1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Oil change
[x] Cancel search: Oil changePage 1656 of 2627

STEERING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STEERING
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
STEERING SYSTEM....................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
STEERING FLOW AND PRESSURE........4
SPECIAL TOOLS
STEERING...........................5COLUMN...............................6
GEAR - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSION..17
GEAR - LINK/COIL.......................20
LINKAGE - INDEPENDENT FRONT
SUSPENSION...........................32
LINKAGE - LINK/COIL....................34
PUMP.................................39
STEERING
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: MOPARTATF+4 is to be used in the
power steering system. No other power steering or
automatic transmission fluid is to be used in the
system. Damage may result to the power steering
pump and system if any other fluid is used, and do
not overfill.
Power steering systems consist of:
²Steering column
²Rack and pinion steering gear
²Belt driven hydraulic steering pump
²Pump pressure and return hoses
²Oil Cooler
OPERATION
The steering column shaft is attached to the gear
pinion. The rotation of the pinion moves the gear
rack from side-to-side. This lateral action of the rack
pushes and pulls the tie rods to change the direction
of the front wheels (Fig. 1).
Power assist is provided by an engine mounted
hydraulic pump which supplies hydraulic fluid pres-
sure to the steering gear.
Fig. 1 STEERING COMPONENTS
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP ASSEMBLY
2 - RESERVOIR
3 - HOSES
4 - TIE ROD ENDS
5 - MOUNTING BOLTS
6 - RACK & PINION
DRSTEERING 19 - 1
Page 1694 of 2627

PUMP
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................40
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PUMP LEAKAGE . 40
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER
STEERING PUMP - INITIAL OPERATION....40
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUSHING
POWER STEERING SYSTEM............40
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - GAS......................41
REMOVAL - DIESEL...................41
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - GAS..................42
INSTALLATION - DIESEL................42
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................42
FLUID
DESCRIPTION.........................43
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER
STEERING FLUID LEVEL CHECKING......43
FLUID COOLER
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
HOSES - I.F.S.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - RETURN HOSE - GEAR TO
COOLER............................44
REMOVAL - PRESSURE HOSE...........44
REMOVAL - RETURN HOSE - RESERVOIR
TO COOLER.........................44INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - RETURN HOSE - GEAR TO
COOLER............................44
INSTALLATION - PRESSURE HOSE.......44
INSTALLATION - RETURN HOSE -
RESERVOIR TO COOLER...............44
HOSES - LINK/COIL
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - RETURN HOSE - GEAR TO
COOLER............................45
REMOVAL - PRESSURE HOSE...........45
REMOVAL - RETURN HOSE - RESERVOIR
TO COOLER.........................45
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - RETURN HOSE - GEAR TO
COOLER............................45
INSTALLATION - PRESSURE HOSE.......45
INSTALLATION - RETURN HOSE -
RESERVOIR TO COOLER...............45
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
REMOVAL - 3.7L & 5.7L..................46
INSTALLATION - 3.7L & 5.7L...............46
PULLEY
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
RESERVOIR
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
PUMP
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: MOPARTATF+4 is to be used in the
power steering system. No other power steering or
automatic transmission fluid is to be used in the
system. Damage may result to the power steering
pump and system if any other fluid is used, and do
not overfill.The pump is connected to the steering gear via the
pressure hose and the return hose. The pump shaft
has a pressed-on pulley that is belt driven by the
crankshaft pulley.
All vehicles are equipped with a power steering
fluid cooler.
NOTE: Power steering pumps are not interchange-
able with pumps installed on other vehicles.
DRPUMP 19 - 39
Page 1698 of 2627

FLUID
DESCRIPTION
The recommended fluid for the power steering sys-
tem is MopartATF +4.
MopartATF+4, when new is red in color. The
ATF+4 is dyed red so it can be identified from other
fluids used in the vehicle such as engine oil or anti-
freeze. The red color is not permanent and is not an
indicator of fluid condition, As the vehicle is driven,
the ATF+4 will begin to look darker in color and may
eventually become brown.THIS IS NORMAL.
ATF+4 also has a unique odor that may change with
age. Consequently, odor and color cannot be used to
indicate the fluid condition or the need for a fluid
change.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER STEERING
FLUID LEVEL CHECKING
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION: MOPARTATF+4 is to be used in the
power steering system. No other power steering or
automatic transmission fluid is to be used in the
system. Damage may result to the power steering
pump and system if any other fluid is used, and do
not overfill.
The power steering fluid level can be viewed on the
dipstick attached to the filler cap. There are two
ranges listed on the dipstick, COLD and HOT. Before
opening power steering system, wipe the reservoir
filler cap free of dirt and debris. Remove the cap and
check the fluid level on its dipstick. When the fluid is
at normal ambient temperature, approximately 21ÉC
to 27ÉC (70ÉF to 80ÉF), the fluid level should read
between the minimum and maximum area of the cold
range. When the fluid is hot, fluid level is allowed to
read up to the highest end of the HOT range. Only
add fluid when the vehicle is cold.
Use only MopartATF+4Do not overfill the
power steering system.
FLUID COOLER
REMOVAL
(1) Drain and siphon the power steering fluid.
(2) Disconnect the return and supply hoses con-
nected to the power steering fluid cooler.
(3) Remove the mounting bracket bolts securing
the fluid cooler to the brace. (Fig. 4)& (Fig. 5)(4) Remove the fluid cooler from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the fluid cooler to the vehicle.
(2) Install the mounting bracket bolts securing the
fluid cooler to the brace (Fig. 4)& (Fig. 5).
(3) Reclamp the return and supply hoses to the
power steering fluid cooler.
(4) Refill the power steering fluid (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 4 V6 & V8 P/S FLUID COOLER
1 - POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
Fig. 5 V10 & DIESEL P/S FLUID COOLER
1 - RADIATOR
2 - POWER STEERING HOSES
3 - MOUNTING BOLTS
4 - P/S FLUID COOLER
DRPUMP 19 - 43
Page 1846 of 2627

(3) Have helper start and run engine at 1600 rpm
for test.
(4)
Move transmission shift lever four detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is Reverse range.
(5) Move transmission throttle lever fully forward
then fully rearward and note reading at Gauge
C-3293-SP.
(6) Pressure should be 145 - 175 psi (1000-1207
kPa) with throttle lever forward and increase to 230 -
280 psi (1586-1931 kPa) as lever is gradually moved
rearward.
Test Five - Governor Pressure
This test checks governor operation by measuring
governor pressure response to changes in vehicle
speed. It is usually not necessary to check governor
operation unless shift speeds are incorrect or if the
transmission will not downshift. The test should be
performed on the road or on a hoist that will allow
the rear wheels to rotate freely.
(1) Move 100 psi Test Gauge C-3292 to governor
pressure port.
(2) Move transmission shift lever two detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is D range.
(3) Have helper start and run engine at curb idle
speed. Then firmly apply service brakes so wheels
will not rotate.
(4) Note governor pressure:
²
Governor pressure should be no more than 20.6
kPa (3 psi) at curb idle speed and wheels not rotating.
²If pressure exceeds 20.6 kPa (3 psi), a fault
exists in governor pressure control system.
(5) Release brakes, slowly increase engine speed,
and observe speedometer and pressure test gauge (do
not exceed 30 mph on speedometer). Governor pres-
sure should increase in proportion to vehicle speed.
Or approximately 6.89 kPa (1 psi) for every 1 mph.
(6) Governor pressure rise should be smooth and
drop back to no more than 20.6 kPa (3 psi), after
engine returns to curb idle and brakes are applied to
prevent wheels from rotating.
(7)
Compare results of pressure test with analysis
chart.
Test Six - Transmission In Overdrive Fourth Gear
This test checks line pressure at the overdrive
clutch in fourth gear range. Use 300 psi Test Gauge
C-3293-SP for this test. The test should be performed
on the road or on a chassis dyno.
(1)
Remove tachometer; it is not needed for this test.
(2) Move 300 psi Gauge to overdrive clutch pres-
sure test port. Then remove other gauge and reinstall
test port plug.
(3) Lower vehicle.
(4) Turn OD switch on.(5) Secure test gauge so it can be viewed from
drivers seat.
(6) Start engine and shift into D range.
(7) Increase vehicle speed gradually until 3-4 shift
occurs and note gauge pressure.
(8) Pressure should be 524-565 kPa (76-82 psi)
with closed throttle and increase to 690-896 kPa
(100-130 psi) at 1/2 to 3/4 throttle. Note that pres-
sure can increase to around 965 kPa (140 psi) at full
throttle.
(9) Return to shop or move vehicle off chassis
dyno.
PRESSURE TEST ANALYSIS CHART
TEST CONDITION INDICATION
Line pressure OK during
any one testPump and regulator
valve OK
Line pressure OK in R
but low in D, 2, 1Leakage in rear clutch
area (seal rings, clutch
seals)
Pressure low in D Fourth
Gear RangeOverdrive clutch piston
seal, or check ball
problem
Pressure OK in 1, 2 but
low in D3 and RLeakage in front clutch
area
Pressure OK in 2 but low
in R and 1Leakage in rear servo
Front servo pressure in 2 Leakage in servo; broken
servo ring or cracked
servo piston
Pressure low in all
positionsClogged filter, stuck
regulator valve, worn or
faulty pump, low oil level
Governor pressure too
high at idle speedGovernor pressure
solenoid valve system
fault. Refer to diagnostic
book.
Governor pressure low at
all mph figuresFaulty governor pressure
solenoid, transmission
control module, or
governor pressure
sensor
Lubrication pressure low
at all throttle positionsClogged fluid cooler or
lines, seal rings leaking,
worn pump bushings,
pump, clutch retainer, or
clogged filter.
Line pressure high Output shaft plugged,
sticky regulator valve
Line pressure low Sticky regulator valve,
clogged filter, worn pump
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 143
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1850 of 2627
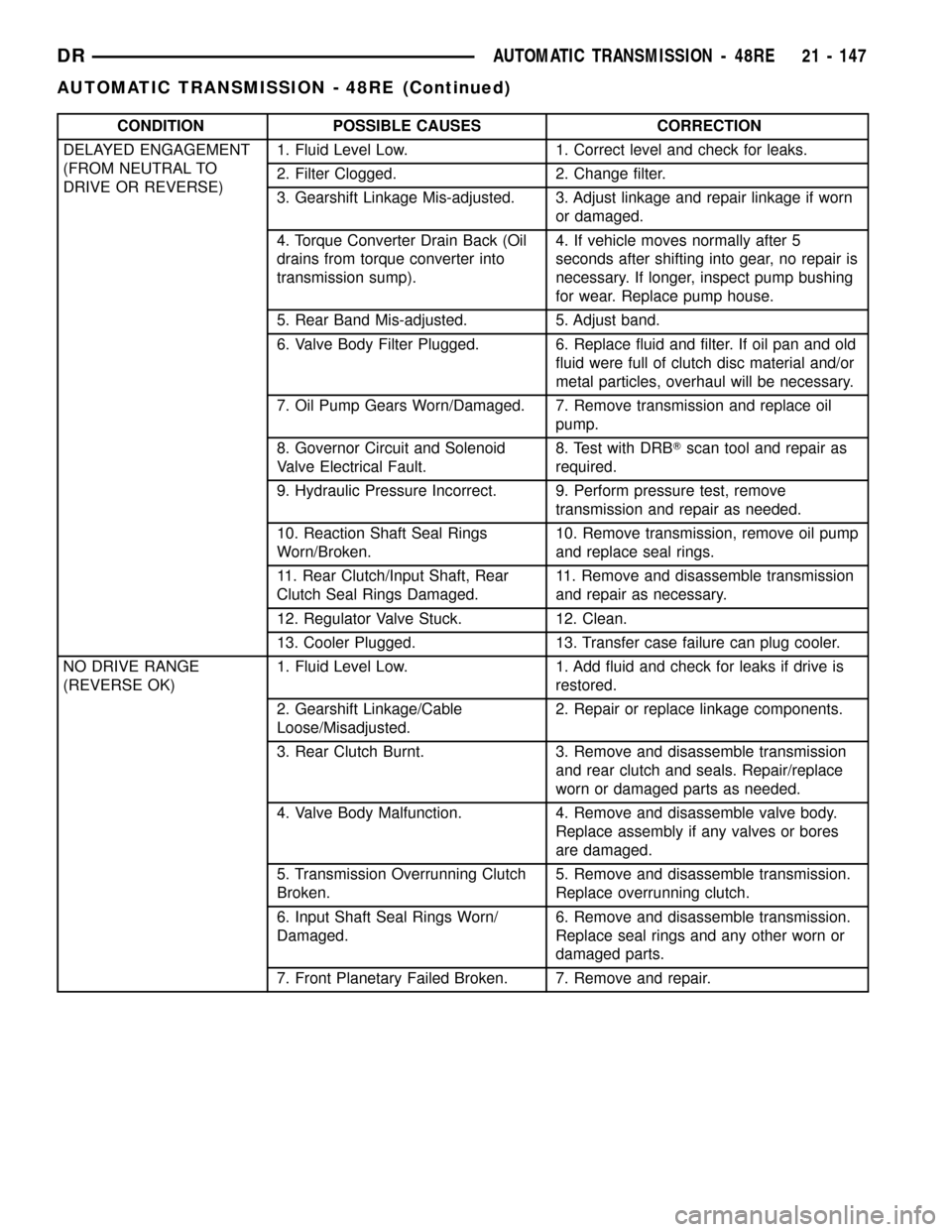
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
DELAYED ENGAGEMENT
(FROM NEUTRAL TO
DRIVE OR REVERSE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Correct level and check for leaks.
2. Filter Clogged. 2. Change filter.
3. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 3. Adjust linkage and repair linkage if worn
or damaged.
4. Torque Converter Drain Back (Oil
drains from torque converter into
transmission sump).4. If vehicle moves normally after 5
seconds after shifting into gear, no repair is
necessary. If longer, inspect pump bushing
for wear. Replace pump house.
5. Rear Band Mis-adjusted. 5. Adjust band.
6. Valve Body Filter Plugged. 6. Replace fluid and filter. If oil pan and old
fluid were full of clutch disc material and/or
metal particles, overhaul will be necessary.
7. Oil Pump Gears Worn/Damaged. 7. Remove transmission and replace oil
pump.
8. Governor Circuit and Solenoid
Valve Electrical Fault.8. Test with DRBTscan tool and repair as
required.
9. Hydraulic Pressure Incorrect. 9. Perform pressure test, remove
transmission and repair as needed.
10. Reaction Shaft Seal Rings
Worn/Broken.10. Remove transmission, remove oil pump
and replace seal rings.
11. Rear Clutch/Input Shaft, Rear
Clutch Seal Rings Damaged.11. Remove and disassemble transmission
and repair as necessary.
12. Regulator Valve Stuck. 12. Clean.
13. Cooler Plugged. 13. Transfer case failure can plug cooler.
NO DRIVE RANGE
(REVERSE OK)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks if drive is
restored.
2. Gearshift Linkage/Cable
Loose/Misadjusted.2. Repair or replace linkage components.
3. Rear Clutch Burnt. 3. Remove and disassemble transmission
and rear clutch and seals. Repair/replace
worn or damaged parts as needed.
4. Valve Body Malfunction. 4. Remove and disassemble valve body.
Replace assembly if any valves or bores
are damaged.
5. Transmission Overrunning Clutch
Broken.5. Remove and disassemble transmission.
Replace overrunning clutch.
6. Input Shaft Seal Rings Worn/
Damaged.6. Remove and disassemble transmission.
Replace seal rings and any other worn or
damaged parts.
7. Front Planetary Failed Broken. 7. Remove and repair.
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 147
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1893 of 2627
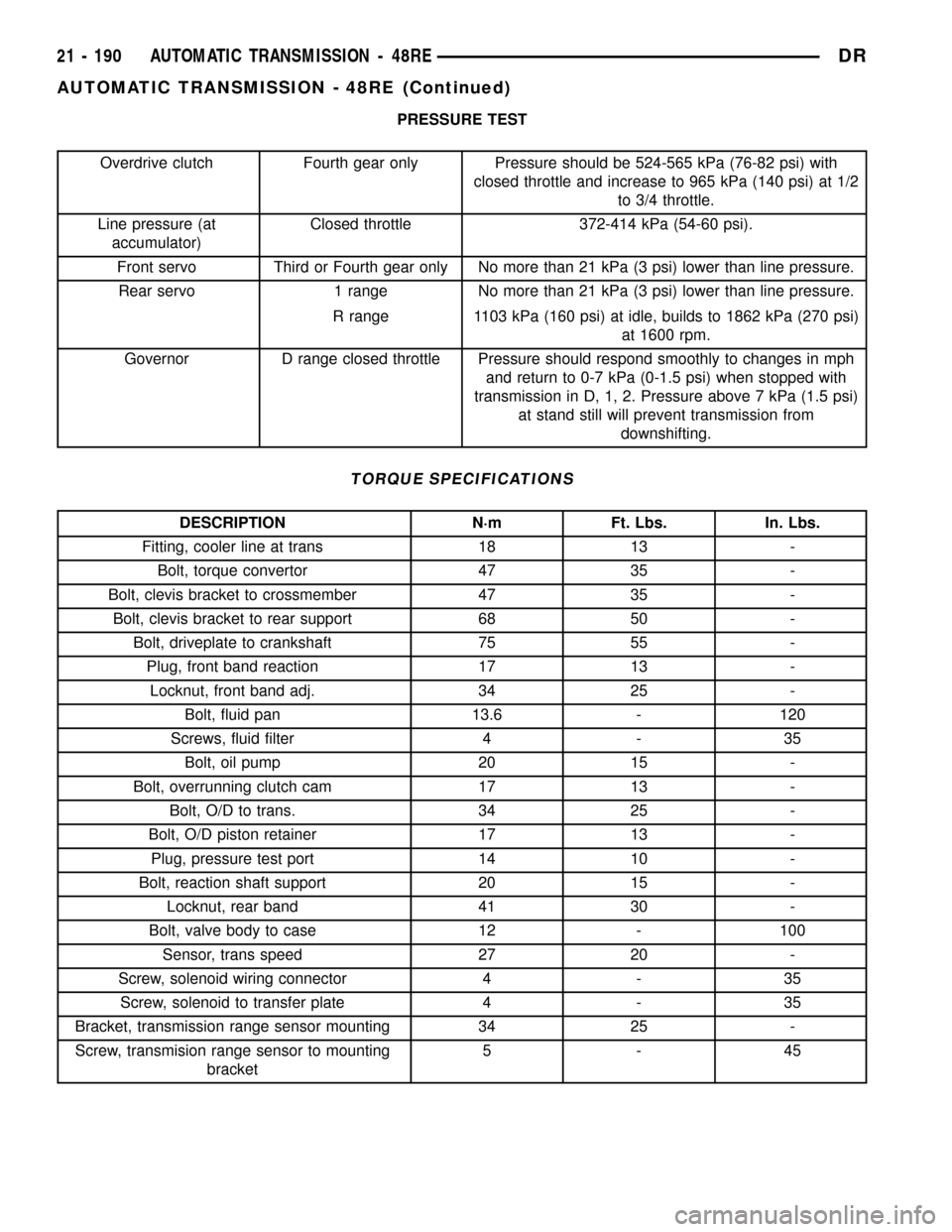
PRESSURE TEST
Overdrive clutch Fourth gear only Pressure should be 524-565 kPa (76-82 psi) with
closed throttle and increase to 965 kPa (140 psi) at 1/2
to 3/4 throttle.
Line pressure (at
accumulator)Closed throttle 372-414 kPa (54-60 psi).
Front servo Third or Fourth gear only No more than 21 kPa (3 psi) lower than line pressure.
Rear servo 1 range No more than 21 kPa (3 psi) lower than line pressure.
R range 1103 kPa (160 psi) at idle, builds to 1862 kPa (270 psi)
at 1600 rpm.
Governor D range closed throttle Pressure should respond smoothly to changes in mph
and return to 0-7 kPa (0-1.5 psi) when stopped with
transmission in D, 1, 2. Pressure above 7 kPa (1.5 psi)
at stand still will prevent transmission from
downshifting.
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fitting, cooler line at trans 18 13 -
Bolt, torque convertor 47 35 -
Bolt, clevis bracket to crossmember 47 35 -
Bolt, clevis bracket to rear support 68 50 -
Bolt, driveplate to crankshaft 75 55 -
Plug, front band reaction 17 13 -
Locknut, front band adj. 34 25 -
Bolt, fluid pan 13.6 - 120
Screws, fluid filter 4 - 35
Bolt, oil pump 20 15 -
Bolt, overrunning clutch cam 17 13 -
Bolt, O/D to trans. 34 25 -
Bolt, O/D piston retainer 17 13 -
Plug, pressure test port 14 10 -
Bolt, reaction shaft support 20 15 -
Locknut, rear band 41 30 -
Bolt, valve body to case 12 - 100
Sensor, trans speed 27 20 -
Screw, solenoid wiring connector 4 - 35
Screw, solenoid to transfer plate 4 - 35
Bracket, transmission range sensor mounting 34 25 -
Screw, transmision range sensor to mounting
bracket5-45
21 - 190 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1902 of 2627

sure curve is higher than normal to make the
transmission shift at normal speeds and sooner. The
PCM uses a temperature sensor in the transmission
oil sump to determine when low temperature gover-
nor pressure is needed.
NORMAL OPERATION
Normal operation is refined through the increased
computing power of the PCM and through access to
data on engine operating conditions provided by the
PCM that were not available with the previous
stand-alone electronic module. This facilitated the
development of a load adaptive shift strategy - the
ability to alter the shift schedule in response to vehi-
cle load condition. One manifestation of this capabil-
ity is grade9hunting9prevention - the ability of the
transmission logic to delay an upshift on a grade if
the engine does not have sufficient power to main-
tain speed in the higher gear. The 3-2 downshift and
the potential for hunting between gears occurs with a
heavily loaded vehicle or on steep grades. When
hunting occurs, it is very objectionable because shifts
are frequent and accompanied by large changes in
noise and acceleration.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE OPERATION
In wide-open throttle (WOT) mode, adaptive mem-
ory in the PCM assures that up-shifts occur at the
preprogrammed optimum speed. WOT operation is
determined from the throttle position sensor, which
is also a part of the emission control system. The ini-
tial setting for the WOT upshift is below the opti-
mum engine speed. As WOT shifts are repeated, the
PCM learns the time required to complete the shifts
by comparing the engine speed when the shifts occur
to the optimum speed. After each shift, the PCM
adjusts the shift point until the optimum speed is
reached. The PCM also considers vehicle loading,
grade and engine performance changes due to high
altitude in determining when to make WOT shifts. It
does this by measuring vehicle and engine accelera-
tion and then factoring in the shift time.
TRANSFER CASE LOW RANGE OPERATION
On four-wheel drive vehicles operating in low
range, the engine can accelerate to its peak more
rapidly than in Normal range, resulting in delayed
shifts and undesirable engine9flare.9The low range
governor pressure curve is also higher than normal
to initiate upshifts sooner. The PCM compares elec-
tronic vehicle speed signal used by the speedometer
to the transmission output shaft speed signal to
determine when the transfer case is in low range.REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Remove transmission fluid pan and filter.
(3) Disengage wire connectors from pressure sen-
sor and solenoid (Fig. 78).
(4) Remove screws holding pressure solenoid
retainer to governor body.
(5) Separate solenoid retainer from governor (Fig.
79).
Fig. 78 Governor Solenoid And Pressure Sensor
1 - PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 79 Pressure Solenoid Retainer
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID RETAINER
2 - GOVERNOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 199
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1906 of 2627

PROCEDURE TWO
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select engine.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
chart.
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the chart (Fig. 88).
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION). The service fluid fill after a
filter change is approximately 3.8 liters (4.0 quarts).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission (Fig. 89).
(4) Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmis-
sion.
Fig. 88 48RE Fluid Fill Graph
Fig. 89 Transmission Pan
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - REUSABLE GASKET
3-PAN
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 203
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)