1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Y case
[x] Cancel search: Y casePage 1824 of 2627

(10) Place Gauge Bar 6311 across the housing face.
Measure the distance from the top of the bar to the
bottom of the reverse countershaft bearing race bore
(Fig. 93).
(11) Subtract thickness of the gauge bar from the
measurement and record the result.
(12) The difference between the two measurements
is the end-play for the reverse countershaft gear
assembly.
(13) Install shims to achieve 0.15-0.25 mm (0.006-
0.010 in.) end-play for the reverse countershaft gear
assembly into the reverse countershaft bearing race
bore.
(14) Use Installer to install the reverse counter-
shaft bearing race into the extension/adapter hous-
ing.
(15) Install back-up lamp switch into the exten-
sion/adapter housing and tighten to 28 N´m (20
ft.lbs.).
(16) Install crossover cam into the extension/
adapter housing.
(17) Install bolt to hold the crossover cam to the
extension/adapter housing (Fig. 94).
(18) Install crossover detent plunger, spring and
plug into the extension/adapter housing. Tighten the
plug to 47.5 N´m (35 ft.lbs.) (Fig. 95).
(19) Apply sealer to the surface of the transmis-
sion case.
(20) Install extension/adapter housing onto the
transmission case.(21) Install bolts to hold the extension/adapter
housing onto the transmission gear case. Tighten
bolts to 48 N´m (35 ft.lbs.).
(22) Install shift rail blocker bolt and tighten bolt
to 55 N´m (41 ft.lbs.).
(23) Install primary shift rail detent plunger,
spring and plug into the transmission case. Tighten
detent plug to 47.5 N´m (35 ft.lbs.).
(24) Install shift tower onto the transmission case
and tighten bolts to 9 N´m (7 ft.lbs.).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If installing a new transmission, use all com-
ponents supplied with the transmission. If a new
shift tower is supplied with the new transmission,
do not re-use the original shift tower.
Fig. 93 MEASURE DEPTH OF REVERSE
COUNTERSHAFT GEAR BEARING RACE BORE
1 - GAUGE BAR TO BEARING RACE BORE MEASUREMENT
Fig. 94 CROSSOVER CAM BOLT
1 - CROSSOVER CAM
2 - BOLT
3 - EXTENSION HOUSING
Fig. 95 CROSSOVER CAM DETENT PLUG
1 - DETENT PLUG
2 - EXTENSION HOUSING
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 21 - 121
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1825 of 2627

(1) Apply a light coat of Mopar high temperature
bearing grease or equivalent to contact surfaces of
following components:
²input shaft splines.
²release bearing slide surface of front retainer.
²release bearing bore.
²release fork.
²release fork ball stud.
²propeller shaft slip yoke.
(2) Apply sealer to threads of bottom PTO cover
bolt and install bolt in case.
(3) Mount transmission on jack and position trans-
mission under vehicle.
(4) Raise transmission until input shaft is centered
in clutch disc hub.
(5) Move transmission forward and start input
shaft in clutch disc and pilot bushing/bearing.
(6)
Work transmission forward until seated against
engine block. Do not allow transmission to remain
unsupported after input shaft has entered clutch disc.
(7) Install and tighten transmission-to-engine
block bolts.
(8) Install clutch slave cylinder.
(9) Connect backup light switch wires.
(10) Position transmission harness wires in clips
on transmission.
(11) Install transmission mount on transmission or
rear crossmember.
(12) Install rear crossmember.
(13) Remove transmission jack and engine support
fixture.
(14)
Fill transmission with required lubricant (Fig.
96). Check lubricant level in transfer case if equipped.
TWO WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Install propeller shaft with referece marks
aligned.
(2) Install exhaust system components.(3) Remove support and lower vehicle.
(4) Shift transmission into third gear.
(5) Clean the mating surfaces of shift tower and
isolator plate with suitable wax and grease remover.
(6) Apply Mopar Gasket Maker or equivalent to
sealing surface of the transmission case. Do not over
apply sealant.
(7) Install isolator plate onto the transmission case
metal side down.
(8) Install shift tower onto the isolator plate. No
sealant is necessary between the shift tower and top
of isolator plate.
(9) Verify shift tower, isolator plate and the shift
socket are properly aligned.
(10) Install bolts to hold the shift tower to the iso-
lator plate and the transmission case. Tighten bolts
to 10.2±11.25 N´m (7.5±8.3 ft. lbs.).
(11) Install shift boot and bezel.
FOUR WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Install and secure transfer case on the trans-
mission jack.
(2) Raise and align transfer case input gear with
transmission mainshaft.
(3) Move transfer case forward and seat it on
adapter.
(4)
Install and tighten transfer case mounting nuts to
41-47 N´m (30-35 ft. lbs.) if case has 3/8 studs. If case
has 5/16 studs tighten to 30-41 N´m (22-30 ft. lbs.).
(5) Connect transfer case shift lever to range lever
on transfer case.
(6) Install propeller shafts with reference marks
aligned.
(7) Install transfer case skid plate, if equipped,
and crossmember. Tighten attaching bolts/nuts to 41
N´m (30 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install exhaust system components.
(9) Remove support and lower vehicle.
(10) Shift transmission into third gear.
(11) Clean the mating surfaces of shift tower, iso-
lator plate and transmission case with suitable wax
and grease remover.
(12) Apply Mopar Gasket Maker or equivalent to
the sealing surface of the transmission case. Do not
over apply sealant.
(13) Install isolator plate onto the transmission
case, metal side down.
(14) Install shift tower onto the isolator plate. No
sealant is necessary between the shift tower and top
of isolator plate.
(15) Verify that the shift tower, isolator plate and
the shift tower bushings are properly aligned.
(16) Install the bolts to hold the shift tower to the
isolator plate and the transmission case. Tighten the
shift tower bolts to 10.2-11.25 N´m (7.5-8.3 ft. lbs.).
(17) Install shift lever boot and bezel.
Fig. 96 FILL PLUG
1 - FILL PLUG
21 - 122 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1831 of 2627

ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Mark propeller shaft and yokes for installation
reference and remove shaft.
(3) Remove the transfer case.
(4) Remove the adapter housing seal with a pry
tool or slide hammer with a screw.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install adapter housing seal with Installer and
Handle C-4171.
(2) Install transfer case.
(3) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(4) Check fluid level.
(5) Remove support and lower vehicle.
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Mark propeller shaft and pinion yoke for
installation reference and remove the propeller shaft.
(2) Remove extension housing seal with a pry tool
or a slide hammer and screw.
(3) Remove extension housing bushing with
Remover 8155 (Fig. 97).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install extension housing bushing with
Installer 8156 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 98).
(2) Install extension housing seal with Installer
8154 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 99).
(3) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(4) Check and fill transmission.
Fig. 97 EXTENSION HOUSING BUSHING REMOVAL
1 - REMOVER
Fig. 98 Install Extension Housing Bushing
1 - HANDLE
2 - INSTALLER
3 - BUSHING
Fig. 99 EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL INSTALLER
1 - INSTALLER
2 - HANDLE
21 - 128 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600DR
Page 1832 of 2627

SHIFT COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(2) Unscrew and remove the shift lever extension
from the shift
(3) Remove screws attaching shift boot to floorpan.
Then slide boot upward on the shift lever.
(4) Remove the bolts holding the shift tower to the
isolator plate and transmission gear case.
(5) Remove the shift tower (Fig. 100) and isolator
plate (Fig. 101) from the transmission.
INSTALLATION
(1) Shift transmission into third gear.
(2) Clean the mating surfaces of shift tower, isola-
tor plate and transmission gear case with suitable
wax and grease remover.(3) Apply Mopar Gasket Maker or equivalent to
the sealing surface of the transmission. Do not over
apply sealant.
(4) Install isolator plate onto the transmission,
metal side down.
(5) Install shift tower onto the isolator plate. No
sealant is necessary between the shift tower and iso-
lator plate.
(6) Verify shift tower, isolator plate and shift tower
bushings are properly aligned.
(7) Install shift tower bolts and tighten the shift
tower bolts to 8-10 N´m (7-9 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install shift lever extension, shift boot and
bezel.
Fig. 100 SHIFT TOWER
1 - SHIFT TOWER
2 - TRANSMISSION
Fig. 101 SHIFT TOWER ISOLATOR PLATE
1 - ISOLATOR PLATE
2 - TRANSMISSION
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 21 - 129
Page 1837 of 2627

IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan gas-
ket surface (Fig. 2). Refer to this information when
ordering replacement parts.
GEAR RATIOS
The 48RE gear ratios are:
1st.................................2.45:1
2nd................................1.45:1
3rd................................1.00:1
4th.................................0.69:1
Rev.................................2.20:1
OPERATION
The application of each driving or holding compo-
nent is controlled by the valve body based upon the
manual lever position, throttle pressure, and gover-
nor pressure. The governor pressure is a variable
pressure input to the valve body and is one of the
signals that a shift is necessary. First through fourth
gear are obtained by selectively applying and releas-
ing the different clutches and bands. Engine power is
thereby routed to the various planetary gear assem-
blies which combine with the overrunning clutch
assemblies to generate the different gear ratios. The
torque converter clutch is hydraulically applied and
is released when fluid is vented from the hydraulic
circuit by the torque converter control (TCC) solenoid
on the valve body. The torque converter clutch is con-
trolled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The
torque converter clutch engages in fourth gear, and
in third gear under various conditions, such as when
the O/D switch is OFF, when the vehicle is cruising
on a level surface after the vehicle has warmed up.
The torque converter clutch can also be engaged in
the MANUAL SECOND gear position if high trans-
mission temperatures are sensed by the PCM. The
torque converter clutch will disengage momentarily
when an increase in engine load is sensed by the
PCM, such as when the vehicle begins to go uphill or
the throttle pressure is increased. The torque con-
verter clutch feature increases fuel economy and
reduces the transmission fluid temperature.
Since the overdrive clutch is applied in fourth gear
only and the direct clutch is applied in all ranges
except fourth gear, the transmission operation for
park, neutral, and first through third gear will be
described first. Once these powerflows are described,
the third to fourth shift sequence will be described.
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER 10 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
2 - INPUT SHAFT 11 - DIRECT CLUTCH
3 - OIL PUMP 12 - PLANETARY GEAR
4 - FRONT BAND 13 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
5 - FRONT CLUTCH 14 - OVERDRIVE OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
6 - REAR CLUTCH 15 - DIRECT CLUTCH SPRING
7 - PLANETARIES 16 - OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER
8 - REAR BAND 17 - OIL PAN
9 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH 18 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 2 Transmission Part Number And Serial
Number Location
1 - PART NUMBER
2 - BUILD DATE
3 - SERIAL NUMBER
21 - 134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1838 of 2627

PARK POWERFLOW
As the engine is running and the crankshaft is
rotating, the flexplate and torque converter, which
are also bolted to it, are all rotating in a clockwise
direction as viewed from the front of the engine. The
notched hub of the torque converter is connected to
the oil pump's internal gear, supplying the transmis-
sion with oil pressure. As the converter turns, it
turns the input shaft in a clockwise direction. As the
input shaft is rotating, the front clutch hub-rear
clutch retainer and all their associated parts are also
rotating, all being directly connected to the input
shaft. The power flow from the engine through the
front clutch hub and rear clutch retainer stops at the
rear clutch retainer. Therefore, no power flow to the
output shaft occurs because no clutches are applied.
The only mechanism in use at this time is the park-
ing sprag (Fig. 3), which locks the parking gear on
the output shaft to the transmission case.
NEUTRAL POWERFLOW
With the gear selector in the NEUTRAL position
(Fig. 4), the power flow of the transmission is essen-
tially the same as in the park position. The only
operational difference is that the parking sprag has
been disengaged, unlocking the output shaft from the
transmission case and allowing it to move freely.
Fig. 3 Park Powerflow
1 - PAWL ENGAGED FOR PARK
2 - PARK SPRAG
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT
Fig. 4 Neutral Powerflow
1 - PAWL DISENGAGED FOR NEUTRAL
2 - PARK SPRAG
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT
4 - CAM
5-PAWL
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 135
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1844 of 2627
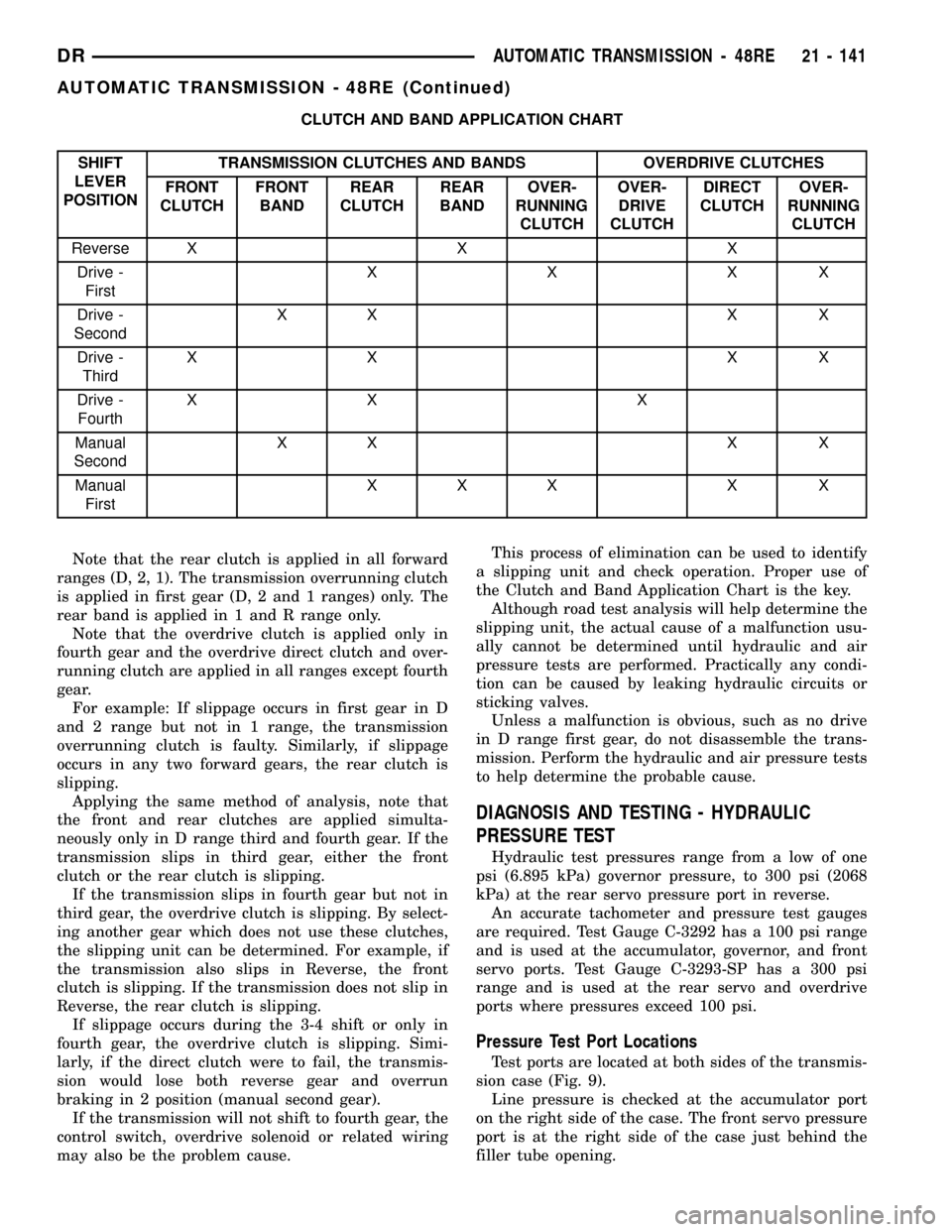
CLUTCH AND BAND APPLICATION CHART
SHIFT
LEVER
POSITIONTRANSMISSION CLUTCHES AND BANDS OVERDRIVE CLUTCHES
FRONT
CLUTCHFRONT
BANDREAR
CLUTCHREAR
BANDOVER-
RUNNING
CLUTCHOVER-
DRIVE
CLUTCHDIRECT
CLUTCHOVER-
RUNNING
CLUTCH
Reverse X X X
Drive -
FirstXXXX
Drive -
SecondXX X X
Drive -
ThirdXX XX
Drive -
FourthXX X
Manual
SecondXX X X
Manual
FirstXXX X X
Note that the rear clutch is applied in all forward
ranges (D, 2, 1). The transmission overrunning clutch
is applied in first gear (D, 2 and 1 ranges) only. The
rear band is applied in 1 and R range only.
Note that the overdrive clutch is applied only in
fourth gear and the overdrive direct clutch and over-
running clutch are applied in all ranges except fourth
gear.
For example: If slippage occurs in first gear in D
and 2 range but not in 1 range, the transmission
overrunning clutch is faulty. Similarly, if slippage
occurs in any two forward gears, the rear clutch is
slipping.
Applying the same method of analysis, note that
the front and rear clutches are applied simulta-
neously only in D range third and fourth gear. If the
transmission slips in third gear, either the front
clutch or the rear clutch is slipping.
If the transmission slips in fourth gear but not in
third gear, the overdrive clutch is slipping. By select-
ing another gear which does not use these clutches,
the slipping unit can be determined. For example, if
the transmission also slips in Reverse, the front
clutch is slipping. If the transmission does not slip in
Reverse, the rear clutch is slipping.
If slippage occurs during the 3-4 shift or only in
fourth gear, the overdrive clutch is slipping. Simi-
larly, if the direct clutch were to fail, the transmis-
sion would lose both reverse gear and overrun
braking in 2 position (manual second gear).
If the transmission will not shift to fourth gear, the
control switch, overdrive solenoid or related wiring
may also be the problem cause.This process of elimination can be used to identify
a slipping unit and check operation. Proper use of
the Clutch and Band Application Chart is the key.
Although road test analysis will help determine the
slipping unit, the actual cause of a malfunction usu-
ally cannot be determined until hydraulic and air
pressure tests are performed. Practically any condi-
tion can be caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or
sticking valves.
Unless a malfunction is obvious, such as no drive
in D range first gear, do not disassemble the trans-
mission. Perform the hydraulic and air pressure tests
to help determine the probable cause.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST
Hydraulic test pressures range from a low of one
psi (6.895 kPa) governor pressure, to 300 psi (2068
kPa) at the rear servo pressure port in reverse.
An accurate tachometer and pressure test gauges
are required. Test Gauge C-3292 has a 100 psi range
and is used at the accumulator, governor, and front
servo ports. Test Gauge C-3293-SP has a 300 psi
range and is used at the rear servo and overdrive
ports where pressures exceed 100 psi.
Pressure Test Port Locations
Test ports are located at both sides of the transmis-
sion case (Fig. 9).
Line pressure is checked at the accumulator port
on the right side of the case. The front servo pressure
port is at the right side of the case just behind the
filler tube opening.
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 141
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1845 of 2627

The rear servo and governor pressure ports are at
the right rear of the transmission case. The overdrive
clutch pressure port is at the left rear of the case.
Test One - Transmission In Manual Low
This test checks pump output, pressure regulation,
and condition of the rear clutch and servo circuit.
Both test gauges are required for this test.
(1) Connect tachometer to engine. Position tachom-
eter so it can be observed from driver seat if helper
will be operating engine. Raise vehicle on hoist that
will allow rear wheels to rotate freely.
(2) Connect 100 psi Gauge C-3292 to accumulator
port. Then connect 300 psi Gauge C-3293-SP to rear
servo port.
(3) Disconnect throttle and gearshift cables from
levers on transmission valve body manual shaft.
(4) Have helper start and run engine at 1000 rpm.
(5) Move transmission shift lever fully forward
into 1 range.
(6) Gradually move transmission throttle lever
from full forward to full rearward position and note
pressures on both gauges:²Line pressure at accumulator port should be
54-60 psi (372-414 kPa) with throttle lever forward
and gradually increase to 90-96 psi (621-662 kPa) as
throttle lever is moved rearward.
²Rear servo pressure should be same as line pres-
sure within 3 psi (20.68 kPa).
Test Two - Transmission In 2 Range
This test checks pump output, line pressure and
pressure regulation. Use 100 psi Test Gauge C-3292
for this test.
(1) Leave vehicle in place on hoist and leave Test
Gauge C-3292 connected to accumulator port.
(2) Have helper start and run engine at 1000 rpm.
(3) Move transmission shift lever one detent rear-
ward from full forward position. This is 2 range.
(4) Move transmission throttle lever from full for-
ward to full rearward position and read pressure on
gauge.
(5) Line pressure should be 54-60 psi (372-414
kPa) with throttle lever forward and gradually
increase to 90-96 psi (621-662 kPa) as lever is moved
rearward.
Test Three - Transmission In D Range Third Gear
This test checks pressure regulation and condition
of the clutch circuits. Both test gauges are required
for this test.
(1) Turn OD switch off.
(2) Leave vehicle on hoist and leave Gauge C-3292
in place at accumulator port.
(3) Move Gauge C-3293-SP over to front servo port
for this test.
(4) Have helper start and run engine at 1600 rpm
for this test.
(5) Move transmission shift lever two detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is D range.
(6) Read pressures on both gauges as transmission
throttle lever is gradually moved from full forward to
full rearward position:
²Line pressure at accumulator in D range third
gear, should be 54-60 psi (372-414 kPa) with throttle
lever forward and increase as lever is moved rear-
ward.
²Front servo pressure in D range third gear,
should be within 3 psi (21 kPa) of line pressure up to
kickdown point.
Test Four - Transmission In Reverse
This test checks pump output, pressure regulation
and the front clutch and rear servo circuits. Use 300
psi Test Gauge C-3293-SP for this test.
(1) Leave vehicle on hoist and leave gauge C-3292
in place at accumulator port.
(2) Move 300 psi Gauge C-3293-SP back to rear
servo port.
Fig. 9 Pressure Test Port Locations
1 - REAR SERVO TEST PORT
2 - GOVERNOR TEST PORT
3 - ACCUMULATOR TEST PORT
4 - FRONT SERVO TEST PORT
5 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH TEST PORT
21 - 142 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)