1998 DODGE RAM 1500 Engine
[x] Cancel search: EnginePage 2094 of 2627

into the appropriate oil pump valve body bore (Fig.
102) (Fig. 103).
(4) Place the separator plate onto the oil pump
body (Fig. 101).
(5) Install the screws to hold the separator plate
onto the oil pump body (Fig. 101). Tighten the screws
to 4.5 N´m (40 in.lbs.).
(6) Position the oil pump cover onto the locating
dowels (Fig. 100).
(7) Seat the two oil pump halves together and
install all bolts finger tight.
(8) Torque all bolts down slowly starting in the
center and working outward. The correct torque is
4.5 N´m (40 in.lbs.).
(9) Verify that the oil pump gears rotate freely and
smoothly.
(10) Position the reaction shaft support into the oil
pump (Fig. 100).
(11) Install and torque the bolts to hold the reac-
tion shaft support to the oil pump (Fig. 100). The cor-
rect torque is 12 N´m (105 in.lbs.).
OIL PUMP FRONT SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission from the vehicle.
(2) Remove the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
(3) Using a screw mounted in a slide hammer,
remove the oil pump front seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean seal bore of the oil pump of any residue
or particles from the original seal.
(2) Install new oil seal in the oil pump housing
using Seal Installer C-3860-A (Fig. 104).
OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Input and Output Speed Sensors are two-wire
magnetic pickup devices that generate AC signals as
rotation occurs. They are mounted in the left side of
the transmission case and are considered primary
inputs to the Transmission Control Module (TCM).
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil, an AC
voltage is generated and sent to the TCM. The TCM
interprets this information as input shaft rpm.
The Output Speed Sensor generates an AC signal
in a similar fashion, though its coil is excited by rota-
tion of the rear planetary carrier lugs. The TCM
interprets this information as output shaft rpm.
The TCM compares the input and output speed
signals to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The TCM also compares the input speed signal and
the engine speed signal to determine the following:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable fluid catch pan under the
transmission.
(3) Remove the wiring connector from the output
speed sensor (Fig. 105).
(4) Remove the bolt holding the output speed sen-
sor to the transmission case.
(5) Remove the output speed sensor from the
transmission case.
Fig. 104 Install Oil Pump Front Seal
1 - TOOL C-3860-A
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 391
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 2102 of 2627

A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
control the current flow through the solenoid to posi-
tion the solenoid plunger at a desired position some-
where between full ON and full OFF. The constant
ON and duty cycled versions control the voltage
across the solenoid to allow either full flow or no flow
through the solenoid's valve.
OPERATION
When an electrical current is applied to the sole-
noid coil, a magnetic field is created which produces
an attraction to the plunger, causing the plunger to
move and work against the spring pressure and the
load applied by the fluid the valve is controlling. The
plunger is normally directly attached to the valve
which it is to operate. When the current is removed
from the coil, the attraction is removed and the
plunger will return to its original position due to
spring pressure.
The plunger is made of a conductive material and
accomplishes this movement by providing a path for
the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap
between the plunger and the coil to the minimum
necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the
magnetic field is maximized.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 117) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, anoverrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The torque
converter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid)
pump and contains an o-ring seal to better control oil
flow.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid.
Fig. 117 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE ASSEMBLY
2-STATOR
3 - CONVERTER HUB
4 - O-RING
5 - IMPELLER ASSEMBLY
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH PISTON
7 - TURBINE HUB
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 399
SOLENOIDS (Continued)
Page 2103 of 2627

IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 118) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving members of the system.
Fig. 118 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE
SECTION5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
21 - 400 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2104 of 2627

TURBINE
The turbine (Fig. 119) is the output, or driven,
member of the converter. The turbine is mounted
within the housing opposite the impeller, but is not
attached to the housing. The input shaft is inserted
through the center of the impeller and splined into
the turbine. The design of the turbine is similar to
the impeller, except the blades of the turbine are
curved in the opposite direction.
Fig. 119 Turbine
1 - TURBINE VANE 4 - PORTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER COVER
2 - ENGINE ROTATION 5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - INPUT SHAFT 6 - OIL FLOW WITHIN TURBINE SECTION
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 401
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2105 of 2627

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 120) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 121).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 122) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston with friction material was added to the tur-
bine assembly to provide this mechanical lock-up.
In order to reduce heat build-up in the transmis-
sion and buffer the powertrain against torsional
vibrations, the TCM can duty cycle the L/R-CC Sole-
noid to achieve a smooth application of the torque
converter clutch. This function, referred to as Elec-
tronically Modulated Converter Clutch (EMCC) can
occur at various times depending on the following
variables:
²Shift lever position
²Current gear range
²Transmission fluid temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Input speed
²Throttle angle²Engine speed
Fig. 120 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 121 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 122 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
21 - 402 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2106 of 2627
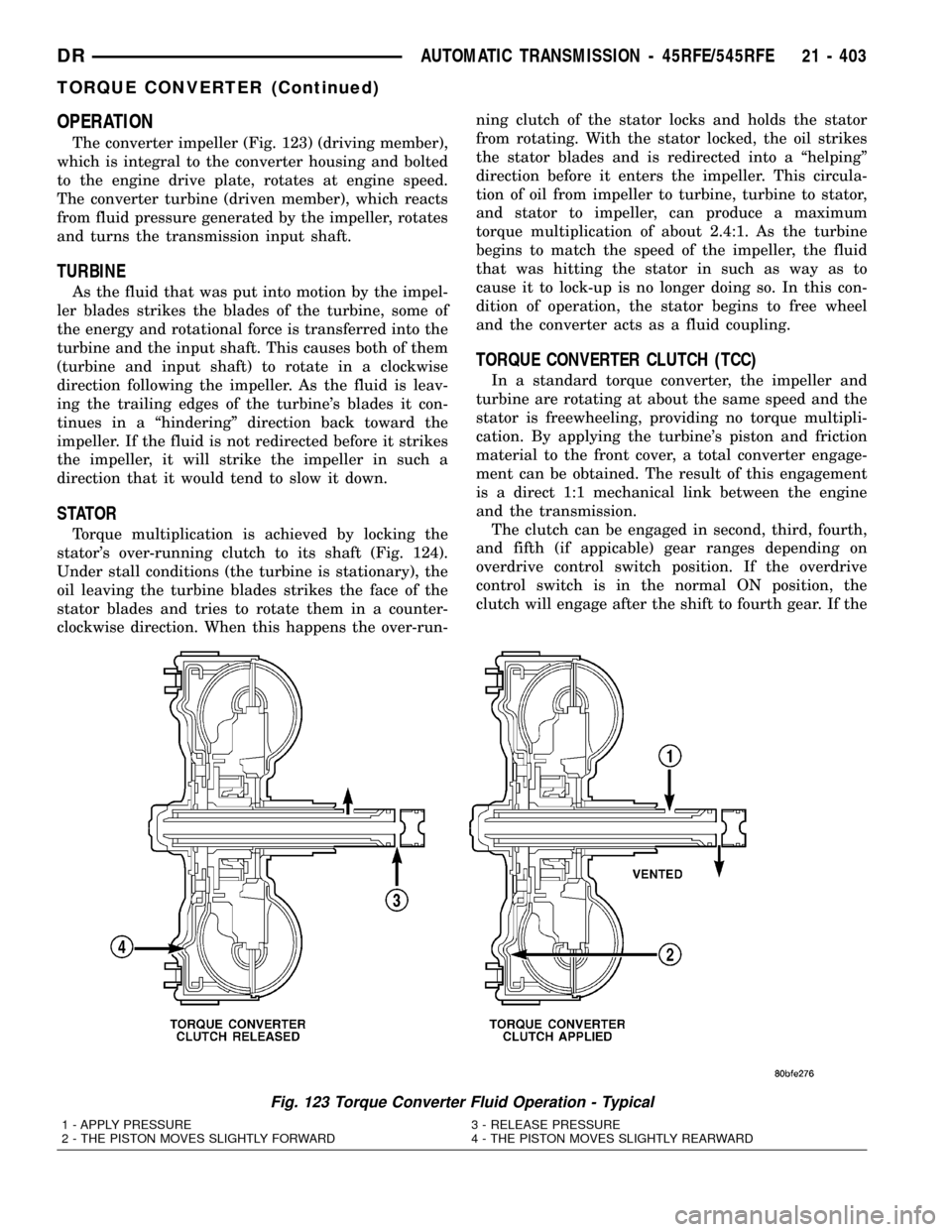
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 123) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 124).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over-run-ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston and friction
material to the front cover, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The clutch can be engaged in second, third, fourth,
and fifth (if appicable) gear ranges depending on
overdrive control switch position. If the overdrive
control switch is in the normal ON position, the
clutch will engage after the shift to fourth gear. If the
Fig. 123 Torque Converter Fluid Operation - Typical
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 403
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2107 of 2627

control switch is in the OFF position, the clutch will
engage after the shift to third gear.
The TCM controls the torque converter by way of
internal logic software. The programming of the soft-
ware provides the TCM with control over the L/R-CC
Solenoid. There are four output logic states that can
be applied as follows:
²No EMCC
²Partial EMCC
²Full EMCC
²Gradual-to-no EMCC
NO EMCC
Under No EMCC conditions, the L/R Solenoid is
OFF. There are several conditions that can result in
NO EMCC operations. No EMCC can be initiated
due to a fault in the transmission or because the
TCM does not see the need for EMCC under current
driving conditions.
PARTIAL EMCC
Partial EMCC operation modulates the L/R Sole-
noid (duty cycle) to obtain partial torque converter
clutch application. Partial EMCC operation is main-
tained until Full EMCC is called for and actuated.
During Partial EMCC some slip does occur. Partial
EMCC will usually occur at low speeds, low load and
light throttle situations.
FULL EMCC
During Full EMCC operation, the TCM increases
the L/R Solenoid duty cycle to full ON after Partial
EMCC control brings the engine speed within thedesired slip range of transmission input speed rela-
tive to engine rpm.
GRADUAL-TO-NO EMCC
This operation is to soften the change from Full or
Partial EMCC to No EMCC. This is done at mid-
throttle by decreasing the L/R Solenoid duty cycle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive flats for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
flats with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if neces-
sary. Verify that the converter hub o-ring is properly
installed and is free from debris. The hub must be
smooth to avoid damaging the pump seal at installa-
tion.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or con-
verter hub o-ring while inserting torque converter
into the front of the transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 125). Surface of converter lugs
should be at least 13 mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle.
Fig. 124 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 404 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2111 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(2) Position the transmission solenoid/TRS assem-
bly onto the valve body. Be sure that both alignment
dowels are fully seated in the valve body and that
the TRS switch contacts are properly positioned in
the selector plate
(3) Install the screws to hold the transmission
solenoid/TRS assembly onto the valve body.
(4) Tighten the solenoid assembly screws adjacent
to the arrows cast into the bottom of the valve body
first. Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(5) Tighten the remainder of the solenoid assembly
screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(6) Install the valve body into the transmission.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transmission temperature sensor is a ther-
mistor that is integral to the Transmission Range
Sensor (TRS).
OPERATION
The transmission temperature sensor is used by
the TCM to sense the temperature of the fluid in the
sump. Since fluid temperature can affect transmis-
sion shift quality and convertor lock up, the TCM
requires this information to determine which shift
schedule to operate in.
Calculated Temperature
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-
dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and a transfer plate. The
valve body contains valves and check balls that con-
trol fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch,
bands, and frictional clutches. The valve body con-
tains the following components (Fig. 129) and (Fig.
130):
²Solenoid switch valve
²Manual valve
²Low/reverse switch valve
²5 Accumulators
²7 check balls
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) controls the direc-
tion of the transmission fluid when the L/R-TCC sole-
noid is energized.
When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve is a relay valve. The purpose of
the manual valve is to direct fluid to the correct cir-
cuit needed for a specific gear or driving range. The
manual valve, as the name implies, is manually oper-
ated by the driver with a lever located on the top of
the valve body. The valve is connected mechanically
by a cable to the gearshift mechanism. The valve is
held in each of its positions by a roller detent spring
(Fig. 131) that engages the ªroostercombº of the TRS
selector plate.
21 - 408 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY (Continued)