1998 AUDI S4 throttle
[x] Cancel search: throttlePage 42 of 72

43
Emergency running program 1
If an angle sender for throttle valve drive fails
or an implausible signal is received:
• Torque-increasing requests on engine, e.g. CCS,
EBC (engine braking control) are suppressed.
• The fault lamp for electrical throttle control K132
comes on.
Prerequisite:
An intact angle sender and plausible
air mass flow. The air mass flow is
indicated by the air mass meter and
the charge pressure sender G31.
Self-diagnosis/emergency running mode
If a fault occurs in the throttle valve control part or in the wiring, three emergency running
programs can be run, depending on fault type.
Emergency running program 2
If the throttle valve drive fails or malfunctions:
• The throttle valve drive is switched off and the
throttle valve goes into the emergency running
position. This results in considerable loss of
power, increased idling speed and possibly also
rough idling .
• Driver inputs are executed as far as possible via
the ignition angle and charge pressure. The
engine shows little response to the throttle.
• The fault lamp for electrical throttle control K132
comes on.
Prerequisite:
Emergency running program 2 is only
run if both angle senders for throttle
valve drive recognise the emergency
running position.
Emergency running program 3
If the throttle valve position is not clearly
recognisable and/or if the throttle valve is not
definitely known to be in the emergency
running position:
• The throttle valve drive is switched off and the
throttle valve goes into the emergency running
position. This results in considerable loss of
power, increased idling speed and possibly also
rough idling.
• The engine speed is limited to approx. 1200 rpm
by restricting the injection.
• The fault lamp for electric throttle control K132
comes on.
Repair work may not be performed on
the throttle valve control part J338! If
G186, G187 or G188 becomes faulty,
unit J338 must be replaced
completely and a
basic setting
performed.
Page 43 of 72
44
Subsystems of the Motronic
120
180
°C 60
90
12
93
6
120
°C 60
12
16
120
100
80
50
30
10140
1234
5
6
7
160
180
200
220
260
Volt8
1/2
1/1
8
0
EPC
EPC
SSP 198/47
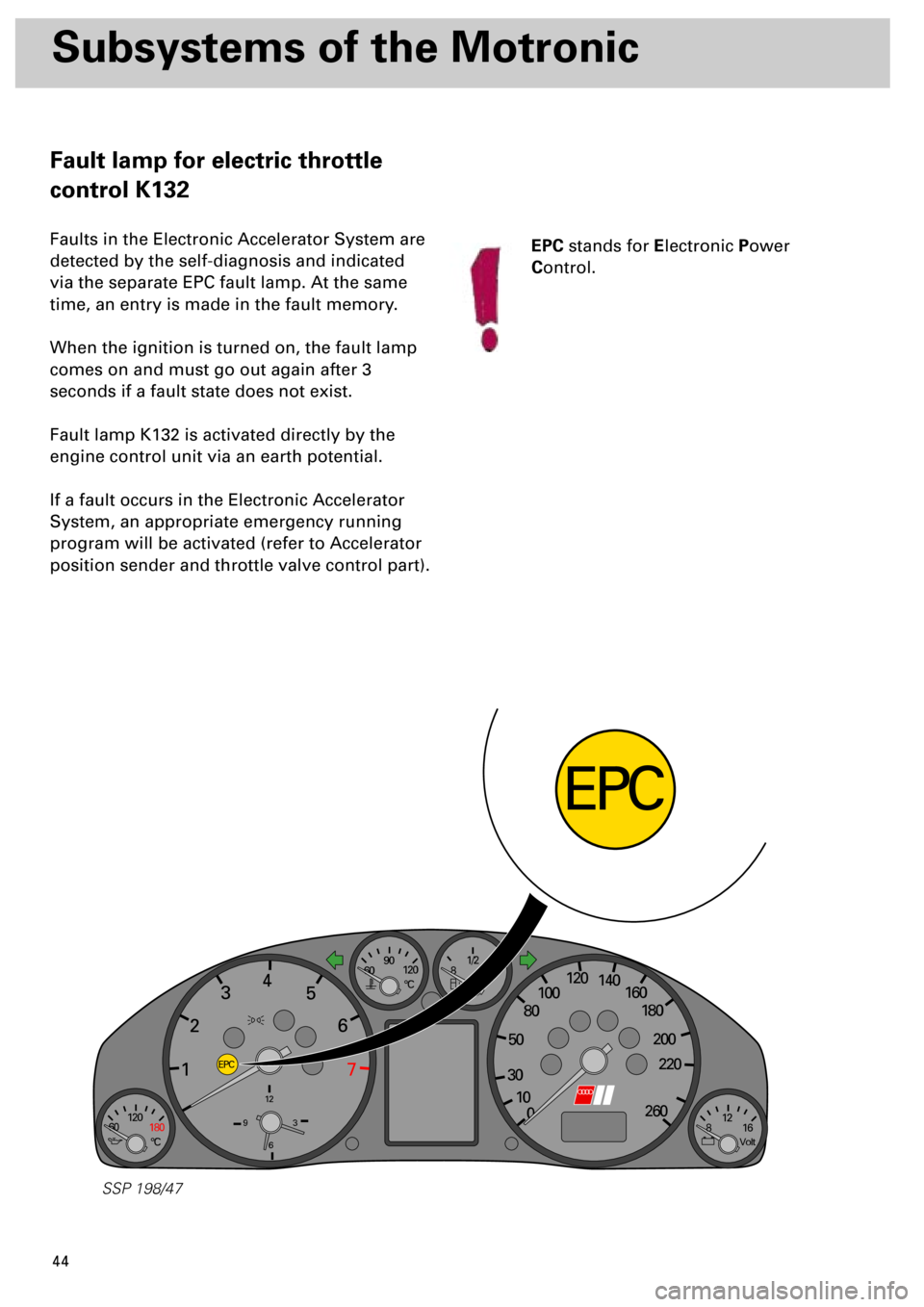
Fault lamp for electric throttle
control K132
Faults in the Electronic Accelerator System are
detected by the self-diagnosis and indicated
via the separate EPC fault lamp. At the same
time, an entry is made in the fault memory.
When the ignition is turned on, the fault lamp
comes on and must go out again after 3
seconds if a fault state does not exist.
Fault lamp K132 is activated directly by the
engine control unit via an earth potential.
If a fault occurs in the Electronic Accelerator
System, an appropriate emergency running
program will be activated (refer to Accelerator
position sender and throttle valve control part).
EPC
stands for
E
lectronic
P
ower
C
ontrol.
Page 48 of 72

49
Sensors
Charge pressure sender G31
The charge pressure sender is located
upstream of the throttle valve control part.
The Motronic supplies the sender with a
voltage of 5 volts and earth.
The signal which the sender generates is a
pressure- proportional voltage ranging from 0
to 5 volts.
At atmospheric pressure (at sea-level), the
voltage is approx. 2.5 volts.
The signal is used for charge pressure control.
The Motronic also needs information on
charge pressure so that it can take counter-
measures if the maximum permissible
pressure is exceeded.
Substitute function and self-diagnosis:
If sender G31 fails, the charge pressure is
controlled via the characteristic curve (engine
speed-dependent). This will result in a
deficiency of engine power.
SSP 198/29
Charge pressure sender G31
The altitude sender F96 ....
... is integrated in the engine control unit, as is
normally the case with turbocharged engines.
... is required to control the charge pressure. In
conditions of decreasing air pressure (lower
density), the charge pressure is reduced to
prevent the turbocharger overspeeding.
... influences the air/fuel mixture composition
at engine start-up. The starting mixture is
leaned down with rising altitude.Substitute function and self-diagnosis
If a signal fails, the charge pressure is reduced
to a safe level, which results in a deficiency of
engine power.
Adaption of the injection quantity at start-up
no longer takes place.
The fault message “Control unit defective“ is
displayed in the self-diagnosis.
The following chapter presents the new features of the sensors, provided that they have not
already been described in the chapter on Subsystems of Motronic.
Page 49 of 72

50
SSP 198/16
Sensors
The hot-film air mass meter
operates on the same principle as
before.
In certain engine operating states,
pulsations occur in the intake tract,
reversing the air flow - and this
gives rise to measurement errors.
The hot-film air mass meter is designed in such
a way that it is able to recognise this returning
air flow (pulsation fault).
This more exact method of intake air
measurement in all operating states improves
engine management and reduces exhaust
emissions.
The hot-film air mass meter is a thermal
flowmeter. A partial airflow from the
measuring pipe is fed past the sensor element
through a measuring channel in the air mass
meter housing.
The ascertained temperature values are
evaluated in the evaluation electronics. The
Motronic applies a voltage proportional to the
air mass to the air mass meter. This voltage is
needed to calculate the injection period and of
actual engine torque.
Substitute function and self-diagnosis:
The air mass meter detects air masses above
or below predefined limits. If the air mass
meter fails, the air mass is calculated on the
basis of a characteristic curve (throttle valve
angle and engine speed).
Hot-film air mass meter
Sensor element
Meas.
channel
Evaluation electronics
Hot-film air mass meter G70
Page 55 of 72

56
Sensors
Brake light switch F and brake
pedal switch F47The information “brake operated“ is required
for the following functions:
• Function of cruise control system
• Safety interrogation of electronic accelerator
function (idling speed recognition during
emergency running mode of accelerator
position sender)
Brake light switch F and brake pedal switch F47
are combined as a unit. Both serve as
information senders for “brake operated“,
which means they are redundant (for safety
reasons).
Brake light switch F is open in the “off”
position and is supplied with voltage from
terminal 30. It serves as an additional
information input for the Motronic.
Brake pedal switch F47 is closed in the “off”
position closed and is supplied with voltage
from terminal 15. It serves exclusively as an
information input for the Motronic.
Substitute function and self-diagnosis:
The two switches are cross-checked for
plausibility by the self-diagnosis.
Please read the note on the “Safety function“
on page 39.
Clutch pedal switch F36 ...
Wrong settings, electrical malfunctions or maloperation (driver keeps foot on clutch
pedal) may result in load change jolts or engine speed overshoots.
... switches the cruise control system off.
... deactivates the load change functions during the gearshift operation. The load change
function is controlled via ignition angle intervention and throttle valve closing speed.
The clutch pedal switch is closed in the “off” position and is supplied with voltage from terminal
15.
Substitute function and self-diagnosis:
The F36 is not included in the self-diagnosis, which means that no substitute functions are
initiated.
SSP 198/63
Brake light switch F and
brake pedal switch F47
Clutch pedal switch F36
Page 61 of 72
62
Functional diagram
Components:
F Brake light switch
F36 Clutch pedal switch
F47 Brake pedal switch
F96 Altitude sender (integrated in engine
control unit)
G2 Coolant temperature sender
G6 Fuel pump
G28 Engine speed sender
G31 Charge pressure sender
G39 Lambda probe (cylinder bank 1)
G40 Hall sender (cylinder bank 2)
G42 Intake air temperature sender
G 61 Knock sensor (cylinder bank 1)
G62 Coolant temperature sender
G66 Knock sensor (cylinder bank 2)
G70 Air mass meter
G79 Accelerator position sender 1
G108 Lambda probe (cylinder bank 2)
G163 Hall sender (cylinder bank 1)
G185 Accelerator position sender 2
G186 Throttle valve drive (electric throttle
control)
G187 Angle sender 1 for throttle valve drive
G188 Angle sender 2 for throttle valve drive
G235 Sender 1 for exhaust gas temperature
G236 Sender 2 for exhaust gas temperature
J17 Fuel pump relay
J220 Motronic control unit
J338 throttle valve control part
K132 Warning lamp for electric throttle
control
N Ignition coil, cylinder 1
N30 Injector, cylinder 1
N31 Injector, cylinder 2
N32 Injector, cylinder 3
N33 Injector , cylinder 4
N75 Solenoid valve for charge pressure
control
N80 Solenoid valve for activated charcoal
canister
N83 Injector, cylinder 5
N84 Injector, cylinder 6
N122 Output stage (cylinder bank 1)
N128 Ignition coil, cylinder 2
N158 Ignition coil, cylinder 3
N163 Ignition coil, cylinder 4
N164 Ignition coil, cylinder 5N189 Ignition coil, cylinder 6
N192 Output stage (cylinder bank 2)
N205 Camshaft adjustment valve 1 (cylinder
bank 1)
N208 Camshaft adjustment valve 2
(cylinder bank 2)
N249 Divert air valve for turbocharger
Z19 Heater for lambda probe
Z28 Heater for lambda probe 2
I To dash panel insert
II To dash panel insert (warning lamp)
Additional signals
1 CAN-high (automatic gearbox)
2 CAN-low (automatic gearbox)
3 „Set/decelerate“ signal for cruise
control system
4 “Off“ signal without cancellation for
cruise control system
5 “On/Off“ signal with cancellation for
cruise control system
6 Resume/accelerate“ signal for cruise
control system
7 Road speed signal
8 Immobiliser/diagnosis signal
9 Air conditioner compressor “On/Off“
signal
10 Coolant temperature signal
11 Engine speed signal
12 Fuel consumption signal
Colour codes:
Input signal
Output signal
Positive
Earth
Bidirectional