1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Valve body
[x] Cancel search: Valve bodyPage 1903 of 2627

(6) Pull solenoid from governor body (Fig. 80).
(7) Pull pressure sensor from governor body.
(8) Remove bolts holding governor body to valve
body.
(9) Separate governor body from valve body (Fig.
81).
(10) Remove governor body gasket.
INSTALLATION
Before installing the pressure sensor and solenoid
in the governor body, replace o-ring seals, clean the
gasket surfaces and replace gasket.
(1) Place gasket in position on back of governor
body (Fig. 82).(2) Place governor body in position on valve body.
(3) Install bolts to hold governor body to valve
body.
(4) Lubricate o-ring on pressure sensor with trans-
mission fluid.
(5) Align pressure sensor to bore in governor body.
(6) Push pressure sensor into governor body.
(7) Lubricate o-ring, on pressure solenoid, with
transmission fluid.
(8) Align pressure solenoid to bore in governor
body (Fig. 83).
(9) Push solenoid into governor body.
Fig. 80 Pressure Solenoid and O-ring
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
2 - O-RING
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 81 Governor Body and Gasket
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GASKET
Fig. 82 Governor Body and Gasket
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GASKET
Fig. 83 Pressure Solenoid and O-ring
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
2 - O-RING
3 - GOVERNOR
21 - 200 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1904 of 2627

(10) Place solenoid retainer in position on governor
(Fig. 84).
(11) Install screws to hold pressure solenoid
retainer to governor body.
(12) Engage wire connectors into pressure sensor
and solenoid (Fig. 85).
(13) Install transmission fluid pan and (new) filter.
(14) Lower vehicle and road test to verify repair.
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Mark propeller shaft and axle yoke for align-
ment reference.
(3) Disconnect and remove propeller shaft.(4) Remove old seal with a screw mounted in a
slide hammer.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place seal in position on overdrive housing.
(2) Drive seal into overdrive housing with Seal
Installer 9037 (Fig. 86).
(3) Carefully guide propeller shaft slip yoke into
housing and onto output shaft splines. Align marks
made at removal and connect propeller shaft to rear
axle pinion yoke.
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has two primary causes.
(1) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
Fig. 84 Pressure Solenoid Retainer
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID RETAINER
2 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 85 Governor Solenoid And Pressure Sensor
1 - PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 86 Installing Overdrive Housing Yoke Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 9037
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 201
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1907 of 2627

(5) Slowly separate front of pan and reusable gas-
ket away from transmission allowing the fluid to
drain into drain pan.
(6) Hold up pan and remove remaining bolt hold-
ing pan to transmission.
(7) While holding pan level, lower pan and gasket
away from transmission.
(8) Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
(9) Remove screws holding filter to valve body
(Fig. 90).
(10) Separate filter from valve body and pour fluid
in filter into drain pan.
(11) Dispose of used trans fluid and filter properly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position a new transmission oil filter onto the
valve body.
(2) Install the screws to hold the filter to the valve
body. Tighten the screws to 4 N´m (35 in.lbs.).
(3) Clean the gasket surfaces of the transmission
oil pan and transmission pan rail.
NOTE: The transmission pan oil gasket is reusable.
Inspect the sealing surfaces of the gasket. If the
sealing ribs on both surfaces appear to be in good
condition, clean the gasket of any foreign material
and reinstall.
(4) Position the oil pan gasket onto the oil pan.
(5) Position the oil pan and gasket onto the trans-
mission and install several bolts to hold the pan and
gasket to the transmission.(6) Install the remainder of the oil pan bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 13.6 N´m (125 in.lbs.).
(7) Lower vehicle and fill transmission. (Refer to
21 - TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC/FLUID - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL
To avoid overfilling transmission after a fluid
change or overhaul, perform the following procedure:
(1) Remove dipstick and insert clean funnel in
transmission fill tube.
(2) Add following initial quantity of MopartAT F
+4 to transmission:
(a) If only fluid and filter were changed, add3
pints (1-1/2 quarts)of ATF +4 to transmission.
(b) If transmission was completely overhauled,
torque converter was replaced or drained, and
cooler was flushed, add12 pints (6 quarts)of ATF
+4 to transmission.
(3) Apply parking brakes.
(4) Start and run engine at normal curb idle
speed.
(5) Apply service brakes, shift transmission
through all gear ranges then back to NEUTRAL, set
parking brake, and leave engine running at curb idle
speed.
(6) Remove funnel, insert dipstick and check fluid
level. If level is low,add fluid to bring level to
MIN mark on dipstick.Check to see if the oil level
is equal on both sides of the dipstick. If one side is
noticably higher than the other, the dipstick has
picked up some oil from the dipstick tube. Allow the
oil to drain down the dipstick tube and re-check.
(7) Drive vehicle until transmission fluid is at nor-
mal operating temperature.
(8) With the engine running at curb idle speed, the
gear selector in NEUTRAL, and the parking brake
applied, check the transmission fluid level.
CAUTION: Do not overfill transmission, fluid foam-
ing and shifting problems can result.
(9) Add fluid to bring level up to MAX arrow
mark.
When fluid level is correct, shut engine off, release
park brake, remove funnel, and install dipstick in fill
tube.
Fig. 90 Transmission Filter
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - FILTER
21 - 204 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1916 of 2627

OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump (Fig. 109) is located in the pump
housing inside the bell housing of the transmission
case. The oil pump consists of an inner and outer
gear, a housing, and a reaction shaft support.
OPERATION
As the torque converter rotates, the converter hub
rotates the inner and outer gears. As the gears
rotate, the clearance between the gear teeth
increases in the crescent area, and creates a suction
at the inlet side of the pump. This suction draws
fluid through the pump inlet from the oil pan. As the
clearance between the gear teeth in the crescent area
decreases, it forces pressurized fluid into the pump
outlet and to the valve body.
Fig. 109 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - OIL SEAL 7 - BOLTS (6)
2 - VENT BAFFLE 8 - #1 THRUST WASHER (SELECTIVE)
3 - OIL PUMP BODY 9 - INNER GEAR
4 - GASKET 10 - OUTER GEAR
5 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT 11 - ªOº RING
6 - SEAL RINGS 12 - TORQUE CONVERTER SEAL RING
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 213
Page 1920 of 2627
INSTALLATION
(1) Place replacement bearing in position in hous-
ing.
(2) Using a suitable driver, drive bearing into
housing until the snap-ring groove is visible.
(3) Install snap-ring to hold bearing into housing
(Fig. 116).
(4) Install overdrive geartrain into housing.
(5) Install overdrive unit in vehicle.
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
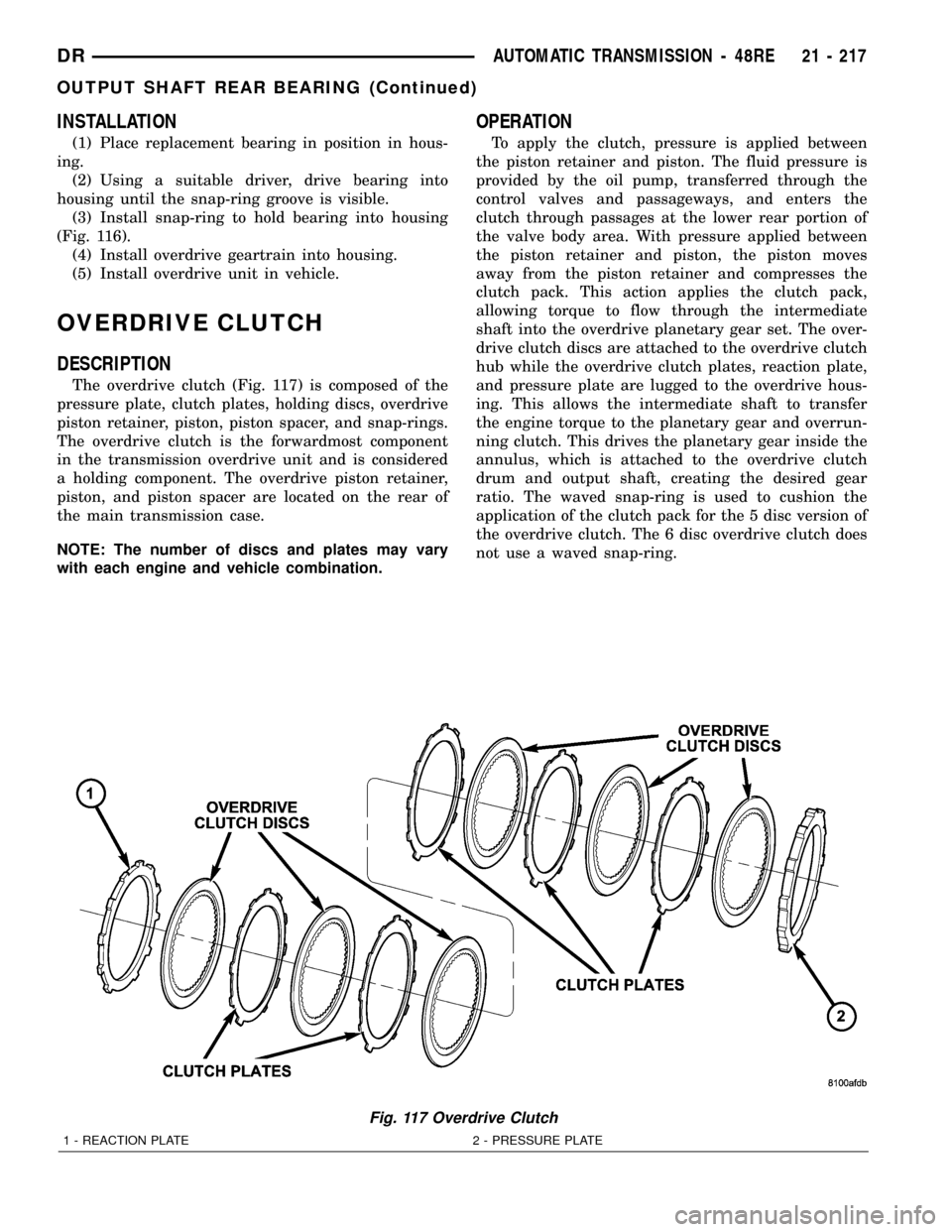
The overdrive clutch (Fig. 117) is composed of the
pressure plate, clutch plates, holding discs, overdrive
piston retainer, piston, piston spacer, and snap-rings.
The overdrive clutch is the forwardmost component
in the transmission overdrive unit and is considered
a holding component. The overdrive piston retainer,
piston, and piston spacer are located on the rear of
the main transmission case.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the piston retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through passages at the lower rear portion of
the valve body area. With pressure applied between
the piston retainer and piston, the piston moves
away from the piston retainer and compresses the
clutch pack. This action applies the clutch pack,
allowing torque to flow through the intermediate
shaft into the overdrive planetary gear set. The over-
drive clutch discs are attached to the overdrive clutch
hub while the overdrive clutch plates, reaction plate,
and pressure plate are lugged to the overdrive hous-
ing. This allows the intermediate shaft to transfer
the engine torque to the planetary gear and overrun-
ning clutch. This drives the planetary gear inside the
annulus, which is attached to the overdrive clutch
drum and output shaft, creating the desired gear
ratio. The waved snap-ring is used to cushion the
application of the clutch pack for the 5 disc version of
the overdrive clutch. The 6 disc overdrive clutch does
not use a waved snap-ring.
Fig. 117 Overdrive Clutch
1 - REACTION PLATE 2 - PRESSURE PLATE
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 217
OUTPUT SHAFT REAR BEARING (Continued)
Page 1943 of 2627
PRESSURE ON A CONFINED FLUID
Pressure is exerted on a confined fluid (Fig. 189)
by applying a force to some given area in contact
with the fluid. A good example of this is a cylinder
filled with fluid and equipped with a piston that is
closely fitted to the cylinder wall. If a force is applied
to the piston, pressure will be developed in the fluid.
Of course, no pressure will be created if the fluid is
not confined. It will simply ªleakº past the piston.
There must be a resistance to flow in order to create
pressure. Piston sealing is extremely important in
hydraulic operation. Several kinds of seals are used
to accomplish this within a transmission. These
include but are not limited to O-rings, D-rings, lip
seals, sealing rings, or extremely close tolerances
between the piston and the cylinder wall. The force
exerted is downward (gravity), however, the principle
remains the same no matter which direction is taken.
The pressure created in the fluid is equal to the force
applied, divided by the piston area. If the force is 100
lbs., and the piston area is 10 sq. in., then the pres-
sure created equals 10 PSI. Another interpretation of
Pascal's Law is that regardless of container shape or
size, the pressure will be maintained throughout, as
long as the fluid is confined. In other words, the
pressure in the fluid is the same everywhere within
the container.
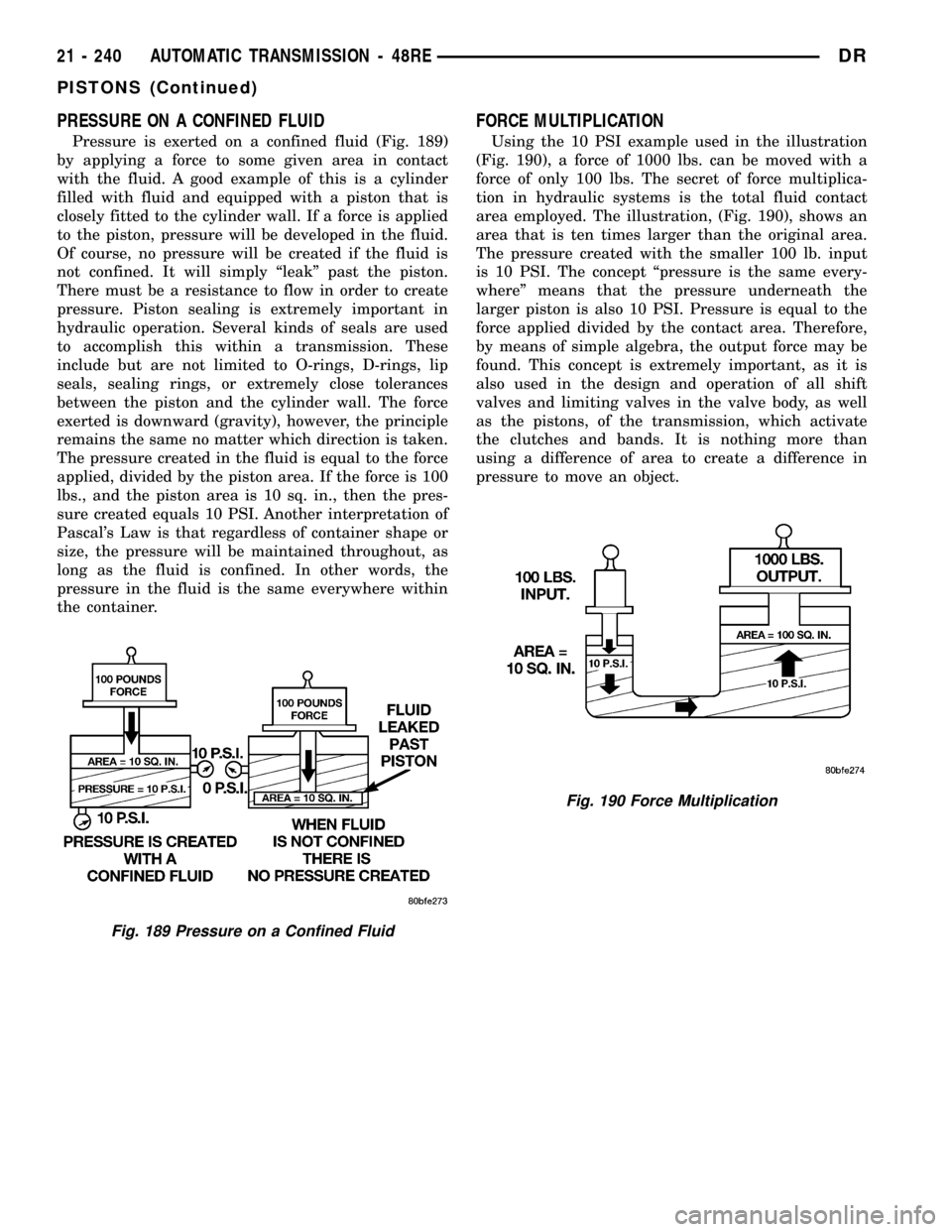
FORCE MULTIPLICATION
Using the 10 PSI example used in the illustration
(Fig. 190), a force of 1000 lbs. can be moved with a
force of only 100 lbs. The secret of force multiplica-
tion in hydraulic systems is the total fluid contact
area employed. The illustration, (Fig. 190), shows an
area that is ten times larger than the original area.
The pressure created with the smaller 100 lb. input
is 10 PSI. The concept ªpressure is the same every-
whereº means that the pressure underneath the
larger piston is also 10 PSI. Pressure is equal to the
force applied divided by the contact area. Therefore,
by means of simple algebra, the output force may be
found. This concept is extremely important, as it is
also used in the design and operation of all shift
valves and limiting valves in the valve body, as well
as the pistons, of the transmission, which activate
the clutches and bands. It is nothing more than
using a difference of area to create a difference in
pressure to move an object.
Fig. 189 Pressure on a Confined Fluid
Fig. 190 Force Multiplication
21 - 240 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
PISTONS (Continued)
Page 1956 of 2627

SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The speed sensor (Fig. 221) is located in the over-
drive gear case. The sensor is positioned over the
park gear and monitors transmission output shaft
rotating speed.
OPERATION
Speed sensor signals are triggered by the park
gear lugs as they rotate past the sensor pickup face.
Input signals from the sensor are sent to the trans-
mission control module for processing. Signals from
this sensor are shared with the powertrain control
module.
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION
Transmission throttle valve cable (Fig. 222) adjust-
ment is extremely important to proper operation.
This adjustment positions the throttle valve, which
controls shift speed, quality, and part-throttle down-
shift sensitivity.
If cable setting is too loose, early shifts and slip-
page between shifts may occur. If the setting is too
tight, shifts may be delayed and part throttle down-
shifts may be very sensitive.
The transmission throttle valve is operated by a
cam on the throttle lever. The throttle lever is oper-
ated by an adjustable cable (Fig. 223). The cable is
attached to an arm mounted on the throttle lever
shaft. A retaining clip at the engine-end of the cable
is removed to provide for cable adjustment. The
retaining clip is then installed back onto the throttle
valve cable to lock in the adjustment.
Fig. 222 Throttle Valve Cable Attachment - At Engine
1 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
2 - CABLE BRACKET
3 - THROTTLE BODY LEVER
4 - ACCELERATOR CABLE
5 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
Fig. 223 Throttle Valve Cable at Throttle Linkage
1 - THROTTLE LINKAGE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE LOCKING CLIP
3 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
Fig. 221 Transmission Output Speed Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION OUTPUT SHAFT SPEED SENSOR
2 - SEAL
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 253
Page 1957 of 2627

ADJUSTMENTS - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
A correctly adjusted throttle valve cable will cause
the throttle lever on the transmission to move simul-
taneously with the throttle body lever from the idle
position. Proper adjustment will allow simultaneous
movement without causing the transmission throttle
lever to either move ahead of, or lag behind the lever
on the throttle body.
ADJUSTMENT VERIFICATION
(1) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
(2) Remove air cleaner.
(3) Verify that lever on throttle body is at curb idle
position (Fig. 224). Then verify that the transmission
throttle lever (Fig. 225) is also at idle (fully forward)
position.
(4) Slide cable off attachment stud on throttle body
lever.
(5) Compare position of cable end to attachment
stud on throttle body lever:
²Cable end and attachment stud should be
aligned (or centered on one another) to within 1 mm
(0.039 in.) in either direction (Fig. 226).
²If cable end and attachment stud are misaligned
(off center), cable will have to be adjusted as
described in Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment proce-
dure.
Fig. 225 Throttle Valve Cable at Transmission
1 - TRANSMISSION SHIFTER CABLE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFTER CABLE
4 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFTER CABLE BRACKET RETAINING
BOLT(1OR2)
5 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE BRACKET RETAINING BOLT
6 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
7 - TRANSMISSION FLUID LINES
Fig. 226 Throttle Valve Cable at Throttle Linkage
1 - THROTTLE LINKAGE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE LOCKING CLIP
3 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
Fig. 224 Throttle Valve Cable Attachment - At
Engine
1 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
2 - CABLE BRACKET
3 - THROTTLE BODY LEVER
4 - ACCELERATOR CABLE
5 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
21 - 254 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)