1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Engine Installation
[x] Cancel search: Engine InstallationPage 1349 of 2627
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
c. Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
REMOVAL
NOTE: Disconnect the battery negative cable to pre-
vent accidental starter engagement.
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 3 and 5
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
exhaust stroke.
(3) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 2 and 8
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(4) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 4 and 6
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #3 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(5) For rocker arm removal on cylinders 1 and 7
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #2 is at TDC
compression stroke.
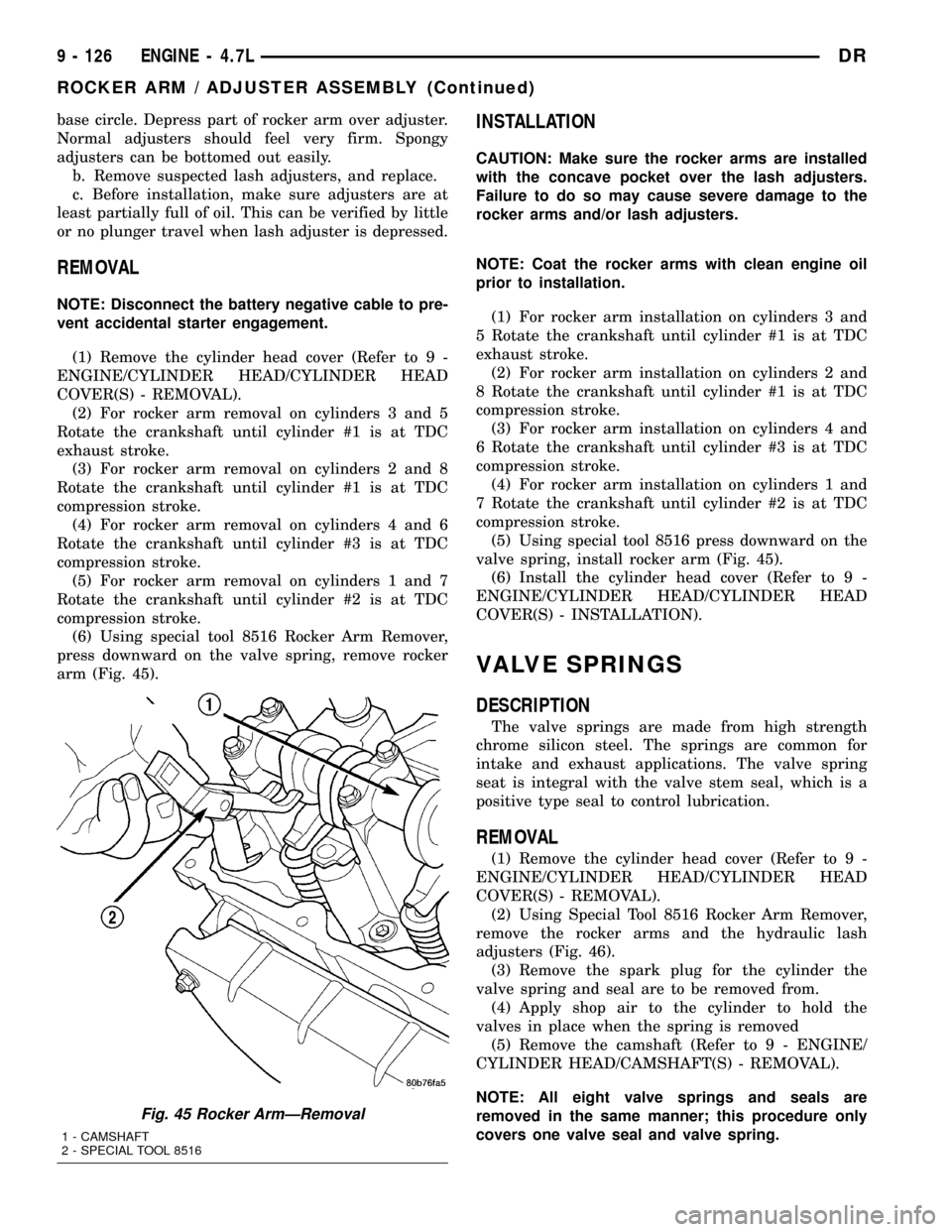
(6) Using special tool 8516 Rocker Arm Remover,
press downward on the valve spring, remove rocker
arm (Fig. 45).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Make sure the rocker arms are installed
with the concave pocket over the lash adjusters.
Failure to do so may cause severe damage to the
rocker arms and/or lash adjusters.
NOTE: Coat the rocker arms with clean engine oil
prior to installation.
(1) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 3 and
5 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
exhaust stroke.
(2) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 2 and
8 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(3) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 4 and
6 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #3 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(4) For rocker arm installation on cylinders 1 and
7 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #2 is at TDC
compression stroke.
(5) Using special tool 8516 press downward on the
valve spring, install rocker arm (Fig. 45).
(6) Install the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION
The valve springs are made from high strength
chrome silicon steel. The springs are common for
intake and exhaust applications. The valve spring
seat is integral with the valve stem seal, which is a
positive type seal to control lubrication.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Using Special Tool 8516 Rocker Arm Remover,
remove the rocker arms and the hydraulic lash
adjusters (Fig. 46).
(3) Remove the spark plug for the cylinder the
valve spring and seal are to be removed from.
(4) Apply shop air to the cylinder to hold the
valves in place when the spring is removed
(5) Remove the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL).
NOTE: All eight valve springs and seals are
removed in the same manner; this procedure only
covers one valve seal and valve spring.
Fig. 45 Rocker ArmÐRemoval
1 - CAMSHAFT
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8516
9 - 126 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1350 of 2627

(6) Using Special Tool 8387 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, compress the valve spring.
NOTE: It may be necessary to tap the top of the
valve spring to loosen the spring retainers locks
enough to be removed.
(7) Remove the two spring retainer lock halves.
NOTE: the valve spring is under tension use care
when releasing the valve spring compressor.
(8) Remove the valve spring compressor.
(9) Remove the spring retainer, and the spring.
(10) Remove the valve stem seal.
NOTE: The valve stem seals are common between
intake and exhaust.
INSTALLATION
(1) coat the valve stem with clean engine oil and
install the valve stem seal. Make sure the seal is
fully seated and that the garter spring at the top of
the seal is intact.
(2) Install the spring and the spring retainer (Fig.
47).
(3) Using Special Tool 8387 Valve Spring Compres-
sor, compress the spring and install the two valve
spring retainer halves.(4) Release the valve spring compressor and make
sure the two spring retainer halves and the spring
retainer are fully seated.
(5) Install the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - INSTALLA-
TION).
(6) Position the hydraulic lash adjusters and
rocker arms (Fig. 46).
(7) Install the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
VALVE STEM SEALS
DESCRIPTION
The valve stem seals are made of rubber and incor-
porate an integral steel valve spring seat. The inte-
gral garter spring maintains consistent lubrication
control to the valve stems.
Fig. 46 Rocker ArmÐRemoval
1 - CAMSHAFT
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8516
Fig. 47 Valve Assembly Configuration
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 127
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 1353 of 2627
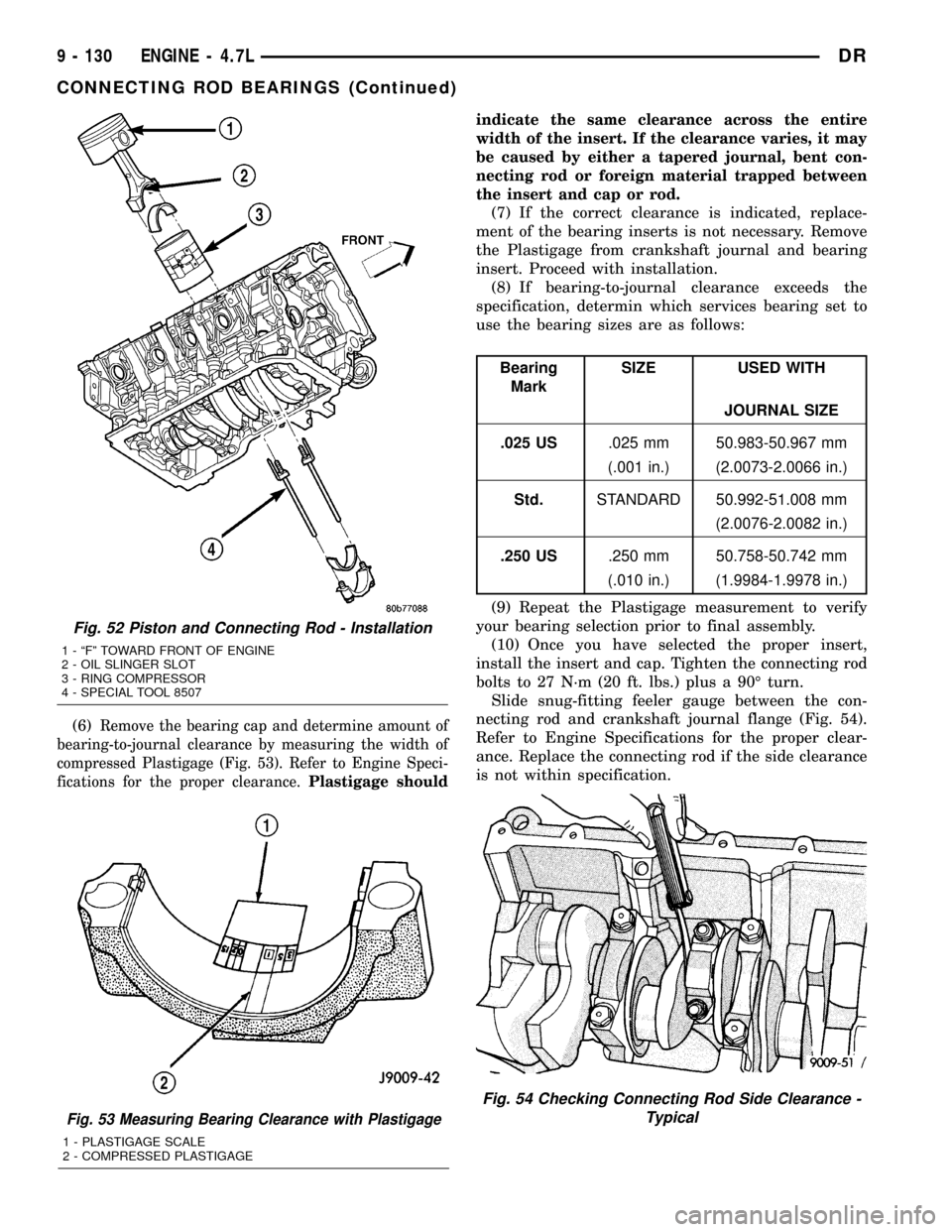
(6)Remove the bearing cap and determine amount of
bearing-to-journal clearance by measuring the width of
compressed Plastigage (Fig. 53). Refer to Engine Speci-
fications for the proper clearance.Plastigage shouldindicate the same clearance across the entire
width of the insert. If the clearance varies, it may
be caused by either a tapered journal, bent con-
necting rod or foreign material trapped between
the insert and cap or rod.
(7) If the correct clearance is indicated, replace-
ment of the bearing inserts is not necessary. Remove
the Plastigage from crankshaft journal and bearing
insert. Proceed with installation.
(8) If bearing-to-journal clearance exceeds the
specification, determin which services bearing set to
use the bearing sizes are as follows:
Bearing
MarkSIZE USED WITH
JOURNAL SIZE
.025 US.025 mm 50.983-50.967 mm
(.001 in.) (2.0073-2.0066 in.)
Std.STANDARD 50.992-51.008 mm
(2.0076-2.0082 in.)
.250 US.250 mm 50.758-50.742 mm
(.010 in.) (1.9984-1.9978 in.)
(9) Repeat the Plastigage measurement to verify
your bearing selection prior to final assembly.
(10) Once you have selected the proper insert,
install the insert and cap. Tighten the connecting rod
bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus a 90É turn.
Slide snug-fitting feeler gauge between the con-
necting rod and crankshaft journal flange (Fig. 54).
Refer to Engine Specifications for the proper clear-
ance. Replace the connecting rod if the side clearance
is not within specification.
Fig. 53 Measuring Bearing Clearance with Plastigage
1 - PLASTIGAGE SCALE
2 - COMPRESSED PLASTIGAGE
Fig. 52 Piston and Connecting Rod - Installation
1 - ªFº TOWARD FRONT OF ENGINE
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
3 - RING COMPRESSOR
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8507
Fig. 54 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance -
Typical
9 - 130 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1354 of 2627

CORE PLUGS
REMOVAL
(1) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screw
driver and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the
cup plug (Fig. 55)
(3) Using a suitable pair of pliers, grasp the core
plug and remove.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Thoroughly clean core plug bore, remove all
of the old sealer.
(1) Coat the edges of the engine core plug and the
core plug bore with Mopar Gasket Maker, or equiva-
lent.
NOTE: It is not necessary to wait for the sealant to
cure on the core plugs. The cooling system can be
filled and the vehicle returned to service immedi-
ately.
(2) Using proper plug driver, drive core plug into
the core plug bore. The sharp edge of the core plug
should be at least 0.50 mm (0.020 in.) inside the lead
in chamfer.
(3) Refill the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft is constructed of nodular cast iron.
The crankshaft is a crosshaped four throw design
with eight counterweights for balancing purposes.
The crankshaft is supported by five select fit main
bearings with the number three serving as the thrust
washer location. The main journals of the crankshaft
are cross drilled to improve rod bearing lubrication.
The number eight counterweight has provisions for
crankshaft position sensor target wheel mounting.
The select fit main bearing markings are located on
the rear side of the target wheel. The crankshaft oil
seals are one piece design. The front oil seal is
retained in the timing chain cover, and the rear seal
is pressed in to a bore formed by the cylinder block
and the bedplate assembly.
REMOVAL
NOTE: To remove the crankshaft from the engine,
the engine must be removed from the vehicle.
(1) Remove the engine. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the engine oil pump.(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL).
CAUTION: DO NOT pry on the oil pan gasket when
removing the oil pan, The oil pan gasket is mounted
to the cylinder block in three locations and will
remain attached to block when removing oil pan.
Gasket can not be removed with oil pan.
(3) Remove oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the oil pump pickup tube and oil pan
gasket /windage tray.
(5) Remove the bedplate mounting bolts. Note the
location of the three stud bolts for installation.
(6) Remove the connecting rods from the crank-
shaft.
CAUTION: The bedplate to cylinder block mating
surface is a critical sealing surface. Do not pry on
or damage this surface in anyway.
NOTE: The bedplate contains the lower main bear-
ing halves. Use care when handling bedplate as not
to drop or damage bearing halves. Installing main
bearing halves in the wrong position will cause
sever damage to the crankshaft.
Fig. 55 Engine Core Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 131
Page 1355 of 2627

NOTE: The bedplate has pry points cast into it. Use
these points only. The pry points are on both the
left and right sides, only the left side is shown.
(7) Carefully pry on the pry points (Fig. 56) to
loosen the bedplate then remove the bedplate.
CAUTION: When removing the crankshaft, use care
not to damage bearing surfaces on the crankshaft.
(8) Remove the crankshaft.
(9) Remove the crankshaft target wheel.
INSPECTION
NOTE: Thoroughly inspect the connecting rod bear-
ing bores and main bearing bores for scoring, blue-
ing or severe scratches. Further disassembly may
be required.
If connecting rod bearing bores show damage, the
cylinder heads must be removed to service the piston
and rod assemblies. If the bedplate or the cylinder
block main bearing bores show damage the engine
must be replaced.
(1) If required, remove the main bearing halves
from the cylinder block and bedplate.(2) Thoroughly clean the bedplate to cylinder block
sealing surfaces and main bearing bores. Remove all
oil and sealant residue.
(3) Inspect the bedplate main bearing bores for
cracks, scoring or severe blueing. If either condition
exists the engine must be replaced.
(4) Inspect the crankshaft thrust washers for scor-
ing, scratches, wear or blueing. If either condition
exist replace the thrust washer.
(5) Inspect the oil pan gasket/windage tray for
splits, tears or cracks in the gasket sealing surfaces.
Replace gasket as necessary.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Main bearings are select fit. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE) for proper
bearing selections.
(1) Lubricate upper main bearing halves with
clean engine oil.
CAUTION: When installing crankshaft, use care not
to damage bearing surfaces on the crankshaft.
NOTE: Apply sealant to the target wheel retaining
screws prior to installation.
(2) Install the crankshaft target wheel. Torque the
mounting screws to 15 N´m (12 ft. lbs.).
(3) Position crankshaft in cylinder block.
(4) Install the thrust washers (Fig. 57).
Fig. 56 Bedplate Pry Point Location
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - BEDPLATE
3 - PRY POINT
Fig. 57 Crankshaft Thrust Washer Installation
1 - CRANKSHAFT THRUST WASHER
9 - 132 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
Page 1356 of 2627

CAUTION: The bedplate to cylinder block mateing
surface must be coated with sealant prior to instal-
lation. Failure to do so will cause severe oil leaks.
NOTE: The installation time to install the bedplate
after the sealant has been applied is critical.
NOTE: Make sure that the bedplate and cylinder
block sealing surfaces are clean and free of oil or
other contaminants. Contaminants on the sealing
surfaces may cause main bearing distortion and/or
oil leaks.
(5) Apply a 2.5mm (0.100 inch) (Fig. 58) bead of
MopartGen II Silicone Rubber Adhesive sealant to
the cylinder block-to-bedplate mating surface as
shown (Fig. 59).(6) Coat the crankshaft main bearing journals
with clean engine oil and position the bedplate onto
the cylinder block.
NOTE: Lubricate the bedplate retaining bolts with
clean engine oil prior to installation.
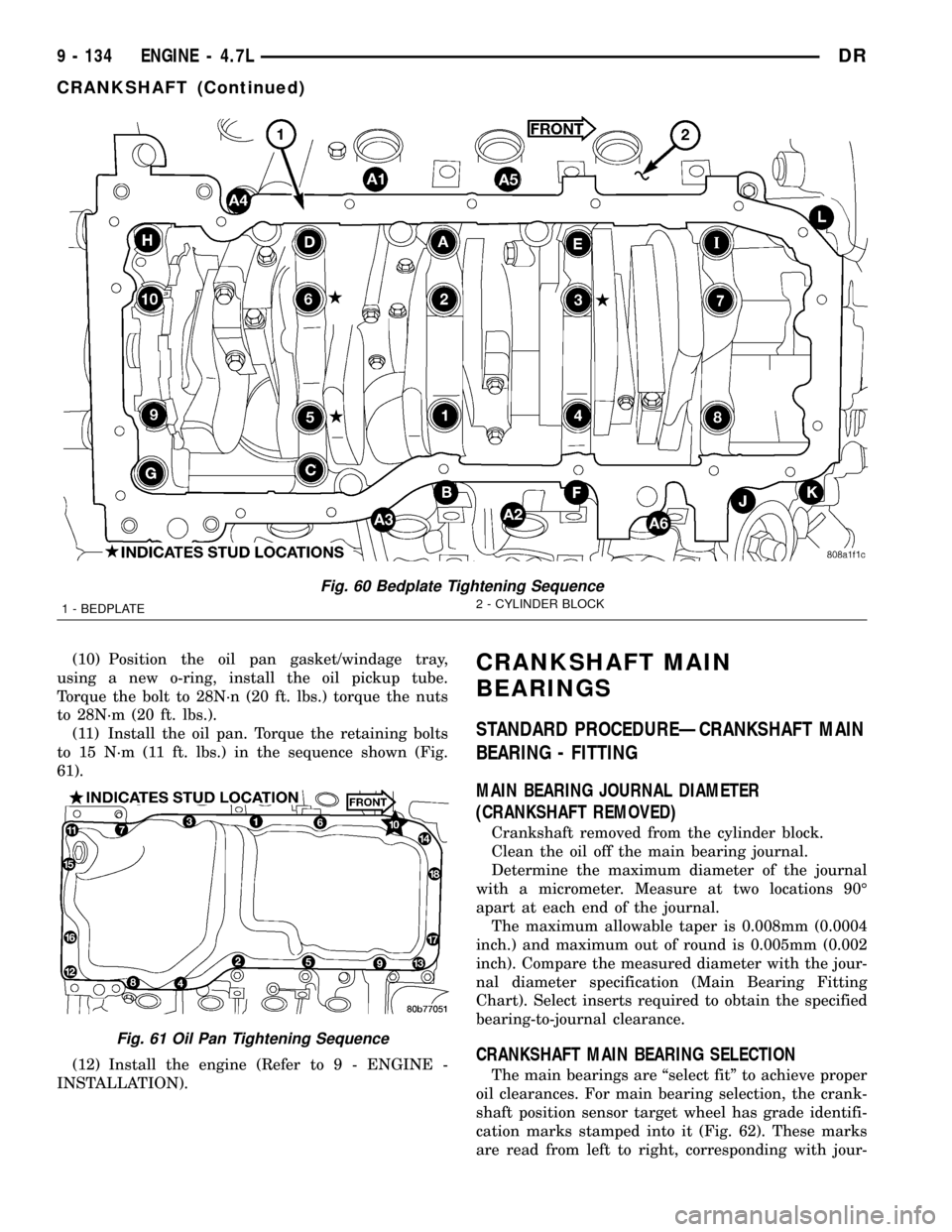
(7) Install the bedplate retaining bolts, making
sure to place the stud bolts in the correct location,
Torque the bolts in the sequence shown (Fig. 60).
²Tighten boltsA± Lto 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
²Tighten bolts1±10to 2.8 N´m (25 in. lbs.)
²Turn bolts1±10an additional 90É.
²Tighten boltsA1± A6to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.)
(8) Measure crankshaft end play. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(9) Install the connecting rods and measure side
clearance. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Fig. 58 Cutting Aplicator to Achieve 2.5mm (0.100
in.) Bead
1 - CUT HERE
Fig. 59 Cylinder Block-to-Bedplate Sealent Bead
Location
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - SEALANT BEAD LOCATION
DRENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 133
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
Page 1357 of 2627

(10) Position the oil pan gasket/windage tray,
using a new o-ring, install the oil pickup tube.
Torque the bolt to 28N´n (20 ft. lbs.) torque the nuts
to 28N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(11) Install the oil pan. Torque the retaining bolts
to 15 N´m (11 ft. lbs.) in the sequence shown (Fig.
61).
(12) Install the engine (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
INSTALLATION).CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARING - FITTING
MAIN BEARING JOURNAL DIAMETER
(CRANKSHAFT REMOVED)
Crankshaft removed from the cylinder block.
Clean the oil off the main bearing journal.
Determine the maximum diameter of the journal
with a micrometer. Measure at two locations 90É
apart at each end of the journal.
The maximum allowable taper is 0.008mm (0.0004
inch.) and maximum out of round is 0.005mm (0.002
inch). Compare the measured diameter with the jour-
nal diameter specification (Main Bearing Fitting
Chart). Select inserts required to obtain the specified
bearing-to-journal clearance.
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING SELECTION
The main bearings are ªselect fitº to achieve proper
oil clearances. For main bearing selection, the crank-
shaft position sensor target wheel has grade identifi-
cation marks stamped into it (Fig. 62). These marks
are read from left to right, corresponding with jour-
Fig. 60 Bedplate Tightening Sequence
1 - BEDPLATE2 - CYLINDER BLOCK
Fig. 61 Oil Pan Tightening Sequence
9 - 134 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
Page 1359 of 2627

(10) Remove damper using Special Tools 8513
Insert and 1026 Three Jaw Puller (Fig. 64).
(11) Using Special Tool 8511, remove crankshaft
front seal (Fig. 65).INSTALLATION
CAUTION: To prevent severe damage to the Crank-
shaft, Damper or Special Tool 8512, thoroughly
clean the damper bore and the crankshaft nose
before installing Damper.
(1) Using Special Tool 8348 and 8512, install
crankshaft front seal (Fig. 66).
(2) Install vibration damper (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER - INSTAL-
LATION).
(3) Install radiator cooling fan and shroud (Refer
to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
INSTALLATION).
(4) Install upper radiator hose.
(5) Install A/C compressor and tighten fasteners to
54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(6) Install accessory drive belt refer (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(7) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
Fig. 64 Crankshaft Damper Removal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8513 INSERT
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 1026
Fig. 65 Crankshaft Front Seal Removal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8511
Fig. 66 Crankshaft Front Seal Installation
1 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8348
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 8512
9 - 136 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT (Continued)