1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Emission
[x] Cancel search: EmissionPage 515 of 2627

board hardware, the cluster overlay, or the EMIC
housing are damaged or faulty, the entire EMIC mod-
ule must be replaced. The cluster lens, hood and
mask unit and the individual incandescent lamp
bulbs with holders are available for individual ser-
vice replacement.
OPERATION
The ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC)
in this model also includes the hardware and soft-
ware necessary to serve as the electronic body control
module and is sometimes referred to as the Cab
Compartment Node or CCN. The following informa-
tion deals primarily with the instrument cluster
functions of this unit. Additional details of the elec-
tronic body control functions of this unit may be
found within the service information for the system
or component that the EMIC controls. For example:
Additional details of the audible warning functions ofthe EMIC are found within the Chime/Buzzer service
information.
The EMIC is designed to allow the vehicle operator
to monitor the conditions of many of the vehicle com-
ponents and operating systems. The gauges and indi-
cators in the EMIC provide valuable information
about the various standard and optional powertrains,
fuel and emissions systems, cooling systems, lighting
systems, safety systems and many other convenience
items. The EMIC is installed in the instrument panel
so that all of these monitors can be easily viewed by
the vehicle operator when driving, while still allow-
ing relative ease of access for service. The micropro-
cessor-based EMIC hardware and software uses
various inputs to control the gauges and indicators
visible on the face of the cluster. Some of these
inputs are hard wired, but most are in the form of
electronic messages that are transmitted by other
electronic modules over the Programmable Communi-
cations Interface (PCI) data bus network. (Refer to 8
Fig. 3 Gauges & Indicators - Gasoline Engine
1 - MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP 13 - ELECTRONIC THROTTLE CONTROL (ETC) INDICATOR
2 - VOLTAGE GAUGE 14 - ENGINE TEMPERATURE GAUGE
3 - LEFT TURN INDICATOR 15 - SECURITY INDICATOR
4 - TACHOMETER 16 - GEAR SELECTOR INDICATOR DISPLAY (INCLUDES
CRUISE & UPSHIFT INDICATORS)
5 - AIRBAG INDICATOR 17 - CHECK GAUGES INDICATOR
6 - HIGH BEAM INDICATOR 18 - BRAKE INDICATOR
7 - SEATBELT INDICATOR 19 - ABS INDICATOR
8 - SPEEDOMETER 20 - ODOMETER/TRIP ODOMETER DISPLAY (INCLUDES
ENGINE HOURS, WASHER FLUID, LAMP OUTAGE, TOW/HAUL
& SERVICE 4x4 INDICATORS)
9 - RIGHT TURN INDICATOR 21 - ODOMETER/TRIP ODOMETER SWITCH BUTTON
10 - OIL PRESSURE GAUGE 22 - FUEL GAUGE
11 - CARGO LAMP INDICATOR 23 - LOW FUEL INDICATOR
12 - DOOR AJAR INDICATOR 24 - TRANSMISSION OVERTEMP INDICATOR
8J - 6 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERDR
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 540 of 2627

MALFUNCTION INDICATOR
LAMP (MIL)
DESCRIPTION
A Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) is standard
equipment on all instrument clusters (Fig. 22). The
MIL is located on the left side of the instrument clus-
ter, to the left of the voltage gauge. The MIL consists
of a stencil-like cutout of the International Control
and Display Symbol icon for ªEngineº in the opaque
layer of the instrument cluster overlay. The dark
outer layer of the overlay prevents the indicator from
being clearly visible when it is not illuminated. An
amber Light Emitting Diode (LED) behind the cutout
in the opaque layer of the overlay causes the icon to
appear in amber through the translucent outer layer
of the overlay when the indicator is illuminated from
behind by the LED, which is soldered onto the
instrument cluster electronic circuit board. The MIL
is serviced as a unit with the instrument cluster.
OPERATION
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) gives an
indication to the vehicle operator when the Power-
train Control Module (PCM) on vehicles with a gaso-
line engine, or the Engine Control Module (ECM) on
vehicles with a diesel engine has recorded a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) for an On-Board Diagnostics
II (OBDII) emissions-related circuit or component
malfunction. The MIL is controlled by a transistor on
the instrument cluster circuit board based upon clus-
ter programming and electronic messages received by
the cluster from the PCM or ECM over the Program-
mable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus. The
MIL Light Emitting Diode (LED) is completely con-
trolled by the instrument cluster logic circuit, and
that logic will only allow this indicator to operate
when the instrument cluster receives a battery cur-
rent input on the fused ignition switch output (run-
start) circuit. Therefore, the LED will always be off
when the ignition switch is in any position except On
or Start. The LED only illuminates when it is pro-
vided a path to ground by the instrument cluster
transistor. The instrument cluster will turn on the
MIL for the following reasons:
²Bulb Test- Each time the ignition switch is
turned to the On position the indicator is illuminated
for about two seconds as a bulb test. The entire two
second bulb test is a function of the PCM or ECM.²MIL Lamp-On Message- Each time the clus-
ter receives a MIL lamp-on message from the PCM
or ECM, the indicator will be illuminated. The indi-
cator can be flashed on and off, or illuminated solid,
as dictated by the PCM or ECM message. For some
DTC's, if a problem does not recur, the PCM or ECM
will send a lamp-off message automatically. Other
DTC's may require that a fault be repaired and the
PCM or ECM be reset before a lamp-off message will
be sent. For more information on the PCM, the ECM,
and the DTC set and reset parameters, (Refer to 25 -
EMISSIONS CONTROL - OPERATION).
²Communication Error- If the cluster receives
no lamp-on message from the PCM or ECM for ten
seconds, the MIL is illuminated by the instrument
cluster to indicate a loss of bus communication. The
indicator remains controlled and illuminated by the
cluster until a valid lamp-on message is received
from the PCM or ECM.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the MIL indicator will be
turned on during the bulb check portion of the test to
confirm the functionality of the LED and the cluster
control circuitry.
On vehicles with a gasoline engine, the PCM con-
tinually monitors the fuel and emissions system cir-
cuits and sensors to decide whether the system is in
good operating condition. On vehicles with a diesel
engine, the ECM continually monitors the fuel and
emissions system circuits and sensors to decide
whether the system is in good operating condition.
The PCM or ECM then sends the proper lamp-on or
lamp-off messages to the instrument cluster. For fur-
ther diagnosis of the MIL or the instrument cluster
circuitry that controls the LED, (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING). If the instrument cluster turns on
the MIL after the bulb test, it may indicate that a
malfunction has occurred and that the fuel and emis-
sions systems may require service. For proper diag-
nosis of the fuel and emissions systems, the PCM,
the ECM, the PCI data bus, or the electronic mes-
sage inputs to the instrument cluster that control the
MIL, a DRBIIItscan tool is required. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
Fig. 22 Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
DRINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 31
Page 1413 of 2627

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION OR
SPARK PLUGS OIL FOULED1. CCV System malfunction 1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS - DESCRIPTION) for
correct operation
2. Defective valve stem seal(s) 2. Repair or replace seal(s)
3. Worn or broken piston rings 3. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings
4. Scuffed pistons/cylinder walls 4. Hone cylinder bores and replace
pistons as required
5. Carbon in oil control ring groove 5. Remove rings and de-carbon piston
6. Worn valve guides 6. Inspect/replace valve guides as
necessary
7. Piston rings fitted too tightly in
grooves7. Remove rings and check ring end
gap and side clearance. Replace if
necessary
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC
LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
REMOVAL
(1) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
ERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(3) Remove the air cleaner resonator and duct
work as an assembly.
(4) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
9 - 190 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1482 of 2627
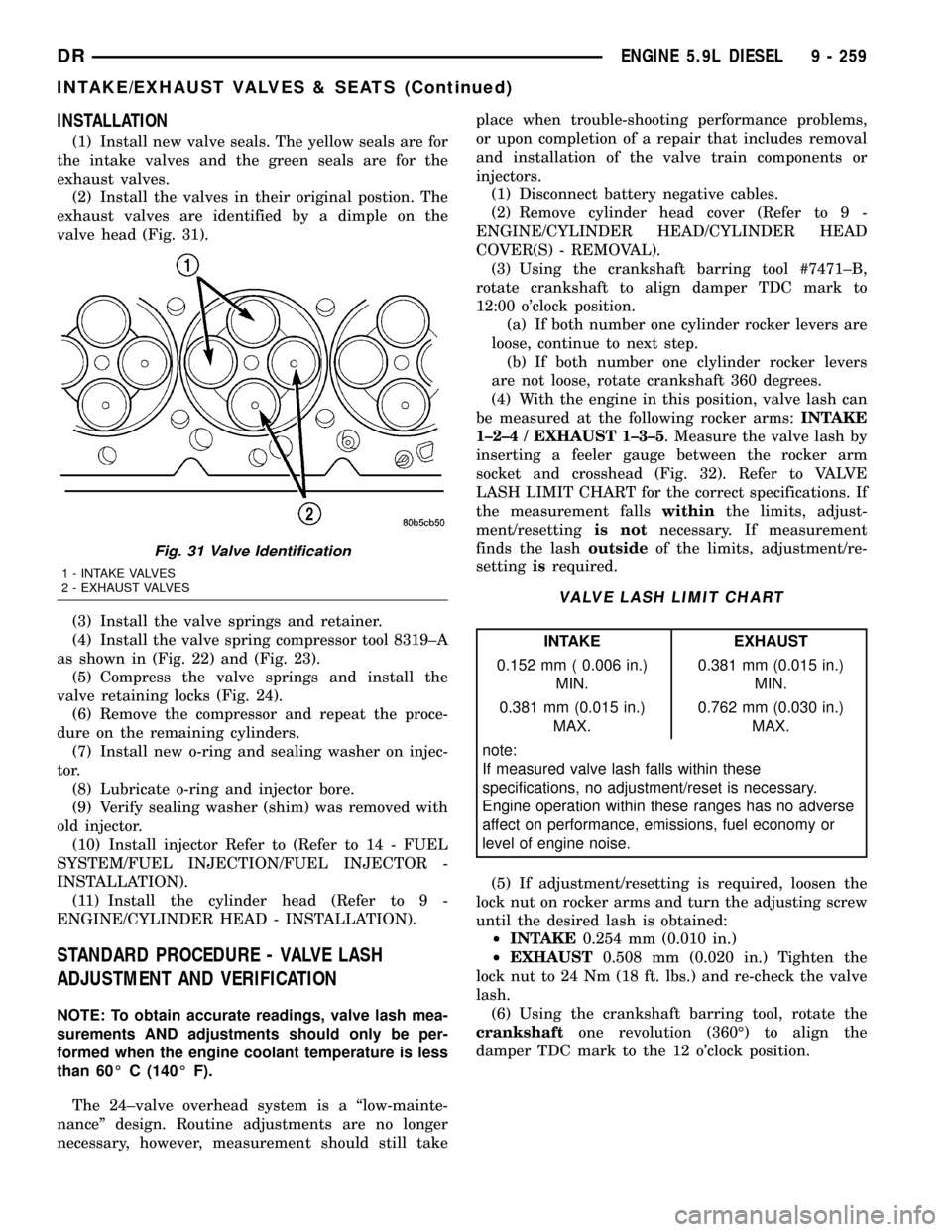
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new valve seals. The yellow seals are for
the intake valves and the green seals are for the
exhaust valves.
(2) Install the valves in their original postion. The
exhaust valves are identified by a dimple on the
valve head (Fig. 31).
(3) Install the valve springs and retainer.
(4) Install the valve spring compressor tool 8319±A
as shown in (Fig. 22) and (Fig. 23).
(5) Compress the valve springs and install the
valve retaining locks (Fig. 24).
(6) Remove the compressor and repeat the proce-
dure on the remaining cylinders.
(7) Install new o-ring and sealing washer on injec-
tor.
(8) Lubricate o-ring and injector bore.
(9) Verify sealing washer (shim) was removed with
old injector.
(10) Install injector Refer to (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
INSTALLATION).
(11) Install the cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VALVE LASH
ADJUSTMENT AND VERIFICATION
NOTE: To obtain accurate readings, valve lash mea-
surements AND adjustments should only be per-
formed when the engine coolant temperature is less
than 60É C (140É F).
The 24±valve overhead system is a ªlow-mainte-
nanceº design. Routine adjustments are no longer
necessary, however, measurement should still takeplace when trouble-shooting performance problems,
or upon completion of a repair that includes removal
and installation of the valve train components or
injectors.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cables.
(2) Remove cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(3) Using the crankshaft barring tool #7471±B,
rotate crankshaft to align damper TDC mark to
12:00 o'clock position.
(a) If both number one cylinder rocker levers are
loose, continue to next step.
(b) If both number one clylinder rocker levers
are not loose, rotate crankshaft 360 degrees.
(4) With the engine in this position, valve lash can
be measured at the following rocker arms:INTAKE
1±2±4 / EXHAUST 1±3±5. Measure the valve lash by
inserting a feeler gauge between the rocker arm
socket and crosshead (Fig. 32). Refer to VALVE
LASH LIMIT CHART for the correct specifications. If
the measurement fallswithinthe limits, adjust-
ment/resettingis notnecessary. If measurement
finds the lashoutsideof the limits, adjustment/re-
settingisrequired.
VALVE LASH LIMIT CHART
INTAKE EXHAUST
0.152 mm ( 0.006 in.)
MIN.0.381 mm (0.015 in.)
MIN.
0.381 mm (0.015 in.)
MAX.0.762 mm (0.030 in.)
MAX.
note:
If measured valve lash falls within these
specifications, no adjustment/reset is necessary.
Engine operation within these ranges has no adverse
affect on performance, emissions, fuel economy or
level of engine noise.
(5) If adjustment/resetting is required, loosen the
lock nut on rocker arms and turn the adjusting screw
until the desired lash is obtained:
²INTAKE0.254 mm (0.010 in.)
²EXHAUST0.508 mm (0.020 in.) Tighten the
lock nut to 24 Nm (18 ft. lbs.) and re-check the valve
lash.
(6) Using the crankshaft barring tool, rotate the
crankshaftone revolution (360É) to align the
damper TDC mark to the 12 o'clock position.
Fig. 31 Valve Identification
1 - INTAKE VALVES
2 - EXHAUST VALVES
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 259
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1526 of 2627
EXHAUST SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EXHAUST SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION........................1
DESCRIPTION - 5.9L DIESEL.............3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GAS ENGINE . . . 4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIESEL
ENGINE..............................5
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE...............5
SPECIAL TOOLS........................6
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION - CATALYTIC CONVERTER.....6
OPERATION............................6
REMOVAL
REMOVAL............................6
REMOVAL............................6
INSPECTION...........................6
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION........................6
INSTALLATION........................7
EXHAUST PIPE
REMOVAL - 3.7L/4.7L/5.7L.................7
INSPECTION...........................7
INSTALLATION - 3.7L/4.7L/5.7L..............7
EXHAUST PIPE
REMOVAL - DIESEL......................7
INSPECTION...........................8
INSTALLATION - DIESEL..................8
HEAT SHIELDS
DESCRIPTION..........................8
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8
MUFFLER
REMOVAL.............................9INSTALLATION..........................9
MUFFLER - 5.9L DIESEL
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
TAILPIPE - 5.9L DIESEL
REMOVAL.............................10
INSPECTION..........................10
INSTALLATION.........................11
TAILPIPE
REMOVAL.............................11
INSPECTION..........................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
TURBOCHARGER BOOST PRESSURE.....11
TURBOCHARGER
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL.............................14
CLEANING............................15
INSPECTION..........................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGE AIR
COOLER SYSTEM - LEAKS..............16
REMOVAL.............................17
CLEANING............................17
INSPECTION..........................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
EXHAUST SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: Avoid application of rust prevention com-
pounds or undercoating materials to exhaust sys-
tem floor pan exhaust heat shields. Light overspray
near the edges is permitted. Application of coating
will result in excessive floor pan temperatures and
objectionable fumes.The federal gasoline engine exhaust system con-
sists of engine exhaust manifolds, exhaust pipes, cat-
alytic converter(s), extension pipe (if needed),
exhaust heat shields, muffler and exhaust tailpipe
(Fig. 1), (Fig. 2), (Fig. 3)
The California emission vehicles exhaust system
also contains the above components as well as mini
catalytic converters added to the exhaust pipe.
The exhaust system must be properly aligned to
prevent stress, leakage and body contact. Minimum
clearance between any exhaust component and the
body or frame is 25.4 mm (1.0 in.). If the system con-
tacts any body panel, it may amplify objectionable
noises from the engine or body.
DREXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 1
Page 1528 of 2627

DESCRIPTION - 5.9L DIESEL
CAUTION: Avoid application of rust prevention com-
pounds or undercoating materials to exhaust sys-
tem floor pan exhaust heat shields. Light overspray
near the edges is permitted. Application of coating
will result in excessive floor pan temperatures and
objectionable fumes.
The diesel engine exhaust system consists of an
engine exhaust manifold, turbocharger, exhaust pipe,
resonator, extension pipe, muffler and exhaust
tailpipe.California emission vehicles include a catalytic con-
verter.
The exhaust system must be properly aligned to
prevent stress, leakage and body contact. The
exhaust components should be kept a minimum of
25.4 mm (1.0 in.) away from the body and frame. If
the system contacts any body panel, it may amplify
objectionable noises from the engine or body.
Fig. 3 Exhaust System 5.7L Engine - Typical
1 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 - TORCA CLAMP
3 - EXTENSION PIPE4 - INSULATOR
5 - MUFFLER
6 - TAILPIPE/RESONATOR
DREXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 3
EXHAUST SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1531 of 2627
SPECIAL TOOLS
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove spark plug wires from
plugs or by any other means short out cylinders.
Failure of the catalytic converter can occur due to a
temperature increase caused by unburned fuel
passing through the converter.
The stainless steel catalytic converter body is
designed to last the life of the vehicle. Excessive heat
can result in bulging or other distortion, but exces-
sive heat will not be the fault of the converter. If
unburned fuel enters the converter, overheating may
occur. If a converter is heat-damaged, correct the
cause of the damage at the same time the converter
is replaced. Also, inspect all other components of the
exhaust system for heat damage.
Unleaded gasoline must be used to avoid con-
taminating the catalyst core.
50 State emission vehicles incorporate two mini
catalytic converters located after the exhaust mani-
folds and before the inline catalytic converter.
OPERATION
The catalytic converter captures and burns any
unburned fuel mixture exiting the combustion cham-
bers during the exhaust stroke of the engine. This
process aids in reducing emissions output.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF TORCHES ARE USED WHEN WORK-
ING ON THE EXHAUST SYSTEM, DO NOT ALLOW
THE FLAME NEAR THE FUEL LINES.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove the bolts from the crossover pipe to the
catalytic converter connection.
(4) Disconnect oxygen sensor wiring.
(5) Loosen the nuts from the clamp that hold the
catalytic converter to the exhaust pipe flange connec-
tion.
NOTE: Do not remove nut from T-Bolt. Only remove
nut far enough, so that the T end can be removed
from the clamp.
(6) Remove the T bolt end of the fastener, from the
clamp.
(7) Spread the clamp, and remove the catalytic
converter from the vehicle.
(8) Discard the clamp.
NOTE: The catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
clamp is not reusable. Always use a new clamp
when reinstalling the catalytic converter.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove clamps and nuts.
(4) Remove the catalytic converter.
INSPECTION
Look at the stainless steel body of the converter,
inspect for bulging or other distortion that could be a
result of overheating. If the converter has a heat
shield attached make sure it is not bent or loose.
If you suspect internal damage to the catalyst, tap-
ping the bottom of the catalyst with a rubber mallet
may indicate a damaged core.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
NOTE: The catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
clamp is not reusable. Always use a new clamp
when reinstalling the catalytic converter.
TURBOCHARGER TESTER 9022
11 - 6 EXHAUST SYSTEMDR
EXHAUST SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1571 of 2627

OPERATION
Fuel is returned through the fuel pump module
and back into the fuel tank through the fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. A separate fuel return line
from the engine to the tank is not used.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock-
nut/gasket, and fuel tank check valve (refer to Fuel
Tank Check Valve for information).
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system. This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in Emission Control
Systems.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE
Use following procedure if the fuel injector
rail is, or is not equipped with a fuel pressure
test port.
(1) Remove fuel fill cap.
Fig. 1 FUEL DELIVERY COMPONENTS
1 - FUEL TANK 8 - LDP FRESH AIR FILTER
2 - CHECK VALVE 9 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
3 - LIQUID EXPANSION CHAMBER 10 - EVAP CANISTERS (2)
4 - FUEL FILTER / FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR 11 - FUEL TANK STRAPS (2)
5 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING AND FUEL LINE (TO ENGINE) 12 - CHECK VALVE
6 - EVAP LINE CONNECTION 13 - FUEL PUMP MODULE LOCK RING
7 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP FRESH AIR LINE 14 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERY - GASDR
FUEL DELIVERY - GAS (Continued)