1998 DODGE RAM 1500 transmission removal
[x] Cancel search: transmission removalPage 1672 of 2627

GEAR - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GEAR - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION.........................17
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................18
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................19BUSHING
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
GEAR - INDEPENDENT FRONT
SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION
A rack and pinion steering gears (Fig. 1) is made
up of two main components, the pinon shaft and the
rack. The gear cannot be adjusted or internally ser-
viced. If a malfunction or a fluid leak occurs, the gear
must be replaced as an assembly.
REMOVAL
NOTE: The steering column on vehicles with an
automatic transmission may not be equipped with
an internal locking shaft that allows the ignition key
cylinder to be locked with the key. Alternative meth-
ods of locking the steering wheel for service will
have to be used.
(1) Lock the steering wheel.(2) Drain and siphon the power steering fluid from
the reservoir.
(3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Remove and discard the steering coupler pinch
bolt.
(5) Remove the power steering hoses from the rack
& pinion.
(6) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
(7) Remove the tie rod end nuts and separate tie
rod ends from the knuckles with Special tool 8677
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/LINKAGE/TIE ROD END -
REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the skid plate (Refer to 13 - FRAME &
BUMPERS/FRAME/FRONT SKID PLATE -
REMOVAL).
(9) Remove the rack & pinion mounting bolts. (Fig.
2) & (Fig. 3)
(10) Remove the rack & pinion from the vehicle.
Fig. 1 STEERING GEAR
1 - OUTER TIE ROD ENDS
2 - MOUNTING BUSHINGS
3 - BELLOWS
Fig. 2 STEERING GEAR MOUNTING BOLTS
1 - STEERING GEAR MOUNTING BOLTS 4X4
DRGEAR - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSION 19 - 17
Page 1675 of 2627
GEAR - LINK/COIL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GEAR - LINK/COIL
DESCRIPTION.........................20
OPERATION...........................20
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT........................21
SPECIFICATIONS
POWER STEERING GEAR..............22
TORQUE CHART......................23
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING GEAR..............23
PITMAN SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - GAS ENGINE...............25REMOVAL - DIESEL...................25
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - GAS ENGINE...........26
INSTALLATION - DIESEL................26
STEERING GEAR INPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................29
PITMAN SHAFT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - GAS......................30
REMOVAL - DIESEL...................30
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - GAS..................31
INSTALLATION - DIESEL................31
GEAR - LINK/COIL
DESCRIPTION
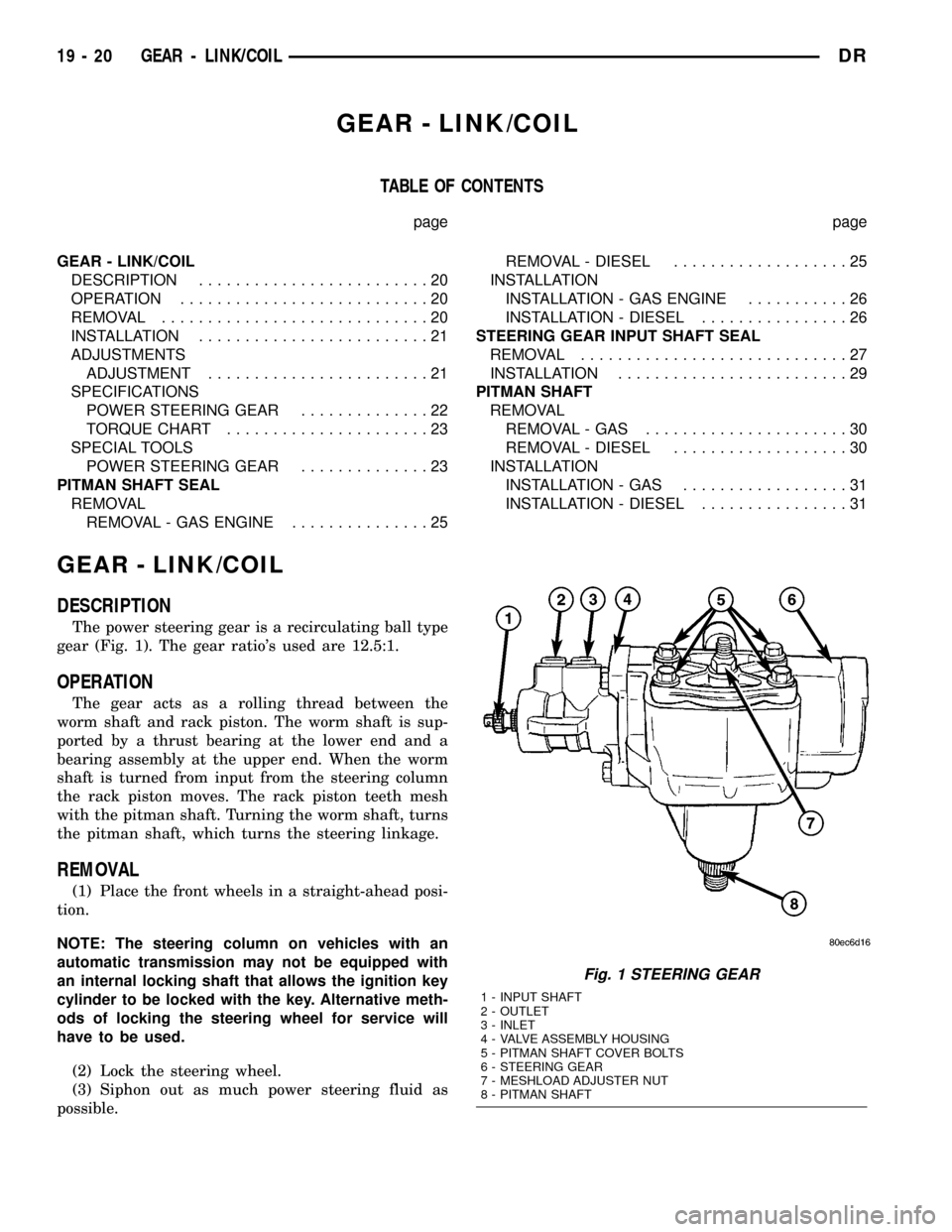
The power steering gear is a recirculating ball type
gear (Fig. 1). The gear ratio's used are 12.5:1.
OPERATION
The gear acts as a rolling thread between the
worm shaft and rack piston. The worm shaft is sup-
ported by a thrust bearing at the lower end and a
bearing assembly at the upper end. When the worm
shaft is turned from input from the steering column
the rack piston moves. The rack piston teeth mesh
with the pitman shaft. Turning the worm shaft, turns
the pitman shaft, which turns the steering linkage.
REMOVAL
(1) Place the front wheels in a straight-ahead posi-
tion.
NOTE: The steering column on vehicles with an
automatic transmission may not be equipped with
an internal locking shaft that allows the ignition key
cylinder to be locked with the key. Alternative meth-
ods of locking the steering wheel for service will
have to be used.
(2) Lock the steering wheel.
(3) Siphon out as much power steering fluid as
possible.
Fig. 1 STEERING GEAR
1 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OUTLET
3 - INLET
4 - VALVE ASSEMBLY HOUSING
5 - PITMAN SHAFT COVER BOLTS
6 - STEERING GEAR
7 - MESHLOAD ADJUSTER NUT
8 - PITMAN SHAFT
19 - 20 GEAR - LINK/COILDR
Page 1694 of 2627

PUMP
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................40
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PUMP LEAKAGE . 40
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER
STEERING PUMP - INITIAL OPERATION....40
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUSHING
POWER STEERING SYSTEM............40
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - GAS......................41
REMOVAL - DIESEL...................41
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - GAS..................42
INSTALLATION - DIESEL................42
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................42
FLUID
DESCRIPTION.........................43
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER
STEERING FLUID LEVEL CHECKING......43
FLUID COOLER
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
HOSES - I.F.S.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - RETURN HOSE - GEAR TO
COOLER............................44
REMOVAL - PRESSURE HOSE...........44
REMOVAL - RETURN HOSE - RESERVOIR
TO COOLER.........................44INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - RETURN HOSE - GEAR TO
COOLER............................44
INSTALLATION - PRESSURE HOSE.......44
INSTALLATION - RETURN HOSE -
RESERVOIR TO COOLER...............44
HOSES - LINK/COIL
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - RETURN HOSE - GEAR TO
COOLER............................45
REMOVAL - PRESSURE HOSE...........45
REMOVAL - RETURN HOSE - RESERVOIR
TO COOLER.........................45
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - RETURN HOSE - GEAR TO
COOLER............................45
INSTALLATION - PRESSURE HOSE.......45
INSTALLATION - RETURN HOSE -
RESERVOIR TO COOLER...............45
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
REMOVAL - 3.7L & 5.7L..................46
INSTALLATION - 3.7L & 5.7L...............46
PULLEY
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
RESERVOIR
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
PUMP
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: MOPARTATF+4 is to be used in the
power steering system. No other power steering or
automatic transmission fluid is to be used in the
system. Damage may result to the power steering
pump and system if any other fluid is used, and do
not overfill.The pump is connected to the steering gear via the
pressure hose and the return hose. The pump shaft
has a pressed-on pulley that is belt driven by the
crankshaft pulley.
All vehicles are equipped with a power steering
fluid cooler.
NOTE: Power steering pumps are not interchange-
able with pumps installed on other vehicles.
DRPUMP 19 - 39
Page 1698 of 2627

FLUID
DESCRIPTION
The recommended fluid for the power steering sys-
tem is MopartATF +4.
MopartATF+4, when new is red in color. The
ATF+4 is dyed red so it can be identified from other
fluids used in the vehicle such as engine oil or anti-
freeze. The red color is not permanent and is not an
indicator of fluid condition, As the vehicle is driven,
the ATF+4 will begin to look darker in color and may
eventually become brown.THIS IS NORMAL.
ATF+4 also has a unique odor that may change with
age. Consequently, odor and color cannot be used to
indicate the fluid condition or the need for a fluid
change.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER STEERING
FLUID LEVEL CHECKING
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION: MOPARTATF+4 is to be used in the
power steering system. No other power steering or
automatic transmission fluid is to be used in the
system. Damage may result to the power steering
pump and system if any other fluid is used, and do
not overfill.
The power steering fluid level can be viewed on the
dipstick attached to the filler cap. There are two
ranges listed on the dipstick, COLD and HOT. Before
opening power steering system, wipe the reservoir
filler cap free of dirt and debris. Remove the cap and
check the fluid level on its dipstick. When the fluid is
at normal ambient temperature, approximately 21ÉC
to 27ÉC (70ÉF to 80ÉF), the fluid level should read
between the minimum and maximum area of the cold
range. When the fluid is hot, fluid level is allowed to
read up to the highest end of the HOT range. Only
add fluid when the vehicle is cold.
Use only MopartATF+4Do not overfill the
power steering system.
FLUID COOLER
REMOVAL
(1) Drain and siphon the power steering fluid.
(2) Disconnect the return and supply hoses con-
nected to the power steering fluid cooler.
(3) Remove the mounting bracket bolts securing
the fluid cooler to the brace. (Fig. 4)& (Fig. 5)(4) Remove the fluid cooler from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the fluid cooler to the vehicle.
(2) Install the mounting bracket bolts securing the
fluid cooler to the brace (Fig. 4)& (Fig. 5).
(3) Reclamp the return and supply hoses to the
power steering fluid cooler.
(4) Refill the power steering fluid (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 4 V6 & V8 P/S FLUID COOLER
1 - POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
Fig. 5 V10 & DIESEL P/S FLUID COOLER
1 - RADIATOR
2 - POWER STEERING HOSES
3 - MOUNTING BOLTS
4 - P/S FLUID COOLER
DRPUMP 19 - 43
Page 1704 of 2627

TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500..........1
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV4500..........43
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600..........88
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE........130
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE.311
TRANSFER CASE - NV241 GENII...........415TRANSFER CASE - NV271................447
TRANSFER CASE - NV243................482
TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII...........512
TRANSFER CASE - NV273................542
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................3
REMOVAL.............................3
DISASSEMBLY..........................4CLEANING............................15
INSPECTION..........................16
ASSEMBLY............................17
INSTALLATION.........................39
SPECIFICATIONS.......................40
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................40
MANUAL TRANSMISSION -
NV3500
DESCRIPTION
The transmission is a medium-duty 5-speed, con-
stant mesh fully synchronized manual transmission
with fifth gear overdrive range. The transmission is
available in two and four-wheel drive configurations.
The transmission gear case consists of two aluminum
housings (Fig. 1). The clutch housing is an integral
part of the transmission front housing.
A combination of roller and ball bearings are used
to support the transmission shafts in the two hous-
ings. The transmission gears all rotate on caged type
needle bearings. A roller bearing is used between the
input and output shaft.
The transmission has a single shaft shift mecha-
nism with three shift forks all mounted on the shaft.
The shaft is supported in the front and rear housings
by bushings and one linear ball bearing. Internal
shift components consist of the forks, shaft, shift
lever socket and detent components
OPERATION
The manual transmission receives power through the
clutch assembly from the engine. The clutch disc issplined to the transmission input shaft and is turned at
engine speed at all times that the clutch is engaged.
The input shaft is connected to the transmission coun-
tershaft through the mesh of fourth speed gear on the
input shaft and the fourth countershaft gear. At this
point, all the transmission gears are spinning.
The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This movement
moves the internal transmission shift components to
begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever moves the
selected shift rail, the shift fork attached to that rail
begins to move. The fork is positioned in a groove in the
outer circumference of the synchronizer sleeve. As the
shift fork moves the synchronizer sleeve, the synchro-
nizer begins to speed-up or slow down the selected gear
(depending on whether we are up-shifting or down-shift-
ing). The synchronizer does this by having the synchro-
nizer hub splined to the mainshaft and moving the
blocker ring into contact with the gear's friction cone. As
the blocker ring and friction cone come together, the
gear speed is brought up or down to the speed of the
synchronizer. As the two speeds match, the splines on
the inside of the synchronizer sleeve become aligned
with the teeth on the blocker ring and the friction cone
and eventually will slide over the teeth, locking the gear
to the mainshaft, or countershaft, through the synchro-
nizer.
DRTRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASE 21 - 1
Page 1706 of 2627
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. Leaks can occur at the
mating surfaces of the gear case, adaptor or exten-
sion housing, or from the front/rear seals. A sus-
pected leak could also be the result of an overfill
condition.
Leaks at the rear of the extension or adapter hous-
ing will be from the housing oil seals. Leaks at com-
ponent mating surfaces will probably be the result of
inadequate sealer, gaps in the sealer, incorrect bolt
tightening or use of a non-recommended sealer.
A leak at the front of the transmission will be from
either the front bearing retainer or retainer seal.
Lubricant may be seen dripping from the clutch
housing after extended operation. If the leak is
severe, it may also contaminate the clutch disc caus-
ing the disc to slip, grab and or chatter.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level. Also allow the lubricant to
settle for a minute or so before checking. These rec-
ommendations will ensure an accurate check and
avoid an underfill or overfill condition. Always check
the lubricant level after any addition of fluid to avoid
an incorrect lubricant level condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants is
noise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Shift component damage or damaged clutch pres-
sure plate or disc are additional probable causes of
increased shift effort. Worn/damaged pressure plate
or disc can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem
is advanced, gear clash during shifts can result.
Worn or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash
when shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds.
Severe highly audible transmission noise is gener-
ally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant will
promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails,
forks and bearings. The overheating caused by a
lubricant problem, can also lead to gear and bearing
damage.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(3) Remove shift boot bezel screws and slide boot
upward on shift lever extension.
(4) Remove shift lever extension from the shift
tower and lever assembly.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(6) Remove skid plate, if equipped.
(7) Drain lubricant if transmission will be disas-
sembled for service.
(8) Mark propeller shaft/shafts and companion
flange yoke/yokes for installation reference and
remove propeller shaft/shafts.
(9) Disconnect harness from clips on transmission
housing.
(10) Remove transfer case linkage if equipped.
(11) Remove transfer case mounting nuts and
remove transfer case if equipped.
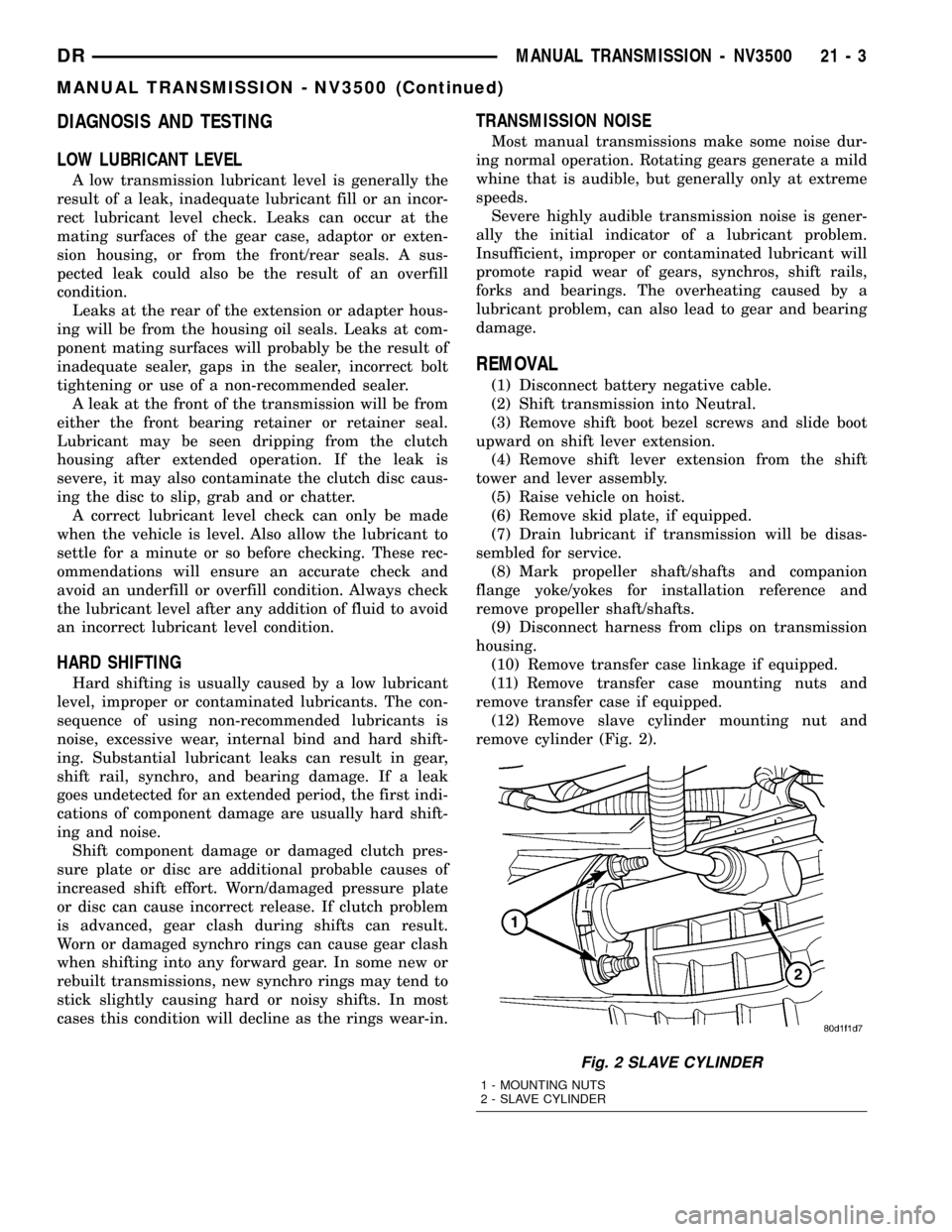
(12) Remove slave cylinder mounting nut and
remove cylinder (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 SLAVE CYLINDER
1 - MOUNTING NUTS
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 21 - 3
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 (Continued)
Page 1707 of 2627

(13) Remove starter motor, structural dust cover
bolts to clutch housing, dust shield bolt and suspen-
sion crossmember (Fig. 3).
CAUTION: Do not remove structural dust cover
from enigne block. If cover is removed clutch hous-
ing and cover must be aligned with the engine.
(14) Remove exhaust pipe from the exhaust mani-
folds.
(15) Support engine with adjustable jack stand
and wood block.
(16) Support and secure transmission to a trans-
mission jack with safety chains.
(17) Remove bolts from the rear transmission
mount.
(18) Remove the rear crossmember and transmis-
sion mount (Fig. 4).
(19) Remove bolts attaching transmission to the
engine.
(20) Move transmission rearward until input shaft
is clear of clutch disc and pressure plate. Then lower
jack and remove transmission from under vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
FRONT HOUSING
(1) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(2) If lubricant was not drained out of transmis-
sion during removal, remove drain plug and drain
lubricant.
(3) Inspect drain plug magnet for debris.
(4) Remove backup light switch located on passen-
ger side of rear housing (Fig. 5).
(5) Remove shift tower bolts and remove tower and
lever assembly (Fig. 6).
Fig. 3 DUST COVER
1 - DUST SHIELD
2 - STARTER MOTOR
3 - DUST COVER
4 - CROSSMEMBER
Fig. 4 CROSSMEMBER
1 - TRANSMISSION MOUNT
2 - CROSSMEMBER
Fig. 5 BACKUP LIGHT SWITCH
1 - BACKUP LIGHT SWITCH
Fig. 6 SHIFT TOWER
1 - SHIFT TOWER
2 - SHIFT SOCKET
3 - SEAL
21 - 4 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 (Continued)
Page 1725 of 2627

(19) Install second gear needle bearing on shaft
(Fig. 65).
(20) Install second gear onto shaft and bearing
(Fig. 66). Verify second gear is seated on synchro
components.
(21) Install two-piece thrust washer with halves
seated in the shaft groove and washer lugs seated in
shaft lug bores (Fig. 67). Verify i.d. grooves and
markings noted during removal are facing the correct
direction.
(22) Start retaining ring around two-piece thrust
washer (Fig. 68). Verify locating dimple is between
thrust washer halves.
Fig. 65 SECOND GEAR BEARING
1 - SECOND GEAR BEARING
2 - COLLAR
Fig. 66 SECOND GEAR
1 - COLLAR
2 - 1-2 SYNCHRO ASSEMBLY
3 - BEARING
4 - SECOND GEAR
Fig. 67 TWO-PIECE THRUST WASHER
1 - WASHER GROOVE IN SHAFT
2 - LUG BORE
3 - THRUST WASHER LUGS
4 - LUG BORE
5 - LUG
6 - WASHER HALF
Fig. 68 RETAINING RING
1 - THRUST WASHER RETAINING RING
2 - THRUST WASHER HALVES
3 - SECOND GEAR
4 - LOCATING DIMPLE
21 - 22 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV3500 (Continued)