1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Transmission install
[x] Cancel search: Transmission installPage 2095 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Install the output speed sensor into the trans-
mission case.
(2) Install the bolt to hold the output speed sensor
into the transmission case. Tighten the bolt to 11.9
N´m (105 in.lbs.).
(3) Install the wiring connector onto the output
speed sensor
(4) Verify the transmission fluid level. Add fluid as
necessary.
(5) Lower vehicle.
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The tow/haul overdrive OFF (control) switch is
located in the shift lever arm (Fig. 106). The switch
is a momentary contact device that signals the PCM
to toggle current status of the overdrive function.
OPERATION
At key-on, overdrive operation is allowed. Pressing
the switch once causes the tow/haul overdrive OFF
mode to be entered and the Tow/Haul lamp to be illu-
minated. Pressing the switch a second time causesnormal overdrive operation to be restored and the
tow/haul lamp to be turned off. The tow/haul over-
drive OFF mode defaults to ON after the ignition
switch is cycled OFF and ON. The normal position
for the control switch is the ON position. The switch
must be in this position to energize the solenoid and
allow a 3-4 upshift. The control switch indicator light
illuminates only when the tow/haul overdrive switch
is turned to the OFF position, or when illuminated
by the transmission control module.
REMOVAL
(1) Using a plastic trim tool, remove the tow/haul
overdrive off switch retainer from the shift lever (Fig.
107).
Fig. 105 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 106 Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch
Fig. 107 Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch Retainer
21 - 392 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR (Continued)
Page 2096 of 2627
(2) Pull the switch outwards to release it from the
connector in the lever (Fig. 108)
INSTALLATION
NOTE: There is enough slack in the wire to pull out
the connector from the lever.
(1) Pull the connector out of the lever just enough
to grasp it.
CAUTION: Be careful not to bend the pins on the
tow/haul overdrive off switch. Use care when
installing the switch, as it is not indexed, and can
be accidentally installed incorrectly.
(2) Install the tow/haul overdrive off switch into
the connector (Fig. 109)
(3) Push the tow/haul overdrive off switch and wir-
ing into the shift lever.
(4) Install the tow/haul overdrive off switch
retainer onto the shift lever.
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION
There are several sizes and types of pistons used in
an automatic transmission. Some pistons are used to
apply clutches, while others are used to apply bands.
They all have in common the fact that they are
round or circular in shape, located within a smooth
walled cylinder, which is closed at one end and con-
verts fluid pressure into mechanical movement. The
fluid pressure exerted on the piston is contained
within the system through the use of piston rings or
seals.
OPERATION
The principal which makes this operation possible
is known as Pascal's Law. Pascal's Law can be stated
as: ªPressure on a confined fluid is transmitted
equally in all directions and acts with equal force on
equal areas.º
PRESSURE
Pressure (Fig. 110) is nothing more than force (lbs.)
divided by area (in or ft.), or force per unit area.
Given a 100 lb. block and an area of 100 sq. in. on
the floor, the pressure exerted by the block is: 100
lbs. 100 in or 1 pound per square inch, or PSI as it is
commonly referred to.
Fig. 108 Remove the Tow/Haul Overdrive Off Switch
Fig. 109 Install the Tow/Haul Overdrive Off SwitchFig. 110 Force and Pressure Relationship
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 393
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2100 of 2627

INSPECTION
Check sun gear and driving shell condition.
Replace the gear if damaged or if the bushings are
scored or worn. The bushings are not serviceable.
Replace the driving shell if worn, cracked or dam-
aged.
Replace planetary gear sets if gears, pinion pins, or
carrier are damaged in any way. Replace the annulus
gears and supports if either component is worn or
damaged.
Replace the output shaft if the machined surfaces
are scored, pitted, or damaged in any way. Also
replace the shaft if the splines are damaged, or
exhibits cracks at any location.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean and inspect all components. Replace any
components which show evidence of excessive wear
or scoring.(2) Install the number 11 bearing into the input
planetary carrier so that the inner race will be
toward the front of the transmission (Fig. 116).
(3) Install the input sun gear into the input carrier
(Fig. 116).
(4) Install the number 10 bearing onto the rear of
the reverse planetary carrier with the inner race
toward the carrier (Fig. 116).
(5) Install the number 9 bearing onto the front of
the reverse planetary carrier with the outer race
toward the carrier and the inner race facing upward
(Fig. 116).
(6) Install the reverse planetary gear carrier into
the input carrier (Fig. 116).
(7) Install the input annulus gear into the input
carrier (Fig. 116).
(8) Install the snap-ring to hold the input annulus
gear into the input carrier (Fig. 116).
Fig. 116 Reverse/Input Planetary Carrier Assembly
1 - SNAP-RING 5 - INPUT PLANETARY CARRIER
2 - BEARING NUMBER 10 6 - INPUT SUN GEAR
3 - BEARING NUMBER 11 7 - REVERSE PLANETARY CARRIER
4 - INPUT ANNULUS
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 397
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN (Continued)
Page 2105 of 2627

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 120) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 121).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 122) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston with friction material was added to the tur-
bine assembly to provide this mechanical lock-up.
In order to reduce heat build-up in the transmis-
sion and buffer the powertrain against torsional
vibrations, the TCM can duty cycle the L/R-CC Sole-
noid to achieve a smooth application of the torque
converter clutch. This function, referred to as Elec-
tronically Modulated Converter Clutch (EMCC) can
occur at various times depending on the following
variables:
²Shift lever position
²Current gear range
²Transmission fluid temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Input speed
²Throttle angle²Engine speed
Fig. 120 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 121 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 122 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
21 - 402 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2107 of 2627

control switch is in the OFF position, the clutch will
engage after the shift to third gear.
The TCM controls the torque converter by way of
internal logic software. The programming of the soft-
ware provides the TCM with control over the L/R-CC
Solenoid. There are four output logic states that can
be applied as follows:
²No EMCC
²Partial EMCC
²Full EMCC
²Gradual-to-no EMCC
NO EMCC
Under No EMCC conditions, the L/R Solenoid is
OFF. There are several conditions that can result in
NO EMCC operations. No EMCC can be initiated
due to a fault in the transmission or because the
TCM does not see the need for EMCC under current
driving conditions.
PARTIAL EMCC
Partial EMCC operation modulates the L/R Sole-
noid (duty cycle) to obtain partial torque converter
clutch application. Partial EMCC operation is main-
tained until Full EMCC is called for and actuated.
During Partial EMCC some slip does occur. Partial
EMCC will usually occur at low speeds, low load and
light throttle situations.
FULL EMCC
During Full EMCC operation, the TCM increases
the L/R Solenoid duty cycle to full ON after Partial
EMCC control brings the engine speed within thedesired slip range of transmission input speed rela-
tive to engine rpm.
GRADUAL-TO-NO EMCC
This operation is to soften the change from Full or
Partial EMCC to No EMCC. This is done at mid-
throttle by decreasing the L/R Solenoid duty cycle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive flats for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
flats with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if neces-
sary. Verify that the converter hub o-ring is properly
installed and is free from debris. The hub must be
smooth to avoid damaging the pump seal at installa-
tion.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or con-
verter hub o-ring while inserting torque converter
into the front of the transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 125). Surface of converter lugs
should be at least 13 mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
Fig. 124 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 404 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2111 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(2) Position the transmission solenoid/TRS assem-
bly onto the valve body. Be sure that both alignment
dowels are fully seated in the valve body and that
the TRS switch contacts are properly positioned in
the selector plate
(3) Install the screws to hold the transmission
solenoid/TRS assembly onto the valve body.
(4) Tighten the solenoid assembly screws adjacent
to the arrows cast into the bottom of the valve body
first. Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(5) Tighten the remainder of the solenoid assembly
screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(6) Install the valve body into the transmission.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transmission temperature sensor is a ther-
mistor that is integral to the Transmission Range
Sensor (TRS).
OPERATION
The transmission temperature sensor is used by
the TCM to sense the temperature of the fluid in the
sump. Since fluid temperature can affect transmis-
sion shift quality and convertor lock up, the TCM
requires this information to determine which shift
schedule to operate in.
Calculated Temperature
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-
dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and a transfer plate. The
valve body contains valves and check balls that con-
trol fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch,
bands, and frictional clutches. The valve body con-
tains the following components (Fig. 129) and (Fig.
130):
²Solenoid switch valve
²Manual valve
²Low/reverse switch valve
²5 Accumulators
²7 check balls
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) controls the direc-
tion of the transmission fluid when the L/R-TCC sole-
noid is energized.
When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve is a relay valve. The purpose of
the manual valve is to direct fluid to the correct cir-
cuit needed for a specific gear or driving range. The
manual valve, as the name implies, is manually oper-
ated by the driver with a lever located on the top of
the valve body. The valve is connected mechanically
by a cable to the gearshift mechanism. The valve is
held in each of its positions by a roller detent spring
(Fig. 131) that engages the ªroostercombº of the TRS
selector plate.
21 - 408 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 2117 of 2627

Inspect all the fluid seals on the valve body (Fig.
141). Replace any seals that are cracked, distorted, or
damaged in any way. These seals pass fluid pressure
directly to the clutches. Any pressure leak at these
points, may cause transmission performance prob-
lems.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate valves, springs, and the housing
valve bores with clean transmission fluid.
(2) Install solenoid switch valve, manual valve,
and the low/reverse switch valve into the valve body.
(3) Install the retainers to hold each valve into the
valve body.
(4) Install the valve body check balls into their
proper locations.
(5) Position the transfer plate onto the valve body.
(6) Install the screws to hold the transfer plate to
the valve body. Tighten the screws to 5.6 N´m (50 in.
lbs.).
(7) Install the accumulator pistons and springs
into the valve body in the location from which they
were removed. Note that all accumulators except the
overdrive have two springs. The overdrive accumula-
tor piston has only one spring.
(8) Position the accumulator cover onto the valve
body.(9) Install the screws to hold the accumulator
cover onto the valve body. Tighten the screws to 8
N´m (70 in. lbs.).
(10) Install the TRS selector plate onto the valve
body and the manual valve.
(11) Install the solenoid and pressure switch
assembly onto the valve body.
(12) Install the screws to hold the solenoid and
pressure switch assembly onto the valve body.
Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in. lbs.). Tighten
the screws adjacent to the arrows cast into the bot-
tom of the transfer plate first.
(13) Position the detent spring onto the valve body.
(14) Install the screw to hold the detent spring
onto the valve body. Tighten the screw to 4.5 N´m (40
in. lbs.).
(15) Install new clutch passage seals onto the
valve body, if necessary
INSTALLATION
(1) Check condition of seals on valve body and the
solenoid and pressure switch assembly. Replace seals
if cut or worn.
(2) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(3) Place the transmission in the PARK position.
(4) Lubricate seal on the solenoid and pressure
switch assembly connector with petroleum jelly.
(5) Position valve body in transmission and align
the manual lever on the valve body to the pin on the
transmission manual shift lever.
(6) Seat valve body in case and install one or two
bolts to hold valve body in place.
(7) Tighten valve body bolts alternately and evenly
to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil
pump inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the
butt end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage to
the transmission will result.
(9) Place replacement filter in position on valve
body and into the oil pump.
(10) Install screw to hold filter to valve body.
Tighten screw to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Connect the solenoid and pressure switch
assembly connector.
(12) Install oil pan. Tighten pan bolts to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Lower vehicle and fill transmission with
MopartATF +4.
(14) Check and adjust gearshift cable, if necessary.
Fig. 141 Valve Body Seals
1 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
2 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
3 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR (2 SPRINGS)
5 - LOW/REVERSE PASSAGE SEAL
6 - 2ND CLUTCH PASSAGE SEAL
7 - 4TH CLUTCH PASSAGE SEAL
8 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR (1 SPRING)
21 - 414 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 2120 of 2627
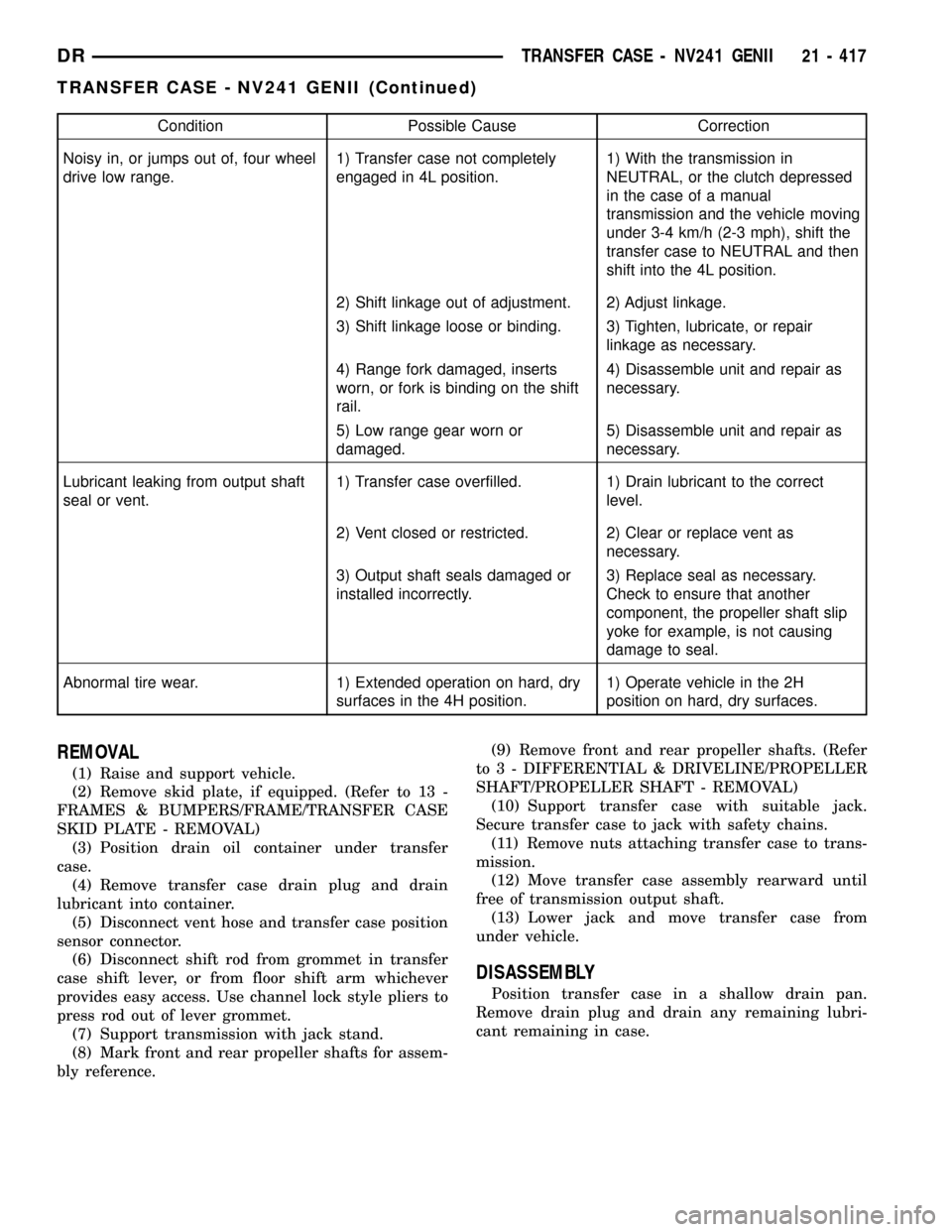
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Noisy in, or jumps out of, four wheel
drive low range.1) Transfer case not completely
engaged in 4L position.1) With the transmission in
NEUTRAL, or the clutch depressed
in the case of a manual
transmission and the vehicle moving
under 3-4 km/h (2-3 mph), shift the
transfer case to NEUTRAL and then
shift into the 4L position.
2) Shift linkage out of adjustment. 2) Adjust linkage.
3) Shift linkage loose or binding. 3) Tighten, lubricate, or repair
linkage as necessary.
4) Range fork damaged, inserts
worn, or fork is binding on the shift
rail.4) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
5) Low range gear worn or
damaged.5) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
Lubricant leaking from output shaft
seal or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Vent closed or restricted. 2) Clear or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Output shaft seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace seal as necessary.
Check to ensure that another
component, the propeller shaft slip
yoke for example, is not causing
damage to seal.
Abnormal tire wear. 1) Extended operation on hard, dry
surfaces in the 4H position.1) Operate vehicle in the 2H
position on hard, dry surfaces.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove skid plate, if equipped. (Refer to 13 -
FRAMES & BUMPERS/FRAME/TRANSFER CASE
SKID PLATE - REMOVAL)
(3) Position drain oil container under transfer
case.
(4) Remove transfer case drain plug and drain
lubricant into container.
(5) Disconnect vent hose and transfer case position
sensor connector.
(6) Disconnect shift rod from grommet in transfer
case shift lever, or from floor shift arm whichever
provides easy access. Use channel lock style pliers to
press rod out of lever grommet.
(7) Support transmission with jack stand.
(8) Mark front and rear propeller shafts for assem-
bly reference.(9) Remove front and rear propeller shafts. (Refer
to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(10) Support transfer case with suitable jack.
Secure transfer case to jack with safety chains.
(11) Remove nuts attaching transfer case to trans-
mission.
(12) Move transfer case assembly rearward until
free of transmission output shaft.
(13) Lower jack and move transfer case from
under vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
Position transfer case in a shallow drain pan.
Remove drain plug and drain any remaining lubri-
cant remaining in case.
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII 21 - 417
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII (Continued)