1997 HONDA CIVIC Automatic trans
[x] Cancel search: Automatic transPage 371 of 2189
Troubleshooting
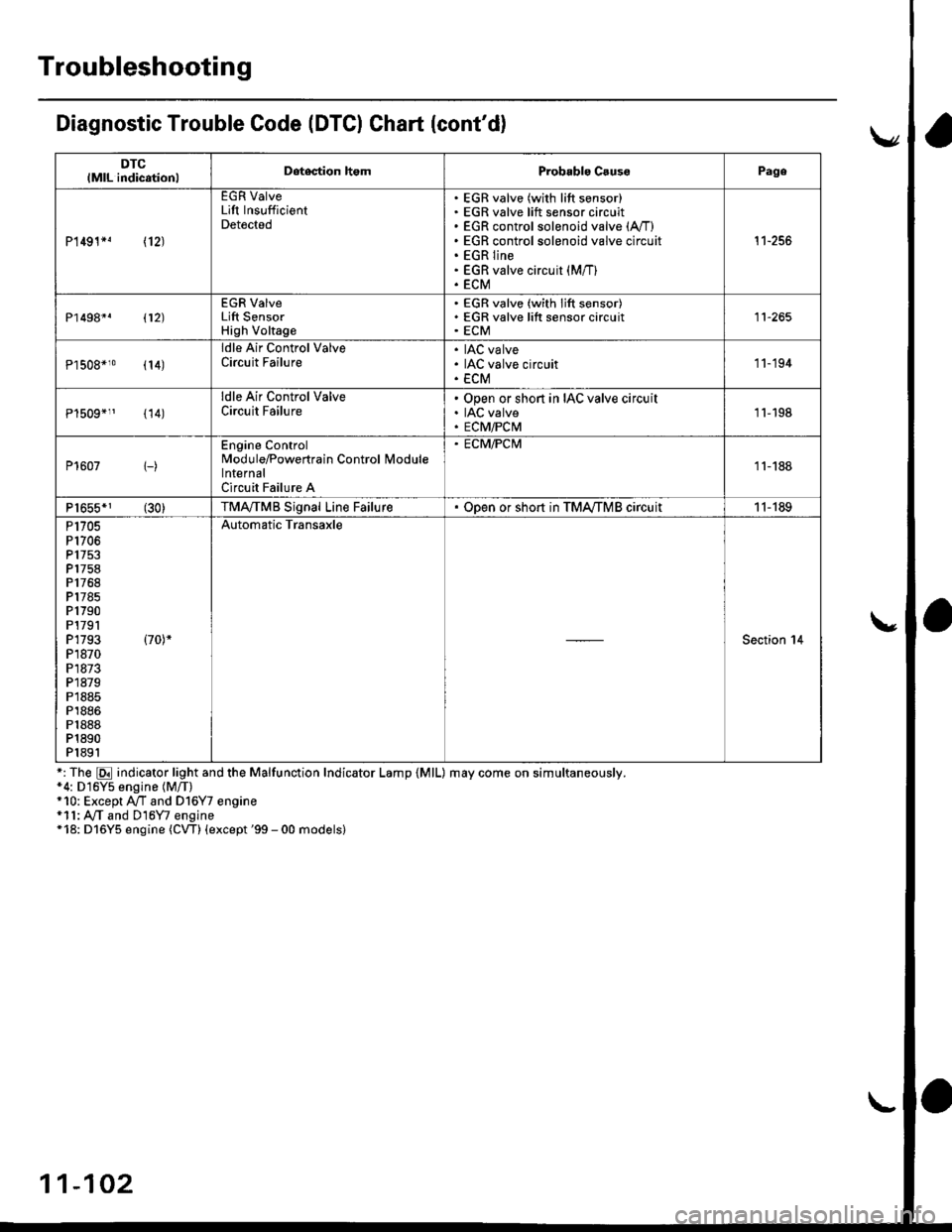
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTCI Ghart (cont'd)
DTClMlL indicationlDetegtion homProbablo CsussPage
P1491*! \12J
EGR ValveLift InsufficientDetected
EGR valve (with lift sensor)EGR valve lift sensor circuitEGR control solenoid valve (A,/I)
EGR control solenoid valve circuitEGR lineEGR valve circuit (M/T)
ECM
't1-256
P1498*. 112)
EGR ValveLift SensorHigh Voltage
EGR valve (with lift sensor)EGR valve lift sensor circuitECM11-265
Pl508*10 (14)
ldle Air Control ValveCircuit FailureIAC valveIAC valve circuitECM
'11-194
{14)
ldle Air Control ValveCircuit FailureOpen or short in IAC valve circuitIAC valveECM/PCM1l-198
P1607 1-)
Engine ControlModule/Powertrain Control lvlodulelnternalCircuit Failure A
. ECM/PCM
11-188
P1655*1 (30)TMA,/TMB Signal Line FailureODen or sho.t in TMA,/TMB circuit11-189
P1705P1706P 1753P1758P1768P1785P1790P1791P1793 (70)*
P1870P1873P1879P1885P1886P1888P1890P1891
Automatic Transaxle
Section 14
*: The E indicator light and the Malfunction Indicator Lamp {MlL) may come on simultaneously.*4: D16Y5 engine (M/T)+10: Except A/T and Dl6Y7 engine*11: A,/T and D16Y7 engine*18: D16Y5 engine (CW) (except '99 - 00 models)
11-102
Page 485 of 2189
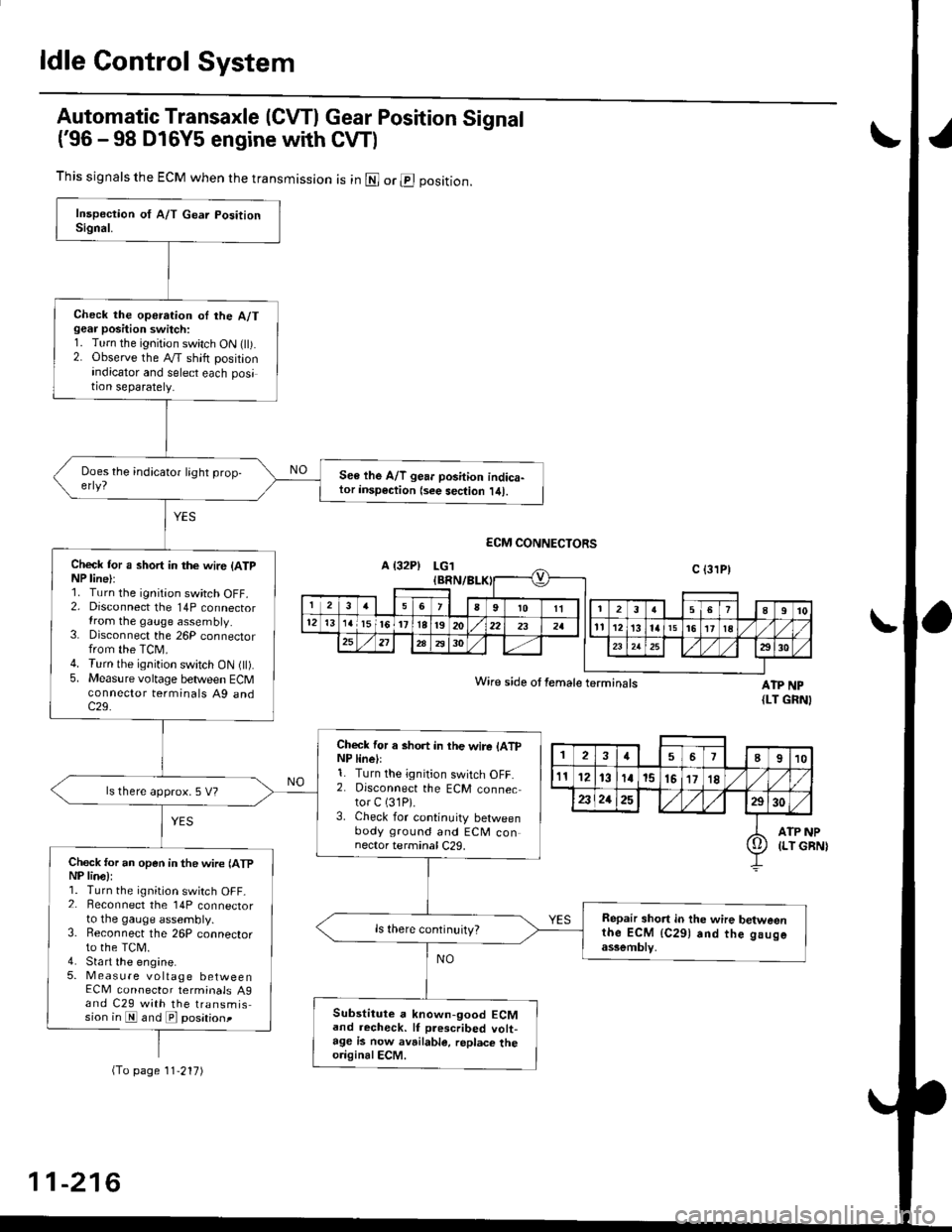
ldle Control System
Automatic Transaxle (CVTI Gear Position Signal
('96 -98 D16Y5 engine with CW)
ATP NP{LT GRNI
INP
GBN)
This signals the ECM when the transmission is in @ or @ position.
Check the operation oI the A/Tgear position switch:1. Turn the ignition switch ON flt).2. Observe the A/T shift positionindicator and select each position separately.
See lhe A/T gear position indica-tor insp€ction {see sec{ion l/tl.
Check tor a short in the wir6 (ATpNP line):1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the 14P connectorIrom the gauge assembly.3. Disconnect the 26P connectorfrom the TCM.4. Turn the ignition switch ON fll).5. Measure voltage between ECMconnector terminals A9 andc29.
Check for a short in the wire lATpNP linell1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the ECM connector C (31P).
3. Check for continuity betweenbody ground and ECM connector terminal C29.
ls there approx. 5 V?
Check for an open in the wire lATpNP lina):1. Turn the ignition switch OFF_2. Beconnect the 14P connectorto the gauge assembly.3. Reconnect the 26P connectorto the TCM.4. Sta rt the engine.5. Measure voltage betweenECM connector terminals A9and C29 with the transmission in E and E posationt
Repair short in the wire betweenthe ECM {C291 and the gaugeassemblv,
Substitute a known-good ECMand recheck. lf prescribed volt-age is now avrilable, replace theo.iginalECM.
Wire side ot female terminals
2457I910
t112131a15151718
2321252930
ATP(LT io
(To page 11'217)
11-216
Page 567 of 2189

J
Transaxle
cf utch .""""" 12'1
Manual Transmission ............"'.'..".'...'. 13-1
Automatic Transmission ........ "........ " ". 1 4-1
Differential ... 15-1
Driveshafts ." 16-1
Page 678 of 2189
Automatic Transmission
Automatic Transmission'.... "'..'.. "...'..' 14-1
Continuously Variable Transmission
(Cy1l .......... 14-193
t
ro
Page 679 of 2189

Automatic Transmission
Special Tools ......... .....'."".'-.-.' 14'2
Description .,....................-...... 14-3
power Flow ......,................. 14"6
Elestronic Control System .... . ................'..'.'.. 14-13
Hvdraulic Control .....'......" 1'l-19
Hydraulic F|ow...... .'.'.".'....11-21
Lock-up System '............ ... t/t'33
Electrical System
Component Locations....,.............'......'.............'.,. 14'39
PCM Circuit Diagram
lA/T Control Syst€m: '96 - 98 Models) .........'.. 1/t-40
PCM Tarminal Volt8ge/Measuring Condhions
{'96 - 98 ModeblA/T Control System ............
PCM Circuit Disgram(A/T Conlrol System: '99 - 00 Modsls) '..........' 14-44
PCM Terminal Voltage/Measuring Conditions('99 - 00 Models)A/T Control System ...
Troubleshooting Proceduros ....
Symptom-to-ComPonent Chari
Efectricaf SFiem - '96 - 98 Models '..-.-..."'.'..11-52
Eloqtrical System -'99 - 00 Modols ... .........". 1+54
EleclricatTroubl$hooting ('96 - 98 Models)
Valve Body
Repair .................... ........'.... 14-139
Valve
Assembly
ATF Pump
1,1-1i10
Inspection ...........'.......... 14-141
Main Valvs Body
Disass€mbf y/lnspoction/R.sssembly .'.'.'.'.. -. -. 1 1-1 12
Secondsry Valve BodY
Disa$embfy/lnspoction/Rsassembly ......'.'.'.'. 11-111
Regulator Valve Body
Disa$embly/lnspoction/Rea3sembly ..........'... 14-1{5
Servo Body
Disassombly/lnsp€ction/Reassembly .".'........ 14-146
Lock-up Valv6 Body
Dis$s.mbf y/ln3poction/Rea$embly .'.. -. -..'.'.' 1 1-1 17
Mainsh!ft
Dkassembly/lnep€ction Reassembly ..'...'........ 14'148
Inspoction .............'..........'. l it-149
Countsrshaft
Disa$embly/lnspeqtion/Rea3sembly .......'...'.. 1a-l51
Dba$ombly/Re$s.mblY11-152
til-46
I rl-48
Troubleshooting Flowcharts
Electrical Troubleshooting ('9!t - 00 Models)
Troublsshooting Flowchart3
Lock-up Control Solenoid vslvo A/B AssemblY
RePlacoment
Shift Cont.ol Solenoid Valve A/B A3sembly
Inspestion
Ona-way Clutch
Disassembh/lrupoction/Rca$embly .. "'........ l4-155
Clutch
lllustlttcd Ind.x {A48A, B4RA Transmlssion) ..' 14-156
tustr.tod Index (MrnA Transmi$ionl ............ til-158
...................... 14-153
L
14-56
1+81'
14-105
1+105
Replacoment ......
Mainshaft/Countorshaft Spo€d Sonsors
Replacemsnt ......'."'........... lit'108
Hydraulic System
Symptom-to-Componeni Chart
Hydraulic Sydemr+109
t4-113
1+116
11-117
Rea$emblY
14-106 Difforrr ial
llhdraied Index........ t4-156
B.ckhrh ln3poction. 14-167
Boaring Roplacemont..-..........11-167
..... 14-108 Diftrrsniial Carrior Repl8cemeni .'.-.............'...' lil-168
Oil Sall Romovalt4-t 59
Oil Soal ln3tallstion/Sidc Clearance'......'.....'... 1'l'169
Torqua Convertcr Housing Boarings
Mlin3haft Besring/Oil Scal Roplac.ment ."..'.. lil-172
Counio6hatt Betring R.plscem.nt ..'...... ....... 14-173
Test.....,......14-106
14-107
14-160
11-162
11-171
11-175
Replacement
Test .....,.,..........
Road Te3t
Linear Solenoid AsssmblY
Stall Speed
lllustrated Indax
Transmission/End Cover'. ....
Transmission Hou3ing,.............'.'......'....""..-.-.. 11-128
Torque Conve.ter Housing/Valvo Body ........... 14-130
End Cover
14-itB Park Stop
1+119 In3pection/Adiustmsnt...'......'.'............'...."""'14-175
Transmbgion
Reassombly
11-122 Torquo Convertet/Drivr Plsie ............'.'............'.. . l4-182
Transmission
11.726 Inrtallation
Tranlmission Housing Boarings
Msinsh.ft /CounteEhaft Bearings
B!pltcomgnt
Rcvo.3s ldlor Gear
lnrtallation
Cooler Flushing ..
Shift Cabls
Test
Fluid Level
Checkin9 .........."..'.'.....
Changing
Pressure Testing
Transmission
Transmission
Rgmoval ..
lil-176
.'..........'.'.'..... 1'l-183
.... lil-187
11-132Adiustmont
RemovaUlnttallation1,1-190
lit-191Transmisgion Housing
Removal ... '.'...... ......'..... 14-l3il
Tolque Convgrter Housing/valvs Body
Rsmoval .........,...... ............. 14-136
Valve CaDs
Description .......'................. t 4'138
Shift lndicator Panel
Adiu3tmant ..'.................. 14-192
ATF Coolor Hoses
Connection ..,............,.,....... l'l-192
Shift Lever .,........
Page 681 of 2189

Description
The automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides
4 soeeds forward and 1 reverse.
Torque Convertel, Geats, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator, assembled in a single unit. They are connected to the engine
crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is a ring gear
which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started. The entire torque converter assembly seryes as a
flywheel while transmiuing power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in Iine with the engine
crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd and 4th clutches, gears tor 2nd, 4th, reverse and lst (3rd gear is integral
with the mainshaft, while the reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch, and
gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse. 1st and park. The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the counter-
shaft. When certain combinations of gears in transmission are engaged by clutches. power is transmitted from the main-
shaft to the countershaft to provide E, ld, E, and E positions.
Electronic Control
The electronic control svstem consists of the Powertrain Control Module {PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four
solenojd valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comtonable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main vatve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body and the
lock-up valve body through the respective separator plates, They are bolted on the torque converter housang
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve. the 2nd orifice control valve, the CPB {Clutch Pressure
Back-up) valve, the modulator valve. the servo control valve, the relief valve, and ATF pump gears The secondary valve
body contains the 2-3 shift valve. the 3-4 shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch
pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve,
the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up control valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the
reverse shift fork, and the accumulators. The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing
valve. The linear solenoid and the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid from regulator
passes through the manual valve to the various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective teed pipes
or internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will activate
Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes a line
to one of the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear, The shift control solenoid valves A and B are con-
trolled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
In ,Dt1 position, in 3rd and 4th. and in E position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter
through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the PCM optimizes the timing of
the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and
B, and linear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes The lock-
up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
(cont'd)
14-3
Page 682 of 2189

Description
(cont'dl
Gear Selection
The shift lever has six positions: E PARK. E REVERSE, N NEUTRAL, E 1st through 4th gear ranges, E 1st through 3rdgear ranges, @ 2nd gear.
Starting is possible only in E and E positions through the use of a slide-type, neutral-safety switch.
Automatic Transaxle (A/f, Gear Position Indicator
The Ay'T gear position indicator in the instrument panel shows which gear has been selected without having to look downat the console.
Clutch€s
The four-speed automatic transmission uses hydraulically-actuated clutches to engage or disengage the transmission gears.When hydraulic pressure is introduced into the clutch drum, the clutch piston moves. This presses the friction discs andsteel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is then transmitted through the engaged clutch pack to itshub-mounted gear. Likewise, when the hydraulic pressure is bled from the clutch pack, the piston releases the friction discsand the steel plates, and they are free to slide past each other. This allows the gear to spin independently on its shaft,transmitting no power.
lst Clutch
The 1st clutch engages/disengages 1st gear, and is located at the end of the mainshaft, just behind the right sroe cover.The 1st clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the mainshaft.
2nd Clulch
The 2nd clutch engagegdisengages 2nd gear, and is located at the middle of the mainshaft. The 2nd clutch is joined
back-to-back to the 4th clutch. The 2nd clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure through the mainshaft by a circutr connect-ed to the internal hvdraulic circuit,
3rd Clutch
The 3rd clutch engages/disengages 3rd gear, and is located at the end of the countershaft. The 3rd clutch is suooliedhydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the countershaft.
ilth Clutch
The 4th clutch engages/disengages 4th gear, as well as reverse gear, and is located at the middle of the mainshaft. The4th clutch is joined back-to-back to the 2nd clutch. The 4th clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipewith in the mainshaft.
\-a
PositionDe3cription
E PARK
E REVERSE
N NEUTRAL
E DRIVE
{1st through 4th)
Ei DRtvE('lst through 3rd)
B SECOND
Front wheels locked; park pawl engaged with pa* on countershaft. All clutches released.
Reverse; reverse selector engaged with countershaft reverse gear and 4th clutch locked.
All clutches released.
General driving; starts off in 1st, shifts automatically to 2nd, 3rd, then 4th, depending on vehiclespeed and throttle position. Downshift through 3rd, 2nd and 1st on deceleration to stop. The lock-upmechanism comes into operation in @ position in 3rd and 4th gear.
Use for rapid acceleration at highway speeds and general driving; up-hill and down,hill dfiving; stansotf in 1st, shifts automatically to 2nd, then 3rd, depending on vehicle speed and throttle position.
Downshifts through 2nd to lst on deceleration to stop. The lock-up mechanism comes into operationin 3rd gear,
Use for engine braking or better traction starting off on loose or slippery surfaces; stays in 2ndgear, does not shift up and down.
14-4
Page 686 of 2189

Description
Power Flow (cont'dl
lst Gesr (E or @ position)
In lE or E position, the optimum gear is automatically selected from 1st,2nd,3rd and 4th gears, according to conditionssuch as the balance between throttle opening (engine load) and vehicle speed.
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 1st clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, causing the mainshaft 1stgear to rotate.
Power is transmitted to the countershaft 1st gear, which drives the countershaft via the one-way clutch.
Power is transmitted to the final drive gear, which drives the final driven gear.
TOROUE CONVERTER
MAINSHAFT 1ST GEAR
lST CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
AY CLUTCH
FINAL DRIVE GEAR
PARK GEAR
L
COUNTERSHAFT1ST GEAR
14-8