FAN RPM(Min)
500 490
1000 950
1500 1420
2000 1850
2500 2230
3000 2440
(13) If the fan speed does increase and there is
still a concern, refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnosis Manual to diagnosis the electronically con-
trolled viscous fan drive control circuit.
CAUTION: If the viscous fan drive is replaced
because of mechanical damage, the cooling fan
blades should also be inspected. Inspect for fatigue
cracks or chips that could result in excessive vibra-
tion. Replace fan blade assembly if any of these
conditions are found.
Fig. 35 Electronically Controlled Viscous Fan Drive
Connector
1 - ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED VISCOUS FAN DRIVE
CONNECTOR
2 - TOOL 6801
3 - PIN 1
DRENGINE 7 - 53
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1460 of 2627
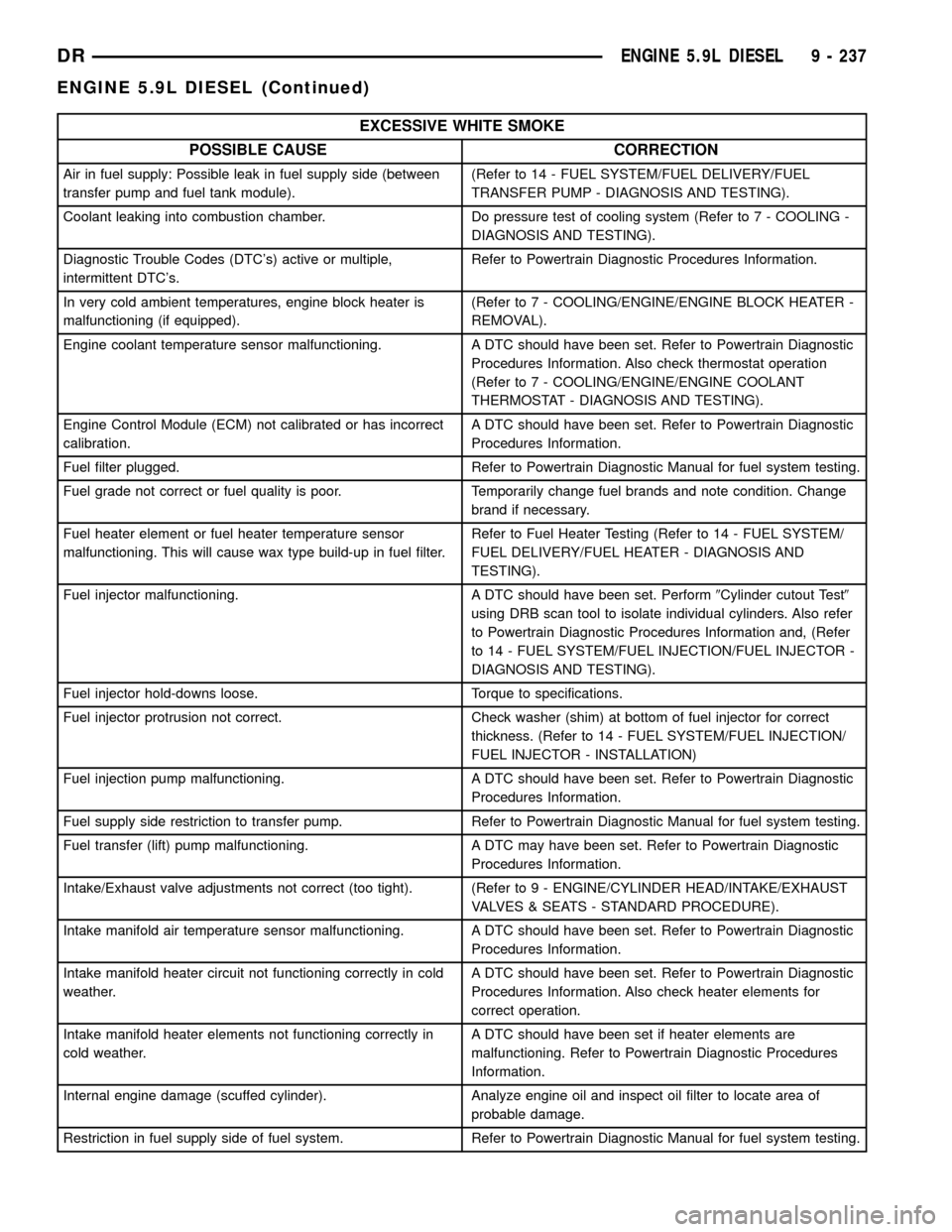
EXCESSIVE WHITE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air in fuel supply: Possible leak in fuel supply side (between
transfer pump and fuel tank module).(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL
TRANSFER PUMP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Coolant leaking into combustion chamber. Do pressure test of cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC's.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
In very cold ambient temperatures, engine block heater is
malfunctioning (if equipped).(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK HEATER -
REMOVAL).
Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information. Also check thermostat operation
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or has incorrect
calibration.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Fuel filter plugged. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system testing.
Fuel grade not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition. Change
brand if necessary.
Fuel heater element or fuel heater temperature sensor
malfunctioning. This will cause wax type build-up in fuel filter.Refer to Fuel Heater Testing (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL HEATER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Perform9Cylinder cutout Test9
using DRB scan tool to isolate individual cylinders. Also refer
to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information and, (Refer
to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel injector hold-downs loose. Torque to specifications.
Fuel injector protrusion not correct. Check washer (shim) at bottom of fuel injector for correct
thickness. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
FUEL INJECTOR - INSTALLATION)
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Fuel supply side restriction to transfer pump. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system testing.
Fuel transfer (lift) pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Intake/Exhaust valve adjustments not correct (too tight). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST
VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Intake manifold air temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Intake manifold heater circuit not functioning correctly in cold
weather.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information. Also check heater elements for
correct operation.
Intake manifold heater elements not functioning correctly in
cold weather.A DTC should have been set if heater elements are
malfunctioning. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
Information.
Internal engine damage (scuffed cylinder). Analyze engine oil and inspect oil filter to locate area of
probable damage.
Restriction in fuel supply side of fuel system. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system testing.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 237
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1471 of 2627
ENGINE DATA PLATE
DESCRIPTION
The engine data plate contains specific information
that is helpful to servicing and obtaining parts for
the engine. The data plate can be found affixed to the
breather cover on the left side of the engine. Informa-
tion that can be found on the data plate includes:
²Date of Engine Manufacture
²Engine Serial Number
²Control Parts List (CPL)
²Engine Rated Horsepower
²Engine Firing Order
²Engine Displacement
²Valve Lash Reset Specifications
If the engine data plate is missing or not legible,
the engine serial number is used for engine identifi-
cation. The engine serial number is stamped on the
right side of the block, on top of the oil cooler cavity
(Fig. 5).
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL
Testing Air Cleaner Element using Filter MinderŸ
Do not attempt to unnecessarily remove top
of air cleaner housing for air cleaner element
inspection on diesel engines.
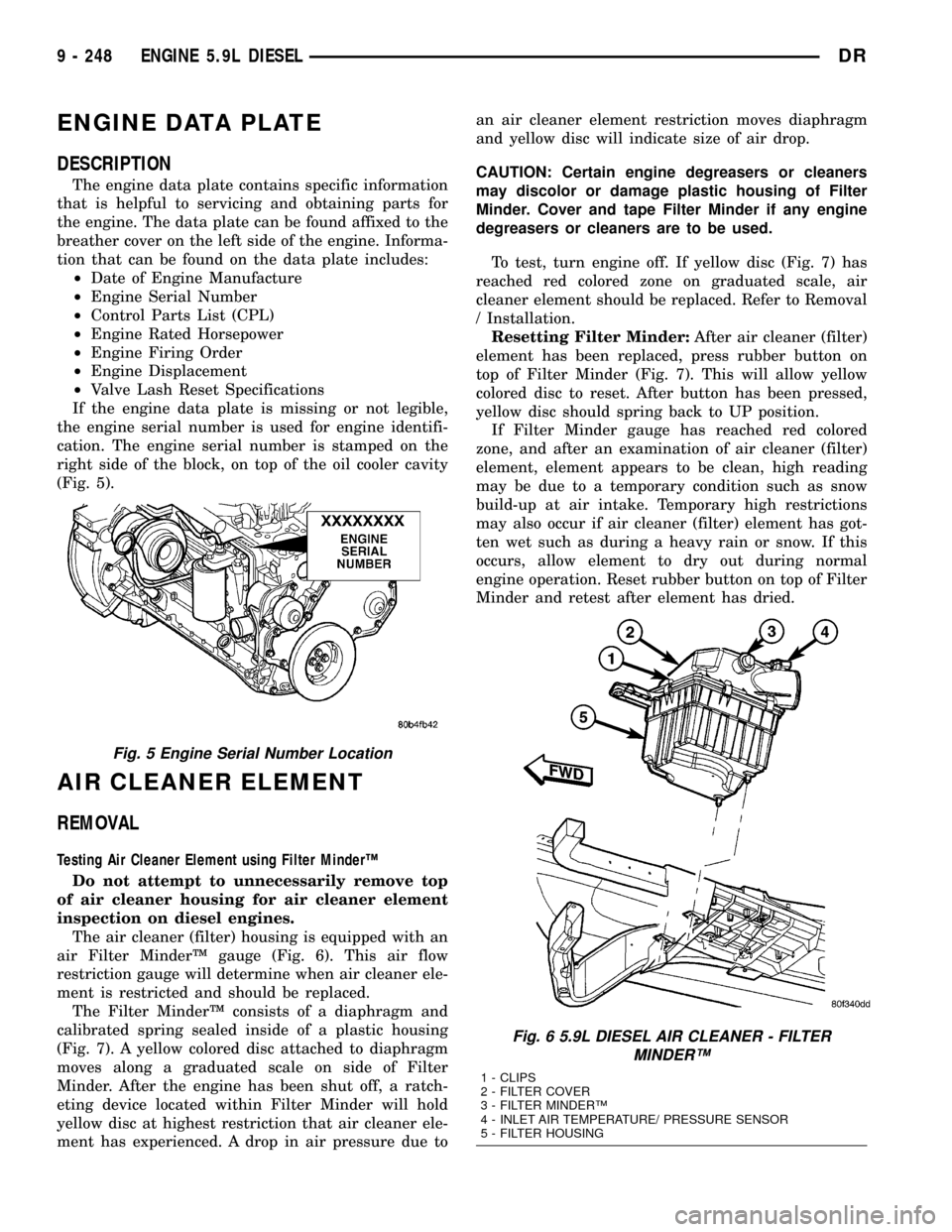
The air cleaner (filter) housing is equipped with an
air Filter MinderŸ gauge (Fig. 6). This air flow
restriction gauge will determine when air cleaner ele-
ment is restricted and should be replaced.
The Filter MinderŸ consists of a diaphragm and
calibrated spring sealed inside of a plastic housing
(Fig. 7). A yellow colored disc attached to diaphragm
moves along a graduated scale on side of Filter
Minder. After the engine has been shut off, a ratch-
eting device located within Filter Minder will hold
yellow disc at highest restriction that air cleaner ele-
ment has experienced. A drop in air pressure due toan air cleaner element restriction moves diaphragm
and yellow disc will indicate size of air drop.
CAUTION: Certain engine degreasers or cleaners
may discolor or damage plastic housing of Filter
Minder. Cover and tape Filter Minder if any engine
degreasers or cleaners are to be used.
To test, turn engine off. If yellow disc (Fig. 7) has
reached red colored zone on graduated scale, air
cleaner element should be replaced. Refer to Removal
/ Installation.
Resetting Filter Minder:After air cleaner (filter)
element has been replaced, press rubber button on
top of Filter Minder (Fig. 7). This will allow yellow
colored disc to reset. After button has been pressed,
yellow disc should spring back to UP position.
If Filter Minder gauge has reached red colored
zone, and after an examination of air cleaner (filter)
element, element appears to be clean, high reading
may be due to a temporary condition such as snow
build-up at air intake. Temporary high restrictions
may also occur if air cleaner (filter) element has got-
ten wet such as during a heavy rain or snow. If this
occurs, allow element to dry out during normal
engine operation. Reset rubber button on top of Filter
Minder and retest after element has dried.
Fig. 5 Engine Serial Number Location
Fig. 6 5.9L DIESEL AIR CLEANER - FILTER
MINDERŸ
1 - CLIPS
2 - FILTER COVER
3 - FILTER MINDERŸ
4 - INLET AIR TEMPERATURE/ PRESSURE SENSOR
5 - FILTER HOUSING
9 - 248 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR