1998 DODGE RAM 1500 ecm
[x] Cancel search: ecmPage 411 of 2627

NOTE: ECM Inputs:
²Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) Volts
²APPS1 Signal Ð For off engine APPS
²APPS2 Signal Ð For off engine APPS
²APPS idle validation switches #1 and #2
²Battery Temperature
²Battery voltage
²Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP)
²CCD bus (+) circuits
²CCD bus (-) circuits
²Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP)
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
²Fuel pressure sensor
²Fan speed (engine cooling fan)
²Ground circuits
²Inlet air temperature sensor/pressure sensor
²Intake air temperature sensor/MAP sensor
²Oil Pressure switch
²Power ground
²Sensor return
²Signal ground
²Water-In-Fuel (WIF) sensor
NOTE: ECM Outputs:
After inputs are received by the ECM, certain sen-
sors, switches and components are controlled or reg-
ulated by the ECM. These are consideredECM
Outputs.These outputs are for:
²CCD bus (+) circuits
²CCD bus (-) circuits
²CKP and APPS outputs to the PCM
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²Fan Clutch PWM
²Five volt sensor supply
²Fuel Control Actuator
²Fuel transfer (lift) pump
²Intake manifold air heater relays #1 and #2 con-
trol circuits
²Malfunction indicator lamp (Check engine lamp)
(databus)
²Oil Pressure Swith/warning lamp (databus)
²Wait-to-start warning lamp (databus)
²Water-In-Fuel (WIF) warning lamp (databus)
REMOVAL
The engine control module (ECM) is bolted to a
support bracket near the fuel filter. The support
bracket mounts to the block with four capscrews and
vibration isolators. A ground wire is fastened to the
bracket. The other end of the wire is fastened to the
engine block.
(1) Record any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
found in the ECM.To avoid possible voltage spike damage to the
ECM, ignition key must be off, and both negative
battery cables must be disconnected before unplug-
ging ECM connectors.
(2) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(3) Remove the 50±way and 60±way connector
bolts at the ECM. Note: The connector bolt is a
female allen head. As bolt is being removed, very
carefully remove connectors from the ECM.
(4) Remove five ECM mounting bolts and remove
ECM from the vehicle (Fig. 2).
INSTALLATION
Do not apply paint to ECM or a poor ground will
result.
(1) Position the ECM to the ECM support bracket
and install the five mounting bolts. Tighten the bolts
to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(2) Check pin connectors in ECM, 50±way and
60±way connectors for corrosion or damage. Repair
as necessary.
(3) Clean pins in the 50±way and 60±way electri-
cal connectors with a electrical contact cleaner.
(4) Install the 50±way and 60±way connectors to
ECM. Tighten connector bolts to 3 N´m (27 in. lbs.).
(5) Reconnect both negative battery cables.
(6) Use DRBIIItscan tool to erase any stored com-
panion DTC's from ECM.
Fig. 2 Diesel ECM
1 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
2 - ECM MOUNTING BOLT
3 - 50-WAY CONNECTOR
4 - SUPPORT PLATE
5 - 60-WAY CONNECTOR
8E - 4 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESDR
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 420 of 2627

(8) If the previous step is not performed, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) will be set.
(9) If necessary, use DRB IIItScan Tool to erase
any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) from PCM.
Also use the DRB scan tool to reprogram new PCM
with vehicles original Vehicle Identification Number
(VIN) and original vehicle mileage.
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) con-
tains a Radio Frequency (RF) transceiver and a cen-
tral processing unit, which includes the Sentry Key
Immobilizer System (SKIS) program logic. The SKIS
programming enables the SKIM to program and
retain in memory the codes of at least two, but no
more than eight electronically coded Sentry Key
transponders. The SKIS programming also enables
the SKIM to communicate over the Programmable
Communication Interface (PCI) bus network with the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or Electronic Con-
trol Module (ECM), depending on engine application,
and/or the DRBIIItscan tool.
OPERATION
The SKIM transmits and receives RF signals
through a tuned antenna enclosed within a molded
plastic ring that is integral to the SKIM housing.
When the SKIM is properly installed on the steering
column, the antenna ring is oriented around the igni-
tion lock cylinder housing. This antenna ring must be
located within eight millimeters (0.31 inches) of the
Sentry Key in order to ensure proper RF communica-
tion between the SKIM and the Sentry Key tran-
sponder.
For added system security, each SKIM is pro-
grammed with a unique ªSecret Keyº code and a
security code. The SKIM keeps the ªSecret Keyº code
in memory. The SKIM also sends the ªSecret Keyº
code to each of the programmed Sentry Key tran-
sponders. The security code is used by the assembly
plant to access the SKIS for initialization, or by the
dealer technician to access the system for service.
The SKIM also stores in its memory the Vehicle
Identification Number (VIN), which it learns through
a PCI bus message from the PCM (NGC) or ECM
(Cummins) during initialization.The SKIM and the PCM/ECM both use software
that includes a rolling code algorithm strategy, which
helps to reduce the possibility of unauthorized SKIS
disarming. The rolling code algorithm ensures secu-
rity by preventing an override of the SKIS through
the unauthorized substitution of the SKIM or the
PCM/ECM. However, the use of this strategy also
means that replacement of either the SKIM or the
PCM/ECM units will require a system initialization
procedure to restore system operation.
When the ignition switch is turned to the ON or
START positions, the SKIM transmits an RF signal
to excite the Sentry Key transponder. The SKIM then
listens for a return RF signal from the transponder
of the Sentry Key that is inserted in the ignition lock
cylinder. If the SKIM receives an RF signal with
valid ªSecret Keyº and transponder identification
codes, the SKIM sends a ªvalid keyº message to the
PCM/ECM over the PCI bus. If the SKIM receives an
invalid RF signal or no response, it sends ªinvalid
keyº messages to the PCM/ECM. The PCM/ECM will
enable or disable engine operation based upon the
status of the SKIM messages.
The SKIM also sends messages to the Instrument
Cluster which controls the VTSS indicator LED. The
SKIM sends messages to the Instrument Cluster to
turn the LED on for about three seconds when the
ignition switch is turned to the ON position as a bulb
test. After completion of the bulb test, the SKIM
sends bus messages to keep the LED off for a dura-
tion of about one second. Then the SKIM sends mes-
sages to turn the LED on or off based upon the
results of the SKIS self-tests. If the VTSS indicator
LED comes on and stays on after the bulb test, it
indicates that the SKIM has detected a system mal-
function and/or that the SKIS has become inopera-
tive.
If the SKIM detects an invalid key when the igni-
tion switch is turned to the ON position, it sends
messages to flash the VTSS indicator LED. The
SKIM can also send messages to flash the LED as an
indication to the customer that the SKIS has been
placed in it's ªCustomer Learnº programming mode.
See Sentry Key Immobilizer System Transponder
Programming in this section for more information on
the ªCustomer Learnº programming mode.
For diagnosis or initialization of the SKIM and the
PCM/ECM, a DRBIIItscan tool and the proper Pow-
ertrain Diagnostic Procedures manual are required.
The SKIM cannot be repaired and, if faulty or dam-
aged, the unit must be replaced.
DRELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 13
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 421 of 2627

STANDARD PROCEDURE - PCM/SKIM
PROGRAMMING
NOTE: There are two procedures for transfering the
secret key to the SKIM:
²When ONLY the SKIM module is replaced, the
secret key is transfered from the PCM (NGC- gaso-
line engine) or ECM (Cummins - diesel engine) to
the SKIM. The ORGINAL KEYS may then be pro-
grammed to the SKIM.
²When ONLY the PCM/ECM is replaced, then the
secret key is transfered from the SKIM to the PCM/
ECM. The ORGINAL KEYS may be used.
²When BOTH the SKIM and the PCM/ECM are
replaced the secret key is transferred from the
SKIM to the PCM/ECM, and NEW KEYS must be
programmed.
NOTE: Before replacing the PCM/ECM (depending
on engine application), for a failed driver, control
circuit, or ground circuit, be sure to check the
related component/circuit integrity for failures not
detected due to a double fault in the circuit. Most
PCM/ECM driver/control circuit failures are caused
by internal component failures (i.e. relay and sole-
noids) and shorted circuits (i.e. pull-ups, drivers
and switched circuits). These failures are difficult to
detect when a double fault has occurred and only
one Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) has set.
When a PCM/ECM and the Sentry Key Immobi-
lizer Module (SKIM) are replaced at the same time
perform the following steps in order:
(1) Program the new PCM/ECM.
(2) Program the new SKIM.
(3) Replace all ignition keys and program them to
the new SKIM.
PROGRAMMING THE PCM (NGC) or ECM
(CUMMINS)
The Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) Secret
Key is an ID code that is unique to each SKIM. This
code is programmed and stored in the SKIM, PCM/
ECM and transponder chip (ignition keys). When
replacing the PCM/ECM it is necessary to program
the secret key into the new PCM/ECM using the
DRBIIItscan tool. Perform the following steps to
program the secret key into the PCM/ECM.
(1) Turn the ignition switch on (transmission in
park/neutral).
(2) Use the DRBIIItscan tool and select THEFT
ALARM, SKIM then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select PCM REPLACED (GAS ENGINE) or
CUMMINS ECM REPLACED (DIESEL ENGINE).(4) Enter secured access mode by entering the
vehicle four-digit PIN.
(5) Select ENTER to update PCM/ECM VIN.
NOTE: If three attempts are made to enter secure
access mode using an incorrect PIN, secured
access mode will be locked out for one hour. To
exit this lockout mode, turn the ignition to the RUN
position for one hour then enter the correct PIN.
(Ensure all accessories are turned OFF. Also moni-
tor the battery state and connect a battery charger
if necessary).
(6) Press ENTER to transfer the secret key (the
SKIM will send the secret key to the PCM/ECM).
(7) Press Page Back to get to the Select System
menu and select ENGINE, MISCELLANEOUS, and
SRI MEMORY CHECK.
(8) On gasoline engine applications (NGC), the
DRBIIItscan tool will ask, Is odometer reading
between XX and XX? Select the YES or NO button on
the DRB IIItscan tool. If NO is selected, the
DRBIIItscan tool will read, Enter odometer
Reading
reading from the instrument cluster and press
ENTER.
PROGRAMMING THE SKIM
(1) Turn the ignition switch on (transmission in
park/neutral).
(2) Use the DRBIIItscan tool and select THEFT
ALARM, SKIM then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select SKIM REPLACED.
(4) Program the vehicle four-digit PIN into SKIM.
(5) Select COUNTRY CODE and enter the correct
country.
NOTE: Be sure to enter the correct country code. If
the incorrect country code is programmed into the
SKIM, the SKIM must be replaced.
(6) Select YES to update the VIN (the SKIM will
learn the VIN from the PCM/ECM).
(7) Press ENTER to transfer the secret key (the
PCM/ECM will send the secret key information to
the SKIM).
(8) Program ignition keys to the SKIM.
NOTE: If the PCM/ECM and the SKIM are replaced
at the same time, all vehicle keys will need to be
replaced and programmed to the new SKIM.
PROGRAMMING IGNITION KEYS TO THE SKIM
(1) Turn the ignition switch on (transmission in
park/neutral).
8E - 14 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESDR
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE (Continued)
Page 427 of 2627

TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) (Fig. 9)
may be sub-module within the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM), Engine Control Module (ECM - Diesel
only) (Fig. 10), or a standalone module, depending on
the vehicle engine. The PCM, and TCM when
equipped, is located at the right rear of the engine
compartment, near the right inner fender.
OPERATION
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) controls
all electronic operations of the transmission. The
TCM receives information regarding vehicle opera-
tion from both direct and indirect inputs, and selects
the operational mode of the transmission. Direct
inputs are hardwired to, and used specifically by the
TCM. Indirect inputs are shared with the TCM via
the vehicle communication bus.
Some examples ofdirect inputsto the TCM are:
²Battery (B+) voltage
²Ignition ªONº voltage
²Transmission Control Relay (Switched B+)
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Transmission Range Sensor
²Pressure Switches
²Transmission Temperature Sensor
²Input Shaft Speed Sensor
²Output Shaft Speed Sensor
²Line Pressure Sensor
Some examples ofindirect inputsto the TCM
are:²Engine/Body Identification
²Manifold Pressure
²Target Idle
²Torque Reduction Confirmation
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Ambient/Battery Temperature
²DRBIIItScan Tool Communication
Based on the information received from these var-
ious inputs, the TCM determines the appropriate
shift schedule and shift points, depending on the
present operating conditions and driver demand.
This is possible through the control of various direct
and indirect outputs.
Some examples of TCMdirect outputsare:
²Transmission Control Relay
²Solenoids
²Torque Reduction Request
Some examples of TCMindirect outputsare:
²Transmission Temperature (to PCM)
²PRNDL Position (to BCM)
In addition to monitoring inputs and controlling
outputs, the TCM has other important responsibili-
ties and functions:
²Storing and maintaining Clutch Volume Indexes
(CVI)
²Storing and selecting appropriate Shift Sched-
ules
²System self-diagnostics
Fig. 9 PCM/TCM Location
1 - RIGHT FENDER
2 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE
3 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
Fig. 10 Diesel ECM
1 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
2 - ECM MOUNTING BOLT
3 - 50-WAY CONNECTOR
4 - SUPPORT PLATE
5 - 60-WAY CONNECTOR
8E - 20 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESDR
Page 450 of 2627

CHARGING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGING
SYSTEM............................19
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR RATINGS.................20
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - GENERATOR
/ CHARGING SYSTEM..................20
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................21OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................21
OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................24
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................25
OPERATION...........................25
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION
The charging system consists of:
²Generator
²Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) circuitry
within the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Elec-
tronic Control Module (ECM) for diesel engines.
²Ignition switch
²Battery (refer to 8, Battery for information)
²Battery temperature sensor
²Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped)
²Voltmeter (refer to 8, Instrument Panel and
Gauges for information)
²Wiring harness and connections (refer to 8, Wir-
ing Diagrams for information)
OPERATION
The charging system is turned on and off with the
ignition switch. The system is on when the engine is
running and the ASD relay is energized. When the
ASD relay is on, voltage is supplied to the ASD relay
sense circuit at the PCM (ECM Diesel). This voltage
is connected through the PCM (ECM Diesel) and sup-
plied to one of the generator field terminals (Gen.
Source +) at the back of the generator.
The amount of direct current produced by the gen-
erator is controlled by the EVR (field control) cir-
cuitry contained within the PCM (ECM Diesel). This
circuitry is connected in series with the second rotor
field terminal and ground.
A battery temperature sensor, located in the bat-
tery tray housing, is used to sense battery tempera-
ture. This temperature data, along with data from
monitored line voltage, is used by the PCM (ECM
Diesel) to vary the battery charging rate. This isdone by cycling the ground path to control the
strength of the rotor magnetic field. The PCM then
compensates and regulates generator current output
accordingly.
All vehicles are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems, including EVR
(field control) circuitry, are monitored by the PCM
(ECM Diesel). Each monitored circuit is assigned a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a
DTC in electronic memory for certain failures it
detects.
The Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped) monitors:
charging system voltage,engine coolant tempera-
ture and engine oil pressure. If an extreme condition
is indicated, the lamp will be illuminated. This is
done as reminder to check the three gauges. The sig-
nal to activate the lamp is sent via the CCD bus cir-
cuits. The lamp is located on the instrument panel.
Refer to 8, Instrument Panel and Gauges for addi-
tional information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGING
SYSTEM
The following procedures may be used to diagnose
the charging system if:
²the check gauges lamp (if equipped) is illumi-
nated with the engine running
²the voltmeter (if equipped) does not register
properly
²an undercharged or overcharged battery condi-
tion occurs.
Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
²accessories being left on with the engine not
running
DRCHARGING 8F - 19
Page 451 of 2627

²a faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. Refer to Ignition-Off Draw
Test in 8, Battery for more information.
INSPECTION
The PCM (Powertrain Control Module), or ECM
(Diesel) monitors critical input and output circuits of
the charging system, making sure they are opera-
tional. A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned
to each input and output circuit monitored by the
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) system. Some charging
system circuits are checked continuously, and some
are checked only under certain conditions.
Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in; Powertrain
Control Module; Electronic Control Modules for more
DTC information. This will include a complete list of
DTC's including DTC's for the charging system.
To perform a complete test of the charging system,
refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual and the DRBtscan tool. Per-
form the following inspections before attaching the
scan tool.
(1) Inspect the battery condition. Refer to 8, Bat-
tery for procedures.(2) Inspect condition of battery cable terminals,
battery posts, connections at engine block, starter
solenoid and relay. They should be clean and tight.
Repair as required.
(3) Inspect all fuses in both the fuseblock and
Power Distribution Center (PDC) for tightness in
receptacles. They should be properly installed and
tight. Repair or replace as required.
(4) Inspect generator mounting bolts for tightness.
Replace or tighten bolts if required. Refer to the Gen-
erator Removal/Installation section of this group for
torque specifications.
(5) Inspect generator drive belt condition and ten-
sion. Tighten or replace belt as required. Refer to
Belt Tension Specifications in 7, Cooling System.
(6) Inspect automatic belt tensioner (if equipped).
Refer to 7, Cooling System for information.
(7) Inspect generator electrical connections at gen-
erator field, battery output, and ground terminal (if
equipped). Also check generator ground wire connec-
tion at engine (if equipped). They should all be clean
and tight. Repair as required.
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR RATINGS
TYPE PART NUMBER RATED SAE AMPS ENGINES
DENSO 56029700AA 136 3.7L / 4.7L
BOSCH 56041120AC 136 3.7L / 4.7L
DENSO 56028696AA 136 5.7L Gas/5.9L Diesel
BOSCH 56028699AA 136 5.7L Gas/5.9L Diesel
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - GENERATOR /
CHARGING SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Generator Mounting Bolts
- 5.7L41 30 -
Generator Support
Bracket Bolt/Nuts - 5.7L41 30 -
Generator Upper Mounting
Bolt - 5.9L Diesel Engine41 30 -
Generator Vertical
Mounting Bolt - 3.7L / 4.7L
Engines55 40 -
Generator (long)
Horizontal Mounting Bolt -
3.7L / 4.7L Engines55 40 -
8F - 20 CHARGINGDR
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 452 of 2627
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Generator (short)
Horizontal Mounting Bolt -
3.7L / 4.7L Engines74 55 -
Generator B+ Output
Cable Terminal Nut12 - 108
BATTERY TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
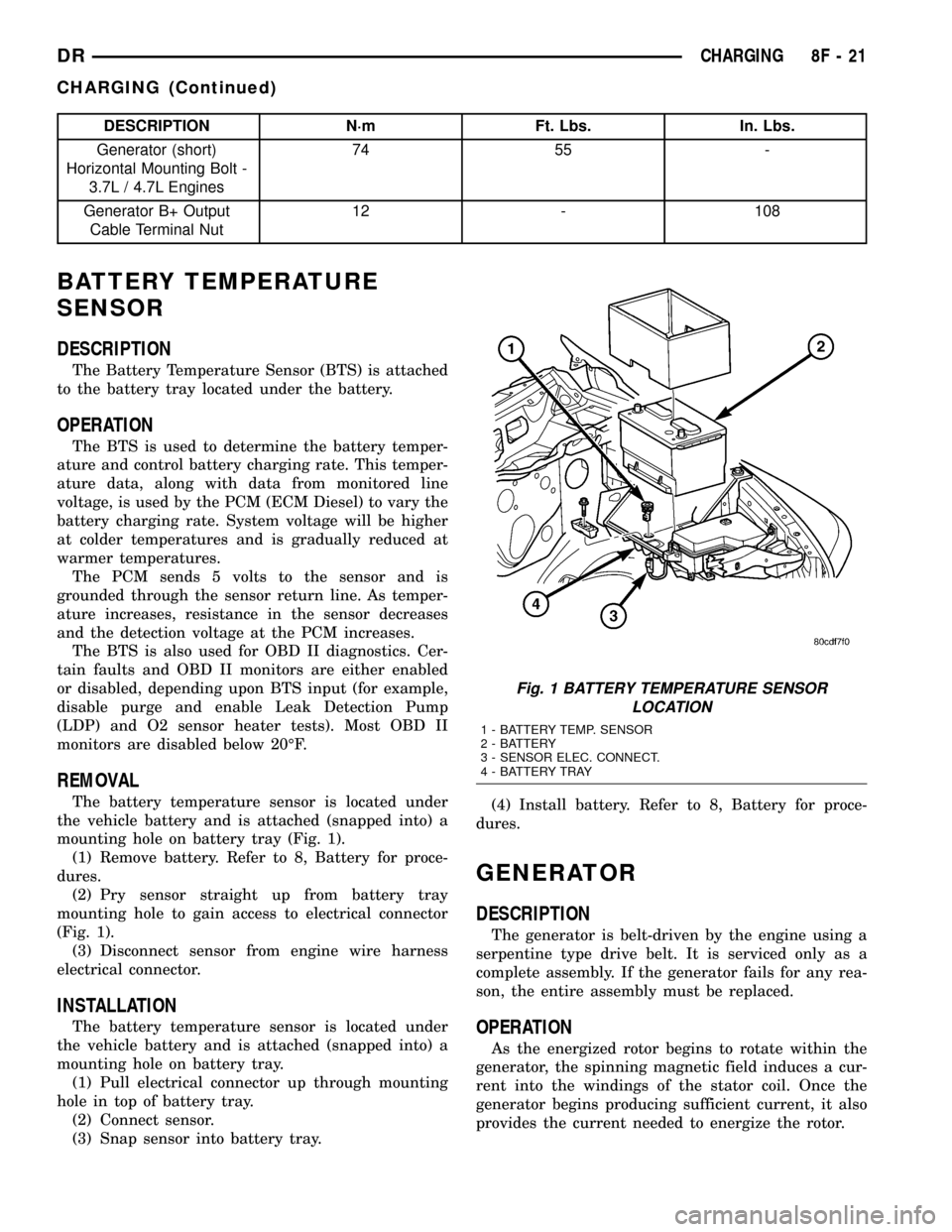
The Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) is attached
to the battery tray located under the battery.
OPERATION
The BTS is used to determine the battery temper-
ature and control battery charging rate. This temper-
ature data, along with data from monitored line
voltage, is used by the PCM (ECM Diesel) to vary the
battery charging rate. System voltage will be higher
at colder temperatures and is gradually reduced at
warmer temperatures.
The PCM sends 5 volts to the sensor and is
grounded through the sensor return line. As temper-
ature increases, resistance in the sensor decreases
and the detection voltage at the PCM increases.
The BTS is also used for OBD II diagnostics. Cer-
tain faults and OBD II monitors are either enabled
or disabled, depending upon BTS input (for example,
disable purge and enable Leak Detection Pump
(LDP) and O2 sensor heater tests). Most OBD II
monitors are disabled below 20ÉF.
REMOVAL
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery and is attached (snapped into) a
mounting hole on battery tray (Fig. 1).
(1) Remove battery. Refer to 8, Battery for proce-
dures.
(2) Pry sensor straight up from battery tray
mounting hole to gain access to electrical connector
(Fig. 1).
(3) Disconnect sensor from engine wire harness
electrical connector.
INSTALLATION
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery and is attached (snapped into) a
mounting hole on battery tray.
(1) Pull electrical connector up through mounting
hole in top of battery tray.
(2) Connect sensor.
(3) Snap sensor into battery tray.(4) Install battery. Refer to 8, Battery for proce-
dures.
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION
The generator is belt-driven by the engine using a
serpentine type drive belt. It is serviced only as a
complete assembly. If the generator fails for any rea-
son, the entire assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
As the energized rotor begins to rotate within the
generator, the spinning magnetic field induces a cur-
rent into the windings of the stator coil. Once the
generator begins producing sufficient current, it also
provides the current needed to energize the rotor.
Fig. 1 BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
LOCATION
1 - BATTERY TEMP. SENSOR
2 - BATTERY
3 - SENSOR ELEC. CONNECT.
4 - BATTERY TRAY
DRCHARGING 8F - 21
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 456 of 2627

(6) Install both negative battery cables to both bat-
teries.
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) is not a
separate component. It is actually a voltage regulat-
ing circuit located within the PCM (Powertrain Con-
trol Module) (within the ECM for diesel engines). The
EVR is not serviced separately. If replacement is nec-
essary, the PCM must be replaced.
OPERATION
The amount of direct current produced by the gen-
erator is controlled by EVR circuitry contained
within the PCM. This circuitry is connected in series
with the generators second rotor field terminal and
its ground.Voltage is regulated by cycling the ground path to
control the strength of the rotor magnetic field. The
EVR circuitry monitors system line voltage (B+) and
battery temperature (refer to Battery Temperature
Sensor for more information). It then determines a
target charging voltage. If sensed battery voltage is
0.5 volts or lower than the target voltage, the PCM
grounds the field winding until sensed battery volt-
age is 0.5 volts above target voltage. A circuit in the
PCM cycles the ground side of the generator field up
to 100 times per second (100Hz), but has the capabil-
ity to ground the field control wire 100% of the time
(full field) to achieve the target voltage. If the charg-
ing rate cannot be monitored (limp-in), a duty cycle
of 25% is used by the PCM in order to have some
generator output. Also refer to Charging System
Operation for additional information.
DRCHARGING 8F - 25
GENERATOR (Continued)