1998 DODGE RAM 1500 check oil
[x] Cancel search: check oilPage 1863 of 2627

DISASSEMBLY
(1) Clean exterior of transmission with suitable
solvent or pressure washer.
(2) Place transmission in vertical position.
(3) Measure the input shaft end play as follows
(Fig. 17).
(a) Attach Adapter 8266-5 to Handle 8266-8.
(b) Attach dial indicator C-3339 to Handle
8266-8.
(c) Install the assembled tool onto the input
shaft of the transmission and tighten the retaining
screw on Adapter 8266-5 to secure it to the input
shaft.
(d) Position the dial indicator plunger against a
flat spot on the oil pump and zero the dial indica-
tor.
(e) Move input shaft in and out and record read-
ing. Record the maximum travel for assembly ref-
erence
(4) Remove the overdrive unit from the main
transmission case. If overdrive unit is not to be ser-
viced, install Alignment Shaft 6227-2 into the over-
drive unit to prevent misalignment of the overdrive
clutches during service of main transmission compo-
nents.
(5) Remove throttle and shift levers from valve
body manual shaft and throttle lever shaft.
(6) Remove transmission oil pan and gasket.(7) Remove filter from valve body (Fig. 18). Keep
filter screws separate from other valve body screws.
Filter screws are longer and should be kept with fil-
ter.
(8) Remove the transmission range sensor.
(9) Remove hex head bolts attaching valve body to
transmission case (Fig. 19). A total of 10 bolts are
used. Note different bolt lengths for assembly refer-
ence.
Fig. 19 Valve Body Bolt Locations
1 - VALVE BODY BOLTS
2 - VALVE BODY BOLTS
Fig. 17 Checking Input Shaft End Play
1 - TOOL 8266-8
2 - TOOL 8266-5
3 - TOOL C-3339
Fig. 18 Oil Filter Removal
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - VALVE BODY
3 - FILTER SCREWS (2)
21 - 160 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1875 of 2627

(4) Check seal rings on reaction shaft support. Be
sure rings are hooked together correctly. Also be sure
fiber thrust washer is in position (Fig. 55). Use extra
petroleum jelly to hold washer in place if necessary.
(5) Check the torque converter hub seal ring on
the reaction shaft for damage. Also check that the
seal ring rotates freely in the reaction shaft groove.
Replace the seal if necessary.
(6) Lubricate oil pump seals with petroleum
MopartATF +4.
(7) Mount oil pump on pilot studs and slide pump
into case opening (Fig. 56).Work pump into case
by hand. Do not use a mallet or similar tools to
seat pump.
(8) Remove pilot studs and install oil pump bolts.
Tighten pump bolts alternately and evenly to fully
seat pump in case. Then final-tighten pump bolts to
20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Verify correct installation. Rotate input and
intermediate shafts and check for bind. If bind exists,
components are either mis-assembled, or not seated.
Disassemble and correct as necessary before proceed-
ing.
INPUT SHAFT END PLAY CHECK
NOTE: Overdrive unit must be installed in order to
correctly measure the input shaft end-play.
(1) Measure input shaft end play (Fig. 57).NOTE: If end play is incorrect, transmission is
incorrectly assembled, or reaction shaft thrust
washer is incorrect. The reaction shaft thrust
washer is selective.
(a) Attach Adapter 8266-5 to Handle 8266-8.
(b) Attach dial indicator C-3339 to Handle
8266-8.
(c) Install the assembled tool onto the input
shaft of the transmission and tighten the retaining
screw on Adapter 8266-5 to secure it to the input
shaft.
(d) Position the dial indicator plunger against a
flat spot on the oil pump and zero the dial indica-
tor.
(e) Move input shaft in and out and record read-
ing. End play should be 0.86 - 2.13 mm (0.034 -
0.084 in.). Adjust as necessary.
ACCUMULATOR, VALVE BODY, OIL PAN, AND
TORQUE CONVERTER
(1) Install accumulator inner spring, piston and
outer spring (Fig. 58).
(2) Verify that the transmission range sensor has
notbeen installed in case. Valve body can not be
installed if sensor is in position.
(3) Install new valve body manual shaft seal in
case (Fig. 59). Lubricate seal lip and manual shaft
with petroleum jelly. Start seal over shaft and into
case. Seat seal with 15/16 inch, deep well socket.
(4) Install valve body as follows:Fig. 56 Oil Pump
1 - SEAT OIL PUMP IN CASE BY HAND
2 - REMOVE PILOT STUDS WHEN PUMP IS SEATED
Fig. 57 Checking Input Shaft End Play
1 - TOOL 8266-8
2 - TOOL 8266-5
3 - TOOL C-3339
21 - 172 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1877 of 2627

(9) Install the two screws to hold the TRS to the
mounting bracket. Tighten the screws to 5 N´m (45
in.lbs.).
(10) Verify proper sensor operation (Fig. 62).
(11) Move the transmission manual shaft lever to
the PARK position.
(12) Install torque converter. Use C-clamp or metal
strap to hold converter in place for installation.
BAND ADJUSTMENT AND FINAL
(1) Adjust front and rear bands as follows:
(a) Loosen locknut on each band adjusting screw
4-5 turns.
(b) Tighten both adjusting screws to 8 N´m (72
in. lbs.).
(c) Back off front band adjusting screw 1-3/4
turns.
(d) Back off rear band adjusting screw 3 turns.
(e) Hold each adjusting screw in position and
tighten locknut to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install magnet in oil pan. Magnet seats on
small protrusion at corner of pan.
(3) Position new oil pan gasket on case and install
oil pan. Tighten pan bolts to 13.6 N´m (125 in. lbs.).
(4) Install throttle valve and shift selector levers
on valve body manual lever shaft.
(5) Apply small quantity of dielectric grease to ter-
minal pins of solenoid case connector and neutral
switch.
(6) Fill transmission with recommended fluid.
INSTALLATION
(1) Check torque converter hub inner and outer
diameters and hub drive notches for sharp edgesburrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and notches
with 320/400 grit paper and crocus cloth if necessary.
The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging pump
seal at installation.
(2) Lubricate pocket in the rear oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid.
(3) Lubricate converter pilot hub of the crankshaft
with a light coating of MopartHigh Temp Grease.
(4) Align and install converter in oil pump.
(5) Carefully insert converter in oil pump. Then
rotate converter back and forth until fully seated in
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with steel scale and
straightedge (Fig. 63). Surface of converter lugs
should be 19mm (0.75 in.) to rear of straightedge
when converter is fully seated.
(7) Temporarily secure converter with C-clamp.
(8) Position transmission on jack and secure it
with chains.
(9) Check condition of converter driveplate.
Replace the plate if cracked, distorted or damaged.
Also be sure transmission dowel pins are seated
in engine block and protrude far enough to
hold transmission in alignment.
(10) Raise transmission and align converter with
drive plate and converter housing with engine block.
(11) Move transmission forward. Then raise, lower
or tilt transmission to align converter housing with
engine block dowels.
(12) Carefully work transmission forward and over
engine block dowels until converter hub is seated in
crankshaft.
Fig. 62 Transmission Range Sensor Operation
1 - NEUTRAL CONTACT
2 - MANUAL LEVER AND SENSOR PLUNGER IN REVERSE
POSITION
3 - PARK CONTACT
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 63 Checking Converter Seating - Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 174 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1897 of 2627

INSPECTION
Inspect the accumulator piston and seal rings.
Replace the seal rings if worn or cut. Replace the pis-
ton if chipped or cracked.
Check condition of the accumulator inner and
outer springs. Replace the springs if the coils are
cracked, distorted or collapsed.
BANDS
DESCRIPTION
KICKDOWN (FRONT) BAND
The kickdown, or ªfrontº, band (Fig. 70) holds the
common sun gear of the planetary gear sets. The
front (kickdown) band is made of steel, and faced on
its inner circumference with a friction-type lining.
One end of the band is anchored to the transmission
case, and the other is acted on with a pushing force
by a servo piston. The front band is a single-wrap
design (the band does not completely encompass/
wrap the drum that it holds).
LOW/REVERSE (REAR) BAND
The low/reverse band, or ªrearº, band (Fig. 71) is
similar in appearance and operation to the front
band. The rear band is slightly different in that it
does not use a link bar, but is acted directly on by
the apply lever. This is referred to as a double-wrapband design (the drum is completely encompassed/
wrapped by the band). The double-wrap band pro-
vides a greater holding power in comparison to the
single-wrap design.
OPERATION
KICKDOWN (FRONT) BAND
The kickdown band holds the common sun gear of
the planetary gear sets by applying and holding the
front clutch retainer, which is splined to the sun gear
driving shell, and in turn splined directly to the sun
gear. The application of the band by the servo is typ-
ically done by an apply lever and link bar.
Fig. 69 Accumulator in SECOND Gear Position
1 - BOTTOM OF BORE
2 - LINE PRESSURE
3 - SHUTTLE VALVE
Fig. 70 Front Band
1 - FRONT BAND
2 - TRANSMISSION HOUSING
Fig. 71 Rear Band
1 - ADJUSTING SCREW
2 - LOCKNUT
3 - LEVER
4 - REAR BAND
5 - REACTION PIN
6 - O-RINGS
7 - PIVOT PIN
21 - 194 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
ACCUMULATOR (Continued)
Page 1905 of 2627

(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced when-
ever a failure generates sludge and debris. This is
necessary because normal converter flushing proce-
dures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, thegeartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in NEUTRAL and
the transmission fluid at normal operating tempera-
ture.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.
The transmission fluid level can be checked two
ways.
PROCEDURE ONE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operat-
ing temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive
vehicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).
(2) Position vehicle on level surface.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to NEUTRAL.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep
dirt from entering tube.
(7) Remove dipstick (Fig. 87) and check fluid level
as follows:
(a) Correct acceptable level is in crosshatch area.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN line.
(d) If fluid is low, add only enough MopartAT F
+4 to restore correct level. Do not overfill.
Fig. 87 Dipstick Fluid Level Marks - Typical
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - MAXIMUM CORRECT FLUID LEVEL
3 - ACCEPTABLE FLUID LEVEL
21 - 202 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1906 of 2627

PROCEDURE TWO
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5) Hook up DRBtscan tool and select engine.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
chart.
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the chart (Fig. 88).
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION). The service fluid fill after a
filter change is approximately 3.8 liters (4.0 quarts).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission (Fig. 89).
(4) Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmis-
sion.
Fig. 88 48RE Fluid Fill Graph
Fig. 89 Transmission Pan
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - REUSABLE GASKET
3-PAN
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 203
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1907 of 2627

(5) Slowly separate front of pan and reusable gas-
ket away from transmission allowing the fluid to
drain into drain pan.
(6) Hold up pan and remove remaining bolt hold-
ing pan to transmission.
(7) While holding pan level, lower pan and gasket
away from transmission.
(8) Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
(9) Remove screws holding filter to valve body
(Fig. 90).
(10) Separate filter from valve body and pour fluid
in filter into drain pan.
(11) Dispose of used trans fluid and filter properly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position a new transmission oil filter onto the
valve body.
(2) Install the screws to hold the filter to the valve
body. Tighten the screws to 4 N´m (35 in.lbs.).
(3) Clean the gasket surfaces of the transmission
oil pan and transmission pan rail.
NOTE: The transmission pan oil gasket is reusable.
Inspect the sealing surfaces of the gasket. If the
sealing ribs on both surfaces appear to be in good
condition, clean the gasket of any foreign material
and reinstall.
(4) Position the oil pan gasket onto the oil pan.
(5) Position the oil pan and gasket onto the trans-
mission and install several bolts to hold the pan and
gasket to the transmission.(6) Install the remainder of the oil pan bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 13.6 N´m (125 in.lbs.).
(7) Lower vehicle and fill transmission. (Refer to
21 - TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC/FLUID - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL
To avoid overfilling transmission after a fluid
change or overhaul, perform the following procedure:
(1) Remove dipstick and insert clean funnel in
transmission fill tube.
(2) Add following initial quantity of MopartAT F
+4 to transmission:
(a) If only fluid and filter were changed, add3
pints (1-1/2 quarts)of ATF +4 to transmission.
(b) If transmission was completely overhauled,
torque converter was replaced or drained, and
cooler was flushed, add12 pints (6 quarts)of ATF
+4 to transmission.
(3) Apply parking brakes.
(4) Start and run engine at normal curb idle
speed.
(5) Apply service brakes, shift transmission
through all gear ranges then back to NEUTRAL, set
parking brake, and leave engine running at curb idle
speed.
(6) Remove funnel, insert dipstick and check fluid
level. If level is low,add fluid to bring level to
MIN mark on dipstick.Check to see if the oil level
is equal on both sides of the dipstick. If one side is
noticably higher than the other, the dipstick has
picked up some oil from the dipstick tube. Allow the
oil to drain down the dipstick tube and re-check.
(7) Drive vehicle until transmission fluid is at nor-
mal operating temperature.
(8) With the engine running at curb idle speed, the
gear selector in NEUTRAL, and the parking brake
applied, check the transmission fluid level.
CAUTION: Do not overfill transmission, fluid foam-
ing and shifting problems can result.
(9) Add fluid to bring level up to MAX arrow
mark.
When fluid level is correct, shut engine off, release
park brake, remove funnel, and install dipstick in fill
tube.
Fig. 90 Transmission Filter
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - FILTER
21 - 204 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1908 of 2627
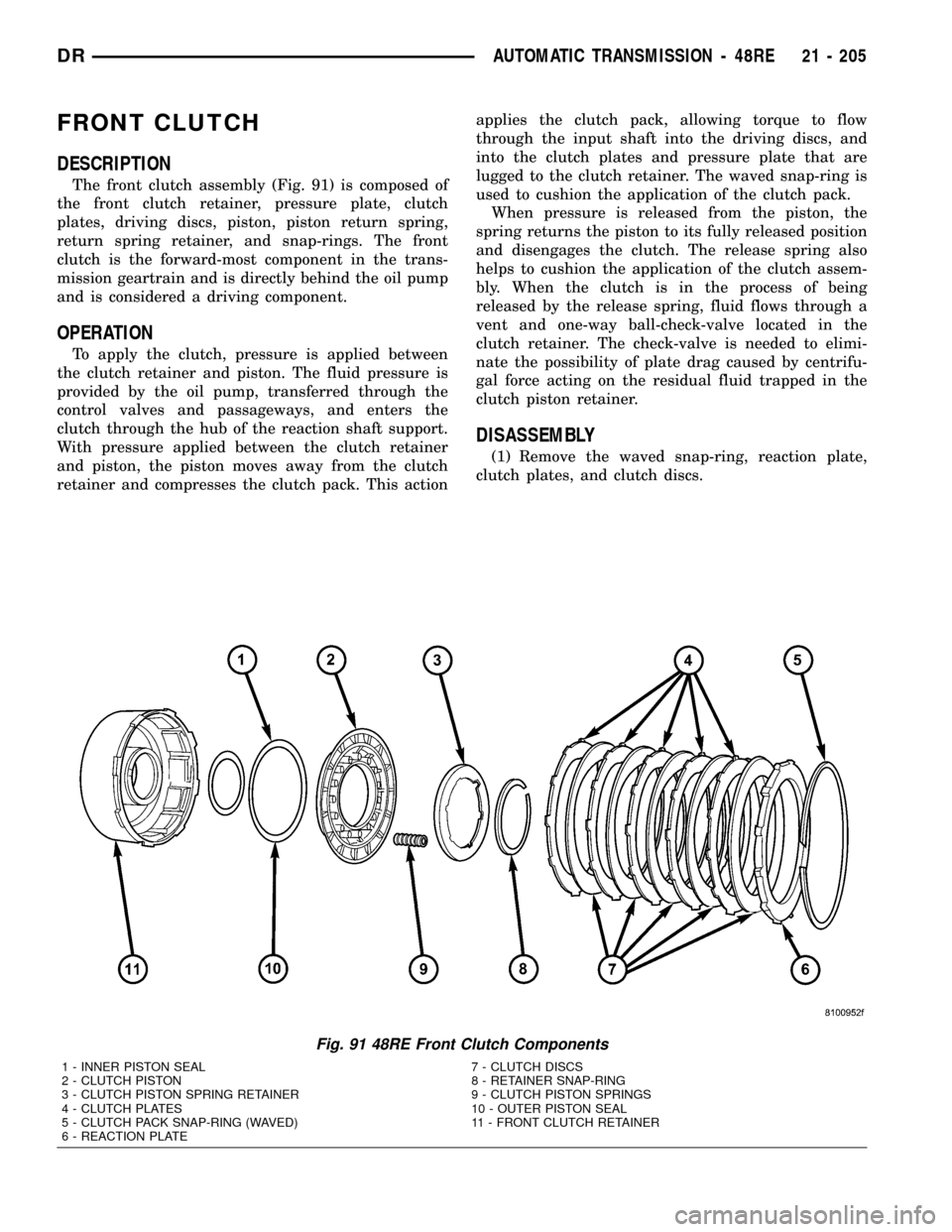
FRONT CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The front clutch assembly (Fig. 91) is composed of
the front clutch retainer, pressure plate, clutch
plates, driving discs, piston, piston return spring,
return spring retainer, and snap-rings. The front
clutch is the forward-most component in the trans-
mission geartrain and is directly behind the oil pump
and is considered a driving component.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the clutch retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through the hub of the reaction shaft support.
With pressure applied between the clutch retainer
and piston, the piston moves away from the clutch
retainer and compresses the clutch pack. This actionapplies the clutch pack, allowing torque to flow
through the input shaft into the driving discs, and
into the clutch plates and pressure plate that are
lugged to the clutch retainer. The waved snap-ring is
used to cushion the application of the clutch pack.
When pressure is released from the piston, the
spring returns the piston to its fully released position
and disengages the clutch. The release spring also
helps to cushion the application of the clutch assem-
bly. When the clutch is in the process of being
released by the release spring, fluid flows through a
vent and one-way ball-check-valve located in the
clutch retainer. The check-valve is needed to elimi-
nate the possibility of plate drag caused by centrifu-
gal force acting on the residual fluid trapped in the
clutch piston retainer.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the waved snap-ring, reaction plate,
clutch plates, and clutch discs.
Fig. 91 48RE Front Clutch Components
1 - INNER PISTON SEAL 7 - CLUTCH DISCS
2 - CLUTCH PISTON 8 - RETAINER SNAP-RING
3 - CLUTCH PISTON SPRING RETAINER 9 - CLUTCH PISTON SPRINGS
4 - CLUTCH PLATES 10 - OUTER PISTON SEAL
5 - CLUTCH PACK SNAP-RING (WAVED) 11 - FRONT CLUTCH RETAINER
6 - REACTION PLATE
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 205