1998 DODGE RAM 1500 key battery
[x] Cancel search: key batteryPage 1504 of 2627
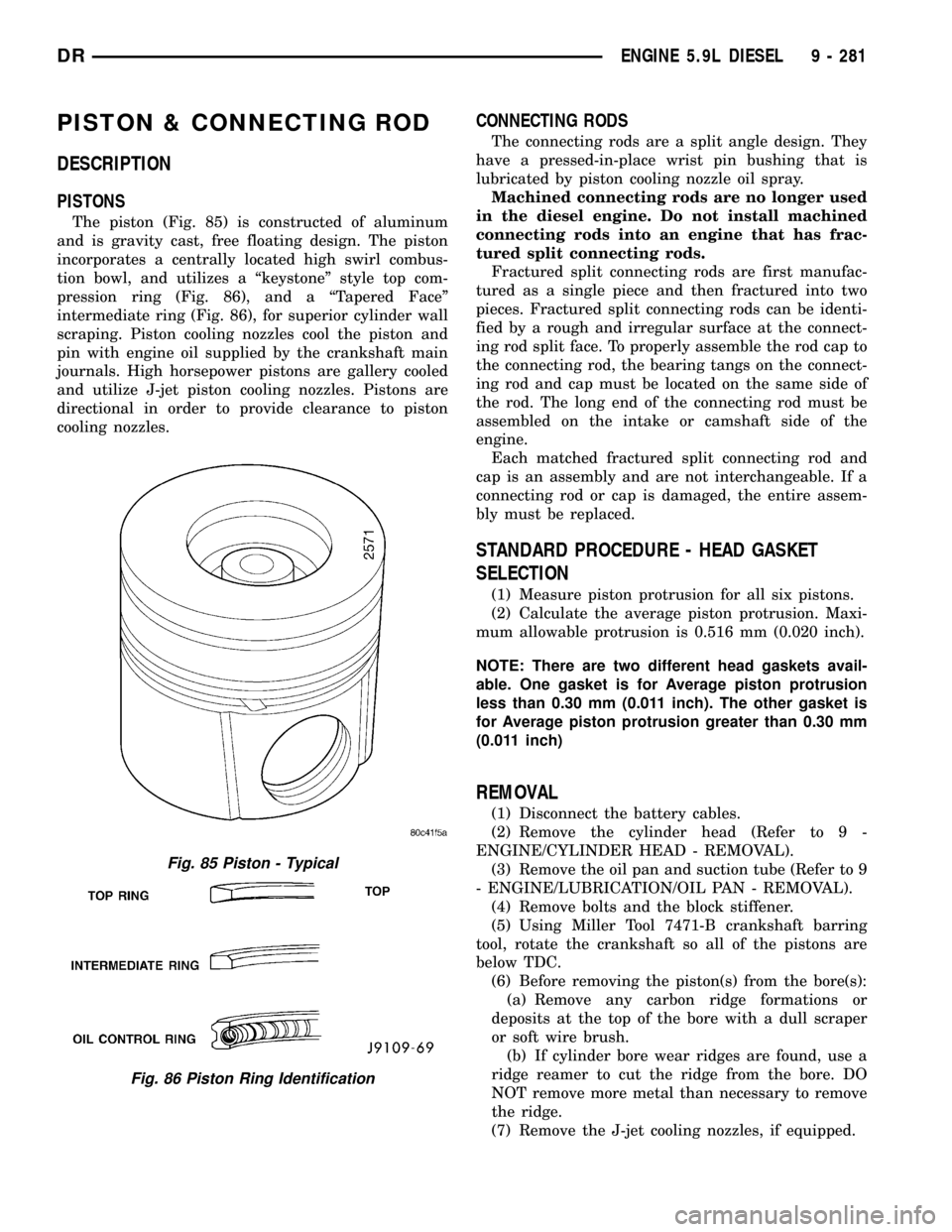
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
PISTONS
The piston (Fig. 85) is constructed of aluminum
and is gravity cast, free floating design. The piston
incorporates a centrally located high swirl combus-
tion bowl, and utilizes a ªkeystoneº style top com-
pression ring (Fig. 86), and a ªTapered Faceº
intermediate ring (Fig. 86), for superior cylinder wall
scraping. Piston cooling nozzles cool the piston and
pin with engine oil supplied by the crankshaft main
journals. High horsepower pistons are gallery cooled
and utilize J-jet piston cooling nozzles. Pistons are
directional in order to provide clearance to piston
cooling nozzles.
CONNECTING RODS
The connecting rods are a split angle design. They
have a pressed-in-place wrist pin bushing that is
lubricated by piston cooling nozzle oil spray.
Machined connecting rods are no longer used
in the diesel engine. Do not install machined
connecting rods into an engine that has frac-
tured split connecting rods.
Fractured split connecting rods are first manufac-
tured as a single piece and then fractured into two
pieces. Fractured split connecting rods can be identi-
fied by a rough and irregular surface at the connect-
ing rod split face. To properly assemble the rod cap to
the connecting rod, the bearing tangs on the connect-
ing rod and cap must be located on the same side of
the rod. The long end of the connecting rod must be
assembled on the intake or camshaft side of the
engine.
Each matched fractured split connecting rod and
cap is an assembly and are not interchangeable. If a
connecting rod or cap is damaged, the entire assem-
bly must be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEAD GASKET
SELECTION
(1) Measure piston protrusion for all six pistons.
(2) Calculate the average piston protrusion. Maxi-
mum allowable protrusion is 0.516 mm (0.020 inch).
NOTE: There are two different head gaskets avail-
able. One gasket is for Average piston protrusion
less than 0.30 mm (0.011 inch). The other gasket is
for Average piston protrusion greater than 0.30 mm
(0.011 inch)
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery cables.
(2) Remove the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the oil pan and suction tube (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove bolts and the block stiffener.
(5) Using Miller Tool 7471-B crankshaft barring
tool, rotate the crankshaft so all of the pistons are
below TDC.
(6) Before removing the piston(s) from the bore(s):
(a) Remove any carbon ridge formations or
deposits at the top of the bore with a dull scraper
or soft wire brush.
(b) If cylinder bore wear ridges are found, use a
ridge reamer to cut the ridge from the bore. DO
NOT remove more metal than necessary to remove
the ridge.
(7) Remove the J-jet cooling nozzles, if equipped.
Fig. 85 Piston - Typical
Fig. 86 Piston Ring Identification
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 281
Page 1522 of 2627

(3) Install heat shield and torque nuts to 15 Nm
(11 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install cab heater tube.
(5) Install exhaust manifold bolt retention straps.
(6) Install the cab heater return hose to the man-
ifold bolt stud. Tighten the nut to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(7) Install the turbocharger and a new gasket.
Apply anti-seize to the studs and then tighten the
turbocharger mounting nuts to 43 N´m (32 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(8)Pre-lube the turbocharger.Pour 50 to 60 cc
(2 to 3 oz.) clean engine oil in the oil supply line fit-
ting on the turbo. Rotate the turbocharger impeller
by hand to distrubute the oil thoroughly.
(9) Install and tighten the oil supply line fitting
nut to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Position the charge air cooler inlet pipe to the
turbocharger. With the clamp in position, tighten the
clamp nut to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Position the air inlet hose to the turbocharger.
Tighten the clamp to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.) torque.
(12) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(13) Install the oil drain tube and a new gasket to
the turbocharger. Tighten the drain tube bolts to 24
N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(14) Connect the exhaust pipe to the turbocharger
and tighten the bolts to 11 N´m (100 ft. lbs.) torque.
(15) Lower the vehicle.
(16) Connect the battery negative cables.
(17) Start the engine to check for leaks.
VALVE TIMING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIMING
VERIFICATION
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove fuel injector from cylinder number
1(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
FUEL INJECTOR - REMOVAL).
(3) Using Special Tool 7471B rotate the engine
until the TDC mark on the damper is at 12 o'clock.
(4) Using a 8 in.x 1/4 in. dowel rod inserted into
cylinder number 1, rock the crankshaft back and
forth to verify piston number 1 is at TDC.
(5) With cylinder number still at TDC, inspect the
keyway on the crankshaft gear for proper alignment
(12 o'clock position).
(6) If the keyway is not at 12 o'clock position
replace the crankshaft gear assembly.
(7) If the keyway is at 12 o'clock position, remove
front gear cover and verify timing mark alignmentbetween the camshaft gear and crankshaft gear, if
not aligned inspect keyway on camshaft gear.
(8) Inspect keyway on camshaft gear for proper
alignment with the key in the camshaft, if alignment
is off replace the camshaft/gear assembly.
(9) If timing marks alignment is off and no dam-
age is found at either the crankshaft or camshaft
gear keyways, realign timing marks as necessary.
GEAR HOUSING
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Partially drain engine coolant into container
suitable for re-use (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Remove radiator upper hose.
(6) Disconnect coolant recovery bottle hose from
radiator filler neck and lift bottle off of fan shroud.
(7) Disconnect windshield washer pump supply
hose and electrical connections and lift washer bottle
off of fan shroud.
(8) Remove lower fan shroud fasteners. Disconnect
fan drive wire harness.
(9) Remove the upper fan shroud-to-radiator
mounting bolts.
(10) Remove viscous fan/drive assembly (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(11) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(12) Remove the cooling fan support/hub from the
front of the engine.
(13) Raise the vehicle on hoist.
(14) Remove the crankshaft damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL) and speed indicator ring.
(15) Lower the vehicle.
(16) Remove the power steering pump.
(17) Remove the accessory drive belt tensioner.
(18) Remove the gear cover-to-housing bolts and
gently pry the cover away from the housing, taking
care not to mar the gasket surfaces.
(19) Remove the fuel injection pump (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL INJEC-
TION PUMP - REMOVAL).
(20) Disconnect the camshaft position sensor con-
nector.
(21) Disconnect and remove engine speed sensor.
(22) Remove the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - REMOVAL).
(23) Remove the six front oil pan fasteners.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 299
EXHAUST MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1572 of 2627
(2) Remove fuel pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.
(3) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(4) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(5) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
CAUTION: Steps 1, 2, 3 and 4 must be performed to
relieve high pressure fuel from within fuel rail. Do
not attempt to use following steps to relieve this
pressure as excessive fuel will be forced into a cyl-
inder chamber.
(6) Unplug connector from any fuel injector.
(7) Attach one end of a jumper wire with alligator
clips (18 gauge or smaller) to either injector terminal.
(8) Connect other end of jumper wire to positive
side of battery.(9) Connect one end of a second jumper wire to
remaining injector terminal.
CAUTION: Powering an injector for more than a few
seconds will permanently damage the injector.
(10) Momentarily touch other end of jumper wire
to negative terminal of battery for no more than a
few seconds.
(11) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(12) Disconnect quick-connect fitting at fuel rail.
Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(13) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(14) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRBtscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
58 psi +/- 2 psi
TORQUE - FUEL SYSTEM - EXCEPT DIESEL
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Accelerator Pedal Bracket
Mounting12 - 105
Accelerator Pedal Position
Sensor Bracket-to-Battery
Tray Bolts3-30
Crankshaft Position
Sensor - 3.7L28 21 -
Crankshaft Position
Sensor - 4.7L28 21 -
Crankshaft Position
Sensor - 5.7L12 - 105 (+/-20)
Camshaft Position Sensor
- 3.7L12 - 106
Camshaft Position Sensor
- 4.7L12 - 106
Camshaft Position Sensor
- 5.7L12 9 105 (+/-) 20
Engine Coolant
Temperature Sensor -
3.7L11 - 9 6
Engine Coolant
Temperature Sensor -
4.7L11 - 9 6
DRFUEL DELIVERY - GAS 14 - 3
FUEL DELIVERY - GAS (Continued)
Page 1596 of 2627

stream. The spraying action atomizes the fuel, add-
ing it to the air entering the combustion chamber.
The nozzle (outlet) ends of the injectors are posi-
tioned into openings in the intake manifold just
above the intake valve ports of the cylinder head.
The engine wiring harness connector for each fuel
injector is equipped with an attached numerical tag
(INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.). This is used to identify each fuel
injector.
The injectors are energized individually in a
sequential order by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM will adjust injector pulse width by
switching the ground path to each individual injector
on and off. Injector pulse width is the period of time
that the injector is energized. The PCM will adjust
injector pulse width based on various inputs it
receives.
Battery voltage is supplied to the injectors through
the ASD relay.
The PCM determines injector pulse width based on
various inputs.
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The nozzle ends of the injectors are positioned into
openings in the intake manifold just above the intake
valve ports of the cylinder head. The engine wiring
harness connector for each fuel injector is equipped
with an attached numerical tag (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.).
This is used to identify each fuel injector with its
respective cylinder number.
The injectors are energized individually in a
sequential order by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM will adjust injector pulse width by
switching the ground path to each individual injector
on and off. Injector pulse width is the period of time
that the injector is energized. The PCM will adjust
injector pulse width based on various inputs it
receives.
Battery voltage (12 volts +) is supplied to the injec-
tors through the ASD relay. The ASD relay will shut-
down the 12 volt power source to the fuel injectors if
the PCM senses the ignition is on, but the engine is
not running. This occurs after the engine has not
been running for approximately 1.8 seconds.
The PCM determines injector on-time (pulse width)
based on various inputs.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove fuel rail. Refer to Fuel Injector Rail
Removal.
(2) Disconnect clip(s) that retain fuel injector(s) to
fuel rail (Fig. 12).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install fuel injector(s) into fuel rail assembly
and install retaining clip(s).(2) If same injector(s) is being reinstalled, install
new o-ring(s).
(3) Apply a small amount of clean engine oil to
each injector o-ring. This will aid in installation.
(4) Install fuel rail. Refer to Fuel Rail Installation.
(5) Start engine and check for fuel leaks.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The 5±pin, 12±volt, fuel pump relay is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the
label on the PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) energizes
the electric fuel pump through the fuel pump relay.
The fuel pump relay is energized by first applying
battery voltage to it when the ignition key is turned
ON, and then applying a ground signal to the relay
from the PCM.
Whenever the ignition key is turned ON, the elec-
tric fuel pump will operate. But, the PCM will shut-
down the ground circuit to the fuel pump relay in
approximately 1±3 seconds unless the engine is oper-
ating or the starter motor is engaged.
Fig. 12 INJECTOR RETAINING CLIP
1 - PLIERS
2 - INJECTOR CLIP
3 - FUEL INJECTOR - TYPICAL
4 - FUEL RAIL - TYPICAL
DRFUEL INJECTION - GAS 14 - 27
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1597 of 2627

REMOVAL
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC) (Fig. 13). Refer to label on PDC
cover for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for
relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
A separate IAC motor is not used with the 5.7L V-8
engine.
The IAC stepper motor is mounted to the throttle
body, and regulates the amount of air bypassing the
control of the throttle plate. As engine loads and
ambient temperatures change, engine rpm changes.
A pintle on the IAC stepper motor protrudes into apassage in the throttle body, controlling air flow
through the passage. The IAC is controlled by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to maintain the
target engine idle speed.
OPERATION
A separate IAC motor is not used with the 5.7L V-8
engine.
At idle, engine speed can be increased by retract-
ing the IAC motor pintle and allowing more air to
pass through the port, or it can be decreased by
restricting the passage with the pintle and diminish-
ing the amount of air bypassing the throttle plate.
The IAC is called a stepper motor because it is
moved (rotated) in steps, or increments. Opening the
IAC opens an air passage around the throttle blade
which increases RPM.
The PCM uses the IAC motor to control idle speed
(along with timing) and to reach a desired MAP dur-
ing decel (keep engine from stalling).
The IAC motor has 4 wires with 4 circuits. Two of
the wires are for 12 volts and ground to supply elec-
trical current to the motor windings to operate the
stepper motor in one direction. The other 2 wires are
also for 12 volts and ground to supply electrical cur-
rent to operate the stepper motor in the opposite
direction.
To make the IAC go in the opposite direction, the
PCM just reverses polarity on both windings. If only
1 wire is open, the IAC can only be moved 1 step
(increment) in either direction. To keep the IAC
motor in position when no movement is needed, the
PCM will energize both windings at the same time.
This locks the IAC motor in place.
In the IAC motor system, the PCM will count
every step that the motor is moved. This allows the
PCM to determine the motor pintle position. If the
memory is cleared, the PCM no longer knows the
position of the pintle. So at the first key ON, the
PCM drives the IAC motor closed, regardless of
where it was before. This zeros the counter. From
this point the PCM will back out the IAC motor and
keep track of its position again.
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following:
²Off-idle dashpot (throttle blade will close quickly
but idle speed will not stop quickly)
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
²Power steering load control
The PCM can control polarity of the circuit to con-
trol direction of the stepper motor.
Fig. 13 PDC LOCATION
1 - BATTERY
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
14 - 28 FUEL INJECTION - GASDR
FUEL PUMP RELAY (Continued)
Page 1623 of 2627

REMOVAL
CAUTION: Cleanliness cannot be overemphasized
when handling or replacing diesel fuel system com-
ponents. This especially includes the fuel injectors,
high-pressure fuel lines and fuel injection pump.
Very tight tolerances are used with these parts. Dirt
contamination could cause rapid part wear and pos-
sible plugging of fuel injector nozzle tip holes. This
in turn could lead to possible engine misfire.
Always wash/clean any fuel system component
thoroughly before disassembly and then air dry.
Cap or cover any open part after disassembly.
Before assembly, examine each part for dirt, grease
or other contaminants and clean if necessary. When
installing new parts, lubricate them with clean
engine oil or clean diesel fuel only.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries. Cover and isolate ends of both cables.
(2) Remove intake manifold air intake tube (above
injection pump) and its rubber connector hose (Fig.
7).
(3) Remove accessory drive belt.
(4) Thoroughly clean the rear of injection pump,
and attachment points for its 3 fuel lines (Fig. 8).
Also clean the opposite ends of these same 3 lines at
their attachment points.
(5) Disconnect Fuel Control Actuator (FCA) electri-
cal connector at rear of injection pump (Fig. 9).
CAUTION: Whenever a fuel line fitting is connected
to a secondary fitting, always use a back-up wrench
on the secondary fitting. Do not allow the second-
ary fitting to rotate.
(6) Remove fuel line (injection pump-to-fuel pres-
sure limiting valve).
(7) Remove fuel line (injection pump-to-fuel rail).
Use back-up wrench on fitting at fuel pump.
(8) Remove fuel line (injection pump-to-fuel filter
housing).
(9) Remove fuel pump drive gear access cover
(plate) with a 3/8º drive ratchet. Plate is threaded to
timing gear cover (Fig. 10).
(10) Remove fuel pump drive gear mounting nut
and washer.
(11) Attach C3428B, or L4407A (or equivalent)
gear puller (Fig. 11) to pump drive gear with 2 bolts,
and separate gear from pump (a keyway is not used
on this particular injection pump). Leave drive gear
hanging loose within timing gear cover.
(12) Remove 3 injection pump mounting nuts (Fig.
12), and remove pump from engine.
Fig. 7 INTAKE TUBE AND CONNECTING HOSE
1 - MANIFOLD ABOVE HEATERS
2 - RUBBER CONNECTING HOSE
3 - METAL INTAKE TUBE
4 - CLAMPS (2)
Fig. 8 OVERFLOW VALVE
1 - BANJO BOLTS
2 - PUMP MOUNTING NUTS (3)
3 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
4 - CASCADE OVERFLOW VALVE
14 - 54 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELDR
FUEL INJECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 1640 of 2627

INSTALLATION
Engine Mounted Sensor :
The APPS is serviced (replaced) as one assembly
including the lever, brackets and sensor. The APPS is
calibrated to its mounting bracket.
(1) Snap electrical connector into bottom of sensor.
(2) Position APPS assembly to engine and install 6
bolts. Tighten bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect wiring harness clip at bottom of
bracket.
(4) Refer to Group 21, Transmission for transmis-
sion control cable installation procedures.
(5) Install speed control cable into mounting
bracket. Be sure pinch tabs have secured cable.
(6) Install throttle cable into mounting bracket. Be
sure pinch tabs have secured cable.
(7) Connect throttle cable at lever (snaps on).
(8) Connect speed control cable to lever by pushing
cable connector rearward onto lever pin while hold-
ing lever forward.
(9) Install cable cover.
(10) Connect both negative battery cables to both
batteries.
(11) If necessary, use DRB IIItScan Tool to erase
any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) from ECM.Battery Tray Mounted Sensor :
(1) Install Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
(APPS) cable to accelerator pedal. Refer to Accelera-
tor Pedal Removal / Installation.
(2) Connect electrical connector to APPS.
(3) If necessary, connect cable to APPS lever ball
socket (snaps on).
(4) Snap APPS cable cover closed.
(5) Position APPS assembly to bottom of battery
tray and install 3 bolts. Refer to Torque Specifica-
tions.
(6) Install wheelhouse liner. Refer to Body.
(7) Perform the following procedure:
(a) Connect negative battery cables to both bat-
teries.
(b) Turn key switch ON, but do not crank
engine.
(c) Leave key switch ON for a minimum of 10
seconds. This will allow ECM to learn electrical
parameters.
(8) If necessary, use DRB IIItScan Tool to erase
any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) from ECM.
CAMSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) on the 5.9L
diesel engine is located below the fuel injection
pump. It is bolted to the back of the timing gear
housing.
OPERATION
The diesel Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) con-
tains a hall effect device. A rotating target wheel
(tonewheel) for the CMP is located on the camshaft
gear. This hall effect device detects notches located
on the back side of the camshaft gear. As the cam-
shaft gear rotates, the notches pass the tip of the
CMP.
When the leading edge of the notch passes the tip
of the CMP, the following occurs: The interruption of
magnetic field causes the voltage to switch high
resulting in a signal of approximately 5 volts.
When the trailing edge of the notch passes the tip
of the CMP, the following occurs: The change of the
magnetic field causes the signal voltage to switch low
to 0 volts.
The CMP (Fig. 8) provides a signal to the Engine
Control Module (ECM) at all times when the engine
is running. The ECM uses the CMP information pri-
marily on engine start-up. Once the engine is run-
ning, the ECM uses the CMP as a backup sensor for
engine speed. The Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP)
Fig. 7 APPS CABLE (OFF ENGINE MOUNTING)
1 - APPS LEVER
2 - BALL SOCKET
3 - SWING-DOWN DOOR
4 - CABLE CLIP
5 - CABLE
DRFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 71
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1661 of 2627

COLUMN
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COLUMN
DESCRIPTION..........................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING
COLUMN.............................7
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................9
IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - IGNITION
SWITCH.............................9
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................11
KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - IGNITION
SWITCH AND KEY LOCK CYLINDER.......11
KEY CYLINDER
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12GEAR SHIFT LEVER
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
UPPER STEERING COUPLING
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
LOWER STEERING COUPLING
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - ALL LD & HD EXCEPT 4X4 HD . 14
REMOVAL - 4X4 HD...................14
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - ALL LD & HD EXCEPT 4X4
HD.................................14
INSTALLATION - 4X4 HD................15
STEERING WHEEL
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
TILT LEVER KNOB RELEASE
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
COLUMN
DESCRIPTION
NOTE: The steering column on vehicles with an
automatic transmission may not be equipped with
an internal locking shaft that allows the ignition key
cylinder to be locked with the key. Alternative meth-
ods of locking the steering wheel for service will
have to be used.
The tilt and standard column (Fig. 1) has been
designed to be serviced as an assembly; less wiring,
switches, shrouds, steering wheel, etc. Most steering
column components can be serviced without remov-
ing the steering column from the vehicle.
To service the steering wheel, switches or airbag,
refer to Restraints and follow all WARNINGS and
CAUTIONS.
WARNING: THE AIRBAG SYSTEM IS A SENSITIVE,
COMPLEX ELECTRO-MECHANICAL UNIT. BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO DIAGNOSE, REMOVE OR INSTALL
THE AIRBAG SYSTEM COMPONENTS YOU MUST
FIRST DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY
NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE. THEN WAIT TWO
MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DIS-
CHARGE. FAILURE TO DO SO COULD RESULT INACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT OF THE AIRBAG AND
POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY. THE FASTENERS,
SCREWS, AND BOLTS, ORIGINALLY USED FOR
THE AIRBAG COMPONENTS, HAVE SPECIAL COAT-
INGS AND ARE SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE
AIRBAG SYSTEM. THEY MUST NEVER BE
REPLACED WITH ANY SUBSTITUTES. ANYTIME A
NEW FASTENER IS NEEDED, REPLACE WITH THE
CORRECT FASTENERS PROVIDED IN THE SERVICE
PACKAGE OR FASTENERS LISTED IN THE PARTS
BOOKS.
CAUTION: Do not hammer on steering column
shaft. This may cause damage to the shaft or bear-
ing.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to remove the pivot bolts
to disassemble the tilting mechanism. Do not
remove shaft lock plate or plate retainer. This will
damage the column.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to remove or modify the
park lock slider or link.
19 - 6 COLUMNDR