1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Cylinder head
[x] Cancel search: Cylinder headPage 1675 of 2627
GEAR - LINK/COIL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GEAR - LINK/COIL
DESCRIPTION.........................20
OPERATION...........................20
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT........................21
SPECIFICATIONS
POWER STEERING GEAR..............22
TORQUE CHART......................23
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING GEAR..............23
PITMAN SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - GAS ENGINE...............25REMOVAL - DIESEL...................25
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - GAS ENGINE...........26
INSTALLATION - DIESEL................26
STEERING GEAR INPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................29
PITMAN SHAFT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - GAS......................30
REMOVAL - DIESEL...................30
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - GAS..................31
INSTALLATION - DIESEL................31
GEAR - LINK/COIL
DESCRIPTION
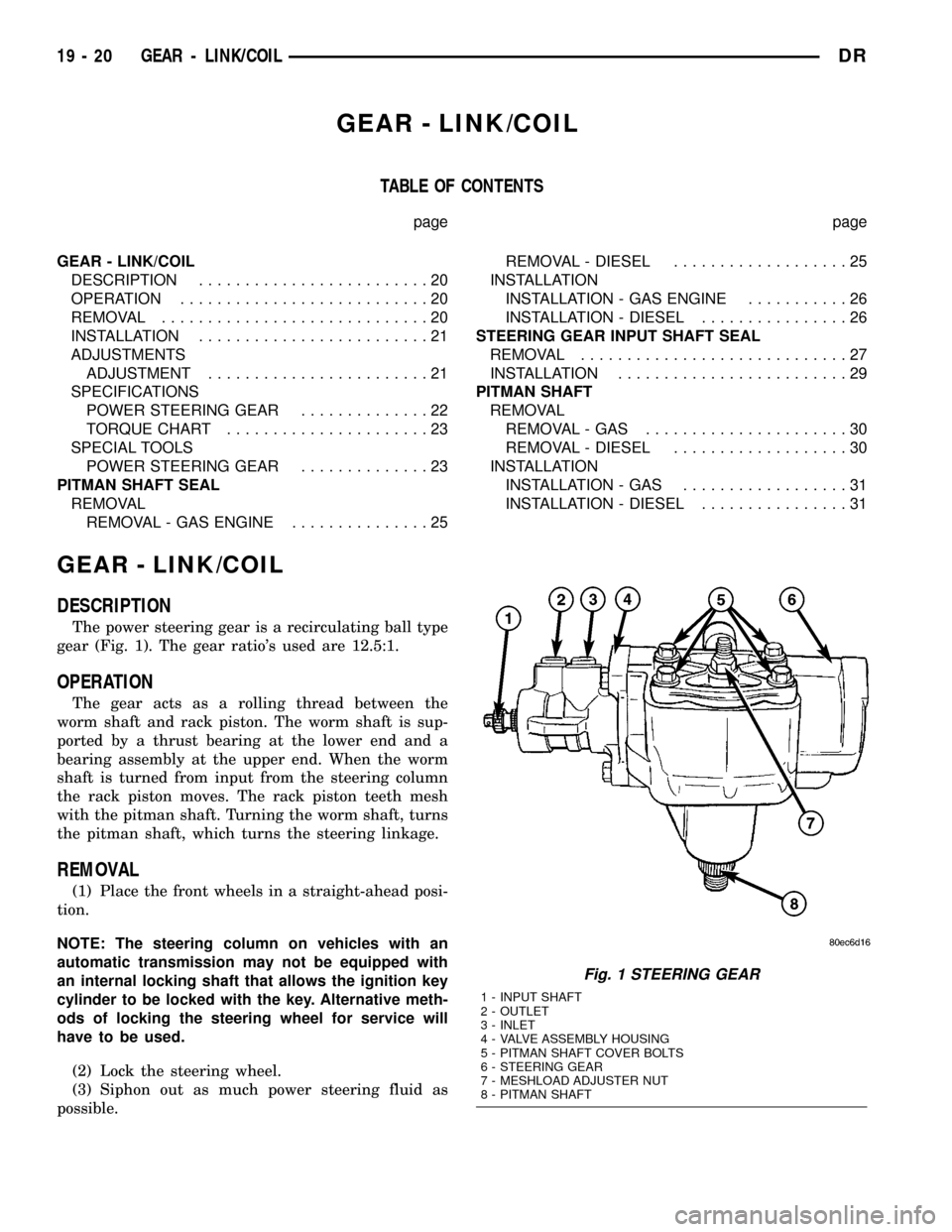
The power steering gear is a recirculating ball type
gear (Fig. 1). The gear ratio's used are 12.5:1.
OPERATION
The gear acts as a rolling thread between the
worm shaft and rack piston. The worm shaft is sup-
ported by a thrust bearing at the lower end and a
bearing assembly at the upper end. When the worm
shaft is turned from input from the steering column
the rack piston moves. The rack piston teeth mesh
with the pitman shaft. Turning the worm shaft, turns
the pitman shaft, which turns the steering linkage.
REMOVAL
(1) Place the front wheels in a straight-ahead posi-
tion.
NOTE: The steering column on vehicles with an
automatic transmission may not be equipped with
an internal locking shaft that allows the ignition key
cylinder to be locked with the key. Alternative meth-
ods of locking the steering wheel for service will
have to be used.
(2) Lock the steering wheel.
(3) Siphon out as much power steering fluid as
possible.
Fig. 1 STEERING GEAR
1 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OUTLET
3 - INLET
4 - VALVE ASSEMBLY HOUSING
5 - PITMAN SHAFT COVER BOLTS
6 - STEERING GEAR
7 - MESHLOAD ADJUSTER NUT
8 - PITMAN SHAFT
19 - 20 GEAR - LINK/COILDR
Page 1696 of 2627

(8) Fill the system with fluid and perform Steering
Pump Initial Operation, (Refer to 19 - STEERING/
PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(9) Start the engine and run it for fifteen minutes
then stop the engine.
(10) Remove the return line/lines from the pump
and plug the pump port/ports.
(11) Pour fresh fluid into the reservoir and check
the draining fluid for contamination. If the fluid is
still contaminated, then flush the system again.
(12) Install the return line/lines and perform
Steering Pump Initial Operation, (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - GAS
(1) Drain and siphon the power steering fluid from
the reservoir.
(2) Remove the serpentine belt.
CAUTION: Do not remove the fitting on the pump
that the high pressure hose screws into. The fitting
may come loose unless it is backed up using
another wrench. If the fitting does come loose, it
must be retightened before continuing. (57 - 67Nm,
40 - 50 lbft) If this fitting comes out of the pump
body, the internal spring and valve parts will fall out
of the pump and they cannot be reinstalled prop-
erly. If this occurs the pump needs to be replaced
with a new pump.
(3) Disconnect the return hose. (Fig. 2)
(4) Disconnect the pressure hose. (Fig. 2)
(5) Access to remove the three bolts securing the
pump to the cylinder head can be gained thru the
pulley holes. (Fig. 2)
REMOVAL - DIESEL
(1) Drain and siphon the power steering fluid from
the reservoir.
(2) Remove the serpentine belt.
CAUTION: Do not remove the fitting on the pump
that the high pressure hose screws into. The fitting
may come loose unless it is backed up using
another wrench. If the fitting does come loose, it
must be retightened before continuing. (57 - 67Nm,
40 - 50 lbft) If this fitting comes out of the pump
body, the internal spring and valve parts will fall out
of the pump and they cannot be reinstalled prop-
erly. If this occurs the pump needs to be replaced
with a new pump.
(3) Disconnect the return hose.
(4) Disconnect the pressure hose.(5) Access to remove the three bolts securing the
pump to the cylinder head can be gained thru the
pulley holes.
(6) Loosen the pump bracket to the block.
(7) Remove the 6 intake plenum bolts (Fig. 3).
(8) loosen the inner cooler tube clamp at the
intake plenum and remove the intake plenum.
(9) Loosen the inner cooler tube clamp at the radi-
ator support side and remove the tube from the vehi-
cle.
(10) Remove the power steering pump from the top
of the engine compartment where the intake plenum
was (Fig. 3).
Fig. 2 POWER STEERING PUMP
1 - POWER STEERING PULLEY
2 - POWER STEERING RESERVOIR
3 - RETURN HOSE
4 - HIGH PRESSURE HOSE
Fig. 3 POWER STEERING PUMP ACCESS
1 - INTAKE PLENUM MOUNTING
2 - POWER STEERING PUMP
DRPUMP 19 - 41
PUMP (Continued)
Page 1697 of 2627

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - GAS
(1) Align the pump with the mounting holes in the
left cylinder head.
(2) Install 3 pump mounting bolts through the pul-
ley access holes. Tighten the bolts to 28 N´m (21 ft.
lbs.).
(3) Reconnect the pressure line and return hose to
the pump and reservoir. Tighten the pressure line to
37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install the serpentine drive belt, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Fill the power steering pump, (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATION - DIESEL
(1) Set the power steering pump in place in the
engine compartment from the top (Fig. 3).(2) Install the inner cooler tube.
(3) Tighten the inner cooler tube clamp at the
radiator support side.
(4) Install the 6 intake plenum bolts (Fig. 3).
(5) Tighten the inner cooler tube clamp at the
intake plenum.
(6) Install 3 pump mounting bolts through the pul-
ley access holes. Tighten the bolts to 28 N´m (21 ft.
lbs.).
(7) Tighten the pump bracket to the block.
(8) Reconnect the pressure line and return hose to
the pump and reservoir. Tighten the pressure line to
37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install the serpentine drive belt, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Fill the power steering pump, (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Power Steering Pressure
Switch10 Ð 80
Power Steering Line
Pressure Line32 23 Ð
Power Steering Line
Return Line
HD51 38 Ð
Power Steering Line
Return Line
LD70 52 Ð
Power Steering Line
Pressure Line To Pump37 27 Ð
Power Steering Pump
Mounting Bolts28 27 Ð
Power Steering Pump
Reservoir Bolts13 10 120
Power Steering Pump
Bracket Bolts5562
19 - 42 PUMPDR
PUMP (Continued)
Page 2357 of 2627

INTERIOR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
INTERIOR
CAUTION.............................62
4WD FLOOR SHIFT BOOT
REMOVAL.............................62
INSTALLATION.........................62
A-PILLAR TRIM/GRAB HANDLE
REMOVAL.............................63
INSTALLATION.........................63
B-PILLAR LOWER TRIM
REMOVAL.............................63
INSTALLATION.........................64
B-PILLAR UPPER TRIM
REMOVAL.............................64
INSTALLATION.........................64
CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS
REMOVAL.............................65
INSTALLATION.........................65
COAT HOOK
REMOVAL.............................66
INSTALLATION.........................66
COWL TRIM
REMOVAL.............................66
INSTALLATION.........................66
C-PILLAR LOWER TRIM
REMOVAL.............................66
INSTALLATION.........................67
C-PILLAR UPPER TRIM
REMOVAL.............................67
INSTALLATION.........................67
FLOOR CONSOLE
REMOVAL.............................67
INSTALLATION.........................67
HEADLINER
REMOVAL.............................68INSTALLATION.........................68
B-PILLAR GRAB HANDLE
REMOVAL.............................68
INSTALLATION.........................68
REAR CAB BACK PANEL TRIM
REMOVAL.............................68
INSTALLATION.........................69
REAR VIEW MIRROR
REMOVAL.............................69
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION.......................70
INSTALLATION - REAR VIEW MIRROR
SUPPORT BRACKET...................70
SUN VISOR
REMOVAL.............................70
INSTALLATION.........................70
SUN VISOR SUPPORT
REMOVAL.............................70
INSTALLATION.........................71
BODY VENT
REMOVAL.............................71
INSTALLATION.........................71
REAR DOOR SILL TRIM COVER
REMOVAL.............................71
INSTALLATION.........................71
LOAD FLOOR
REMOVAL.............................71
INSTALLATION.........................72
LOAD FLOOR SUPPORT CYLINDER
REMOVAL.............................72
INSTALLATION.........................72
INTERIOR
CAUTION
CAUTION:: Do not attempt to remove interior trim
panels/moldings without first removing the neces-
sary adjacent panels. To avoid damaging the pan-
els, ensure that all the screws and clips are
removed before attempting to remove an interior
trim panel/molding. Trim panels are somewhat flex-
ible but can be damaged if handled improperly.
4WD FLOOR SHIFT BOOT
REMOVAL
(1) Using a small pry bar or equivalent, remove
the insert, the nut and remove the shifter knob. (Fig.
2)
(2) Using a trim stick C-4755 or equivalent, pry up
the boot from the console. (Fig. 1)
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the shift boot over the shifter lever
fully seat onto the console.
23 - 62 INTERIORDR
Page 2535 of 2627

After the system has been tested for leaks and
evacuated, a refrigerant (R-134a) charge can be
injected into the system.
NOTE: When connecting the service equipment
coupling to the line fitting, verify that the valve of
the coupling is fully closed. This will reduce the
amount of effort required to make the connection.
(1) If using a separate vacuum pump close all
valves before disconnecting pump. Connect manifold
gauge set to the A/C service ports.
NOTE: Always refer to the underhood HVAC Speci-
fication label for the refrigerant fill level of the vehi-
cle being serviced.
(2) Measure refrigerant (refer to capacities). Refer
to the instructions provided with the equipment
being used.
(3) Verify engine is shut off. Open the suction and
discharge valves. Open the charge valve to allow the
refrigerant to flow into the system. When the trans-
fer of refrigerant has stopped, close the suction and
discharge valve.
(4) If all of the charge did not transfer from the
dispensing device, put vehicle controls into the fol-
lowing mode:
²Automatic transmission in park or manual
transmission in neutral
²Engine at idle
²A/C mode control set to outside air
²A/C mode control set to panel mode
²A/C temperature control set to full cool
²Blower motor control set on highest speed
²Vehicle windows closed
If the A/C compressor does not engage, test the
compressor clutch control circuit and correct any fail-
ure (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIRING DIAGRAM
INFORMATION - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(5) Open the suction valve to allow the remaining
refrigerant to transfer to the system.
WARNING: TAKE CARE NOT TO OPEN THE DIS-
CHARGE (HIGH-PRESSURE) VALVE AT THIS TIME.
(6) Close all valves and test the A/C system perfor-
mance.
(7) Disconnect the charging station or manifold
gauge set. Install the service port caps.
REFRIGERANT CHARGE CAPACITY
The R-134a refrigerant system charge capacity for
this vehicle can be found on the underhood HVAC
specfication tag.
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - A/C COMPRESSOR
The A/C system on models equipped with the 5.9L
engine use a Sanden SD-7 reciprocating swash plate-
type compressor. This compressor has a fixed dis-
placement of 165 cubic centimeter (10.068 cubic
inches) and has both the suction and discharge ports
located on the cylinder head.
The A/C system on models equipped with the 3.7L,
4.7L and 5.7L engines use a Denso 10S17 reciprocat-
ing swash plate-type compressor. This compressor
has a fixed displacement of 170 cubic centimeter and
has both the suction and discharge ports located on
the cylinder head.
A label identifying the use of R-134a refrigerant is
located on both A/C compressors.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
A high pressure relief valve is located on the com-
pressor cylinder head, which is on the rear of the
compressor. This mechanical valve is designed to
vent refrigerant from the system to protect against
damage to the compressor and other system compo-
nents, caused by condenser air flow restriction or an
overcharge of refrigerant.
OPERATION
OPERATION - A/C COMPRESSOR
The A/C compressor is driven by the engine
through an electric clutch, drive pulley and belt
arrangement. The compressor is lubricated by refrig-
erant oil that is circulated throughout the refrigerant
system with the refrigerant.
The compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant
vapor from the evaporator through its suction port. It
then compresses the refrigerant into a high-pressure,
high-temperature refrigerant vapor, which is then
pumped to the condenser through the compressor dis-
charge port.
The compressor cannot be repaired. If faulty or
damaged, the entire compressor assembly must be
replaced. The compressor clutch, pulley and clutch
coil are available for service.
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
The high pressure relief valve vents the system
when a discharge pressure of 3445 to 4135 kPa (500
to 600 psi) or above is reached. The valve closes
24 - 48 PLUMBINGDR
PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 2536 of 2627

when a minimum discharge pressure of 2756 kPa
(400 psi) is reached.
The high pressure relief valve vents only enough
refrigerant to reduce the system pressure, and then
re-seats itself. The majority of the refrigerant is con-
served in the system. If the valve vents refrigerant, it
does not mean that the valve is faulty.
The high pressure relief valve is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The valve cannot be adjusted or
repaired, and must not be removed or otherwise dis-
turbed. The valve is only serviced as a part of the
compressor assembly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
When investigating an air conditioning related
noise, you must first know the conditions under
which the noise occurs. These conditions include:
weather, vehicle speed, transmission in gear or neu-
tral, engine speed, engine temperature, and any
other special conditions. Noises that develop during
air conditioning operation can often be misleading.
For example: What sounds like a failed front bearing
or connecting rod, may be caused by loose bolts, nuts,
mounting brackets, or a loose compressor clutch
assembly.
Drive belts are speed sensitive. At different engine
speeds and depending upon belt tension, belts can
develop noises that are mistaken for a compressor
noise. Improper belt tension can cause a misleading
noise when the compressor clutch is engaged, which
may not occur when the compressor clutch is disen-
gaged. Check the serpentine drive belt condition and
tension as described in Cooling before beginning this
procedure.
(1) Select a quiet area for testing. Duplicate the
complaint conditions as much as possible. Switch the
compressor on and off several times to clearly iden-
tify the compressor noise. Listen to the compressor
while the clutch is engaged and disengaged. Probe
the compressor with an engine stethoscope or a long
screwdriver with the handle held to your ear to bet-
ter localize the source of the noise.
(2) Loosen all of the compressor mounting hard-
ware and retighten. Tighten the compressor clutch
mounting nut. Be certain that the clutch coil is
mounted securely to the compressor, and that the
clutch plate and rotor are properly aligned and have
the correct air gap (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH - INSTALLATION).
(3) To duplicate a high-ambient temperature condi-
tion (high head pressure), restrict the air flow
through the condenser. Install a manifold gauge set
or a DRBIIItscan tool to be certain that the dis-
charge pressure does not exceed 2760 kPa (400 psi).(4) Check the refrigerant system plumbing for
incorrect routing, rubbing or interference, which can
cause unusual noises. Also check the refrigerant lines
for kinks or sharp bends that will restrict refrigerant
flow, which can cause noises (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(5) If the noise is from opening and closing of the
high pressure relief valve, recover, evacuate and
recharge the refrigerant system (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE), (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACU-
ATE) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE). If the high
pressure relief valve still does not seat properly,
replace the compressor (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COMPRES-
SOR - REMOVAL).
(6) If the noise is from liquid slugging on the suc-
tion line, replace the accumulator (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/AC-
CUMULATOR - REMOVAL) and check the refriger-
ant oil level and the refrigerant system charge (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING/REFRIGERANT OIL - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/ACCUMULATOR -
REMOVAL). If after replacing the accumulator the
slugging condition still exists then replace the com-
pressor.(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING/A/C COMPRESSOR - REMOVAL).
(7) If the liquid slugging condition continues fol-
lowing accumulator replacement, replace the com-
pressor and repeat Step 1.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
WARNING) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION).
NOTE: The A/C compressor may be removed and
repositioned without disconnecting the refrigerant
lines or discharging the refrigerant system. Dis-
charging is not necessary if servicing the compres-
sor clutch, clutch coil, engine, engine cylinder head
or the generator.
(1) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
DRPLUMBING 24 - 49
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2573 of 2627

CCV HOSE
DESCRIPTION - 8.0L V-10
The 8.0L V-10 engine is equipped with a Crankcase
Ventilation (CCV) system. The CCV system performs
the same function as a conventional PCV system, but
does not use a vacuum controlled valve (PCV valve).
A molded vacuum tube connects manifold vacuum
to the top of the right cylinder head (valve) cover.
The vacuum tube connects to a fixed orifice fitting
(Fig. 2) of a calibrated size 2.6 mm (0.10 inches).
OPERATION - 8.0L V-10
A molded vacuum tube connects manifold vacuum
to the top of the right cylinder head (valve) cover.
The vacuum tube connects to a fixed orifice fitting
(Fig. 2) of a calibrated size 2.6 mm (0.10 inches). The
fitting meters the amount of crankcase vapors drawn
out of the engine.The fixed orifice fitting is grey
in color.A similar fitting (but does not contain a
fixed orifice) is used on the left cylinder head (valve)
cover. This fitting is black in color. Do not inter-
change these two fittings.
When the engine is operating, fresh air enters the
engine and mixes with crankcase vapors. Manifold
vacuum draws the vapor/air mixture through the
fixed orifice and into the intake manifold. The vapors
are then consumed during engine combustion.
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid is
located in the engine compartment. It is attached to
the side of the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) operates
the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop oper-
ation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM ener-
gizes and de-energizes the solenoid 5 or 10 times per
second, depending upon operating conditions. The
PCM varies the vapor flow rate by changing solenoid
pulse width. Pulse width is the amount of time the
solenoid energizes. The PCM adjusts solenoid pulse
width based on engine operating condition.
REMOVAL
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid is
located in the engine compartment. It is attached to
the side of the Power Distribution Center (PDC) (Fig.
3).
(1) Disconnect electrical wiring connector at sole-
noid.
(2) Disconnect vacuum harness at solenoid (Fig. 3).
(3) Remove solenoid from mounting bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install solenoid assembly to mounting bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum harness.
(3) Connect electrical connector.
Fig. 2 FIXED ORIFICE FITTING - 8.0L V-10 ENGINE -
TYPICAL
1 - VACUUM TUBE
2 - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
3 - COIL PACKS
4 - ORIFICE FITTING HOSE CONNECTIONS
25 - 12 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
Page 2578 of 2627

Check the vapor/vacuum lines at the LDP, LDP
filter and EVAP canister purge solenoid for
damage or leaks. If a leak is present, a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
(4) Connect electrical connector to LDP.
ORVR
DESCRIPTION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system consists of a unique fuel tank, flow manage-
ment valve, fluid control valve, one-way check valve
and vapor canister.
OPERATION
The ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor Recovery)
system is used to remove excess fuel tank vapors.
This is done while the vehicle is being refueled.
Fuel flowing into the fuel filler tube (approx. 1º
I.D.) creates an aspiration effect drawing air into the
fuel fill tube. During refueling, the fuel tank is
vented to the EVAP canister to capture escaping
vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there are
no fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once the
refueling vapors are captured by the EVAP canister,
the vehicle's computer controlled purge system draws
vapor out of the canister for the engine to burn. The
vapor flow is metered by the purge solenoid so that
there is no, or minimal impact on driveability or
tailpipe emissions.
As fuel starts to flow through the fuel fill tube, it
opens the normally closed check valve and enters the
fuel tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank
through the control valve and on to the vapor canis-
ter. Vapor is absorbed in the EVAP canister until
vapor flow in the lines stops. This stoppage occurs
following fuel shut-off, or by having the fuel level in
the tank rise high enough to close the control valve.
This control valve contains a float that rises to seal
the large diameter vent path to the EVAP canister.
At this point in the refueling process, fuel tank pres-
sure increases, the check valve closes (preventing liq-
uid fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel
then rises up the fuel filler tube to shut off the dis-
pensing nozzle.
PCV VALVE
DESCRIPTION
3.7L V-6 / 4.7L V-8
The 3.7L V-6 and 4.7L V-8 engines are equipped
with a closed crankcase ventilation system and a
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve.
This system consists of:
²a PCV valve mounted to the oil filler housing
(Fig. 10). The PCV valve is sealed to the oil filler
housing with an o-ring.
²the air cleaner housing
²two interconnected breathers threaded into the
rear of each cylinder head (Fig. 11).
²tubes and hoses to connect the system compo-
nents.
Fig. 10 PCV VALVE - 3.7L V-6 / 4.7L V-8
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
DREVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 17
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)