1998 DODGE RAM 1500 check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 2575 of 2627

OPERATION
The main purpose of the LDP is to pressurize the
fuel system for leak checking. It closes the EVAP sys-
tem vent to atmospheric pressure so the system can
be pressurized for leak testing. The diaphragm is
powered by engine vacuum. It pumps air into the
EVAP system to develop a pressure of about 7.59
H2O (1/4) psi. A reed switch in the LDP allows the
PCM to monitor the position of the LDP diaphragm.
The PCM uses the reed switch input to monitor how
fast the LDP is pumping air into the EVAP system.
This allows detection of leaks and blockage. The LDP
assembly consists of several parts (Fig. 5). The sole-
noid is controlled by the PCM, and it connects theupper pump cavity to either engine vacuum or atmo-
spheric pressure. A vent valve closes the EVAP sys-
tem to atmosphere, sealing the system during leak
testing. The pump section of the LDP consists of a
diaphragm that moves up and down to bring air in
through the air filter and inlet check valve, and
pump it out through an outlet check valve into the
EVAP system. The diaphragm is pulled up by engine
vacuum, and pushed down by spring pressure, as the
LDP solenoid turns on and off. The LDP also has a
magnetic reed switch to signal diaphragm position to
the PCM. When the diaphragm is down, the switch is
closed, which sends a 12 V (system voltage) signal to
the PCM. When the diaphragm is up, the switch is
open, and there is no voltage sent to the PCM. This
allows the PCM to monitor LDP pumping action as it
turns the LDP solenoid on and off.
Fig. 4 TYPICAL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
1 - Throttle Body
2 - Service Vacuum Supply Tee (SVST)
3 - LDP Solenoid
4 - EVAP System Air Filter
5 - LDP Vent Valve
6 - EVAP Purge Orifice
7 - EVAP Purge Solenoid
8 - Service Port
9 - To Fuel Tank
10 - EVAP Canister
11 - LDP
12 - Intake Air Plenum
Fig. 5 EVAP LEAK DETECTION SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
1 - Reed Switch
2 - Solenoid
3 - Spring
4 - Pump Cavity
5 - Diaphragm
6 - Inlet Check Valve
7 - Vent Valve
8 - From Air Filter
9 - To Canister
10 - Outlet Check Valve
11 - Engine Vacuum
25 - 14 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2576 of 2627

LDP AT REST (NOT POWERED)
When the LDP is at rest (no electrical/vacuum) the
diaphragm is allowed to drop down if the internal
(EVAP system) pressure is not greater than the
return spring. The LDP solenoid blocks the engine
vacuum port and opens the atmospheric pressure
port connected through the EVAP system air filter.
The vent valve is held open by the diaphragm. This
allows the canister to see atmospheric pressure (Fig.
6).
DIAPHRAGM UPWARD MOVEMENT
When the PCM energizes the LDP solenoid, the
solenoid blocks the atmospheric port leading through
the EVAP air filter and at the same time opens the
engine vacuum port to the pump cavity above the
diaphragm. The diaphragm moves upward when vac-
uum above the diaphragm exceeds spring force. This
upward movement closes the vent valve. It also
causes low pressure below the diaphragm, unseating
the inlet check valve and allowing air in from the
EVAP air filter. When the diaphragm completes its
upward movement, the LDP reed switch turns from
closed to open (Fig. 7).
DIAPHRAGM DOWNWARD MOVEMENT
Based on reed switch input, the PCM de-energizes
the LDP solenoid, causing it to block the vacuum
port, and open the atmospheric port. This connects
the upper pump cavity to atmosphere through the
EVAP air filter. The spring is now able to push the
diaphragm down. The downward movement of the
diaphragm closes the inlet check valve and opens the
outlet check valve pumping air into the evaporative
system. The LDP reed switch turns from open to
closed, allowing the PCM to monitor LDP pumping
(diaphragm up/down) activity (Fig. 8). During the
pumping mode, the diaphragm will not move down
far enough to open the vent valve. The pumping cycle
is repeated as the solenoid is turned on and off.
When the evaporative system begins to pressurize,
the pressure on the bottom of the diaphragm will
begin to oppose the spring pressure, slowing the
pumping action. The PCM watches the time from
when the solenoid is de-energized, until the dia-
phragm drops down far enough for the reed switch to
change from opened to closed. If the reed switch
changes too quickly, a leak may be indicated. The
longer it takes the reed switch to change state, the
tighter the evaporative system is sealed. If the sys-
tem pressurizes too quickly, a restriction somewhere
in the EVAP system may be indicated.
Fig. 6 LDP AT REST
1 - Diaphragm
2 - Inlet Check Valve (Closed)
3 - Vent Valve (Open)
4 - From Air Filter
5 - To Canister
6 - Outlet Check Valve (Closed)
7 - Engine Vacuum (Closed)
Fig. 7 DIAPHRAGM UPWARD MOVEMENT
1 - Diaphragm
2 - Inlet Check Valve (Open)
3 - Vent Valve (Closed)
4 - From Air Filter
5 - To Canister
6 - Outlet Check Valve (Closed)
7 - Engine Vacuum (Open)
DREVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 15
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2577 of 2627

PUMPING ACTION
Action : During portions of this test, the PCM uses
the reed switch to monitor diaphragm movement.
The solenoid is only turned on by the PCM after the
reed switch changes from open to closed, indicating
that the diaphragm has moved down. At other times
during the test, the PCM will rapidly cycle the LDP
solenoid on and off to quickly pressurize the system.
During rapid cycling, the diaphragm will not move
enough to change the reed switch state. In the state
of rapid cycling, the PCM will use a fixed time inter-
val to cycle the solenoid. If the system does not pass
the EVAP Leak Detection Test, the following DTCs
may be set:
²P0442 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR 0.0409LEAK
DETECTED
²P0455 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR LARGE LEAK
DETECTED
²P0456 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR 0.0209LEAK
DETECTED
²P1486 - EVAP LEAK MON PINCHED HOSE
FOUND
²P1494 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP SW OR
MECH FAULT
²P1495 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP SOLENOID
CIRCUIT
REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) and LDP filter
are attached to the front of the EVAP canister
mounting bracket (Fig. 9). This is located near the
front of the fuel tank. The LDP and LDP filter are
replaced (serviced) as one unit.
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Carefully remove hose at LDP filter.
(3) Remove LDP filter mounting bolt and remove
from vehicle.
(4) Carefully remove vapor/vacuum lines at LDP.
(5) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP.
(6) Remove LDP mounting bolt and remove LDP
from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
The LDP and LDP filter are attached to the front
of the EVAP canister mounting bracket. The LDP
and LDP filter are replaced (serviced) as one unit.
(1) Install LDP to mounting bracket. Refer to
Torque Specifications.
(2) Install LDP filter to mounting bracket. Refer to
Torque Specifications.
(3) Carefully install vapor/vacuum lines to LDP,
and install hose to LDP filter.The vapor/vacuum
lines and hoses must be firmly connected.
Fig. 8 DIAPHRAGM DOWNWARD MOVEMENT
1 - Diaphragm
2 - Inlet Check Valve (Closed)
3 - Vent Valve (Closed)
4 - From Air Filter
5 - To Canister
6 - Outlet Check Valve (Open)
7 - Engine Vacuum (Closed)
Fig. 9 LDP AND LDP FILTER LOCATION
1 - LDP
2 - LDP MOUNTING BOLT
3 - ELEC. CONNEC.
4 - FILTER MOUNTING BOLT
5 - LDP FILTER
6 - CONNECTING HOSE
7 - EVAP CANISTER MOUNTING BRACKET
8 - EVAP CANISTERS (2)
25 - 16 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2578 of 2627

Check the vapor/vacuum lines at the LDP, LDP
filter and EVAP canister purge solenoid for
damage or leaks. If a leak is present, a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
(4) Connect electrical connector to LDP.
ORVR
DESCRIPTION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system consists of a unique fuel tank, flow manage-
ment valve, fluid control valve, one-way check valve
and vapor canister.
OPERATION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system is used to remove excess fuel tank vapors.
This is done while the vehicle is being refueled.
Fuel flowing into the fuel filler tube (approx. 1º
I.D.) creates an aspiration effect drawing air into the
fuel fill tube. During refueling, the fuel tank is
vented to the EVAP canister to capture escaping
vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there are
no fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once the
refueling vapors are captured by the EVAP canister,
the vehicle's computer controlled purge system draws
vapor out of the canister for the engine to burn. The
vapor flow is metered by the purge solenoid so that
there is no, or minimal impact on driveability or
tailpipe emissions.
As fuel starts to flow through the fuel fill tube, it
opens the normally closed check valve and enters the
fuel tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank
through the control valve and on to the vapor canis-
ter. Vapor is absorbed in the EVAP canister until
vapor flow in the lines stops. This stoppage occurs
following fuel shut-off, or by having the fuel level in
the tank rise high enough to close the control valve.
This control valve contains a float that rises to seal
the large diameter vent path to the EVAP canister.
At this point in the refueling process, fuel tank pres-
sure increases, the check valve closes (preventing liq-
uid fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel
then rises up the fuel filler tube to shut off the dis-
pensing nozzle.
PCV VALVE
DESCRIPTION
3.7L V-6 / 4.7L V-8
The 3.7L V-6 and 4.7L V-8 engines are equipped
with a closed crankcase ventilation system and a
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve.
This system consists of:
²a PCV valve mounted to the oil filler housing
(Fig. 10). The PCV valve is sealed to the oil filler
housing with an o-ring.
²the air cleaner housing
²two interconnected breathers threaded into the
rear of each cylinder head (Fig. 11).
²tubes and hoses to connect the system compo-
nents.
Fig. 10 PCV VALVE - 3.7L V-6 / 4.7L V-8
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
DREVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 17
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2581 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE - 3.7L
V-6/ 4.7L V-8
(1) Disconnect PCV line/hose (Fig. 19) by discon-
necting rubber connecting hose at PCV valve fitting.
(2) Remove PCV valve at oil filler tube by rotating
PCV valve downward until locating tabs have been
freed at cam lock (Fig. 19). After tabs have cleared,
pull valve straight out from filler tube.To prevent
damage to PCV valve locating tabs, valve must
be pointed downward for removal. Do not force
valve from oil filler tube.
(3) After valve is removed, check condition of valve
o-ring (Fig. 19). Also, PCV valve should rattle when
shaken.
(4) Reconnect PCV valve to its connecting line/
hose.
(5) Start engine and bring to idle speed.
(6) If valve is not plugged, a hissing noise will be
heard as air passes through valve. Also, a strong vac-
uum should be felt with a finger placed at valve
inlet.
(7) If vacuum is not felt at valve inlet, check line/
hose for kinks or for obstruction. If necessary, clean
out intake manifold fitting at rear of manifold. Do
this by turning a 1/4 inch drill (by hand) through the
fitting to dislodge any solid particles. Blow out the
fitting with shop air. If necessary, use a smaller drill
to avoid removing any metal from the fitting.
(8)Do not attempt to clean the old PCV valve.
(9) Return PCV valve back to oil filler tube by
placing valve locating tabs (Fig. 19) into cam lock.
Press PCV valve in and rotate valve upward. A slight
click will be felt when tabs have engaged cam lock.
Valve should be pointed towards rear of vehicle.
(10) Connect PCV line/hose and connecting rubber
hose to PCV valve.
(11) Disconnect rubber hose from fresh air fitting
at air cleaner resonator box. Start engine and bring
to idle speed. Hold a piece of stiff paper (such as a
parts tag) loosely over the opening of the discon-
nected rubber hose.
(12) The paper should be drawn against the hose
opening with noticeable force. This will be after
allowing approximately one minute for crankcase
pressure to reduce.
(13) If vacuum is not present, disconnect each PCV
system hose at top of each crankcase breather (Fig.
20). Check for obstructions or restrictions.
(14) If vacuum is still not present, remove each
PCV system crankcase breather (Fig. 20) from each
cylinder head. Check for obstructions or restrictions.
If plugged, replace breather. Tighten breather to 12
N´m (106 in. lbs.) torque. Do not attempt to clean
breather.(15) If vacuum is still not present, disconnect each
PCV system hose at each fitting, and at each check
valve (Fig. 21). Check for obstructions or restrictions.
Fig. 19 PCV VALVE - 3.7L V-6 / 4.7L V-8
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
Fig. 20 CRANKCASE BREATHERS (2) - 3.7L V-6 /
4.7L V-8
1 - CRANKCASE BREATHERS (2)
2 - REAR OF ENGINE
25 - 20 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
PCV VALVE (Continued)
Page 2583 of 2627
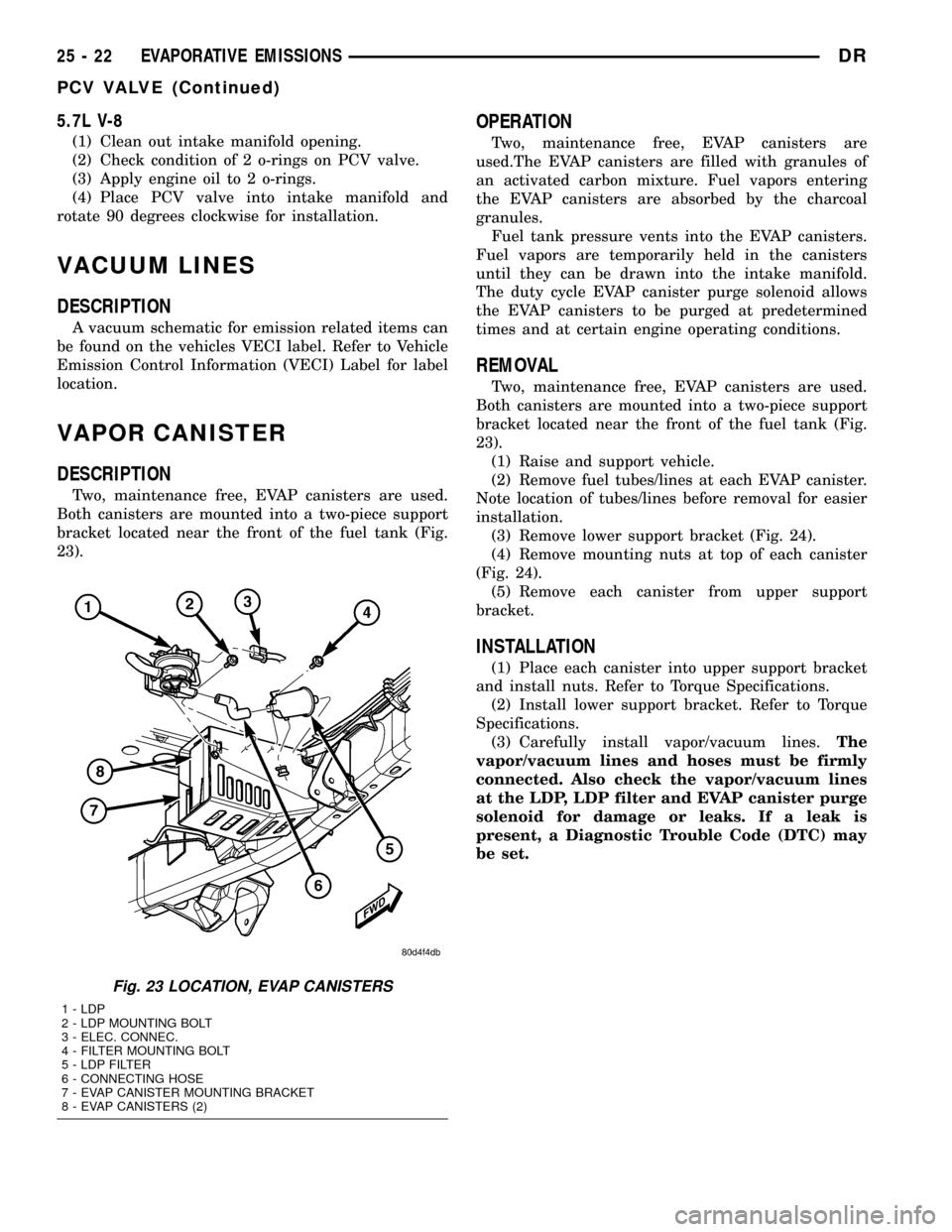
5.7L V-8
(1) Clean out intake manifold opening.
(2) Check condition of 2 o-rings on PCV valve.
(3) Apply engine oil to 2 o-rings.
(4) Place PCV valve into intake manifold and
rotate 90 degrees clockwise for installation.
VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION
A vacuum schematic for emission related items can
be found on the vehicles VECI label. Refer to Vehicle
Emission Control Information (VECI) Label for label
location.
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION
Two, maintenance free, EVAP canisters are used.
Both canisters are mounted into a two-piece support
bracket located near the front of the fuel tank (Fig.
23).
OPERATION
Two, maintenance free, EVAP canisters are
used.The EVAP canisters are filled with granules of
an activated carbon mixture. Fuel vapors entering
the EVAP canisters are absorbed by the charcoal
granules.
Fuel tank pressure vents into the EVAP canisters.
Fuel vapors are temporarily held in the canisters
until they can be drawn into the intake manifold.
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid allows
the EVAP canisters to be purged at predetermined
times and at certain engine operating conditions.
REMOVAL
Two, maintenance free, EVAP canisters are used.
Both canisters are mounted into a two-piece support
bracket located near the front of the fuel tank (Fig.
23).
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove fuel tubes/lines at each EVAP canister.
Note location of tubes/lines before removal for easier
installation.
(3) Remove lower support bracket (Fig. 24).
(4) Remove mounting nuts at top of each canister
(Fig. 24).
(5) Remove each canister from upper support
bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place each canister into upper support bracket
and install nuts. Refer to Torque Specifications.
(2) Install lower support bracket. Refer to Torque
Specifications.
(3) Carefully install vapor/vacuum lines.The
vapor/vacuum lines and hoses must be firmly
connected. Also check the vapor/vacuum lines
at the LDP, LDP filter and EVAP canister purge
solenoid for damage or leaks. If a leak is
present, a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) may
be set.
Fig. 23 LOCATION, EVAP CANISTERS
1 - LDP
2 - LDP MOUNTING BOLT
3 - ELEC. CONNEC.
4 - FILTER MOUNTING BOLT
5 - LDP FILTER
6 - CONNECTING HOSE
7 - EVAP CANISTER MOUNTING BRACKET
8 - EVAP CANISTERS (2)
25 - 22 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
PCV VALVE (Continued)
Page 2585 of 2627

The NVLD device is designed with a normally open
vacuum switch, a normally closed solenoid, and a
seal, which is actuated by both the solenoid and a
diaphragm. The NVLD is located on the atmospheric
vent side of the canister. The NVLD assembly may
be mounted on top of the canister outlet, or in-line
between the canister and atmospheric vent filter. The
normally open vacuum switch will close with about 19
H2O (0.25 KPA) vacuum in the evaporative system.
The diaphragm actuates the switch. This is above the
opening point of the fuel inlet check valve in the fill
tube so cap off leaks can be detected. Submerged fill
systems must have recirculation lines that do not
have the in-line normally closed check valve that pro-
tects the system from failed nozzle liquid ingestion,
in order to detect cap off conditions.
The normally closed valve in the NVLD is intended
to maintain the seal on the evaporative system dur-
ing the engine off condition. If vacuum in the evapo-
rative system exceeds 39to 69H2O (0.75 to 1.5 KPA),
the valve will be pulled off the seat, opening the seal.
This will protect the system from excessive vacuum
as well as allowing sufficient purge flow in the event
that the solenoid was to become inoperative.
The solenoid actuates the valve to unseal the can-
ister vent while the engine is running. It also will be
used to close the vent during the medium and large
leak tests and during the purge flow check. This sole-
noid requires initial 1.5 amps of current to pull the
valve open but after 100 ms. will be duty cycled down
to an average of about 150 mA for the remainder of
the drive cycle.
Another feature in the device is a diaphragm that
will open the seal in the NVLD with pressure in the
evaporative system. The device will9blow off9at
about 0.59H2O (0.12 KPA) pressure to permit the
venting of vapors during refueling. An added benefit
to this is that it will also allow the tank to9breathe9
during increasing temperatures, thus limiting the
pressure in the tank to this low level. This is benefi-
cial because the induced vacuum during a subse-
quent declining temperature will achieve the switch
closed (pass threshold) sooner than if the tank had to
decay from a built up pressure.
The device itself has 3 wires: Switch sense, sole-
noid driver and ground. It also includes a resistor to
protect the switch from a short to battery or a short
to ground. The NGC utilizes a high-side driver to
energize and duty-cycle the solenoid.REMOVAL
The NVLD pump and filter are attached to the
front of the EVAP canister mounting bracket (Fig.
25). This is located near the front of the fuel tank.
The pump and filter are replaced (serviced) as one
unit.
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Carefully remove pump hose clamp and hose at
filter.
(3) Carefully remove other vapor/vacuum hose at
pump.
(4) Disconnect 3±way electrical connector at pump.
(5) The NVLD pump snaps onto the EVAP canister
mounting bracket. Press on release tab (Fig. 26)
while sliding pump from bracket.
Fig. 25 NVLD PUMP LOCATION
1 - EVAP CANISTER MOUNTING BRACKET
2 - NVLD PUMP
3 - FILTER
25 - 24 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
NATURAL VAC LEAK DETECTION ASSY (Continued)
Page 2592 of 2627
BURNT FLUID - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, CAUSES OF..........21-201,21-366
BUSHING - INSTALLATION.............19-19
BUSHING - INSTALLATION, TORSION
BAR CROSS MEMBER..................2-15
BUSHING - REMOVAL.................19-19
BUSHING - REMOVAL, TORSION BAR
CROSSMEMBER......................2-13
BUSHING AND SEAL - INSTALLATION,
EXTENSION HOUSING................21-440
BUSHING AND SEAL - REMOVAL,
EXTENSION HOUSING................21-440
BUSHINGS - 2WD (LD) - INSTALLATION,
LOWER CONTROL ARM................2-15
BUSHINGS - 2WD (LD) - REMOVAL,
LOWER CONTROL ARM................2-13
BUSHINGS - 4WD (LD) - INSTALLATION,
LOWER CONTROL ARM................2-14
BUSHINGS - 4WD (LD) - REMOVAL,
LOWER CONTROL ARM................2-13
BUSHINGS - INSTALLATION.............2-43
BUSHINGS - REMOVAL.................2-43
BUZZ, SQUEAK & RATTLE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE........................23-11
BYPASS - DESCRIPTION, WATER PUMP . . . 7-59
BYPASS - OPERATION, WATER PUMP.....7-60
C205F - ADJUSTMENTS, FRONT AXLE.....3-32
C205F - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
FRONT AXLE.........................3-27
C205F - INSTALLATION, FRONT AXLE.....3-31
C205F - REMOVAL, FRONT AXLE...........3-31
C205F - SPECIAL TOOLS, FRONT AXLE....3-40
C205F - SPECIFICATIONS, FRONT AXLE....3-39
CAB - INSTALLATION, QUAD......8O-36,8O-61
CAB - INSTALLATION, STANDARD . . 8O-35,8O-61
CAB - REMOVAL, QUAD..........8O-33,8O-60
CAB - REMOVAL, STANDARD......8O-32,8O-59
CAB BACK PANEL TRIM -
INSTALLATION, REAR.................23-69
CAB BACK PANEL TRIM - REMOVAL,
REAR..............................23-68
CAB CLEARANCE LAMP - INSTALLATION . . 8L-12
CAB CLEARANCE LAMP - REMOVAL.....8L-11
CABLE - ADJUSTMENTS, THROTTLE
VALVE ............................21-254
CABLE - DESCRIPTION.................8P-4
CABLE - DESCRIPTION, ANTENNA BODY . . . 8A-4
CABLE - DESCRIPTION, SPARK PLUG.....8I-21
CABLE - DESCRIPTION, THROTTLE
VALVE ............................21-253
CABLE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
ANTENNA BODY......................8A-4
CABLE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
GEARSHIFT..................21-210,21-368
CABLE - INSTALLATION................8P-5
CABLE - INSTALLATION, ANTENNA BODY . . 8A-6
CABLE - INSTALLATION, CHECK.........23-15
CABLE - INSTALLATION, FRONT
PARKING BRAKE......................5-38
CABLE - INSTALLATION, GEARSHIFT....21-211,
21-370
CABLE - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT
PANEL ANTENNA......................8A-7
CABLE - INSTALLATION, LEFT REAR......5-39
CABLE - INSTALLATION, REAR PARK
BRAKE..............................5-38
CABLE - INSTALLATION, RIGHT REAR.....5-38
CABLE - INSTALLATION, SPARK PLUG....8I-22
CABLE - INSTALLATION, THROTTLE
CONTROL.....................14-40,14-84
CABLE - OPERATION...................8P-4
CABLE - OPERATION, ANTENNA BODY
.....8A-4
CABLE - OPERATION, SPARK PLUG
.......8I-21
CABLE - REMOVAL
....................8P-4
CABLE - REMOVAL, ANTENNA BODY
......8A-6
CABLE - REMOVAL, CHECK
.............23-15
CABLE - REMOVAL, FRONT PARKING
BRAKE
..............................5-36
CABLE - REMOVAL, GEARSHIFT
. . 21-210,21-369
CABLE - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT PANEL
ANTENNA
...........................8A-7
CABLE - REMOVAL, LEFT REAR
..........5-38
CABLE - REMOVAL, REAR PARK BRAKE
. . . 5-37
CABLE - REMOVAL, RIGHT REAR
.........5-37
CABLE - REMOVAL, SPARK PLUG
........8I-22
CABLE - REMOVAL, THROTTLE
CONTROL
.....................14-38,14-83CABLE, ADJUSTMENTS - GEARSHIFT . . . 21-212,
21-370
CABLE RESISTANCE, SPECIFICATIONS -
SPARK PLUG.........................8I-4
CABLE ROUTING, 5.7L V-8 ENGINE -
FIRING ORDER........................8I-4
CABLE/HANDLE ASSEMBLY -
INSTALLATION, LATCH RELEASE........23-47
CABLE/HANDLE ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL,
LATCH RELEASE.....................23-47
CABLES - DESCRIPTION, BATTERY.......8F-14
CABLES - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
BATTERY...........................8F-15
CABLES - INSTALLATION, BATTERY......8F-17
CABLES - OPERATION, BATTERY........8F-15
CABLES - REMOVAL, BATTERY..........8F-16
CALIBRATION - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
COMPASS...........................8M-3
CALIPER ADAPTER MOUNT -
INSTALLATION, DISC BRAKE............5-22
CALIPERS - DESCRIPTION, DISC BRAKE . . . 5-16
CALIPERS - OPERATION, DISC BRAKE.....5-16
CAM BORE REPAIR - STANDARD
PROCEDURE........................9-267
CAMBER AND CASTER ADJUSTMENT -
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................2-4
CAMBER, CASTER AND TOE
ADJUSTMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE..........................2-4
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
ASSEMBLY, OVERRUNNING CLUTCH....21-237
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
CLEANING, OVERRUNNING CLUTCH.....21-236
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
DESCRIPTION, OVERRUNNING CLUTCH . . 21-236
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
DISASSEMBLY, OVERRUNNING
CLUTCH...........................21-236
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
INSPECTION, OVERRUNNING CLUTCH . . . 21-237
CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER -
OPERATION, OVERRUNNING CLUTCH....21-236
CAMSHAFT - INSTALLATION.......9-206,9-271
CAMSHAFT - REMOVAL..........9-205,9-268
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS - INSTALLATION . . . 9-271
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS - REMOVAL......9-268
CAMSHAFT CORE HOLE PLUG -
INSTALLATION.......................9-206
CAMSHAFT CORE HOLE PLUG -
REMOVAL..........................9-205
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
DESCRIPTION.......................14-71
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
DESCRIPTION.........................8I-7
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
INSTALLATION.......................14-72
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
INSTALLATION.......................8I-10
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
OPERATION.........................14-71
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
OPERATION..........................8I-7
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
REMOVAL..........................14-72
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
REMOVAL............................8I-9
CAMSHAFT(S) - DESCRIPTION.......9-25,9-35
CAMSHAFT(S) - INSTALLATION......9-27,9-36
CAMSHAFT(S) - LEFT - DESCRIPTION....9-114
CAMSHAFT(S) - LEFT - INSTALLATION....9-116
CAMSHAFT(S) - LEFT - REMOVAL.......9-115
CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL..........9-25,9-35
CAMSHAFT(S) - RIGHT - DESCRIPTION . . . 9-119
CAMSHAFT(S) - RIGHT - INSTALLATION . . 9-120
CAMSHAFT(S) - RIGHT - REMOVAL......9-119
CANISTER - DESCRIPTION, VAPOR......25-22
CANISTER - INSTALLATION, VAPOR......25-22
CANISTER - OPERATION, VAPOR........25-22
CANISTER - REMOVAL, VAPOR..........25-22
CAP - DESCRIPTION, FUEL FILLER.......25-13
CAP - DESCRIPTION, RADIATOR
PRESSURE
..........................7-57
CAP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
RADIATOR
...........................7-58
CAP - OPERATION, FUEL FILLER
........25-13
CAP - OPERATION, RADIATOR
PRESSURE
..........................7-58
CAPACITIES, SPECIFICATIONS - FLUID
......0-5CAPACITOR - DESCRIPTION, IGNITION
COIL...............................8I-21
CAPACITOR - INSTALLATION, IGNITION
COIL...............................8I-21
CAPACITOR - OPERATION, IGNITION
COIL...............................8I-21
CAPACITOR - REMOVAL, IGNITION COIL . . . 8I-21
CAP-TO-FILLER NECK SEAL -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, RADIATOR.....7-58
CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS -
ASSEMBLY, DOUBLE...................3-17
CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS -
DISASSEMBLY, DOUBLE................3-16
CARGO BOX - INSTALLATION...........23-37
CARGO BOX - INSTALLATION, WITH.....8L-22,
8L-23,8L-24,8L-7,8L-9
CARGO BOX - INSTALLATION, WITHOUT . . 8L-22,
8L-23,8L-24,8L-8,8L-9
CARGO BOX - REMOVAL...............23-37
CARGO BOX - REMOVAL, WITH....8L-22,8L-24,
8L-7,8L-9
CARGO BOX - REMOVAL, WITHOUT.....8L-22,
8L-23,8L-24,8L-7,8L-9
CARGO BOX - TIE DOWN -
INSTALLATION.......................23-38
CARGO BOX - TIE DOWN - REMOVAL....23-38
CARGO LAMP INDICATOR -
DESCRIPTION.......................8J-20
CARGO LAMP INDICATOR - OPERATION . . 8J-20
CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS -
INSTALLATION.......................23-65
CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS - REMOVAL . . . 23-65
CASCADE OVERFLOW VALVE -
DESCRIPTION.......................14-66
CASCADE OVERFLOW VALVE -
OPERATION.........................14-66
CASE - DESCRIPTION, TRANSFER.........0-4
CASE - NV241 GENII - ASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-428
CASE - NV241 GENII - CLEANING,
TRANSFER.........................21-426
CASE - NV241 GENII - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-415
CASE - NV241 GENII - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TRANSFER.................21-416
CASE - NV241 GENII - DISASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-417
CASE - NV241 GENII - INSPECTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-426
CASE - NV241 GENII - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER.........................21-438
CASE - NV241 GENII - OPERATION,
TRANSFER.........................21-415
CASE - NV241 GENII - REMOVAL,
TRANSFER.........................21-417
CASE - NV243 - ASSEMBLY, TRANSFER . . 21-496
CASE - NV243 - CLEANING, TRANSFER . . 21-493
CASE - NV243 - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-482
CASE - NV243 - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TRANSFER.................21-483
CASE - NV243 - DISASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-484
CASE - NV243 - INSPECTION, TRANSFER . 21-493
CASE - NV243 - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER.........................21-505
CASE - NV243 - OPERATION, TRANSFER . 21-483
CASE - NV243 - REMOVAL, TRANSFER . . 21-484
CASE - NV244 - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, TRANSFER.................21-513
CASE - NV244 GENII - ASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-525
CASE - NV244 GENII - CLEANING,
TRANSFER.........................21-523
CASE - NV244 GENII - DESCRIPTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-512
CASE - NV244 GENII - DISASSEMBLY,
TRANSFER.........................21-514
CASE - NV244 GENII - INSPECTION,
TRANSFER.........................21-523
CASE - NV244 GENII - INSTALLATION,
TRANSFER
.........................21-534
CASE - NV244 GENII - OPERATION,
TRANSFER
.........................21-513
CASE - NV244 GENII - REMOVAL,
TRANSFER
.........................21-514
CASE - NV271 - ASSEMBLY, TRANSFER
. . 21-461
CASE - NV271 - CLEANING, TRANSFER
. . 21-459
DRINDEX 5
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page