1997 GMC SIERRA torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 92 of 436

AUTOMATIC OVERDRIVE (@): This position is for
normal driving. If you need more power for passing, and
you’re:
Going less than about 35 mph (56 km/h), push your
Going about 35 mph (56 km/h) or more, push the
accelerator
pedal about halfway down.
accelerator all
the way down.
You’ll shift down to the next gear and have more power.
AUTOMATIC OVERDRIVE
(a) can be used when
towing
a trailer, carrying a heavy load, driving on steep
hills or for off-road driving.
You may want to shift the
transmission to THIRD
(3) or, if necessary, a lower gear
selection if the transmission shifts too often.
THIRD (3): This position is also used for normal
driving, however it offers more power and lower
fuel
economy than AUTOMATIC OVERDRIVE (a).
SECOND (2): This position gives you more power but
lower fuel economy.
You can use SECOND (2) on hills.
It can help control your speed as you go down steep
mountain roads, but then you would also want
to use
your brakes
off and on.
If you manually select SECOND (2)’ the transmission will
drive in
second gear. You may use this feature for reducing torque to the rear wheels when you are trying
to start your
vehicle from a stop on slippery road surfaces.
FIRST (1): This position gives you even more power
(but lower fuel economy) than
SECOND (2). You can
use it on very steep hills, or in deep snow or mud. If the
selector lever is
put in FIRST (1) while the vehicle is
moving forward,
the transmission won’t shift into first
gear until the vehicle
is going slowly enough.
NOTICE:
~ ~~
If your rear wheels can’t rotate, don’t try to
drive. This might happen if you were stuck in
very deep sand or mud or were up against
a solid
object. You could damage your transmission.
Also, if you stop when going uphill, don’t hold
your vehicle there with only the accelerator
pedal. This could overheat and damage the
transmission. Use your brakes or shift into
PARK (P) to hold your vehicle in position
on a hill.
2-18
ProCarManuals.com
Page 104 of 436

If you have to leave your vehicle with the engine
running, be sure your vehicle is in PARK (P) and the
parking brake is firmly set before you leave
it. After you
move the shift lever into PARK (P), hold the regular
brake pedal down. Then,
see if you can move the shift
lever away from PARK (P) without first pulling it
toward
you. If you can, it means that the shift lever
wasn’t fully locked into PARK
(P).
Torque Lock (Automatic Transmission)
If you are parking on a hill and you don’t shift your
transmission into PARK (P) properly, the weight of the
vehicle may put
too much force on the parking pawl in
the transmission. You may find
it difficult to pull the
shift lever out of PARK (P). This is called “torque lock.”
To prevent torque lock, set the parking brake and then
shift into PARK (P) properly before you leave the
driver’s seat.
To find out how, see “Shifting Into
PARK (P)” in the Index.
When you are ready
to drive, move the shift lever out of
PARK (P)
before you release the parking brake.
If torque lock does occur, you may need to have another
vehicle push yours a little uphill
to take some of the
pressure from the parking pawl in the transmission,
so
you can pull the shift lever out of PARK (P).
Shifting Out of PARK (P)
(Automatic Transmission)
Your vehicle has a brake-transmission shift interlock
system. You have
to fully apply your regular brakes
before you can shift from PARK (P) when the ignition
is in RUN. See “Automatic Transmission” in the Index.
If you cannot shift out of PARK (P), ease pressure on
the shift lever and push the shift lever all the way up
into PARK (P) as you maintain brake application. Then,
move the shift lever to any gear you want.
If you ever hold the brake pedal down but still can’t
shift out
of PARK (P), try this:
1. Turn the key to OFF,
2. Apply and hold the brake until the end of Step 4.
3. Shift to NEUTRAL (N).
4. Start the vehicle and shift to the drive gear you want.
5. Have the brake-transmission shift interlock system
fixed as soon as you can.
2-30
ProCarManuals.com
Page 270 of 436
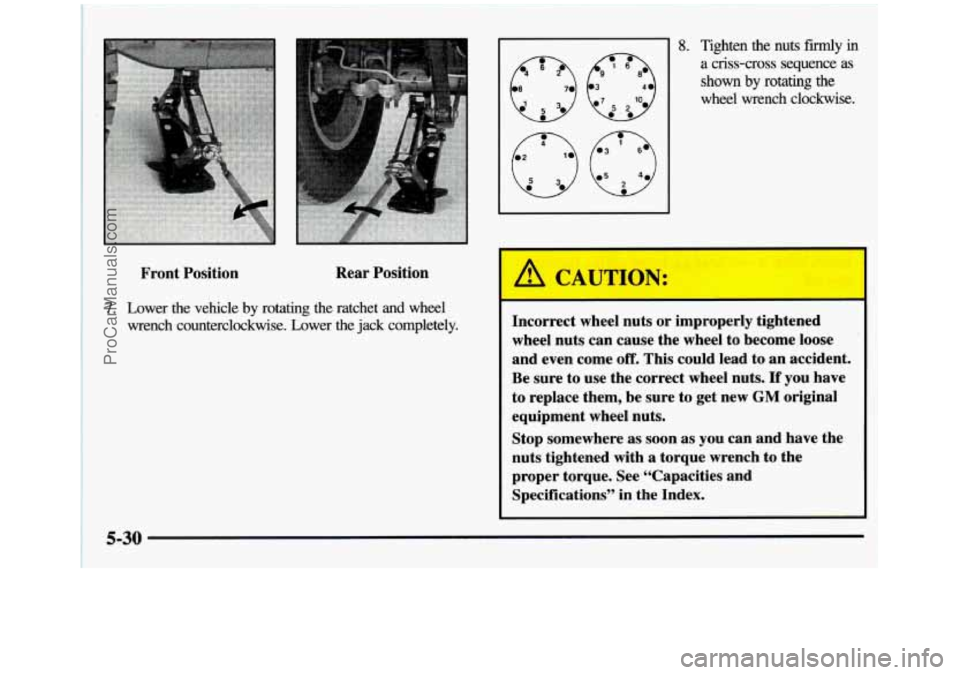
Front Position Rear
Position
7. Lower the vehicle by rotating the ratchet and wheel
wrench counterclockwise. Lower the jack completely.
- 8. Tighten the nuts fdy in
a criss-cross sequence as
shown by rotating the
wheel wrench clockwise.
A CAUTION:
Incorrect wheel nuts or improperly tightened
wheel nuts can cause the wheel to become loose
and even come
off. This could lead to an accident.
Be sure to use the correct wheel nuts.
If you have
to replace them, be sure to get new
GM original
equipment wheel nuts.
Stop somewhere as soon as you can and have the
nuts tightened with a torque wrench to the
proper torque. See “Capacities and
Specifications” in the Index.
5-30
ProCarManuals.com
Page 271 of 436

NOTICE:
Improperly tightened wheel nuts can lead to
brake pulsation and rotor damage.
To avoid
expensive brake repairs, evenly tighten the wheel
nuts in the proper sequence and
to the proper
torque specification.
9. Put the wheel trim back on. For vehicles with plastic
wheel nut caps, tighten the caps until they are finger
tight, then tighten them an additional one-half
TI
with the ratchet and wheel wrench.
Storing a Flat or Spare Tire and Tools
'A
Storing a jack, a tire or other equipment in the
passenger compartment
of the vehicle could
cause injury. In
a sudden stop or collision, loose
equipment could strike someone. Store all these
in the proper place.
Store the flat tire where the spare tire was stored.
5-31
ProCarManuals.com
Page 314 of 436

Some driving conditions or climates may cause a brake
squeal when the brakes are first applied or lightly applied.
This does not mean something is wrong with your brakes.
Properly torqued wheel nuts are necessary to help
prevent brake pulsation. When tires are rotated, inspect
brake pads for wear and evenly torque wheel nuts in the
proper sequence
to GM specifications.
If you have rear drum brakes, they don’t have wear
indicators, but if you ever hear
a rear brake rubbing
noise, have the rear brake linings inspected. Also, the
rear brake drums should be removed and inspected each
time the tires are removed for rotation or changing.
When you have the front brake pads replaced, have
the
rear brakes inspected, too.
Brake linings should always be replaced as complete
axle sets.
See “Brake System Inspection” in Section 7 of this manual
under Part
C “Periodic Maintenance Inspections.”
Brake Pedal Travel
See your dealer if the brake pedal does not return to
normal height, or
if there is a rapid increase in pedal
travel. This could be a sign
of brake trouble.
Brake Adjustment
Every time you make a brake stop, your disc brakes
adjust for wear.
If your brake pedal goes down farther than normal, your
rear drum brakes may need adjustment. Adjust them by
backing up and firmly applying the brakes a few times.
Replacing Brake System Parts
The braking system on a modern vehicle is complex.
Its many parts have to be of top quality and work well
together
if the vehicle is to have really good braking.
Your vehicle was designed and tested with top-quality
GM brake parts. When you replace parts of your braking
system
-- for example, when your brake linings wear
down and you have to have new ones put in -- be sure
you get new approved
GM replacement parts. If you
don’t, your brakes may no longer. work properly. For
example, if someone puts
in brake linings that are wrong
for your vehicle,
the balance between your front and
rear brakes can change
-- for the worse. The braking
performance you’ve come to expect can change in many
other ways
if someone puts in the wrong replacement
brake parts.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 329 of 436
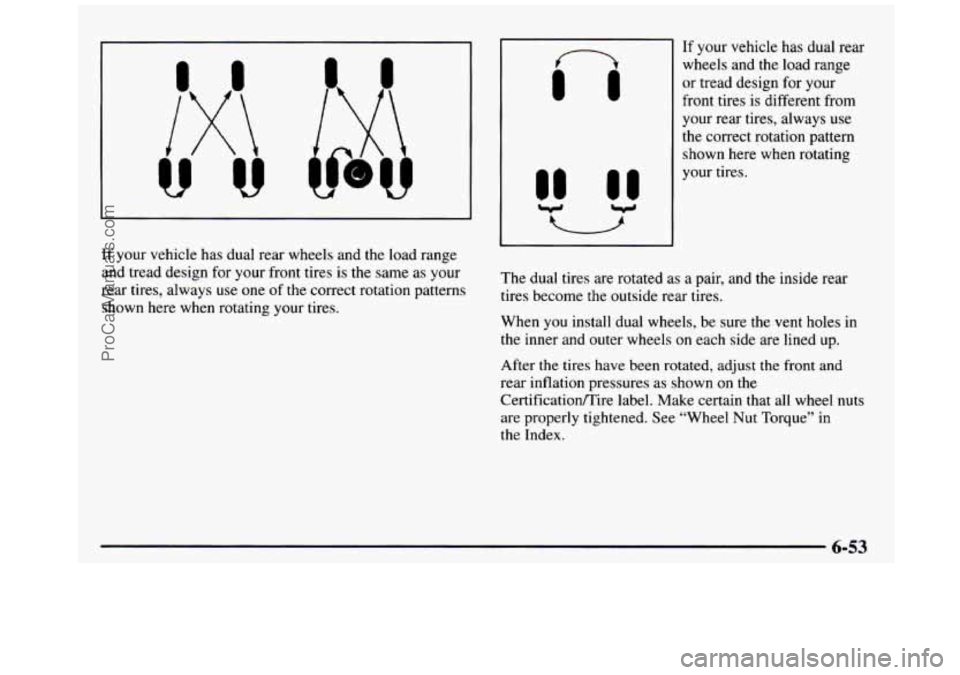
111
V
n
111
If your vehicle has dual rear
wheels and the load range
or tread design for your
front tires is different from
your rear tires, always use
the correct rotation pattern
shown here
when rotating
your tires.
If your vehicle has dual rear wheels and the load range
and tread design for your front tires is the same as your
rear tires, always use one of the correct rotation patterns
shown here when rotating your tires. The dual tires are rotated as
a pair, and the inside rear
tires become the outside rear tires.
When you install dual wheels, be sure the vent holes
in
the inner and outer wheels on each side are lined up.
After the tires have been rotated,
adjust the front and
rear inflation pressures as shown on the
Certificatiomire label. Make certain that all wheel nuts
are properly tightened. See “Wheel Nut Torque” in
the Index.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 331 of 436

Dual Tire Operation Buying New Tires
To find
out what kind and size of tires you need, look
at the CertificationEire label. When the vehicle is new, or whenever a wheel, wheel bolt
or wheel
nut is replaced, check the wheel nut torque after
100,
1,OOO and 6,000 miles (160, 1 600 and 10 OOO km)
of driving. For proper torque, see “Wheel Nut Torque” in
the Index.
The outer tire on a dual wheel setup generally wears faster
than
the inner tire. Your tires will wear more evenly and
last longer if you rotate the tires periodically.
If you’re
going to be doing a lot of driving on high-crown roads,
you can reduce tire wear by adding 5 psi (35 kPa) to the
tire pressure in the outer tires.
Be sure to return to the
recommended pressures when no longer driving under
those conditions. See “Changing a Flat Tire”
in the
Index for more information.
If you operate your vehicle with a tire that is badly
underinflated, the
tire can overheat. An overheated
tire
can lose air suddenly or catch fire. You or others
could be injured. Be sure all tires (including the
spare,
if any) are properly inflated.
The tires installed on your vehicle when it was new had
a Tire Performance Criteria Specification
(TPC Spec)
number on each
tire’s sidewall. When you get new tires,
get ones with that same TPC Spec number. That way
your vehicle will continue to have tires that are designed
to give proper endurance, handling, speed rating,
traction, ride and other things during normal service
on your vehicle.
If your tires have an all-season tread
design, the TPC number will be followed by an
“MS”
(for mud and snow).
If you ever replace your tires with those not having a
TPC Spec number, make sure they are the same size,
load range, speed rating and construction type (bias,
bias-belted or radial) as your original tires.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 334 of 436

I a CAUTION:
Using the wrong replacement wheels, wheel bolts
or wheel nuts on your vehicle can be dangerous.
It could affect the braking and handling of your
vehicle, make your tires lose air and make you
lose control.
You could have a collision in which
you or others could be injured. Always use the
correct wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts
for replacement.
I NOTICE:
The wrong wheel can also cause problems with
bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer or
odometer calibration, headlamp aim, bumper
height, vehicle ground clearance and tire or tire
chain clearance
to the body and chassis.
Whenever a wheel, wheel bolt or wheel
nut is replaced
on a dual wheel setup, check the wheel
nut torque after
100, 1,000 and 6,000 miles ( 160, 1 600 and 10 000 km)
of driving. For proper torque, see “Wheel Nut Torque’’
in the Index. See
“Changing a
Flat Tire” in the Index for
more information.
Used Replacement Wheels
~
Putting a used wheel on your vehicle is dangerous.
You can’t know how it’s been used or how far it’s
been driven. It could fail suddenly and
cause an
new
GM original equipment wheel.
~ accident. If you have to replace a wheel, use a
Tire Chains
I NOTICE:
If your vehicle has dual wheels or P26975R16 size
tires, don’t use tire chains. They can damage
your
vehicle because there’s not enough clearance.
NOTICE: (Continued)
6-58
ProCarManuals.com