1997 HONDA CIVIC Start
[x] Cancel search: StartPage 681 of 2189

Description
The automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides
4 soeeds forward and 1 reverse.
Torque Convertel, Geats, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator, assembled in a single unit. They are connected to the engine
crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is a ring gear
which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started. The entire torque converter assembly seryes as a
flywheel while transmiuing power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in Iine with the engine
crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd and 4th clutches, gears tor 2nd, 4th, reverse and lst (3rd gear is integral
with the mainshaft, while the reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch, and
gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse. 1st and park. The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the counter-
shaft. When certain combinations of gears in transmission are engaged by clutches. power is transmitted from the main-
shaft to the countershaft to provide E, ld, E, and E positions.
Electronic Control
The electronic control svstem consists of the Powertrain Control Module {PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four
solenojd valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comtonable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main vatve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body and the
lock-up valve body through the respective separator plates, They are bolted on the torque converter housang
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve. the 2nd orifice control valve, the CPB {Clutch Pressure
Back-up) valve, the modulator valve. the servo control valve, the relief valve, and ATF pump gears The secondary valve
body contains the 2-3 shift valve. the 3-4 shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch
pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve,
the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up control valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the
reverse shift fork, and the accumulators. The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing
valve. The linear solenoid and the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid from regulator
passes through the manual valve to the various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective teed pipes
or internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will activate
Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes a line
to one of the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear, The shift control solenoid valves A and B are con-
trolled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
In ,Dt1 position, in 3rd and 4th. and in E position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter
through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the PCM optimizes the timing of
the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and
B, and linear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes The lock-
up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
(cont'd)
14-3
Page 682 of 2189

Description
(cont'dl
Gear Selection
The shift lever has six positions: E PARK. E REVERSE, N NEUTRAL, E 1st through 4th gear ranges, E 1st through 3rdgear ranges, @ 2nd gear.
Starting is possible only in E and E positions through the use of a slide-type, neutral-safety switch.
Automatic Transaxle (A/f, Gear Position Indicator
The Ay'T gear position indicator in the instrument panel shows which gear has been selected without having to look downat the console.
Clutch€s
The four-speed automatic transmission uses hydraulically-actuated clutches to engage or disengage the transmission gears.When hydraulic pressure is introduced into the clutch drum, the clutch piston moves. This presses the friction discs andsteel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is then transmitted through the engaged clutch pack to itshub-mounted gear. Likewise, when the hydraulic pressure is bled from the clutch pack, the piston releases the friction discsand the steel plates, and they are free to slide past each other. This allows the gear to spin independently on its shaft,transmitting no power.
lst Clutch
The 1st clutch engages/disengages 1st gear, and is located at the end of the mainshaft, just behind the right sroe cover.The 1st clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the mainshaft.
2nd Clulch
The 2nd clutch engagegdisengages 2nd gear, and is located at the middle of the mainshaft. The 2nd clutch is joined
back-to-back to the 4th clutch. The 2nd clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure through the mainshaft by a circutr connect-ed to the internal hvdraulic circuit,
3rd Clutch
The 3rd clutch engages/disengages 3rd gear, and is located at the end of the countershaft. The 3rd clutch is suooliedhydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the countershaft.
ilth Clutch
The 4th clutch engages/disengages 4th gear, as well as reverse gear, and is located at the middle of the mainshaft. The4th clutch is joined back-to-back to the 2nd clutch. The 4th clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipewith in the mainshaft.
\-a
PositionDe3cription
E PARK
E REVERSE
N NEUTRAL
E DRIVE
{1st through 4th)
Ei DRtvE('lst through 3rd)
B SECOND
Front wheels locked; park pawl engaged with pa* on countershaft. All clutches released.
Reverse; reverse selector engaged with countershaft reverse gear and 4th clutch locked.
All clutches released.
General driving; starts off in 1st, shifts automatically to 2nd, 3rd, then 4th, depending on vehiclespeed and throttle position. Downshift through 3rd, 2nd and 1st on deceleration to stop. The lock-upmechanism comes into operation in @ position in 3rd and 4th gear.
Use for rapid acceleration at highway speeds and general driving; up-hill and down,hill dfiving; stansotf in 1st, shifts automatically to 2nd, then 3rd, depending on vehicle speed and throttle position.
Downshifts through 2nd to lst on deceleration to stop. The lock-up mechanism comes into operationin 3rd gear,
Use for engine braking or better traction starting off on loose or slippery surfaces; stays in 2ndgear, does not shift up and down.
14-4
Page 703 of 2189
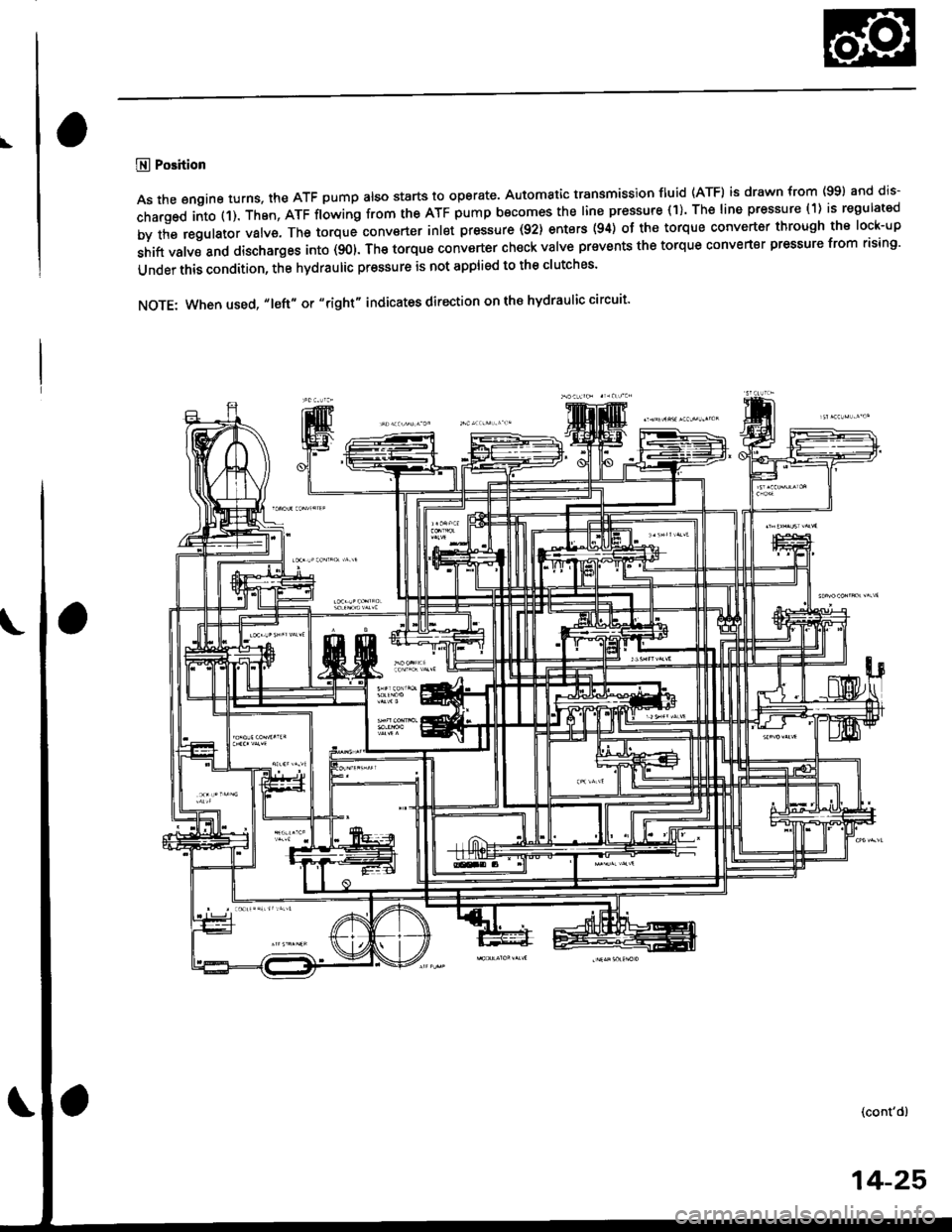
\
@ Position
As the engine turns, the ATF pump also starts to operate, Automatic transmission fluid (ATF) is drawn from (99) and dis-
charged into (1). Then, ATF flowing from the ATF pump becomes the line pressure (1). The line pressure (1) is regulated
by the regulator valve. The torque conv€rter inlet pressure (92) enters (94) of the torque converter through the lock-up
shift valve and discharges into (901. The torque converter ch€ck valve prevents the torque converter pressure from rising'
Under this condition, the hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches'
NOTE: When used, "1eft" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit'
14-25
Page 722 of 2189
![HONDA CIVIC 1997 6.G Workshop Manual PCM Gircuit Diagram (A/T Gontrol System:99 - 00 Models)
UNOEF DASIFL]SE/FELAY BOX
ta T06 T Dr.
INT€RLOCKCCNTFOLuN|l
ert*rll
I STARTEF
r-->lIl__ sL!
I
UISEF,DASHFISSIEL YmXr,Jo 25 (7 5A) GAUGE ISSEM HONDA CIVIC 1997 6.G Workshop Manual PCM Gircuit Diagram (A/T Gontrol System:99 - 00 Models)
UNOEF DASIFL]SE/FELAY BOX
ta T06 T Dr.
INT€RLOCKCCNTFOLuN|l
ert*rll
I STARTEF
r-->lIl__ sL!
I
UISEF,DASHFISSIEL YmXr,Jo 25 (7 5A) GAUGE ISSEM](/manual-img/13/6068/w960_6068-721.png)
PCM Gircuit Diagram (A/T Gontrol System:'99 - 00 Models)
UNOEF DASIFL]SE/FELAY BOX
ta T06 T Dr.
INT€RLOCKCCNTFOLuN|l
ert*rll
I STARTEF
r-->lIl__ sL!
I
UISEF,DASHFISSIEL YmXr,Jo 25 (7 5A) GAUGE ISSEMBLY
Lr GRN -----l l"-- LTGRll
L eultru ----iF erk€Lu
14-44
Page 787 of 2189

Symptom-to-Component Chart
Hydraulic System
SYMPTOMCheck these items on the Check lhese lems on
PROBABLE CAUSE List the NOTES LIst
Engine runs, but vehicle does not move in any gear.1.2,3,5,6,7.36,38 K, L, R, S
Vehicle moves in E, E, but not in lrl, pr-, position.6, 8, 9, 10, 30, 54c,M,o
Vehicle moves in Dl, E, El,lut not in E position.6,11,12.24C,L
Vehicle moves in -o1], @, @, Uut not in E position.4, 6, 14, 15c,L,o
Vehicle moves in E position.10, 12, 13,14, 16, 29, 33, 34, 35C,D
Excessive idle vibration.1.2, 19,32,36, 45, 41, 4a
Poor acceleration; flares on starting otf in E, [Dl] position
Stall rpm hiqh in !!1, p!1, E position.1,2,3,6,34, 41K,L,R
stall rom hioh in D.r, lD,l oosition.6. 8. 10C,D
5t"[ rprn rsn ^ a"t"t-at6,12C,D
14N
11 , 32. 45, 41 , 48
No shift19,20, 40, 48, 49G,L
Fails to shift in 81, pll position; from lst to 3rd gear22, 49
Fails to shift in 03, D. oosition; from lstto4th qear22.23, 48
Erratic upshifting.
1'2 upshift, 2-3 upshift, 3-4 upshift
1-2 upshift
3'4 upshift
58
21, 48
22, t9
23,la
Harsh upshift {1 2).12, 19, 20, 29. 50, 51, 57. 54
Harsh upshift (2'3).13, 19, 20, 24, 27 , 29, 50. 51 , 51 , 58C,D,E,H,L
Harsh upshift (3'4).14, 19, 20, 25, 28, 29. 50, 51 , 51 , IC, D, E, I,L
Harsh downshift (2-1)19, 20. 24, 43, 54, 57 , 58o
Harsh downshift (3-2).12, 19, 20,25, 43, 55, 57,5AC,D,E,H
Harsh downshift (4-3).13, 19, 20, 26, 43, 56, 57, 58C, D, E, I
Flares on 2-3 upshift.13, 19,20,24.21,51FI
Flares on 3-4 upshift.14, 19 . 20, 25. 24, 51E,L,N
Excessive shock on 2-3 uPshift.13. 19, 20, 24, 27 . 43. 50. 51 , 58E,L,N
Excessive shock on 3-4 uPshift.14, 19, 20, 25. 2A, 8, 50, 51 , 58E,L,N
Late shift from El position to Lq! or &l position.10, 30
Late shift from E position to E position.4, 14, 21,53o
Noise from transmission in all shift lever positions2,31K,L,O
Vehicle does not acceletate more than 31 mph {50 km/h)17
shift lever does not operate smoothly.6, 39P
Fails to shift; stuck in 4th gear.19, 48, 49
Transmission will not shift into park in [a] position6, 18, 39
Stall rpm high; all clutch pressures are in specification.41D,K,O
Lock up clutch does not disengage.19, 44, 45, 46. 41,50,51.54
Lock up clutch does not operate smoothly.19, 41, 44, 45, 46, 47, 50, 51, 58L
Lock-up clutch does not engage.19, 41, 4t, 15, 46, 41 ,50, 51, 57, 58FI
Vibration in all positions
(cont'd)
Page 791 of 2189
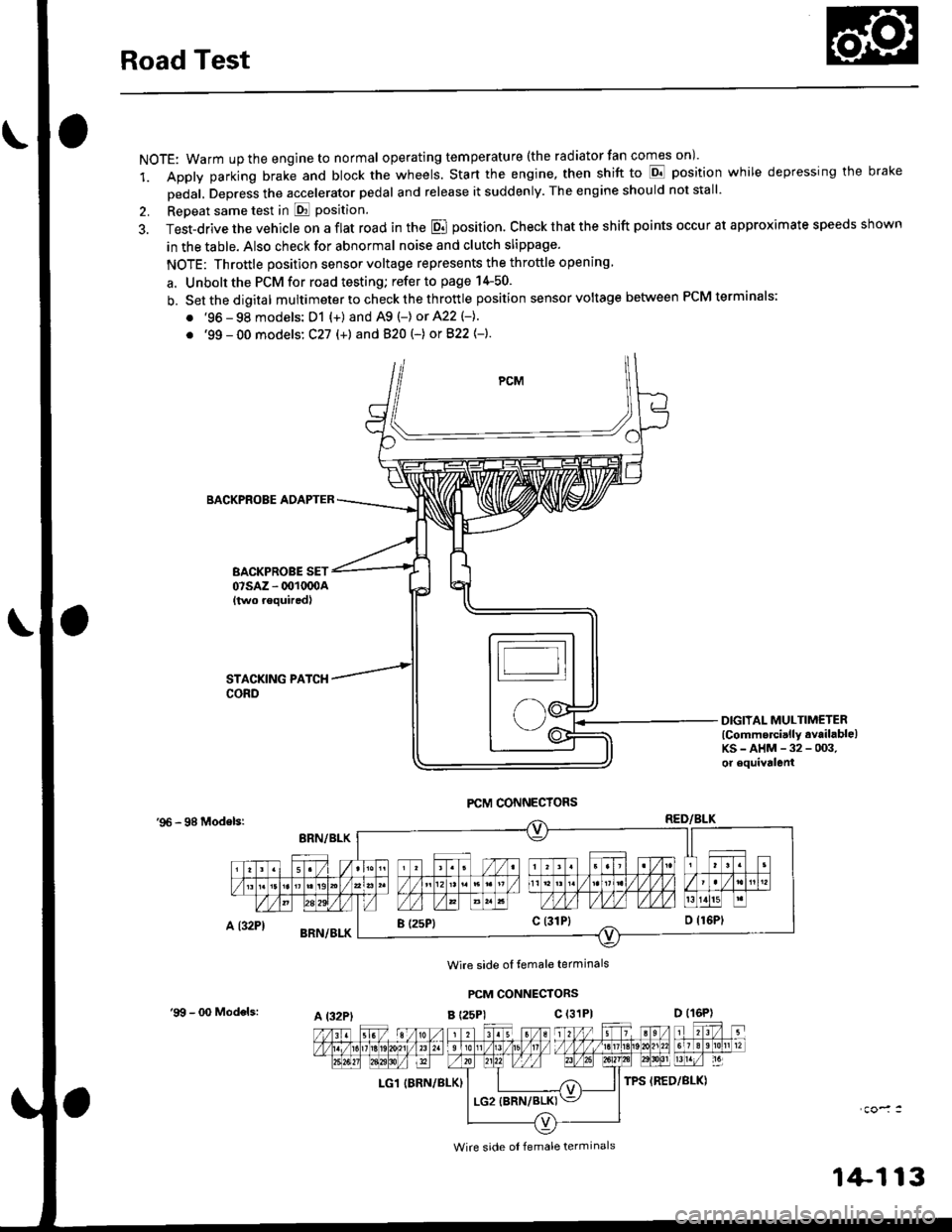
Road Test
NOTE: Warm up the engine to normal operating tem peratu re (the rad iator fan comes on )'
1. Apply parking brake and block the wheels. Start the engine, then shift to E position while depressing the brake
Dedal, Depress the accelerator pedal and release it suddenly. The engine should not stall'
2. Repeat same test in E Position.
3. Test-drive the vehicle on a flat road in the E position. Check that the shift points occur at approximate speeds shown
in the table. Also check for abnormal noise and clutch slippage.
NOTE: Throttle position sensor voltage represents the throttle opening
a. Unbolt the PCM for road testing; refer to page 14-50.
b. Setthedigital multimeter to check the th rottle position sensor voltage between PCM terminals;
. '96 - 98 models: D1 {+) and A9 (-) or 422 (-}.
. '99 - 00 models: C27 (+) andB20t-) orB22{-}.
BACKPROBE ADAPTER
BACKPROBE SET07sAz - 001oq)A{two requiredl
DIGIIAL MULTIMETERlCommercially available)KS-AHM-32-003,or equivalenl
'96 - 98 Modelsr
Wire side ol temale terminals
PCM CONNECTORS
B t25Pl c (31P)
LG1 IBRN/BLK)
I (25P1c (31P}
A t32PtD (16P)
Wire side ol female terminals
'9!t - 00 Models:
1+113
Page 794 of 2189

Stall Speed
Test
CAUTION:
. To prev€nt transmission damage, do not t6st stall speed for more than ro sgconds at a time.. Do not shift the levor while raising the engine speed.. Bo sule lo remove the pressure gauge betoro testing stall speed.
'1. Engage the parking brake, and block the front wheels.
2. Connect a tachometer to the engine, and start the engine.
3. Make sure the Ay'C switch is OFF.
4. After the engine has warmed up to normal operating temperature (the radiator fan comes on). shift into E position.
5. Fully depress the brake pedal and accelerator for 6 to g seconds, and note engine speed.
6. Allow two minutes for cooling, then repeat the test in @ and @ positions.
NOTE:
. Stall speed tests should be used for diagnostic purposes only,. Stall speed should be the same in o., E and E positions.
Stall Spsed RPM:
Specification: 2.700 rpm
Service Limit: 2,550 - 2,850 rDm
TROUBLEPROBABLE CAUSE
. Low fluid level or ATF pump outDur. Clogged ATF strainer. Pressure regulator valve sluck closeo. Slipping clutch
. Slippage of 4th ctutch
. Slippage of 2nd clutch
. Slippage of lst clut"tr or. t"t g""io*-*"y "lut"h
Stall rpm high in D., E and E positions
Stall rpm high in El position
Stall rpm high in E posirion
Stall rpm high in E position
Stall rpm low in LDa . El and E positrons. Engine output low. Torque converter one-way clutch slipping
14-116
Page 797 of 2189

Pressure Testing
@I While testing, be caroful of th€ rotating front wheels.
. Make sure lifts, iacks, and satoty stands are placod properly (see section 1)'
CAUTION:
. Beforo iesting, be sure the transmission fluid is tilled to tho proper level'
. Warm up tho engine before testing'
1. Raise the vehicle (see section 1).
2. Warm up the engine, then stop the engine and connect a tachometer'
3. Connect the oil pressure gauges to each inspection hole.
TOROUE: 18 N.m (1.8 kgf'm, 13 lbnft)
cAUTloN: connact the oil pressuro gauges securely; be suro not to allow dust and other foreign Parlicles to entel
the inspestion holos'
A/T OIL PRESSURE GAUGESET w/PANEL07t06 - 0020400
A/T LOW PRESSURE GAUGE
SET WPANEL07406 - 0070300
A/T OIL PRESSURE HOSEADAPTER07Mru - PY0120(4 requiJedl
A/T OIL PBESSURE HOSE
2210 mmOTMAJ - PY4{)llA
14 roquircdl
Start the engine, and measure the respective ptessure as follows'
a Line Pressure
. 1st Clutch Pressure
. 2nd,3rd and 4th Clutch Pressure
Install a new washer and the sealing bolt in the inspection hole. and tighten to the specified torque'
TOROUE: l8 N.m (1.8 kgf'm,13lbf'ft)
NOTE: Do not reuse old sealing washers; always replace washers'
(cont'd)
14-119