1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Oil pan
[x] Cancel search: Oil panPage 1522 of 2627

(3) Install heat shield and torque nuts to 15 Nm
(11 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install cab heater tube.
(5) Install exhaust manifold bolt retention straps.
(6) Install the cab heater return hose to the man-
ifold bolt stud. Tighten the nut to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(7) Install the turbocharger and a new gasket.
Apply anti-seize to the studs and then tighten the
turbocharger mounting nuts to 43 N´m (32 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(8)Pre-lube the turbocharger.Pour 50 to 60 cc
(2 to 3 oz.) clean engine oil in the oil supply line fit-
ting on the turbo. Rotate the turbocharger impeller
by hand to distrubute the oil thoroughly.
(9) Install and tighten the oil supply line fitting
nut to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Position the charge air cooler inlet pipe to the
turbocharger. With the clamp in position, tighten the
clamp nut to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Position the air inlet hose to the turbocharger.
Tighten the clamp to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.) torque.
(12) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(13) Install the oil drain tube and a new gasket to
the turbocharger. Tighten the drain tube bolts to 24
N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(14) Connect the exhaust pipe to the turbocharger
and tighten the bolts to 11 N´m (100 ft. lbs.) torque.
(15) Lower the vehicle.
(16) Connect the battery negative cables.
(17) Start the engine to check for leaks.
VALVE TIMING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIMING
VERIFICATION
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove fuel injector from cylinder number
1(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
FUEL INJECTOR - REMOVAL).
(3) Using Special Tool 7471B rotate the engine
until the TDC mark on the damper is at 12 o'clock.
(4) Using a 8 in.x 1/4 in. dowel rod inserted into
cylinder number 1, rock the crankshaft back and
forth to verify piston number 1 is at TDC.
(5) With cylinder number still at TDC, inspect the
keyway on the crankshaft gear for proper alignment
(12 o'clock position).
(6) If the keyway is not at 12 o'clock position
replace the crankshaft gear assembly.
(7) If the keyway is at 12 o'clock position, remove
front gear cover and verify timing mark alignmentbetween the camshaft gear and crankshaft gear, if
not aligned inspect keyway on camshaft gear.
(8) Inspect keyway on camshaft gear for proper
alignment with the key in the camshaft, if alignment
is off replace the camshaft/gear assembly.
(9) If timing marks alignment is off and no dam-
age is found at either the crankshaft or camshaft
gear keyways, realign timing marks as necessary.
GEAR HOUSING
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Partially drain engine coolant into container
suitable for re-use (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Remove radiator upper hose.
(6) Disconnect coolant recovery bottle hose from
radiator filler neck and lift bottle off of fan shroud.
(7) Disconnect windshield washer pump supply
hose and electrical connections and lift washer bottle
off of fan shroud.
(8) Remove lower fan shroud fasteners. Disconnect
fan drive wire harness.
(9) Remove the upper fan shroud-to-radiator
mounting bolts.
(10) Remove viscous fan/drive assembly (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(11) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(12) Remove the cooling fan support/hub from the
front of the engine.
(13) Raise the vehicle on hoist.
(14) Remove the crankshaft damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL) and speed indicator ring.
(15) Lower the vehicle.
(16) Remove the power steering pump.
(17) Remove the accessory drive belt tensioner.
(18) Remove the gear cover-to-housing bolts and
gently pry the cover away from the housing, taking
care not to mar the gasket surfaces.
(19) Remove the fuel injection pump (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL INJEC-
TION PUMP - REMOVAL).
(20) Disconnect the camshaft position sensor con-
nector.
(21) Disconnect and remove engine speed sensor.
(22) Remove the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - REMOVAL).
(23) Remove the six front oil pan fasteners.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 299
EXHAUST MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1523 of 2627
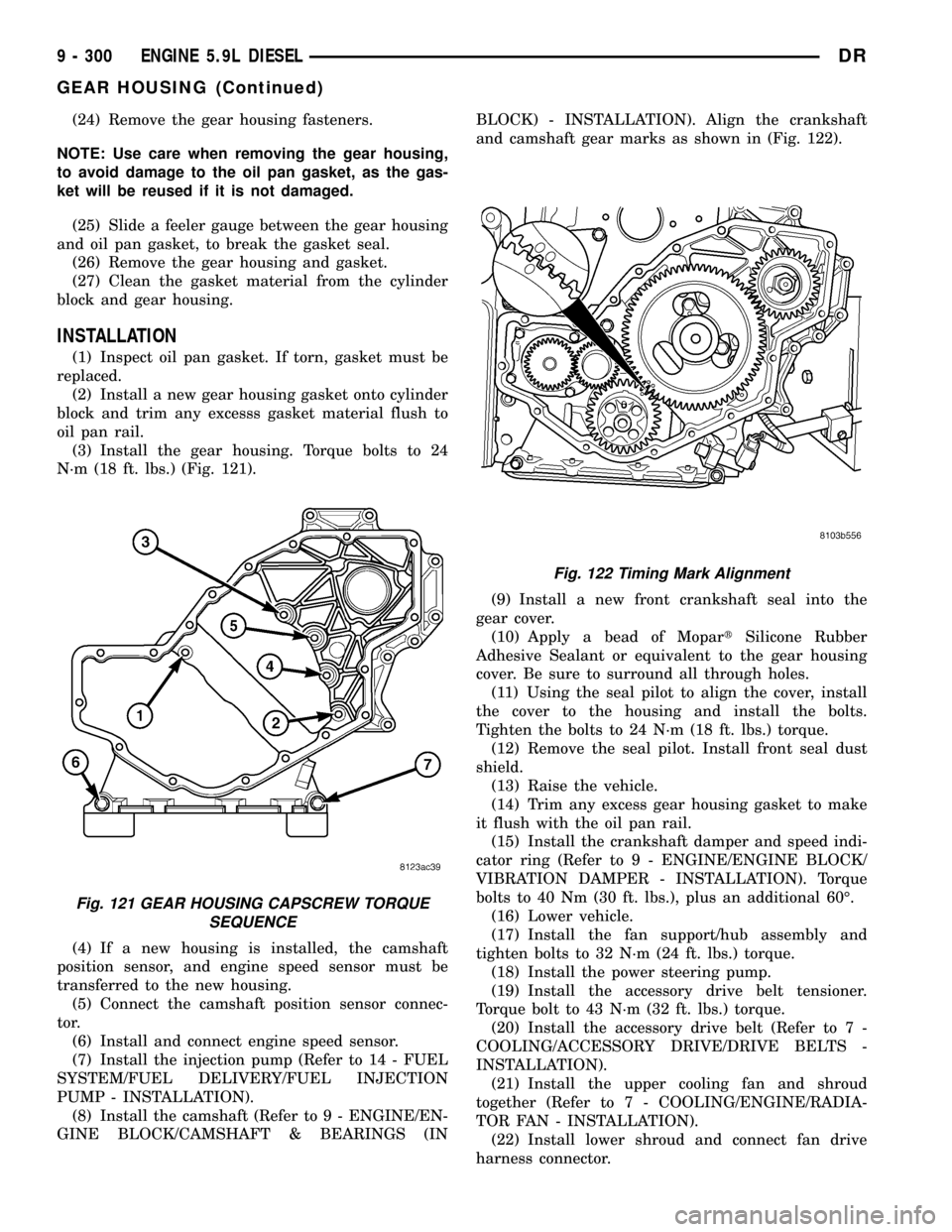
(24) Remove the gear housing fasteners.
NOTE: Use care when removing the gear housing,
to avoid damage to the oil pan gasket, as the gas-
ket will be reused if it is not damaged.
(25) Slide a feeler gauge between the gear housing
and oil pan gasket, to break the gasket seal.
(26) Remove the gear housing and gasket.
(27) Clean the gasket material from the cylinder
block and gear housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Inspect oil pan gasket. If torn, gasket must be
replaced.
(2) Install a new gear housing gasket onto cylinder
block and trim any excesss gasket material flush to
oil pan rail.
(3) Install the gear housing. Torque bolts to 24
N´m (18 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 121).
(4) If a new housing is installed, the camshaft
position sensor, and engine speed sensor must be
transferred to the new housing.
(5) Connect the camshaft position sensor connec-
tor.
(6) Install and connect engine speed sensor.
(7) Install the injection pump (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL INJECTION
PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (INBLOCK) - INSTALLATION). Align the crankshaft
and camshaft gear marks as shown in (Fig. 122).
(9) Install a new front crankshaft seal into the
gear cover.
(10) Apply a bead of MopartSilicone Rubber
Adhesive Sealant or equivalent to the gear housing
cover. Be sure to surround all through holes.
(11) Using the seal pilot to align the cover, install
the cover to the housing and install the bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(12) Remove the seal pilot. Install front seal dust
shield.
(13) Raise the vehicle.
(14) Trim any excess gear housing gasket to make
it flush with the oil pan rail.
(15) Install the crankshaft damper and speed indi-
cator ring (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
VIBRATION DAMPER - INSTALLATION). Torque
bolts to 40 Nm (30 ft. lbs.), plus an additional 60É.
(16) Lower vehicle.
(17) Install the fan support/hub assembly and
tighten bolts to 32 N´m (24 ft. lbs.) torque.
(18) Install the power steering pump.
(19) Install the accessory drive belt tensioner.
Torque bolt to 43 N´m (32 ft. lbs.) torque.
(20) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(21) Install the upper cooling fan and shroud
together (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIA-
TOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(22) Install lower shroud and connect fan drive
harness connector.
Fig. 121 GEAR HOUSING CAPSCREW TORQUE
SEQUENCE
Fig. 122 Timing Mark Alignment
9 - 300 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
GEAR HOUSING (Continued)
Page 1533 of 2627

INSPECTION
Discard rusted clamps, broken or worn supports
and attaching parts. Replace a component with orig-
inal equipment parts, or equivalent. This will assure
proper alignment with other parts in the system and
provide acceptable exhaust noise levels.
INSTALLATION - DIESEL
(1) Install the exhaust pipe into the transmission
support and onto the turbocharger flange.
(2) Install the exhaust pipe-to-turbocharger elbow
clamp and tighten to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the extension pipe and clamp to the
exhaust pipe using a new clamp and tighten the
clamp nuts to 54.2 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Lower the vehicle.
(5) Connect the battery negative cables.
(6) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks.
Reair exhaust leaks as necessary.
(7) Check the exhaust system for contact with the
body panels. A minimum of 25.4 mm (1.0 in.) is
required between the exhaust system components
and body/frame parts. Make the necessary adjust-
ments, if needed..
HEAT SHIELDS
DESCRIPTION
There are two types of heat shields used. One is
stamped steel the other is molded foil sheets. The
shields attach to the vehicle around the exhaust sys-
tem to prevent heat from the exhaust system from
entering the passenger area and other areas where
the heat can cause damage to other components.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the nuts or bolts holding the exhaust
heat shield to the floor pan (Fig. 6) (Fig. 7) (Fig. 8),
crossmember or bracket.
(3) Slide the shield out around the exhaust system.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the exhaust heat shield to the floor
pan, crossmember or bracket and install the nuts or
bolts.
(2) Tighten the nuts and bolts 11 N´m (100 in.
lbs.).
(3) Lower the vehicle.
Fig. 5 Exhaust Pipe
1 - Clamp
2 - Support
3 - EXHAUST PIPE
Fig. 6 HEAT SHIELDS - RH - REG CAB
1 - HEAT SHIELD
2 - FASTENER
3 - NUT
4 - HEAT SHIELD
11 - 8 EXHAUST SYSTEMDR
EXHAUST PIPE (Continued)
Page 1677 of 2627

CAUTION: Do not overtighten the vise on the gear
case. This may affect the adjustment
(3) Hold the steering gear upside down over a
drain pan and rotate the input shaft back and forth
several times lock-to-lock to discharge the fluid from
the steering gear
(4) Rotate the input shaft to the left stop and then
back-off approximately 45 degrees. Using an inch-
pound torque wrench on the input shaft, record the
peak torque required to slowly and evenly rotate the
input shaft clockwise
1¤2turn (180 degrees) starting
from the 45 degree position. This peak torque read-
ing is the preload torque. The preload torque must be
within2-10in-lbs.
(5) Rotate the input shaft to its center of travel
(approximately 1.5 turns from either stop). Place the
torque wrench on the input shaft with the handle in
the vertical position. Rotate the torque wrench slowly
and evenly
1¤4turn (90 degrees) each side of center
and record the peak torque measure on or near cen-ter. This total on-center torque reading must be5-9
in-lbs higher than the previously measured preload
torque without exceeding a total of 17 in-lbs. The
value of the total on-center minus the preload torque
is defined as the meshload torque
(6) If required, adjust the on-center torque by loos-
ening the adjuster screw lock nut and turning the
adjuster screw until the total on-center and meshload
torque readings fall within the specified values. Turn
the adjuster screw clockwise to increase and counter-
clockwise to decrease the torque reading. While hold-
ing the adjuster screw in place, tighten the lock nut
to 31 N´m (23 ft. lbs.).
(7) Re-check the preload and on-center torque
readings.
(8) Install pitman arm on the steering gear (Refer
to 19 - STEERING/LINKAGE/PITMAN ARM -
INSTALLATION).
(9) Reinstall steering gear to the vehicle (Refer to
19 - STEERING/GEAR - INSTALLATION).
SPECIFICATIONS
POWER STEERING GEAR
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Steering Gear
TypeRecirculating Ball
Gear Code & Ratio 12.5:1
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Preload
Torque0.23-1.13 Ð 2-10
Meshload Torque 0.56-1.02 Ð 5-9
+ Preload (17 Max)
19 - 22 GEAR - LINK/COILDR
GEAR - LINK/COIL (Continued)
Page 1682 of 2627

(11) Install the pitman arm (Refer to 19 - STEER-
ING/LINKAGE/PITMAN ARM - INSTALLATION).
(12) Perform a wheel alignment (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
STEERING GEAR INPUT
SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the steering gear from the vehicle
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/GEAR - REMOVAL).
CAUTION: Do not overtighten the vise on the gear
case. This may affect the adjustment
(2) Mount the steering gear upside down over a
drain pan in a soft jawed vise.
(3) Place a drain pan under the gear and rotate
the input shaft back and forth several times lock-to-
lock to discharge the fluid from the steering gear
(4) Drain all the remaining fluid from the gear.
(5) Rotate the input shaft from stop to stop and
count the number of turns using a 12 point socket
(Fig. 9).
NOTE: The pitman shaft will not clear the housing if
it is not centered.
(6) Center the input shaft by rotating it from the
stop back 1 1/2 turns to achieve center position (Fig.
9).(7) Remove the pitman shaft (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/GEAR/PITMAN SHAFT - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the four bolts securing the valve hous-
ing.
(9) Remove the valve housing from the steering
gear (Fig. 10).
(10) Remove the valve housing and wormshaft
assembly from the steering gear housing and place
the valve housing in a soft jawed vise (Fig. 11).
Fig. 9 CENTERING STEERING GEAR
1 - STEERING GEAR
2 - 12 POINT SOCKET
3 - RATCHET
4 - INPUT SHAFT
Fig. 10 VALVE ASSEMBLY
1 - VALVE HOUSING
2 - WORMSHAFT BALLS
3 - STEERING GEAR HOUSING
Fig. 11 VALVE HOUSING AND WORMSHAFT
1 - VALVE HOUSING
2 - SET SCREW
3 - RETAINER RING
DRGEAR - LINK/COIL 19 - 27
PITMAN SHAFT SEAL (Continued)
Page 1706 of 2627
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. Leaks can occur at the
mating surfaces of the gear case, adaptor or exten-
sion housing, or from the front/rear seals. A sus-
pected leak could also be the result of an overfill
condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will probably be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal.
Lubricant may be seen dripping from the clutch
housing after extended operation. If the leak is
severe, it may also contaminate the clutch disc caus-
ing the disc to slip, grab and or chatter.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level. Also allow the lubricant to
settle for a minute or so before checking. These rec-
ommendations will ensure an accurate check and
avoid an underfill or overfill condition. Always check
the lubricant level after any addition of fluid to avoid
an incorrect lubricant level condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants is
noise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Shift component damage or damaged clutch pres-
sure plate or disc are additional probable causes of
increased shift effort. Worn/damaged pressure plate
or disc can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem
is advanced, gear clash during shifts can result.
Worn or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash
when shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds.
Severe highly audible transmission noise is gener-
ally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant will
promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails,
forks and bearings. The overheating caused by a
lubricant problem, can also lead to gear and bearing
damage.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(3) Remove shift boot bezel screws and slide boot
upward on shift lever extension.
(4) Remove shift lever extension from the shift
tower and lever assembly.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(6) Remove skid plate, if equipped.
(7) Drain lubricant if transmission will be disas-
sembled for service.
(8) Mark propeller shaft/shafts and companion
flange yoke/yokes for installation reference and
remove propeller shaft/shafts.
(9) Disconnect harness from clips on transmission
housing.
(10) Remove transfer case linkage if equipped.
(11) Remove transfer case mounting nuts and
remove transfer case if equipped.
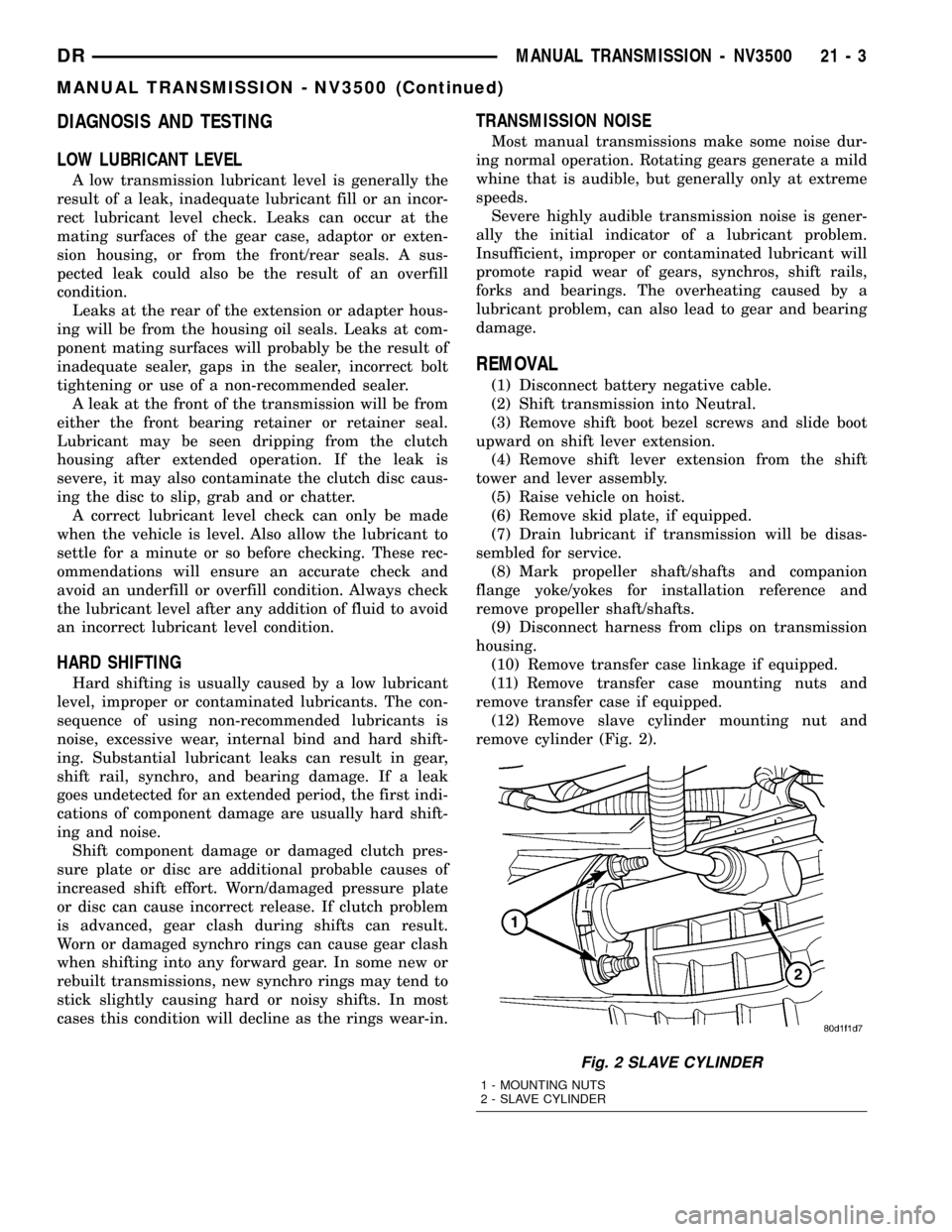
(12) Remove slave cylinder mounting nut and
remove cylinder (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 SLAVE CYLINDER
1 - MOUNTING NUTS
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 21 - 3
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 (Continued)
Page 1747 of 2627

The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This move-
ment moves the internal transmission shift compo-
nents to begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever
moves the selected shift rail, the shift fork attached
to that rail begins to move. The fork is positioned in
a groove in the outer circumference of the synchro-
nizer sleeve. As the shift fork moves the synchronizer
sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed-up or slow
down the selected gear (depending on whether the
driver is up-shifting or down-shifting). The synchro-
nizer does this by having the synchronizer hub
splined to the mainshaft, or the countershaft in some
cases, and moving the blocker ring into contact with
the gear's friction cone. As the blocker ring and fric-
tion cone come together, the gear speed is brought up
or down to the speed of the synchronizer. As the two
speeds match, the splines on the inside of the syn-
chronizer sleeve become aligned with the teeth on
the blocker ring and the friction cone and eventually
will slide over the teeth, locking the gear to the
mainshaft, or countershaft, through the synchronizer.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. A correct lubricant level
check can only be made when the vehicle is level.
Also allow the lubricant to settle for a minute or so
before checking. These recommendations will ensure
an accurate check and avoid an underfill or overfill
condition. Always check the lubricant level after any
addition of fluid to avoid an incorrect lubricant level
condition.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, adaptor or extension housing, or from the front/
rear seals. A suspected leak could also be the result
of an overfill condition. Leaks at the rear of the
extension or adapter housing will be from the hous-
ing oil seals. Leaks at component mating surfaces
will probably be the result of inadequate sealer, gaps
in the sealer, incorrect bolt tightening or use of a
non-recommended sealer. A leak at the front of the
transmission will be from either the front bearing
retainer or retainer seal. Lubricant may be seen drip-
ping from the clutch housing after extended opera-
tion. If the leak is severe, it may also contaminate
the clutch disc causing the disc to slip, grab and or
chatter.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants isnoise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Component damage, incorrect clutch adjustment or
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc are additional
probable causes of increased shift effort. Incorrect
adjustment or a worn/damaged pressure plate or disc
can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem is
advanced, gear clash during shifts can result. Worn
or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash when
shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds. Severe highly audible transmission noise is
generally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant
will promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift
rails, forks and bearings. The overheating caused by
a lubricant problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(2) Remove shift boot screws from floorpan and
slide boot upward on the shift lever.
(3) Remove shift lever extension from shift tower
and lever assembly.
(4) Remove shift tower bolts (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 SHIFT TOWER
1 - SHIFT TOWER
2 - SHIFTER
3 - BOLTS
21 - 44 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1837 of 2627

IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan gas-
ket surface (Fig. 2). Refer to this information when
ordering replacement parts.
GEAR RATIOS
The 48RE gear ratios are:
1st.................................2.45:1
2nd................................1.45:1
3rd................................1.00:1
4th.................................0.69:1
Rev.................................2.20:1
OPERATION
The application of each driving or holding compo-
nent is controlled by the valve body based upon the
manual lever position, throttle pressure, and gover-
nor pressure. The governor pressure is a variable
pressure input to the valve body and is one of the
signals that a shift is necessary. First through fourth
gear are obtained by selectively applying and releas-
ing the different clutches and bands. Engine power is
thereby routed to the various planetary gear assem-
blies which combine with the overrunning clutch
assemblies to generate the different gear ratios. The
torque converter clutch is hydraulically applied and
is released when fluid is vented from the hydraulic
circuit by the torque converter control (TCC) solenoid
on the valve body. The torque converter clutch is con-
trolled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The
torque converter clutch engages in fourth gear, and
in third gear under various conditions, such as when
the O/D switch is OFF, when the vehicle is cruising
on a level surface after the vehicle has warmed up.
The torque converter clutch can also be engaged in
the MANUAL SECOND gear position if high trans-
mission temperatures are sensed by the PCM. The
torque converter clutch will disengage momentarily
when an increase in engine load is sensed by the
PCM, such as when the vehicle begins to go uphill or
the throttle pressure is increased. The torque con-
verter clutch feature increases fuel economy and
reduces the transmission fluid temperature.
Since the overdrive clutch is applied in fourth gear
only and the direct clutch is applied in all ranges
except fourth gear, the transmission operation for
park, neutral, and first through third gear will be
described first. Once these powerflows are described,
the third to fourth shift sequence will be described.
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER 10 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
2 - INPUT SHAFT 11 - DIRECT CLUTCH
3 - OIL PUMP 12 - PLANETARY GEAR
4 - FRONT BAND 13 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
5 - FRONT CLUTCH 14 - OVERDRIVE OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
6 - REAR CLUTCH 15 - DIRECT CLUTCH SPRING
7 - PLANETARIES 16 - OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER
8 - REAR BAND 17 - OIL PAN
9 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH 18 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 2 Transmission Part Number And Serial
Number Location
1 - PART NUMBER
2 - BUILD DATE
3 - SERIAL NUMBER
21 - 134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)