1998 DODGE RAM 1500 air conditioning
[x] Cancel search: air conditioningPage 2500 of 2627

NOTE: The air gap is determined by the spacer
shims. When installing an original, or a new clutch
assembly, try the original shims first. When install-
ing a new clutch onto a compressor that previously
did not have a clutch, use a 1.0, 0.50, and 0.13 mil-
limeter (0.040, 0.020, and 0.005 inch) shims from the
new clutch hardware package that is provided with
the new clutch.
(9) To complete the procedure (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - INSTALLATION).
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The A/C compressor clutch relay (Fig. 10) is a
International Standards Organization (ISO) micro-re-
lay. Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The ISO
micro-relay terminal functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the ISO micro-relay
terminal pattern (or footprint) is different, the cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the physical dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
The A/C compressor clutch relay is located in the
intergrated power module (IPM) in the engine com-
partment. See the fuse and relay layout label affixed
to the inside surface of the IPM cover for A/C com-
pressor clutch relay identification and location.
The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the A/C compressor clutch relay. Fivemale spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of
the base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical
system, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.
²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
OPERATION
The A/C compressor clutch relay is an electrome-
chanical switch that uses a low current input from
the powertrain control module (PCM) or engine con-
trol module (ECM) depending on engine application,
to control the high current output to the compressor
clutch electromagnetic coil. The movable common
feed contact point is held against the fixed normally
closed contact point by spring pressure. When the
relay coil is energized, an electromagnetic field is
produced by the coil windings. This electromagnetic
field draws the movable relay contact point away
from the fixed normally closed contact point, and
holds it against the fixed normally open contact
point. When the relay coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns the movable contact point back
against the fixed normally closed contact point. The
resistor or diode is connected in parallel with the
relay coil in the relay, and helps to dissipate voltage
Fig. 9 Check Clutch Air Gap - Typical
1 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 10 A/C Compressor Clutch Micro-Relay
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
DRCONTROLS 24 - 13
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL (Continued)
Page 2501 of 2627

spikes and electromagnetic interference that can be
generated as the electromagnetic field of the relay
coil collapses.
The A/C compressor clutch relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a
receptacle in the integrated power module (IPM). The
inputs and outputs of the A/C compressor clutch
relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from a fuse in the IPM through a
fused B(+) circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (86) receives a ground
input from the PCM/ECM through the A/C compres-
sor clutch relay control circuit only when the PCM/
ECM electronically pulls the control circuit to
ground.
²The coil battery terminal (85) receives a battery
current input from PTC 1 in the IPM through a
fused ignition switch output (run) circuit only when
the ignition switch is in the On position.
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the compressor clutch coil
through the A/C compressor clutch relay output cir-
cuit only when the A/C compressor clutch relay coil is
energized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the A/C compres-
sor clutch relay coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for com-
plete HVAC wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the integrated power
module (IPM) (Fig. 11).
(3) Refer to the fuse and relay layout label on the
IPM cover for compressor clutch relay identification
and location.
(4) Remove the A/C compressor clutch relay from
the IPM.
INSTALLATION
(1) See the fuse and relay layout label affixed to
the underside of the IPM cover for A/C compressor
clutch relay location.
(2) Position the A/C compressor clutch relay in the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(3) Align the A/C compressor clutch relay termi-
nals with the terminal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(4) Push down firmly on the A/C compressor clutch
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(5) Install the cover onto the IPM.(6) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The heater and air conditioning systems use elec-
trical controls. These controls provide the vehicle
operator with a number of setting options to help
control the climate and comfort within the vehicle.
The A/C-heater control for the Single Zone system
(Fig. 12) or Dual Zone system (Fig. 13) is located to
the right of the instrument cluster on the instrument
panel.
The Single Zone control panel contains a rotary-
type temperature control switch, a rotary-type mode
control switch and a rotary-type blower motor speed
switch. The A/C-heater control also has a push but-
ton to activate the optional heated side view mirror
defroster elements and to turn the A/C on.
The Dual Zone control panel contains a pair of slid-
er-type temperature control switches, a rotary-type
mode control switch and a rotary-type blower motor
speed switch. The control also has buttons to activate
the optional heated sideview mirror defroster ele-
ments, turn the A/C on and set the system to Max
A/C.
The A/C-heater control panel cannot be repaired. If
faulty or damaged, the entire unit must be replaced.
Fig. 11 Integrated Power Module (IPM)
1 - BATTERY
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
24 - 14 CONTROLSDR
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 2503 of 2627

The A/C pressure transducer cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The A/C pressure transducer monitors the pres-
sures in the high side of the refrigerant system
through its connection to a fitting on the discharge
line. The transducer will change its internal resis-
tance in response to the pressures it monitors. The
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or the Engine
Control Module (ECM) depending on engine applica-
tion, provides a five volt reference signal and a sen-
sor ground to the transducer, then monitors the
output voltage of the transducer on a sensor return
circuit to determine refrigerant pressure. The PCM/
ECM is programmed to respond to this and other
sensor inputs by controlling the operation of the air
conditioning compressor clutch and the radiator cool-
ing fan to help optimize air conditioning system per-
formance and to protect the system components from
damage. The A/C pressure transducer input to the
PCM/ECM will also prevent the air conditioning com-
pressor clutch from engaging when ambient temper-
atures are below about 10É C (50É F) due to the
pressure/temperature relationship of the refrigerant.
The Schrader-type valve in the discharge line fitting
permits the A/C pressure transducer to be removed
or installed without disturbing the refrigerant in the
system. The A/C pressure transducer is diagnosed
using a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
The A/C pressure transducer is tested using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information. Before testing the A/C pressure
transducer, be certain that the transducer wire har-
ness connection is clean of corrosion and properly
connected. For the air conditioning system to operate,
an A/C pressure transducer voltage reading between
0.451 and 4.519 volts is required. Voltages outside
this range indicate a low or high refrigerant system
pressure condition to the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) or Engine Control Module (ECM) depending
on engine application. The PCM/ECM is programmed
to respond to a low or high refrigerant system pres-
sure by suppressing operation of the compressor.
Refer to the A/C Pressure Transducer Voltage chart
for the possible conditions indicated by the trans-
ducer voltage reading.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER VOLTAGE
CHART
Voltage Possible Indication
0.0 1. No sensor supply voltage from
PCM/ECM.
2. Shorted sensor circuit.
3. Faulty transducer.
0.150 TO 0.450 1. Ambient temperature below
10É C (50É F).
2. Low refrigerant system
pressure.
0.451 TO 4.519 1. Normal refrigerant system
pressure.
4.520 TO 4.850 1. High refrigerant system
pressure.
5.0 1. Open sensor circuit.
2. Faulty transducer.
REMOVAL
NOTE: Note: It is not necessary to discharge the
refrigerant system to replace the A/C pressure
transducer.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
A/C pressure transducer.
(3) Remove the A/C pressure transducer from the
fitting on the discharge line (Fig. 15).
(4) Remove the O-ring seal from the A/C pressure
transducer fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Replace the O-ring seal before installing the
A/C pressure transducer.
(1) Lubricate a new rubber O-ring seal with clean
refrigerant oil and install it on the A/C pressure
transducer fitting. Use only the specified O-rings as
they are made of a special material for the R-134a
system. Use only refrigerant oil of the type recom-
mended for the A/C compressor in the vehicle.
(2) Install and tighten the A/C pressure transducer
onto the discharge line fitting. The transducer should
be hand-tightened securely onto the discharge line
fitting.
(3) Connect the wire harness connector to the A/C
pressure transducer.
24 - 16 CONTROLSDR
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER (Continued)
Page 2505 of 2627
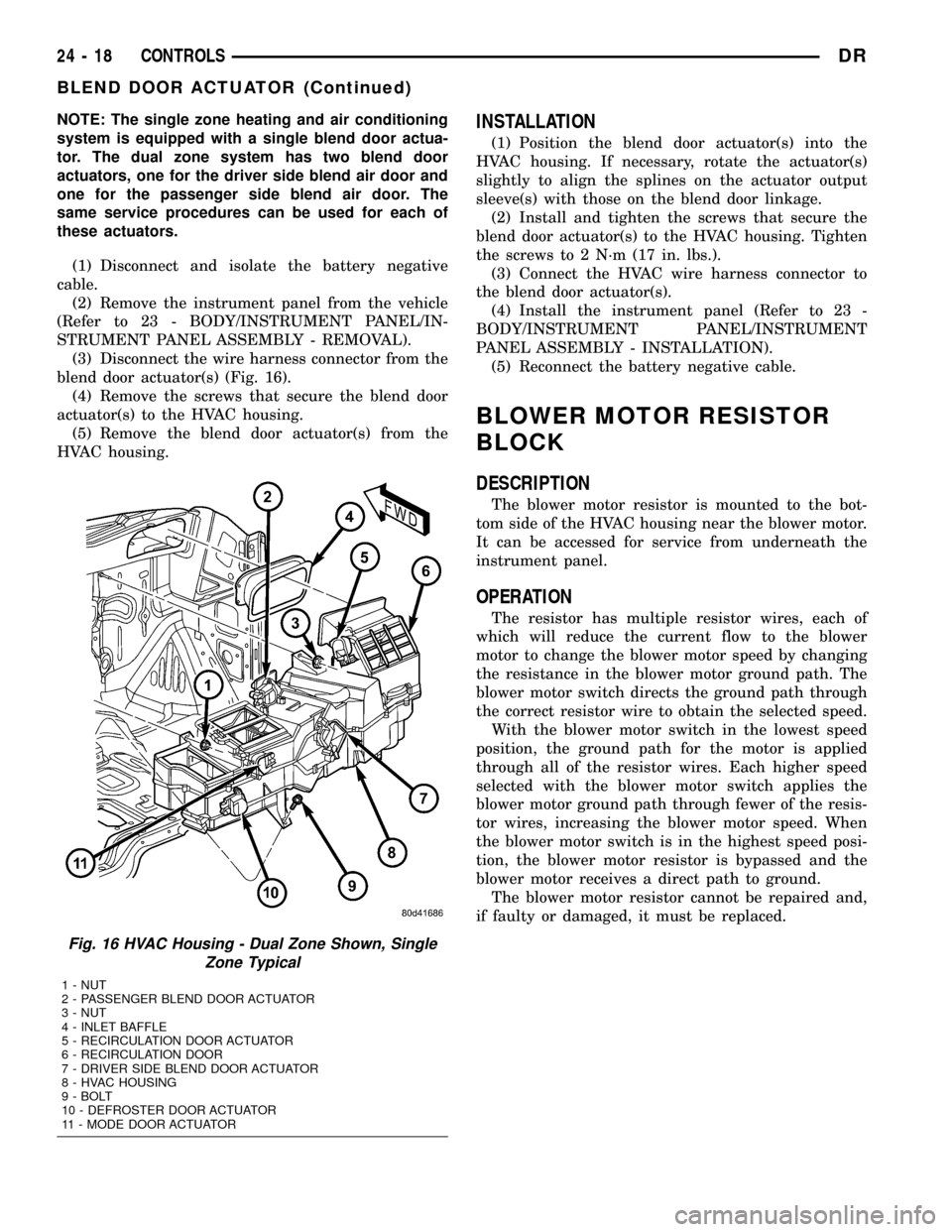
NOTE: The single zone heating and air conditioning
system is equipped with a single blend door actua-
tor. The dual zone system has two blend door
actuators, one for the driver side blend air door and
one for the passenger side blend air door. The
same service procedures can be used for each of
these actuators.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the instrument panel from the vehicle
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
blend door actuator(s) (Fig. 16).
(4) Remove the screws that secure the blend door
actuator(s) to the HVAC housing.
(5) Remove the blend door actuator(s) from the
HVAC housing.INSTALLATION
(1) Position the blend door actuator(s) into the
HVAC housing. If necessary, rotate the actuator(s)
slightly to align the splines on the actuator output
sleeve(s) with those on the blend door linkage.
(2) Install and tighten the screws that secure the
blend door actuator(s) to the HVAC housing. Tighten
the screws to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the HVAC wire harness connector to
the blend door actuator(s).
(4) Install the instrument panel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL ASSEMBLY - INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
The blower motor resistor is mounted to the bot-
tom side of the HVAC housing near the blower motor.
It can be accessed for service from underneath the
instrument panel.
OPERATION
The resistor has multiple resistor wires, each of
which will reduce the current flow to the blower
motor to change the blower motor speed by changing
the resistance in the blower motor ground path. The
blower motor switch directs the ground path through
the correct resistor wire to obtain the selected speed.
With the blower motor switch in the lowest speed
position, the ground path for the motor is applied
through all of the resistor wires. Each higher speed
selected with the blower motor switch applies the
blower motor ground path through fewer of the resis-
tor wires, increasing the blower motor speed. When
the blower motor switch is in the highest speed posi-
tion, the blower motor resistor is bypassed and the
blower motor receives a direct path to ground.
The blower motor resistor cannot be repaired and,
if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
Fig. 16 HVAC Housing - Dual Zone Shown, Single
Zone Typical
1 - NUT
2 - PASSENGER BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
3 - NUT
4 - INLET BAFFLE
5 - RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR
6 - RECIRCULATION DOOR
7 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
8 - HVAC HOUSING
9 - BOLT
10 - DEFROSTER DOOR ACTUATOR
11 - MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
24 - 18 CONTROLSDR
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)
Page 2509 of 2627

EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The evaporator temperature sensor is a two-wire
temperature sensing element located at the coldest
point on the face of the evaporator. The sensor is
attached to the evaporator coil fins. The evaporator
temperature sensor prevents condensation on the
evaporator coil from freezing and obstructing A/C
system air flow. The evaporator temperature sensor
cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or dam-
aged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The evaporator temperature sensor monitors the
temperature of the evaporator. The sensor will
change its internal resistance in response to the tem-
peratures it monitors. The A/C-heater control module
is connected to the sensor through a sensor ground
circuit and a sensor signal circuit. As the evaporator
temperature increases, the resistance of the sensor
decreases and the voltage monitored by the module
decreases. The module uses this monitored voltage
reading to an indication of the evaporator tempera-
ture. The A/C-heater control module is programmed
to respond to this input by cycling the air condition-
ing compressor clutch as necessary to optimize air
conditioning system performance and to protect the
system from evaporator freezing. The external loca-
tion of the sensor allows the sensor to be removed or
installed without disturbing the refrigerant in the
system. The evaporator temperature sensor is diag-
nosed using a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to Body Diag-
nostic Procedures.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the HVAC wire harness connector
from the evaporator temperature sensor (Fig. 20).
(4) Disassemble the HVAC housing to gain access
to the evaporator coil (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING
- DISASSEMBLY).
(5) Remove the evaporator temperature sensor
probe from the evaporator coil (Fig. 21).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the evaporator temperature sensor
probe into the evaporator coil.
Fig. 20 Evaporator Temperature Sensor Wire
Connector
1 - HVAC HOUSING
2 - EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
3 - HVAC WIRE HARNESS
Fig. 21 Evaporator Temperature Sensor Probe
1 - EVAPORATOR COIL
2 - EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR PROBE
3 - BLEND DOOR
4 - HVAC HOUSING
24 - 22 CONTROLSDR
Page 2510 of 2627

(2) Assemble the HVAC housing (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - ASSEMBLY).
(3) Connect the HVAC wire harness connector to
the evaporator temperature sensor.
(4) Install the HVAC housing (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC
HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION
The mode door actuator is a reversible 12-volt
Direct Current (DC) servo motor. The mode door
actuator is located on the HVAC housing, behind the
instrument panel and is mechanically connected to
the mode door.
The mode door actuator is interchangeable with
the actuators for the blend door(s), defrost door and
the recirculation door. Each actuator is contained
within an identical black molded plastic housing with
an integral wire connector receptacle. Integral
mounting tabs allow the actuator to be secured with
three screws to the HVAC housing. Each actuator
also has an identical output shaft with splines that
connects it to the linkage that drives the proper door.
The mode door actuator does not require mechanical
indexing to the mode door linkage, as it is electroni-
cally calibrated by the heater-A/C control module.
The mode door actuator cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if damaged or faulty, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The mode door actuator is connected to the A/C-
heater control through the vehicle electrical system
by a dedicated two-wire lead and connector from the
HVAC wire harness. The mode door actuator can
move the mode door in two directions. When the A/C-
heater control pulls the voltage on one side of the
motor connection high and the other connection low,
the mode door will move in one direction. When the
A/C-heater control reverses the polarity of the volt-
age to the motor, the mode door moves in the oppo-
site direction. When the A/C-heater control makes
the voltage to both connections high or both connec-
tions low, the mode door stops and will not move.
These same motor connections also provide a feed-
back signal to the A/C-heater control. This feedback
signal allows the A/C-heater control to monitor the
operation and relative position of the mode door
actuator and the mode door. The A/C-heater control
learns the mode door stop positions during the cali-
bration procedure and will store a diagnostic troublecode (DTC) for any problems it detects in the mode
door actuator circuits.
The mode door actuator can be diagnosed using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to Body Diagnostic Proce-
dures for more information. The mode door actuator
cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if damaged or
faulty, it must be replaced.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the instrument panel from the vehicle
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
mode door actuator (Fig. 22).
(4) Remove the screws that secure the mode door
actuator to the HVAC housing.
(5) Remove the mode door actuator from the HVAC
housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the mode door actuator onto the HVAC
housing. If necessary, rotate the actuator slightly to
align the splines on the actuator output sleeve with
those on the mode door linkage.
(2) Install and tighten the screws that secure the
mode door actuator to the HVAC housing. Tighten
the screws to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the HVAC wire harness connector to
the mode door actuator.
(4) Install the instrument panel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL ASSEMBLY - INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
DRCONTROLS 24 - 23
EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 2514 of 2627

NOTE: The instrument panel air outlets are retained
into the outlet housings by a light snap fit.
(1) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-bladed tool, gently pry the panel air outlet(s) out
of the panel outlet housing(s) as required (Fig. 1).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the air outlet(s) onto the outlet hous-
ing(s).
(2) Gently push the air outlet into the housing
until it snaps into position.
BLEND DOOR
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.NOTE: Vehicles equiped with single zone HVAC
systems have one blend door, dual zone systems
have two blend doors.
(1) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL).
(2) Disassemble the HVAC housing (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - DISASSEMBLY).
(3) Remove the levers from the driver and/or pas-
senger side blend door (if equipped) (Fig. 2).
(4) Gently slide the drivers and/or passenger side
blend door toward the out side of the housing. Tilt
and lift the door(s) out of the housing.
(5) Inspect the blend door(s), seals and the HVAC
housing for damage or binding and repair or replace
components as required.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the blend door pivot shafts into the
pivot hole and actuator in the bottom of the lower
half of the HVAC housing.
(2) Install the blend door(s) by carefully tipping
the doors into the HVAC housing, then sliding each
door into it's operating position.
(3) Install the levers to the driver and/or passen-
ger side blend door (if equipped).
(4) Assemble the HVAC housing (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - ASSEMBLY)
Fig. 1 Instrument Panel Air Outlets
1 - HEADLIGHT SWITCH
2 - AIR OUTLETS
3 - INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
4 - CLIMATE CONTROL
5 - RADIO
6 - AIRBAG
7 - GLOVE BOX
8 - HEATED SEAT SWITCH (IF EQUIPPED)
9 - TRANSFER CASE SWITCH (IF EQUIPPED)
10 - CIGAR LIGHTER
11 - CUP HOLDERS
12 - ASH TRAY (IF EQUIPPED)
13 - POWER OUTLET
Fig. 2 Blend Door - Dual Zone Shown, Single Zone
Typical
1 - PASSENGER SIDE BLEND DOOR LEVER
2 - PASSENGER SIDE BLEND DOOR
3 - EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR WIRE
4 - HVAC HOUSING
5 - A/C EVAPORATOR
6 - EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR PROBE
7 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR
8 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR LEVER
DRDISTRIBUTION 24 - 27
AIR OUTLETS (Continued)
Page 2515 of 2627

(5) Install the HVAC housing (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/HVAC
HOUSING - INSTALLATION)
BLOWER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The blower motor and blower wheel are located in
the passenger side end of the HVAC housing, below
the glove box. The blower motor controls the velocity
of air flowing through the HVAC housing by spinning
a squirrel cage-type blower wheel within the housing
at the selected speed. The blower motor and wheel
can be removed from the housing inside the vehicle
without removing the instrument panel or HVAC
housing.
OPERATION
The blower motor will only operate with the igni-
tion switch in the On position and the A/C-heater
mode control switch in any position, except Off. The
blower motor receives a fused battery feed circuit
through a fuse in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC) whenever the ignition switch is in the On posi-
tion. Blower motor speed is controlled by regulating
the ground path through or around the blower motor
resistor block and through the A/C-heater blower
motor switch.
The blower motor and blower motor wheel are ser-
viced only as a unit and cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER MOTOR
BLOWER MOTOR INOPERATIVE
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring, diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, further details on wire
harness routing and retention, as well as pin-out and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
BLOWER MOTOR ELECTRICAL DIAGNOSIS
Refer to the Blower Motor Electrical Diagnosis
chart for basic checks of the blower motor circuit
(Fig. 3).
BLOWER MOTOR NOISE OR VIBRATION
Refer to the Blower Motor Noise/Vibration Diagno-
sis chart for basic checks of the blower motor when a
vibration or noise is present (Fig. 4).
24 - 28 DISTRIBUTIONDR
BLEND DOOR (Continued)