1998 DODGE RAM 1500 engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1963 of 2627

STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 234).
Under stall conditions the turbine is stationary and
the oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of
the stator blades and tries to rotate them in a coun-
terclockwise direction. When this happens the over-
running clutch of the stator locks and holds the
stator from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil
strikes the stator blades and is redirected into a
ªhelpingº direction before it enters the impeller. This
circulation of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to
stator, and stator to impeller, can produce a maxi-
mum torque multiplication of about 1.75:1. As the
turbine begins to match the speed of the impeller, the
fluid that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The torque converter clutch is hydraulically
applied or released when fluid is feed or vented from
the hydraulic circuit by the torque converter control
(TCC) solenoid on the valve body. The torque con-
verter clutch is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The torque converter clutch engages
in FOURTH gear, and in THIRD gear under various
conditions, such as when the O/D switch is OFF, orwhen the vehicle is cruising on a level surface after
the vehicle has warmed up. The torque converter
clutch can also be engaged in the MANUAL SEC-
OND gear position if high transmission temperatures
are sensed by the PCM. The torque converter clutch
may disengage momentarily when an increase in
engine load is sensed by the PCM, such as when the
vehicle begins to go uphill or the throttle pressure is
increased.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
Fig. 234 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 260 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1976 of 2627
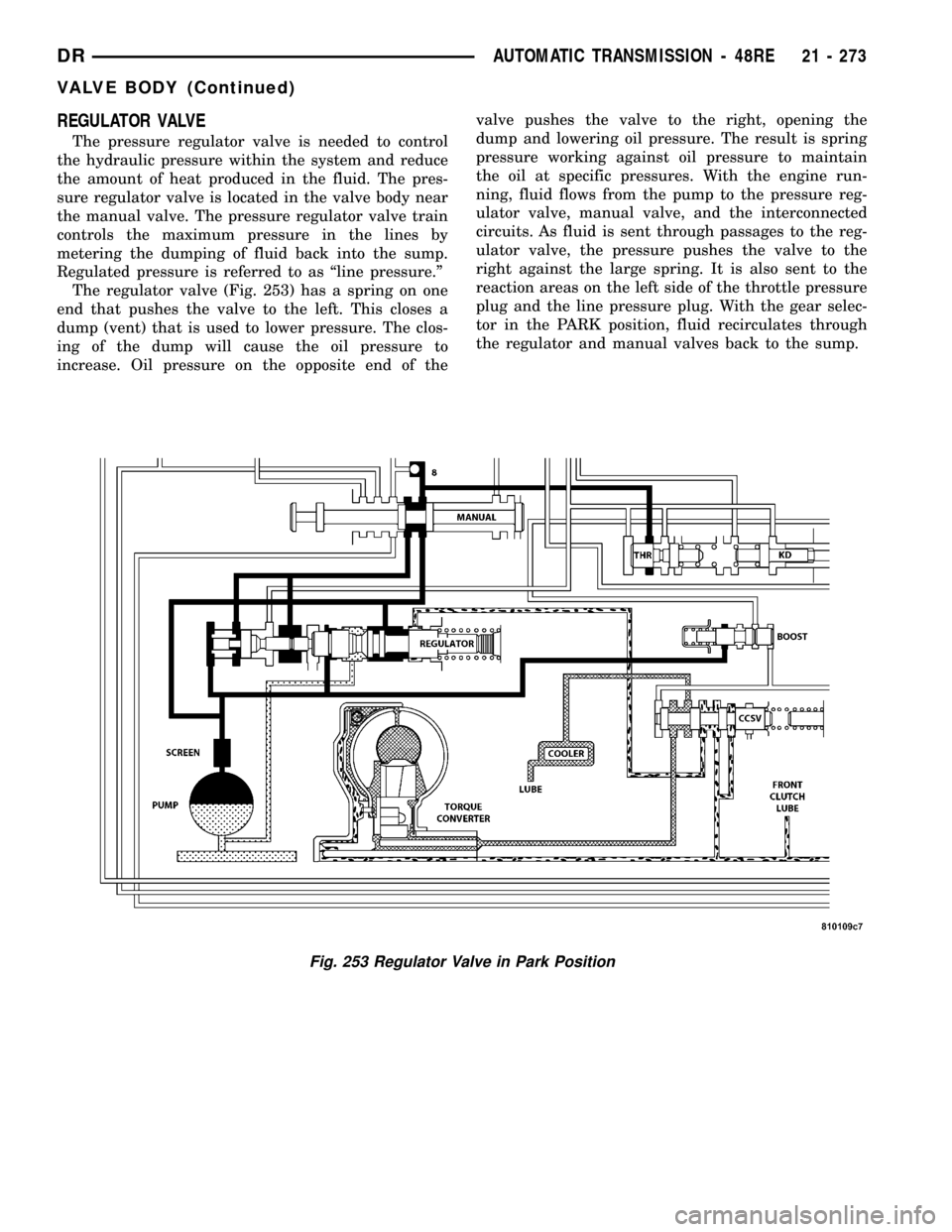
REGULATOR VALVE
The pressure regulator valve is needed to control
the hydraulic pressure within the system and reduce
the amount of heat produced in the fluid. The pres-
sure regulator valve is located in the valve body near
the manual valve. The pressure regulator valve train
controls the maximum pressure in the lines by
metering the dumping of fluid back into the sump.
Regulated pressure is referred to as ªline pressure.º
The regulator valve (Fig. 253) has a spring on one
end that pushes the valve to the left. This closes a
dump (vent) that is used to lower pressure. The clos-
ing of the dump will cause the oil pressure to
increase. Oil pressure on the opposite end of thevalve pushes the valve to the right, opening the
dump and lowering oil pressure. The result is spring
pressure working against oil pressure to maintain
the oil at specific pressures. With the engine run-
ning, fluid flows from the pump to the pressure reg-
ulator valve, manual valve, and the interconnected
circuits. As fluid is sent through passages to the reg-
ulator valve, the pressure pushes the valve to the
right against the large spring. It is also sent to the
reaction areas on the left side of the throttle pressure
plug and the line pressure plug. With the gear selec-
tor in the PARK position, fluid recirculates through
the regulator and manual valves back to the sump.
Fig. 253 Regulator Valve in Park Position
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 273
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 2016 of 2627

TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan
sealing surface (Fig. 1). Refer to this information
when ordering replacement parts. A label is attached
to the transmission case above the stamped numbers.
The label gives additional information which may
also be necessary for identification purposes.
GEAR RATIOS
The 45RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime...........................1.50:1
3rd.................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
Reverse.............................3.00:1
GEAR RATIOS
The 545RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime...........................1.50:1
3rd.................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
5th .................................0.67:1
Reverse.............................3.00:1
OPERATION
The 45RFE/545RFE offers full electronic control of
all automatic up and downshifts, and features real-
time adaptive closed-loop shift and pressure control.
Electronic shift and torque converter clutch controls
help protect the transmission from damage due to
high temperatures, which can occur under severe
operating conditions. By altering shift schedules, line
pressure, and converter clutch control, these controls
reduce heat generation and increase transmission
cooling.
To help reduce efficiency-robbing parasitic losses,
the transmissions includes a dual-stage transmission
fluid pump with electronic output pressure control.
Under most driving conditions, pump output pres-
sure greatly exceeds that which is needed to keep the
clutches applied. The 45RFE/545RFE pump-pressure
control system monitors input torque and adjusts the
pump pressure accordingly. The primary stage of the
pump works continuously; the second stage is
bypassed when demand is low. The control system
also monitors input and output speed and, if incipi-
ent clutch slip is observed, the pressure control sole-
noid duty cycle is varied, increasing pressure in
proportion to demand.
A high-travel torque converter damper assembly
allows earlier torque converter clutch engagement to
reduce slippage. Needle-type thrust bearings reduce
internal friction. The 45RFE/545RFE is packaged in
a one-piece die-cast aluminum case. To reduce NVH,
the case has high lateral, vertical and torsional stiff-
ness. It is also designed to maximize the benefit of
the structural dust cover that connects the bottom of
the bell housing to the engine bedplate, enhancing
overall power train stiffness. Dual filters protect the
pump and other components. A pump return filter is
added to the customary main sump filter. Indepen-
dent lubrication and cooler circuits assure ample
pressure for normal transmission operation even if
the cooler is obstructed or the fluid cannot flow due
to extremely low temperatures.
The hydraulic control system design (without elec-
tronic assist) provides the transmission with PARK,
REVERSE, NEUTRAL, SECOND, and THIRD gears,
based solely on driver shift lever selection. This
design allows the vehicle to be driven (in ªlimp-inº
mode) in the event of a electronic control system fail-
ure, or a situation that the Transmission Control
Module (TCM) recognizes as potentially damaging to
the transmission.
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic
functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRBtscan tool.
Fig. 1 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
1 - IDENTIFICATION NUMBERS (STAMPED)
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 313
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2017 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a RFE
automatic transmission, check for Diagnostic Trou-
ble Codes with the DRBTscan tool.
Transmission malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then per-
form a road test to determine if the problem has been
corrected or if more diagnosis is necessary. If the
problem persists after the preliminary tests and cor-
rections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust gearshift cable if complaint was based
on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.(6) Perform air-pressure test to check clutch oper-
ation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift
cable.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged driveplate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that all diagnostic trou-
ble codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, overrunning clutch, or line pressure problems.
A slipping clutch can often be determined by com-
paring which internal units are applied in the vari-
ous gear ranges. The Clutch Application charts
provide a basis for analyzing road test results.
21 - 314 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2019 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST
An accurate tachometer and pressure test gauges
are required. Test Gauge C-3293-SP has a 300 psi
range and is used at all locations where pressures
exceed 100 psi.
Pressure Test Port Locations
Only two pressure ports are supplied on the trans-
mission case. The torque converter clutch apply and
release ports are located on the right side of the
transmission case (Fig. 2).
To determine the line pressure, there are two avail-
able methods. The DRBtscan tool can be used to
read line pressure from the line pressure sensor. The
second method is to install Line Pressure Adapter
8259 (Fig. 4) into the transmission case and then
install the pressure gauge and the original sensor
into the adapter. This will allow a comparison of the
DRBtreadings and the gauge reading to determine
the accuracy of the line pressure sensor. The DRBt
line pressure reading should match the gauge read-
ing within 10 psi.
In order to access any other pressure tap locations,
the transmission oil pan must be removed, the pres-
sure port plugs removed and Valve Body Pressure
Tap Adapter 8258-A (Fig. 5) installed. The extensions
supplied with Adapter 8258-A will allow the installa-
tion of pressure gauges to the valve body. Refer to
(Fig. 3) for correct pressure tap location identifica-
tion.
TEST PROCEDURE
All pressure readings should be taken with the
transmission fluid level full, transmission oil at the
normal operating temperature, and the engine at
1500 rpm. Check the transmission for proper opera-
tion in each gear position that is in question or if a
specific element is in question, check the pressure
readings in at least two gear positions that employ
that element. Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics at
the rear of this section to determine the correct pres-
sures for each element in a given gear position.
Fig. 2 Torque Converter Pressure Locations
1 - TCC RELEASE
2 - TO COOLER
3 - TCC APPLY
4 - FROM COOLER
5 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
Fig. 3 Pressure Tap Locations
Fig. 4 Line Pressure Adapter 8259
1 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR PORT
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - TOOL 8259
4 - PRESSURE TAP
21 - 316 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2020 of 2627
NOTE: The 45RFE/545RFE utilizes closed loop con-
trol of pump line pressure. The pressure readings
may therefore vary greatly but should always follow
line pressure.
Some common pressures that can be measured to
evaluate pump and clutch performance are the
upshift/downshift pressures, garage shift pressures,
and TCC pressure. The upshift/downshift pressure
for all shifts are shown in UPSHIFT PRESSURES
and DOWNSHIFT PRESSURES. In-gear maximum
pressure for each gear position is shown in IN-GEAR
PRESSURES. The garage shift pressure when per-
forming a N-R shift is 220 psi for 3.7L/4.7L equipped
vehicles and 250 psi for 5.7L equipped vehicles. The
garage shift pressure for the R-N shift is 120 psi. The
garage shift pressure for the N-1 shift is 135 psi for
3.7L/4.7L equipped vehicles and 165 psi for 5.7L
equipped vehicles. Torque converter lock-up pressure
is 120 psi for 3.7L/4.7L equipped vehicles and 125 psi
for 5.7L equipped vehicles.
UPSHIFT PRESSURES
ENGINE 1-2 2-3 2prime-3 3-4 2prime-4 2-5 3-5 4-5
5.7L150 125 125 135 135 135 135 135
3.7L/
4.7L120 120 120 120 120 120 120 130
DOWNSHIFT PRESSURES
ENG-
INE5-
45-3 5-2 4-34-2
prime3-23-2
prime2
prime-
12-
13-1
5.7L135 135 135 135 135 135 135 135 135 135
3.7L/
4.7L120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 120
IN-GEAR PRESSURES
ENGINE 1 22
prime345NEUT-
RALREV-
ERSE
5.7L160 135 135 135 135 135 120 250
3.7L/
4.7L135 120 120 120 120 120 120 220
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR CHECKING
TRANSMISSION CLUTCH OPERATION
Air-pressure testing can be used to check transmis-
sion clutch operation. The test can be conducted with
the transmission either in the vehicle or on the work
bench, as a final check.
Air-pressure testing requires that the oil pan and
valve body be removed from the transmission. The
clutch apply passages are shown (Fig. 6).
NOTE: The air supply which is used must be free of
moisture and dirt. Use a pressure of 30 psi to test
clutch operation.
Apply air pressure at each port. If the clutch is
functioning, a soft thump will be heard as the clutch
Fig. 5 Valve Body Pressure Tap Adapter 8258-A
1 - 45RFE TRANSMISSION
2 - TOOL 8258-A
Fig. 6 Air Pressure Test Passages
1 - LOW REVERSE CLUTCH
2 - 4TH CLUTCH
3 - 2ND CLUTCH
4 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
5 - UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
6 - REVERSE CLUTCH
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 317
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2021 of 2627

is applied. The clutch application can also be felt by
touching the appropriate element while applying air
pressure. As the air pressure is released, the clutch
should also release.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONVERTER
HOUSING FLUID LEAK
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
two items must be established before repair.
(1) Verify that a leak condition actually exists.
(2) Determined the true source of the leak.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may
not be leaks at all. They may only be the result of
residual fluid in the converter housing, or excess
fluid spilled during factory fill or fill after repair.
Converter housing leaks have several potential
sources. Through careful observation, a leak source
can be identified before removing the transmission
for repair. Torque converter seal leaks tend to move
along the drive hub and onto the rear of the con-
verter. Pump cover seal tend to run down the cover
and the inside surface of the bellhousing.
Some leaks, or suspected leaks, may be particu-
larly difficult to locate. If necessary, a Mopart
approved dye may be used to locate a leak.
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAK POINTS
Possible sources of converter leaks are:
(1) Leaks at the weld joint around the outside
diameter weld (Fig. 7).
(2) Leaks at the converter hub weld (Fig. 7).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ALUMINUM
THREAD REPAIR
Damaged or worn threads in the aluminum trans-
mission case and valve body can be repaired by the
use of Heli-CoilsŸ, or equivalent. This repair con-
sists of drilling out the worn-out damaged threads.
Then tap the hole with a special Heli-CoilŸ tap, or
equivalent, and installing a Heli-CoilŸ insert, or
equivalent, into the hole. This brings the hole back to
its original thread size.
Heli-CoilŸ, or equivalent, tools and inserts are
readily available from most automotive parts suppli-
ers.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle
(3) Remove any necessary skid plates. (Refer to 13
- FRAMES & BUMPERS/FRAME/TRANSFER CASE
SKID PLATE - REMOVAL)
(4) Mark propeller shaft and axle companion
flanges for assembly alignment.
(5) Remove the rear propeller shaft
(6) Remove the front propeller shaft, if necessary.
(7) Remove the engine to transmission collar (Fig.
8).
(8) Remove the exhaust support bracket from the
rear of the transmission.
(9) Disconnect and lower or remove any necessary
exhaust components.
Fig. 7 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE ASSEMBLY
2-STATOR
3 - CONVERTER HUB
4 - O-RING
5 - IMPELLER ASSEMBLY
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH PISTON
7 - TURBINE HUB
Fig. 8 Transmission Collar
1 - ENGINE
2 - STRUCTURAL DUST COVER
3 - TRANSMISSION
21 - 318 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)
Page 2037 of 2627

o-ring is properly installed and is free of any debris.
The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging pump
seal at installation.
(2) If a replacement transmission is being
installed, transfer any components necessary, such as
the manual shift lever and shift cable bracket, from
the original transmission onto the replacement trans-
mission.
(3) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(4) Align converter and oil pump.(5) Carefully insert converter in oil pump. Then
rotate converter back and forth until fully seated in
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with steel scale and
straightedge (Fig. 53). Surface of converter lugs
should be at least 13mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) Temporarily secure converter with C-clamp.
(8) Position transmission on jack and secure it
with chains.
(9) Check condition of converter driveplate.
Replace the plate if cracked, distorted or damaged.
Also be sure transmission dowel pins are seated
in engine block and protrude far enough to
hold transmission in alignment.
(10) Apply a light coating of MopartHigh Temp
Grease to the torque converter hub pocket in the rear
pocket of the engine's crankshaft.
(11) Raise transmission (Fig. 54) and align the
torque converter with the drive plate and transmis-
sion converter housing with the engine block.
(12) Move transmission forward. Then raise, lower
or tilt transmission to align the converter housing
with engine block dowels.
(13) Carefully work transmission forward and over
engine block dowels until converter hub is seated in
crankshaft. Verify that no wires, or the transmission
vent hose, have become trapped between the engine
block and the transmission.
(14) Install two bolts to attach the transmission to
the engine.
(15) Install remaining torque converter housing to
engine bolts. Tighten to 68 N´m (50 ft.lbs.).
Fig. 51 Install Primary Oil and Cooler Filters
1 - PRIMARY OIL FILTER
2 - COOLER RETURN FILTER
3 - COOLER RETURN FILTER BYPASS VALVE
4 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 52 Install Input, Output, and Line Pressure
Sensors
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 53 Checking Torque Converter Seating - Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 334 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE (Continued)