1998 DODGE RAM 1500 ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 74 of 2627

SPRING
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle. Position a
hydraulic jack under the axle to support it.
(2) Paint or scribe alignment marks on lower sus-
pension arm cam adjusters and axle bracket for
installation reference.
(3) Remove the upper suspension arm and loosen
lower suspension arm bolts.
(4) Mark and disconnect the front propeller shaft
from the axle 4x4 models.
(5) Disconnect the track bar from the frame rail
bracket.
(6) Disconnect the drag link from pitman arm.
(7) Disconnect the stabilizer bar link and shock
absorber from the axle.
(8) Lower the axle until the spring is free from the
upper mount. Remove the coil spring.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the coil spring on the axle pad.
(2) Raise the axle into position until the spring
seats in the upper mount.
(3) Connect the stabilizer bar links and shock
absorbers to the axle bracket. Connect the track bar
to the frame rail bracket.
(4) Install the upper suspension arm.
(5) Install the front propeller shaft to the axle 4x4
model.
(6) Install drag link to pitman arm and tighten
nut to specifications. Install new cotter pin.
(7) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(8) Tighten the following suspension components
to specifications:
²Link to stabilizer bar nut.
²Lower shock bolt.
²Track bar bolt at axle shaft tube bracket.
²Upper suspension arm nut at axle bracket.
²Upper suspension nut at frame bracket.
²Align lower suspension arm reference marks and
tighten cam nut.
²Lower suspension nut at frame bracket.
STABILIZER BAR
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Hold the stabilizer link shafts with a wrench
and remove the link nuts at the stabilizer bar.
(3) Remove the retainers and grommets from the
stabilizer bar links.
(4) Remove the stabilizer bar link nuts from the
axle brackets.
Fig. 23 Shock Absorber and Bracket
1 - GROMMET
2 - RETAINER
3 - BRACKET
4 - RETAINER
5 - SHOCK
6 - GROMMET
Fig. 24 Shock Absorber Axle Mount
1 - SHOCK
2 - SPRING
3 - FLAG NUT
4 - SHOCK BOLT
DRFRONT - LINK/COIL 2 - 39
SHOCK (Continued)
Page 76 of 2627

REAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR
DESCRIPTION.........................41
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPRING AND
SHOCK.............................41
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................42
BUSHINGS
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
JOUNCE BUMPER
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
AUXILIARY SPRING BUMPERS (3500)
REMOVAL.............................43INSTALLATION.........................43
SHOCK
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
SPRING
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
SPRING TIP INSERTS
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................45
REAR
DESCRIPTION
The rear suspension is comprised of:
²Shock Absorbers
²Jounce Bumpers
²Leaf Springs
²Auxiliary Leaf Spring (3500 series)
²Auxiliary Spring Bumpers (3500 series)
²Drive Axle
CAUTION: A vehicle should always be loaded so
the vehicle weight center-line is located immedi-
ately forward of the rear axle. Correct vehicle load-
ing provides proper front tire-to-road contact. This
results in maximum vehicle handling stability and
safety. Incorrect vehicle weight distribution can
cause excessive tire tread wear, spring fatigue or
failure, and erratic steering.
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber/ure-
thane bushings (except stabilizer bar) should be
tightened with the vehicle at normal ride height. It is
important to have the springs supporting the weight
of the vehicle when the fasteners are torqued. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPRING AND
SHOCK
A knocking or rattling noise from a shock absorber
may be caused by movement between mounting
bushings and metal brackets or attaching compo-
nents. These noises can usually be stopped by tight-
ening the attaching nuts. If the noise persists,
inspect for damaged and worn bushings, and attach-
ing components. Repair as necessary if any of these
conditions exist.
A squeaking noise from the shock absorber may be
caused by the hydraulic valving and may be intermit-
tent. This condition is not repairable and the shock
absorber must be replaced.
The shock absorbers are not refillable or adjust-
able. If a malfunction occurs, the shock absorber
must be replaced. To test a shock absorber, hold it in
an upright position and force the piston in and out of
the cylinder four or five times. The action throughout
each stroke should be smooth and even.
The spring eye and shock absorber bushings do not
require any type of lubrication. Do not attempt to
stop spring bushing noise by lubricating them.
Grease and mineral oil-base lubricants will deterio-
rate the bushing rubber.
If the vehicle is used for severe, off-road operation,
the springs should be examined periodically. Check
for broken and shifted leafs, loose and missing clips,
and broken center bolts. Refer to Spring and Shock
Absorber Diagnosis chart for additional information.
DRREAR 2 - 41
Page 77 of 2627
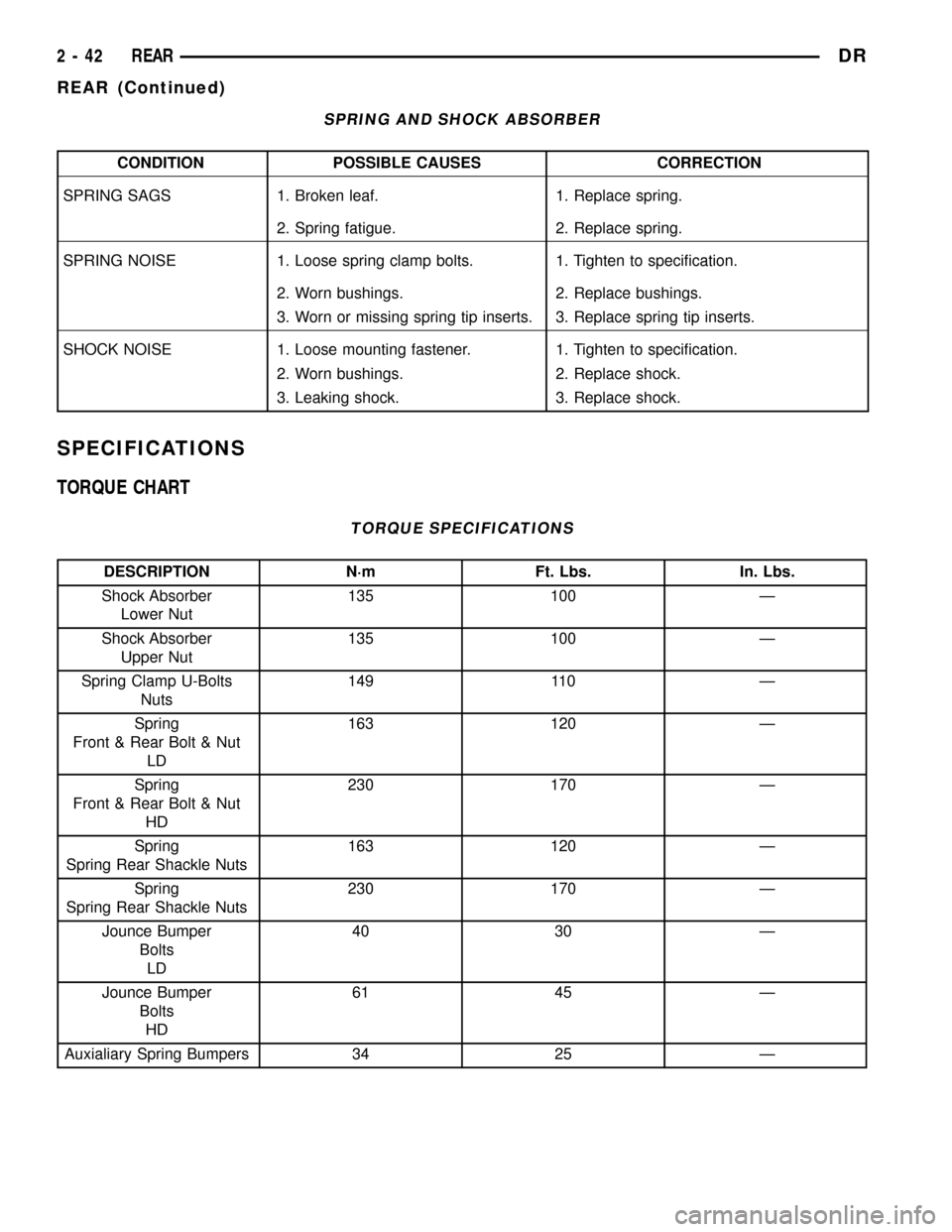
SPRING AND SHOCK ABSORBER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SPRING SAGS 1. Broken leaf. 1. Replace spring.
2. Spring fatigue. 2. Replace spring.
SPRING NOISE 1. Loose spring clamp bolts. 1. Tighten to specification.
2. Worn bushings. 2. Replace bushings.
3. Worn or missing spring tip inserts. 3. Replace spring tip inserts.
SHOCK NOISE 1. Loose mounting fastener. 1. Tighten to specification.
2. Worn bushings. 2. Replace shock.
3. Leaking shock. 3. Replace shock.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Shock Absorber
Lower Nut135 100 Ð
Shock Absorber
Upper Nut135 100 Ð
Spring Clamp U-Bolts
Nuts149 110 Ð
Spring
Front & Rear Bolt & Nut
LD163 120 Ð
Spring
Front & Rear Bolt & Nut
HD230 170 Ð
Spring
Spring Rear Shackle Nuts163 120 Ð
Spring
Spring Rear Shackle Nuts230 170 Ð
Jounce Bumper
Bolts
LD40 30 Ð
Jounce Bumper
Bolts
HD61 45 Ð
Auxialiary Spring Bumpers 34 25 Ð
2 - 42 REARDR
REAR (Continued)
Page 78 of 2627

BUSHINGS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the spring from the vehicle.
(2) Make small relief cuts in the flared up end of
the bushing metal being careful not to cut the spring.
Use a punch to bend the flared bushing metal down
for push out.
(3) Position the spring eye in a press.
(4) Press the bushing out with an appropriate size
driver.
INSTALLATION
(1) Press new bushing into the spring eye with an
appropriate size driver. The bushing should be cen-
tered in the spring eye.
(2) Stake the outermetal of the bushing in a mini-
mum of six points to retain the bushing.
(3) Install the spring on the vehicle.
JOUNCE BUMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the two bolts securing the jounce
bumper to the bracket (Fig. 1).
(2) Remove the jounce bumper.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the jounce bumper.
(2) Install the two bolts securing the jounce
bumper to the bracket. Tighten the bolts to 40 N´m
(30 ft. lbs.)(LD) or Tighten the bolts to 61 N´m (45 ft.
lbs.)(HD).
AUXILIARY SPRING BUMPERS
(3500)
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the nut securing the auxiliary spring
bumper to the bracket (Fig. 2).
(2) Remove the auxiliary spring bumper.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the auxiliary spring bumper.
(2) Install the nut securing the auxiliary spring
bumper to the bracket (Fig. 2). Tighten the nut to 25
N´m (34 ft. lbs.).
SHOCK
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and support the axle.
NOTE: The rear upper shock attachment uses a flag
nut. Do not use an air tool to remove the bolt, the
flag may rotate into the bottom of the bed and
cause damage. Use a wrench to hold the nut when
loosening.
(2) Remove the upper shock bolt and nut (Fig. 3).
(3) Remove the lower shock bolt and nut.
(4) Remove the rear shock absorber from the vehi-
cle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the shock absorber in the brackets.
(2) Install the bolts through the brackets and the
shock. Install the flag nut on the top bolt and nut on
lower bolt.
Fig. 1 JOUNCE BUMPER
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS
2 - JOUNCE BUMPER
Fig. 2 AUXILIARY SPRING BUMPER (3500)
1 - NUTS
2 - AUXILIARY SPRING BUMPERS
DRREAR 2 - 43
Page 79 of 2627

(3) Tighten the upper and lower bolt/nuts Tighten
to 135 N.m (100 ft. lbs.)
(4) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
SPRING
DESCRIPTION
The rear suspension system uses a multi-leaf
springs and a solid drive axle. The forward end of the
springs are mounted to the body rail hangers
through rubber bushings. The rearward end of the
springs are attached to the body by the use of shack-
les. The spring and shackles use rubber bushings.
OPERATION
The springs control ride quality and maintain vehi-
cle ride height. The shackles allow the springs to
change their length as the vehicle moves over various
road conditions.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Support the axle with a suitable holding fix-
ture.
(3) Remove the nuts, spring clamp bolts and the
plate that attach the spring to the axle (Fig. 4).
(4) Remove the nuts and bolts from the spring
front and rear shackle (Fig. 4).
(5) Remove the spring from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position spring on axle shaft tube so spring
center bolt is inserted into the locating hole in the
axle tube.(2) Align the front of the spring with the bolt hole
in the front bracket. Install the eye pivot bolt and
nut.
(3) Align the rear of the spring into the shackle
and install the bolt and nut.
(4) Tighten the spring front and rear eye pivot bolt
snug do not torque.
(5) Install the spring clamp bolts, plate and the
retaining nuts.
(6) Remove the holding fixture for the rear axle.
(7) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle so
that the weight is being supported by the tires.
(8) Tighten the spring clamp retaining nuts to 149
N´m (110 ft. lbs.).
(9) Tighten the spring front and rear pivot bolt
nuts to 163 N´m (120 ft. lbs.)(LD) or 230 N´m (170 ft.
lbs.)(HD).
SPRING TIP INSERTS
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove both rear tireand wheel assemblies
(3) Position a large C-Clamp adjacent to the spring
clinch clip and clamp the leaves of the spring
together
Fig. 3 SHOCK ABSORBER
1 - NUT
2 - AXLE
3 - SHOCK ABSORBER
Fig. 4 REAR SPRING
1 - LEAF SPRING
2 - PLATE
3 - NUTS
4 - FRONT NUT & BOLT
5 - SPRING CLAMP BOLTS
6 - SHACKLES
2 - 44 REARDR
SHOCK (Continued)
Page 101 of 2627

HALF SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION.............................20
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................20
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
SPECIFICATIONS.......................21
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................21CV JOINT-OUTER
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................23
CV JOINT-INNER
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION
CAUTION:: Never grasp half shaft assembly by the
boots. This may cause the boot to pucker or crease
and reduce the service life of the boot.
Avoid over angulating or stroking the C/V joints
when handling the half shaft.
Half shafts exposed to battery acid, transmission
fluid, brake fluid, differential fluid or gasoline may
cause the boots to deteriorate. Failure to heed cau-
tion may result in damage.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Check inboard and outboard C/V joint for leaking
grease. This is a sign of boot or boot clamp damage.
NOISE/VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise or vibration in turns could be
caused by a damaged outer C/V or inner tripod joint
seal boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the
loss/contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint. Noise could also
be caused by another component of the vehicle com-
ing in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a damaged or worn C/V joint. A
torn boot or loose/missing clamp on the inner/outer
joint which has allowed the grease to be lost will
damage the C/V joint.
SHUDDER/VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
This could be a worn/damaged inner tripod joint or
a sticking tripod joint. Improper wheel alignment
may also cause a shudder or vibration.
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
This problem could be a result of out of balance
front tires or tire/wheel runout. Foreign material
(mud, etc.) packed on the backside of the wheel(s)
will also cause a vibration.
REMOVAL
(1) With vehicle in neutral, position vehicle on
hoist.
(2) Remove half shaft hub nut.
(3) Remove brake caliper and rotor.
(4) Position hydraulic jack under lower suspension
arm and raise jack to unload rebound bumper.
(5) Remove lower shock absorber bolt.
(6) Remove upper ball joint nut and seperate ball
with Remover 8677 (Fig. 1).
(7) Disengage inner C/V joint from axle shaft with
two pry bars between the C/V housing and axle hous-
ing.
Fig. 1 UPPER BALL JOINT SEPARATION
1 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
2 - REMOVER
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
3 - 20 HALF SHAFTDR
Page 102 of 2627

(8) Tilt knuckle out and push half shaft out of the
knuckle (Fig. 2).
(9) Remove half shaft from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean hub bearing bore, hub bearing mating
surface and half shaft splines.
(2) Apply a light coating of grease to the front axle
shaft output splines.
(3) Install half shaft into the knuckle (Fig. 3).(4) Install half shaft on axle shaft. Push firmly to
engage axle shaft snap ring into the inner C/V hous-
ing.
(5) Install upper ball joint into the knuckle.
(6) Install upper ball joint nut and tighten to spec-
ification.
(7) Install lower shock absorber bolt and tighten to
specification.
(8) Install brake rotor and caliper.
(9) Install half shaft hub nut and tighten to 251
N´m (185 ft. lbs.).
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Half Shaft Nut 251 185 -
SPECIAL TOOLS
Fig. 2 STEERING KNUCKLE
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - SHOCK
3 - HALFSHAFT
4 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
5 - HUB/BEARING
Fig. 3 HALF SHAFT AND HUB/BEARING
1 - HUB/BEARING MOUNTING NUTS
2 - HALF SHAFT
CLAMP INSTALLER C-4975A
DRHALF SHAFT 3 - 21
HALF SHAFT (Continued)
Page 103 of 2627

CV JOINT-OUTER
REMOVAL
(1) Clamp shaft in a vise (with soft jaws) and sup-
port C/V joint.
CAUTION: Do not damage C/V housing or half
shaft.
(2) Remove clamps (2) (4) with a cut-off wheel or
grinder (Fig. 4).
(3) Slide the boot down the shaft.
(4) Remove lubricant to expose the C/V joint snap
ring.(5) Spread snap ring (1) and slide the joint off the
shaft (Fig. 5).
(6) Slide boot off the shaft and discard old boot.
(7) Mark alignment marks (1) on the inner race/
hub (2), bearing cage (3) and housing with dabs of
paint (Fig. 6).
(8) Clamp C/V joint in a vertical position in a soft
jawed vise.
(9) Press down one side of the bearing cage (3) to
gain access to the ball at the opposite side.
NOTE: If joint is tight, use a hammer and brass drift
to loosen the bearing hub. Do not contact the bear-
ing cage with the drift.
Fig. 4 BOOT CLAMP LOCATIONS
1 - C/V HOUSING
2 - CLAMP
3 - HALF SHAFT
4 - CLAMP
5 - C/V BOOT
Fig. 5 OUTER C/V JOINT
1 - SNAP RING
2 - SNAP RING GROVE
3 - SNAP RING PLIERS
Fig. 6 BEARING ACCESS
1 - ALIGNMENT MARKS
2 - BEARING HUB
3 - BEARING CAGE
4 - HOUSING
Fig. 7 BEARING
1 - HOUSING
2 - INNER RACE/HUB
3 - BEARING CAGE
4 - BALL
3 - 22 HALF SHAFTDR