1998 DODGE RAM 1500 one
[x] Cancel search: onePage 76 of 2627

REAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR
DESCRIPTION.........................41
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPRING AND
SHOCK.............................41
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................42
BUSHINGS
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
JOUNCE BUMPER
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
AUXILIARY SPRING BUMPERS (3500)
REMOVAL.............................43INSTALLATION.........................43
SHOCK
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
SPRING
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
SPRING TIP INSERTS
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................45
REAR
DESCRIPTION
The rear suspension is comprised of:
²Shock Absorbers
²Jounce Bumpers
²Leaf Springs
²Auxiliary Leaf Spring (3500 series)
²Auxiliary Spring Bumpers (3500 series)
²Drive Axle
CAUTION: A vehicle should always be loaded so
the vehicle weight center-line is located immedi-
ately forward of the rear axle. Correct vehicle load-
ing provides proper front tire-to-road contact. This
results in maximum vehicle handling stability and
safety. Incorrect vehicle weight distribution can
cause excessive tire tread wear, spring fatigue or
failure, and erratic steering.
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber/ure-
thane bushings (except stabilizer bar) should be
tightened with the vehicle at normal ride height. It is
important to have the springs supporting the weight
of the vehicle when the fasteners are torqued. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPRING AND
SHOCK
A knocking or rattling noise from a shock absorber
may be caused by movement between mounting
bushings and metal brackets or attaching compo-
nents. These noises can usually be stopped by tight-
ening the attaching nuts. If the noise persists,
inspect for damaged and worn bushings, and attach-
ing components. Repair as necessary if any of these
conditions exist.
A squeaking noise from the shock absorber may be
caused by the hydraulic valving and may be intermit-
tent. This condition is not repairable and the shock
absorber must be replaced.
The shock absorbers are not refillable or adjust-
able. If a malfunction occurs, the shock absorber
must be replaced. To test a shock absorber, hold it in
an upright position and force the piston in and out of
the cylinder four or five times. The action throughout
each stroke should be smooth and even.
The spring eye and shock absorber bushings do not
require any type of lubrication. Do not attempt to
stop spring bushing noise by lubricating them.
Grease and mineral oil-base lubricants will deterio-
rate the bushing rubber.
If the vehicle is used for severe, off-road operation,
the springs should be examined periodically. Check
for broken and shifted leafs, loose and missing clips,
and broken center bolts. Refer to Spring and Shock
Absorber Diagnosis chart for additional information.
DRREAR 2 - 41
Page 81 of 2627

(5) Place one spring clinch clip isolator onto the
outboard side of the spring clinch clip (Fig. 9) and
one isolator on the inboard side of the spring clinch
clip.
(6) Using large adjustable pliers, close the spring
clinch clip until the isolator contacts the leaf spring
(Fig. 10).
CAUTION: DO NOT USE A HAMMER TO CLOSE THE
SPRING CLINCH CLIP. DAMAGE TO THE ISOLATOR
MAY RESULT.(7) Use an appropriate pry bar to bend open the
spring clinch clip. If necessary, remove the existing
spring clinch clip isolators.
(8) Repeat procedure for the other side of the vehi-
cle.
(9) Iinstall the tire wheel assemblies.
(10) Lower the vehicle.
Fig. 9 CLINCH CLIP ISOLATOR
1 - SPRING CLINCH CLIP ISOLATOR
2 - C-CLAMP
Fig. 10 CLINCH CLIP REASSEMBLY
1 - SPRING CLINCH CLIP
2 - ADJUSTABLE PLIERS
3 - C-CLAMP
2 - 46 REARDR
SPRING TIP INSERTS (Continued)
Page 85 of 2627
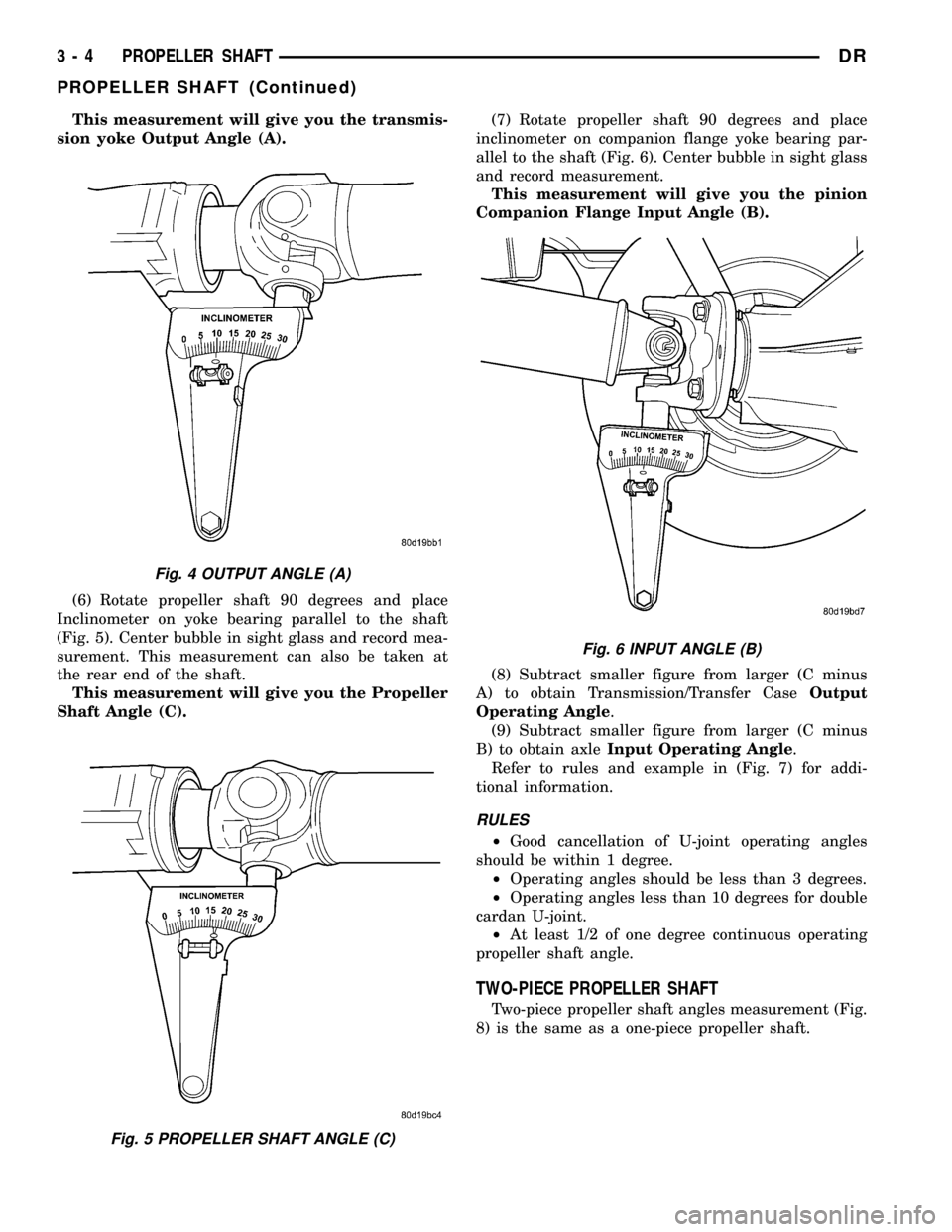
This measurement will give you the transmis-
sion yoke Output Angle (A).
(6) Rotate propeller shaft 90 degrees and place
Inclinometer on yoke bearing parallel to the shaft
(Fig. 5). Center bubble in sight glass and record mea-
surement. This measurement can also be taken at
the rear end of the shaft.
This measurement will give you the Propeller
Shaft Angle (C).(7) Rotate propeller shaft 90 degrees and place
inclinometer on companion flange yoke bearing par-
allel to the shaft (Fig. 6). Center bubble in sight glass
and record measurement.
This measurement will give you the pinion
Companion Flange Input Angle (B).
(8) Subtract smaller figure from larger (C minus
A) to obtain Transmission/Transfer CaseOutput
Operating Angle.
(9) Subtract smaller figure from larger (C minus
B) to obtain axleInput Operating Angle.
Refer to rules and example in (Fig. 7) for addi-
tional information.
RULES
²Good cancellation of U-joint operating angles
should be within 1 degree.
²Operating angles should be less than 3 degrees.
²Operating angles less than 10 degrees for double
cardan U-joint.
²At least 1/2 of one degree continuous operating
propeller shaft angle.
TWO-PIECE PROPELLER SHAFT
Two-piece propeller shaft angles measurement (Fig.
8) is the same as a one-piece propeller shaft.
Fig. 4 OUTPUT ANGLE (A)
Fig. 5 PROPELLER SHAFT ANGLE (C)
Fig. 6 INPUT ANGLE (B)
3 - 4 PROPELLER SHAFTDR
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 94 of 2627

(2) Position cross (1) in yoke with lube fitting
pointing up, if equipped (Fig. 27).
(3) Place a bearing cap (1) over the cross end (2)
and align cap with yoke bore (Fig. 28).
(4) Press bearing cap into the yoke bore enough to
clear snap ring groove.
(5) Repeat Step 3 and Step 4 to install the oppo-
site bearing cap.
NOTE: If joint is stiff or binding, strike the yoke with
a soft hammer to seat the needle bearings.
(6) Add grease to lube fitting, if equipped.
(7) Install propeller shaft.ASSEMBLY - WITH INJECTED RINGS
NOTE: Replacement joint has internal snap rings.
(1) Place joint in flange with one bearing cap.
(2) Position press (3) with receiver (1) on flange
and bearing cap (2) (Fig. 29).
Fig. 28 BEARING AND CROSS
1 - BEARING CAP
2 - CROSSFig. 29 PRESS ON FLANGE
1 - RECEIVER
2 - BEARING
3 - PRESS
Fig. 30 SNAP RING GROOVE
1 - YOKE
2 - GROOVE
DRPROPELLER SHAFT 3 - 13
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS (Continued)
Page 97 of 2627

DOUBLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL
JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove propeller shaft.
(2) Mark propeller shaft, link yoke and flange yoke
for assembly reference.
(3) Tap outside of the bearing cap assembly with
drift to loosen snap rings.
(4) Remove all bearing cap snap rings (Fig. 39).
(5) Remove grease fittings if equipped.
(6) Position a socket on the press with an inside
diameter large enough to receive the bearing cap
under the link yoke.
(7) Place another socket with an outside diameter
smaller than the bearing cap on the upper bearing
cap.(8) Press one bearing cap from outboard side of the
link yoke, enough to grasp the cap with vise jaws
(Fig. 40).
(9) Grasp protruding bearing cap with vise jaws
and tap link yoke with a mallet to remove bearing
cap (Fig. 41).
Fig. 39 SNAP RINGS
Fig. 40 PRESS OUT BEARING
Fig. 41 REMOVE BEARING FROM YOKE
3 - 16 PROPELLER SHAFTDR
Page 99 of 2627

(5) Flip propeller shaft yoke and install other bear-
ing cap onto the opposite trunnion and install a snap
ring (Fig. 46).
(6) Fit link yoke onto remaining trunnions and
press both bearing caps into place and install snap
rings (Fig. 47).(7) Install centering kit assembly inside the link
yoke (Fig. 48).
NOTE: Verify spring is properly positioned.
(8) Place two bearing caps on opposite trunnions of
the remaining cross. Fit open trunnions into the link
yoke bores and bearing caps into the centering kit
(Fig. 49).
Fig. 46 PRESS IN BEARING CAP
Fig. 47 INSTALL LINK YOKE
Fig. 48 INSTALL CENTERING KIT
Fig. 49 INSTALL REMAINING CROSS
3 - 18 PROPELLER SHAFTDR
DOUBLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS (Continued)
Page 101 of 2627

HALF SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION.............................20
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................20
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
SPECIFICATIONS.......................21
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................21CV JOINT-OUTER
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................23
CV JOINT-INNER
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION
CAUTION:: Never grasp half shaft assembly by the
boots. This may cause the boot to pucker or crease
and reduce the service life of the boot.
Avoid over angulating or stroking the C/V joints
when handling the half shaft.
Half shafts exposed to battery acid, transmission
fluid, brake fluid, differential fluid or gasoline may
cause the boots to deteriorate. Failure to heed cau-
tion may result in damage.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Check inboard and outboard C/V joint for leaking
grease. This is a sign of boot or boot clamp damage.
NOISE/VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise or vibration in turns could be
caused by a damaged outer C/V or inner tripod joint
seal boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the
loss/contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint. Noise could also
be caused by another component of the vehicle com-
ing in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a damaged or worn C/V joint. A
torn boot or loose/missing clamp on the inner/outer
joint which has allowed the grease to be lost will
damage the C/V joint.
SHUDDER/VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
This could be a worn/damaged inner tripod joint or
a sticking tripod joint. Improper wheel alignment
may also cause a shudder or vibration.
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
This problem could be a result of out of balance
front tires or tire/wheel runout. Foreign material
(mud, etc.) packed on the backside of the wheel(s)
will also cause a vibration.
REMOVAL
(1) With vehicle in neutral, position vehicle on
hoist.
(2) Remove half shaft hub nut.
(3) Remove brake caliper and rotor.
(4) Position hydraulic jack under lower suspension
arm and raise jack to unload rebound bumper.
(5) Remove lower shock absorber bolt.
(6) Remove upper ball joint nut and seperate ball
with Remover 8677 (Fig. 1).
(7) Disengage inner C/V joint from axle shaft with
two pry bars between the C/V housing and axle hous-
ing.
Fig. 1 UPPER BALL JOINT SEPARATION
1 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
2 - REMOVER
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
3 - 20 HALF SHAFTDR
Page 103 of 2627

CV JOINT-OUTER
REMOVAL
(1) Clamp shaft in a vise (with soft jaws) and sup-
port C/V joint.
CAUTION: Do not damage C/V housing or half
shaft.
(2) Remove clamps (2) (4) with a cut-off wheel or
grinder (Fig. 4).
(3) Slide the boot down the shaft.
(4) Remove lubricant to expose the C/V joint snap
ring.(5) Spread snap ring (1) and slide the joint off the
shaft (Fig. 5).
(6) Slide boot off the shaft and discard old boot.
(7) Mark alignment marks (1) on the inner race/
hub (2), bearing cage (3) and housing with dabs of
paint (Fig. 6).
(8) Clamp C/V joint in a vertical position in a soft
jawed vise.
(9) Press down one side of the bearing cage (3) to
gain access to the ball at the opposite side.
NOTE: If joint is tight, use a hammer and brass drift
to loosen the bearing hub. Do not contact the bear-
ing cage with the drift.
Fig. 4 BOOT CLAMP LOCATIONS
1 - C/V HOUSING
2 - CLAMP
3 - HALF SHAFT
4 - CLAMP
5 - C/V BOOT
Fig. 5 OUTER C/V JOINT
1 - SNAP RING
2 - SNAP RING GROVE
3 - SNAP RING PLIERS
Fig. 6 BEARING ACCESS
1 - ALIGNMENT MARKS
2 - BEARING HUB
3 - BEARING CAGE
4 - HOUSING
Fig. 7 BEARING
1 - HOUSING
2 - INNER RACE/HUB
3 - BEARING CAGE
4 - BALL
3 - 22 HALF SHAFTDR