1998 DODGE RAM 1500 gear
[x] Cancel search: gearPage 2262 of 2627

(16) Remove the rear output shaft bearing from
the rear case using Installer 7888 (Fig. 53).
(17) Install the rear output shaft bearing (Fig. 54)
into the rear case using Installer 8152 and Handle
C-4171.
(18) Install the rear output shaft bearing snap-
ring into the rear case half.INPUT AND PLANETARY GEAR
(1) Lubricate gears and thrust washers with rec-
ommended transmission fluid.
(2) Install bottom thrust washer (Fig. 55) in low
range gear planetary. Be sure washer tabs are prop-
erly aligned in gear notches.
(3) Install input gear in low range gear (Fig. 56).
Be sure input gear is fully seated.
Fig. 53 Remove Rear Output Shaft Bearing
1 - REAR CASE HALF
2 - INSTALLER 7888
Fig. 54 Install Rear Output Shaft Bearing
1 - REAR CASE HALF
2 - HANDLE C-4171
3 - INSTALLER 8152
Fig. 55 Install Bottom Input Gear Thrust Plate
1 - PLANETARY
2 - THRUST PLATE
Fig. 56 Install Input Gear From Planetary
1 - INPUT GEAR
2 - LOW RANGE PLANETARY
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 559
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2263 of 2627

(4) Install remaining thrust washer (Fig. 57) in
low range gear and on top of input gear.
(5) Install retainer (Fig. 58) on input gear and
install snap-ring (Fig. 59).
(6) Align and install low range/input gear assem-
bly in front case (Fig. 60). Be sure low range gear
pinions are engaged in annulus gear and that input
gear shaft is fully seated in front bearing.
Fig. 60 Install Input Planetary Assembly
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - INPUT PLANETARY ASSEMBLY
Fig. 57 Install Input Gear Thrust Plate
1 - INPUT GEAR
2 - THRUST PLATE
Fig. 58 Install Input Gear Retainer
1 - INPUT GEAR
2 - RETAINER
Fig. 59 Install Input Gear Retaining Ring
1 - INPUT GEAR
2 - RETAINING RING
21 - 560 TRANSFER CASE - NV273DR
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2264 of 2627
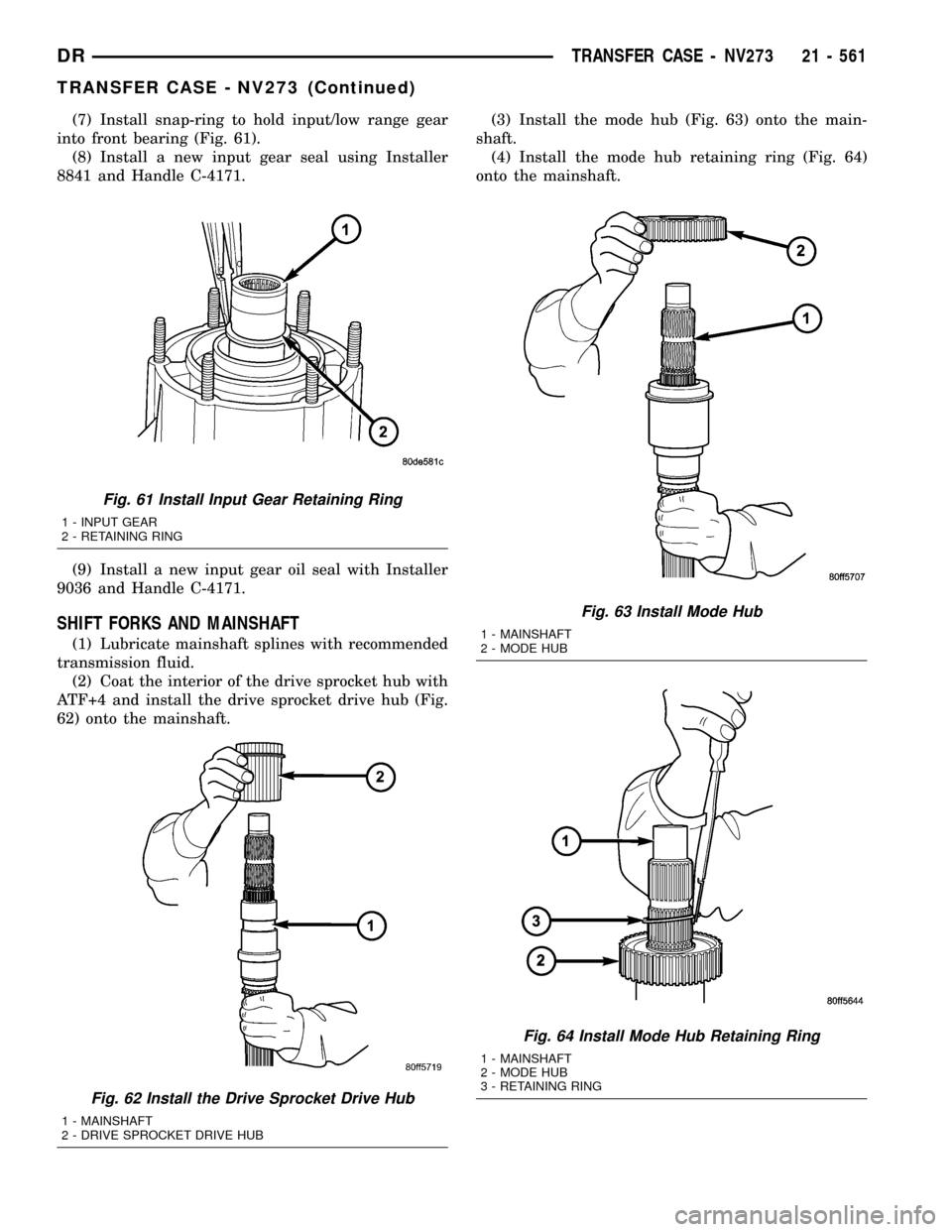
(7) Install snap-ring to hold input/low range gear
into front bearing (Fig. 61).
(8) Install a new input gear seal using Installer
8841 and Handle C-4171.
(9) Install a new input gear oil seal with Installer
9036 and Handle C-4171.
SHIFT FORKS AND MAINSHAFT
(1) Lubricate mainshaft splines with recommended
transmission fluid.
(2) Coat the interior of the drive sprocket hub with
ATF+4 and install the drive sprocket drive hub (Fig.
62) onto the mainshaft.(3) Install the mode hub (Fig. 63) onto the main-
shaft.
(4) Install the mode hub retaining ring (Fig. 64)
onto the mainshaft.
Fig. 61 Install Input Gear Retaining Ring
1 - INPUT GEAR
2 - RETAINING RING
Fig. 62 Install the Drive Sprocket Drive Hub
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - DRIVE SPROCKET DRIVE HUB
Fig. 63 Install Mode Hub
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - MODE HUB
Fig. 64 Install Mode Hub Retaining Ring
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - MODE HUB
3 - RETAINING RING
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 561
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2265 of 2627

(5) Install the clutch gear (Fig. 65) onto the output
shaft. Verify that the pointed ends of the clutch gear
teeth are pointing to the front of the mainshaft.
(6) Lubricate sector shaft with transmission fluid
and install shift sector in case (Fig. 66). Position slot
in sector so it will be aligned with shift fork pin
when shift forks are installed.
(7) Apply LoctiteŸ 242, or equivalent, to the
threads of the sector support to replentish the factory
applied patch. Install the shift sector support.
Tighten the sector support with Socket 9033 to 27-34
N´m (20-25 ft.lbs.).(8) Assemble and install range fork and hub (Fig.
67). Be sure hub is properly seated in low range gear
and engaged to the input gear.
(9) Align and insert range fork pin in shift sector
slot.
(10) Install mode fork and shift rail onto the mode
sleeve.
(11) Install the mode fork, sleeve, and shift rail
into the transfer case (Fig. 68).
Fig. 65 Install Clutch Gear
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT
2 - CLUTCH GEAR
3 - MODE HUB
Fig. 66 Install Shift Sector
1 - SHIFT SECTOR
Fig. 67 Install Range Fork And Hub Assembly
1 - RANGE HUB
2 - RANGE FORK
Fig. 68 Mode Fork And Sleeve Installation
1 - MODE SLEEVE
2 - MODE FORK AND RAIL
21 - 562 TRANSFER CASE - NV273DR
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2267 of 2627

(3) Install mainshaft into the transfer case (Fig.
73). Guide mainshaft through the mode and range
sleeves and into the input gear.
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT AND DRIVE CHAIN
(1) Install the front output shaft (Fig. 74) into the
front output shaft front bearing.
(2) Install the front output shaft bearing inner
snap-ring (Fig. 75) onto the output shaft.
(3) Install the new front output shaft seal with
Installer MB991168A
(4) Insert front drive sprocket in drive chain.
(5) Install drive chain around rear drive sprocket.(6) Position rear drive sprocket (Fig. 76) over the
output shaft and lower the sprocket and chain
assembly until the front sprocket is positioned over
the front output shaft.
(7) Align the splines in the sprockets to the splines
on the output shafts and install the sprockets onto
the output shafts.
Fig. 73 Install Mainshaft Assembly
1 - FRONT CASE HALF
2 - MAINSHAFT ASSEMBLY
Fig. 74 Install Front Output Shaft
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT
Fig. 75 Install Front Output Shaft Bearing Inner
Snap-Ring
1 - FRONT CASE HALF
2 - SNAP-RING
Fig. 76 Install Drive Chain and Sprockets
1 - FRONT CASE HALF
2 - CHAIN
3 - DRIVE SPROCKETS
21 - 564 TRANSFER CASE - NV273DR
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2276 of 2627
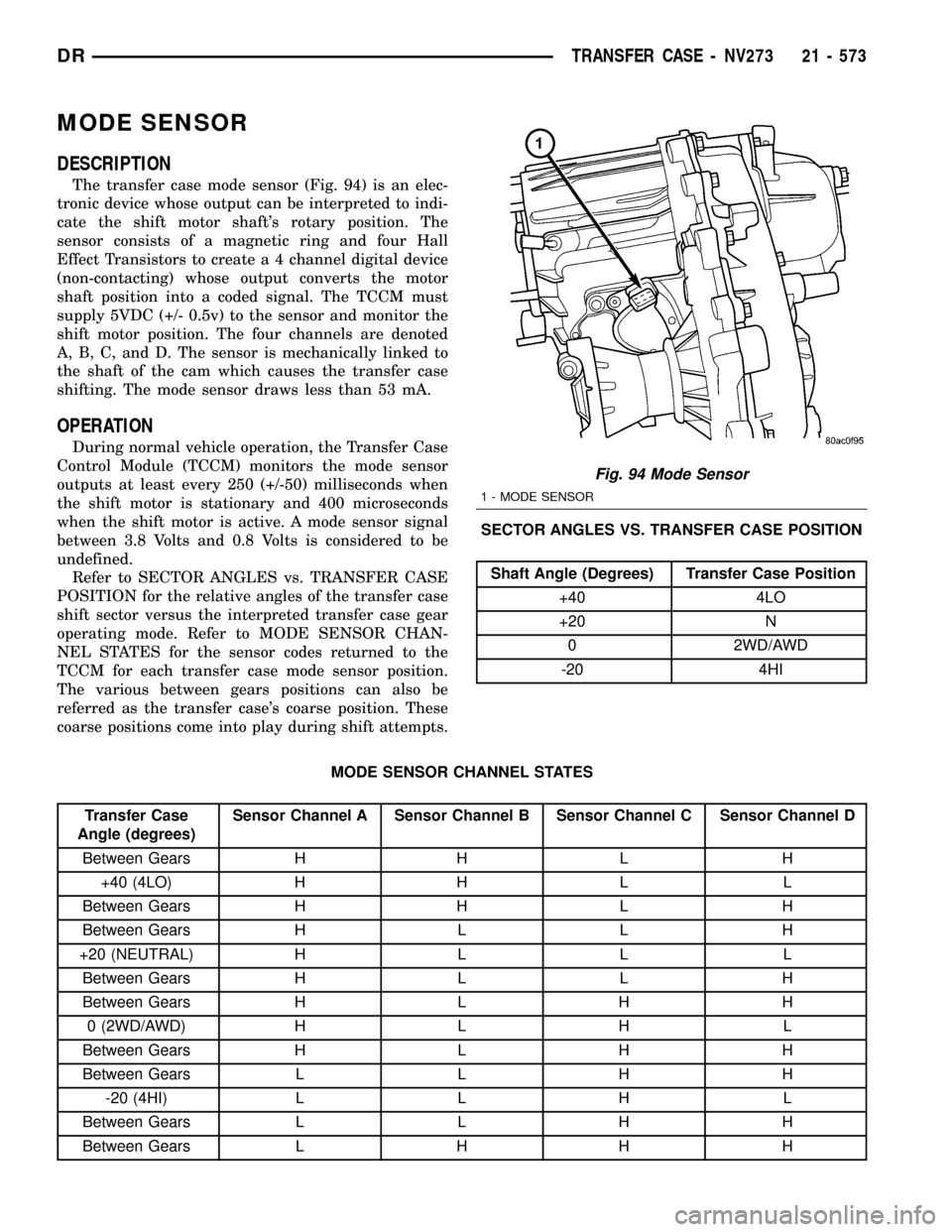
MODE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transfer case mode sensor (Fig. 94) is an elec-
tronic device whose output can be interpreted to indi-
cate the shift motor shaft's rotary position. The
sensor consists of a magnetic ring and four Hall
Effect Transistors to create a 4 channel digital device
(non-contacting) whose output converts the motor
shaft position into a coded signal. The TCCM must
supply 5VDC (+/- 0.5v) to the sensor and monitor the
shift motor position. The four channels are denoted
A, B, C, and D. The sensor is mechanically linked to
the shaft of the cam which causes the transfer case
shifting. The mode sensor draws less than 53 mA.
OPERATION
During normal vehicle operation, the Transfer Case
Control Module (TCCM) monitors the mode sensor
outputs at least every 250 (+/-50) milliseconds when
the shift motor is stationary and 400 microseconds
when the shift motor is active. A mode sensor signal
between 3.8 Volts and 0.8 Volts is considered to be
undefined.
Refer to SECTOR ANGLES vs. TRANSFER CASE
POSITION for the relative angles of the transfer case
shift sector versus the interpreted transfer case gear
operating mode. Refer to MODE SENSOR CHAN-
NEL STATES for the sensor codes returned to the
TCCM for each transfer case mode sensor position.
The various between gears positions can also be
referred as the transfer case's coarse position. These
coarse positions come into play during shift attempts.SECTOR ANGLES VS. TRANSFER CASE POSITION
Shaft Angle (Degrees) Transfer Case Position
+40 4LO
+20 N
0 2WD/AWD
-20 4HI
MODE SENSOR CHANNEL STATES
Transfer Case
Angle (degrees)Sensor Channel A Sensor Channel B Sensor Channel C Sensor Channel D
Between Gears H H L H
+40 (4LO) H H L L
Between Gears H H L H
Between Gears H L L H
+20 (NEUTRAL) H L L L
Between Gears H L L H
Between Gears H L H H
0 (2WD/AWD) H L H L
Between Gears H L H H
Between Gears L L H H
-20 (4HI) L L H L
Between Gears L L H H
Between Gears L H H H
Fig. 94 Mode Sensor
1 - MODE SENSOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 573
Page 2277 of 2627
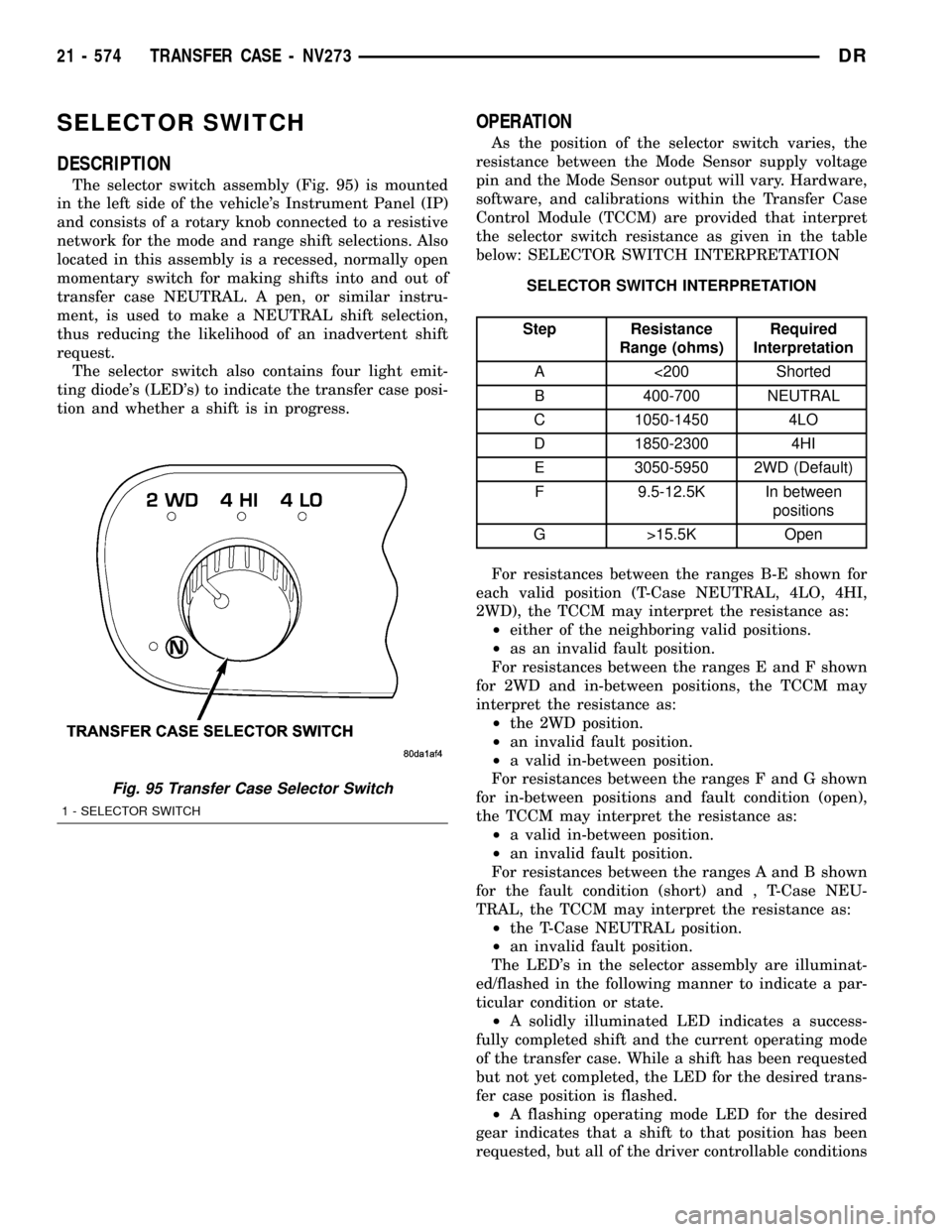
SELECTOR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The selector switch assembly (Fig. 95) is mounted
in the left side of the vehicle's Instrument Panel (IP)
and consists of a rotary knob connected to a resistive
network for the mode and range shift selections. Also
located in this assembly is a recessed, normally open
momentary switch for making shifts into and out of
transfer case NEUTRAL. A pen, or similar instru-
ment, is used to make a NEUTRAL shift selection,
thus reducing the likelihood of an inadvertent shift
request.
The selector switch also contains four light emit-
ting diode's (LED's) to indicate the transfer case posi-
tion and whether a shift is in progress.
OPERATION
As the position of the selector switch varies, the
resistance between the Mode Sensor supply voltage
pin and the Mode Sensor output will vary. Hardware,
software, and calibrations within the Transfer Case
Control Module (TCCM) are provided that interpret
the selector switch resistance as given in the table
below: SELECTOR SWITCH INTERPRETATION
SELECTOR SWITCH INTERPRETATION
Step Resistance
Range (ohms)Required
Interpretation
A <200 Shorted
B 400-700 NEUTRAL
C 1050-1450 4LO
D 1850-2300 4HI
E 3050-5950 2WD (Default)
F 9.5-12.5K In between
positions
G >15.5K Open
For resistances between the ranges B-E shown for
each valid position (T-Case NEUTRAL, 4LO, 4HI,
2WD), the TCCM may interpret the resistance as:
²either of the neighboring valid positions.
²as an invalid fault position.
For resistances between the ranges E and F shown
for 2WD and in-between positions, the TCCM may
interpret the resistance as:
²the 2WD position.
²an invalid fault position.
²a valid in-between position.
For resistances between the ranges F and G shown
for in-between positions and fault condition (open),
the TCCM may interpret the resistance as:
²a valid in-between position.
²an invalid fault position.
For resistances between the ranges A and B shown
for the fault condition (short) and , T-Case NEU-
TRAL, the TCCM may interpret the resistance as:
²the T-Case NEUTRAL position.
²an invalid fault position.
The LED's in the selector assembly are illuminat-
ed/flashed in the following manner to indicate a par-
ticular condition or state.
²A solidly illuminated LED indicates a success-
fully completed shift and the current operating mode
of the transfer case. While a shift has been requested
but not yet completed, the LED for the desired trans-
fer case position is flashed.
²A flashing operating mode LED for the desired
gear indicates that a shift to that position has been
requested, but all of the driver controllable conditions
Fig. 95 Transfer Case Selector Switch
1 - SELECTOR SWITCH
21 - 574 TRANSFER CASE - NV273DR
Page 2278 of 2627

have not been met. This is in an attempt to notify
the driver that the transmission needs to be put into
NEUTRAL, the vehicle speed is too great, or some
other condition outlined (other than a diagnostic fail-
ure that would prevent this shift) elsewhere (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/TRANSFER CASE CONTROL MODULE -
OPERATION) is not met. Note that this flashing will
continue indefinitely until the conditions are eventu-
ally met, or the selector switch position is changed,
or if diagnostic routines no longer allow the
requested shift.
²
If the driver attempts to make a shift into transfer
case NEUTRAL, and any of the driver controllable con-
ditions are not met, the request will be ignored until all
of the conditions are met or until the NEUTRAL select
button is released. Additionally the neutral lamp will
flash, or begin to flash while the button is depressed
and operator controllable conditions are not being met.
All of the LED's except the Neutral will flash if any of
the operator controllable conditions for shifting are not
met while the Neutral button is depressed. This9toggle9
type of feature is necessary because the TCCM would
interpret another request immediately after the shift
into transfer case NEUTRAL has completed.
²No LED's illuminated indicate a fault in the
transfer case control system.
SHIFT MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The shift motor (Fig. 96) consists of a permanent
magnet D.C. motor with gear reduction to convert a
high speed-low torque device into a low speed-high
torque device. The output of the device is coupled to
a shaft which internally moves the mode and range
forks that change the transfer case operating ranges.
The motor is rated at 25 amps maximum at 72É F
with 10 volts at the motor leads.
OPERATION
The transfer case shift motor responds to the
Transfer Case Control Module (TCCM) commands to
move the transfer case shift sector bi-directionally, as
required, to obtain the transfer case operating mode
indicated by the instrument panel mounted selector
switch.
REMOVAL
NOTE: New shift motor assemblies are shipped in
the 2WD/AWD position. If a new shift motor assem-
bly will be installed, it will be necessary to shift the
transfer case to the 2WD/AWD position prior to
motor removal.(1) Raise the vehicle on a suitable hoist.
(2) Disengage the wiring connectors from the shift
motor and mode sensor.
(3) Remove the bolts holding the shift motor and
mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
(4) Separate the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly from the transfer case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify that the shift sector o-ring is clean and
properly positioned over the shift sector and against
the transfer case.
NOTE: Verify that the shift motor position and sec-
tor shaft orientation are aligned. It may be neces-
sary to manually shift the transfer case if the shift
motor and sector shaft are not aligned.
(2) Position the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly onto the transfer case.
(3) Install the bolts to hold the assembly onto the
transfer case. Tighten the bolts to 16-24 N´m (12-18
ft.lbs.).
CAUTION: If the original shift motor and mode sen-
sor assembly bolts are reused, be sure to use
MoparTLock & Seal or LoctiteŸ 242 to replenish
the lock patch material originally found on the bolts
(4) Engage the wiring connectors to the shift motor
and mode sensor.
(5) Refill the transfer case as necessary.
(6) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case
operation.
Fig. 96 Shift Motor - Shown Inverted - Typical
1 - SHIFT MOTOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 575
SELECTOR SWITCH (Continued)