Page 245 of 410
L
The following steps will tell you how to use thc jack and
change
a tire.
Removing the Spare Tire and Tools
The jacking equipment you'll need is stored r~long the
driver's rex
wall. In some cases, you may ha\:e to
remove the spare tire in order to reach the jack. Your
vehicle is also equipped with work gloves and a plastic
ground mat
lo assist in the changing of a flat tire.
To remove your jack cover,
pull
up on the latch at the
end
of the cover. near the
endgate and the latch
on the
top of the cover. Remove
the whecl blocks, jack
and
wheel wrench.
NOTICE:
Never remove or restow a tire from/to a stowage
position under the vehicle while the vehicle
is
supported by a jack. Always tighten the tire fully
against the underside of the vehicle when
restowing.
5-24
Page 249 of 410
Removing the Flat Tire and Installing the
Spare Tire 3. Fit the jack into the appropriate hole nearest the
tlat tire.
1. Using the wheel wrench, loosen all the wheel nuts.
Don't
remove them yet.
2. Turn the jack handle clockwise to raise the jack
lift head.
A. Front Frame Hole
B. Rear Frame Hole (?-Door) or Spring Hanger Hole
(+Door)
5-28
Page 253 of 410

Storing a Flat or Spare Tire and Tools
Incorrect wheel nuts or improperly tightened
wheel nuts can cause the wheel to become loose
and even come
off. This could lead to an accident.
Be sure to use the correct wheel nuts.
If yo11 have
to replace them, be sure to get new GILI original
equipment wheel nuts.
Stop somewhere as soon
as you can and have the
nuts tightened with
a torque wrench to 95 Ib-ft
Improperly tightened wheel nuts can lead to
brake pulsation and rotor damage.
To avoid
expensive brake repairs, evenly tighten the wheel
nuts in the proper sequence and to the proper
' A CAUTION:
-
Storing a jack, a tire or other equipment in the
passenger compartment
of the vehicle could
cause in,jury. In
a sudden stop or collision, loose
equipment could strike someone. Store
all these
in the proper place.
NOTICE:
An aluminum wheel with a flat tire should always
be stored under the vehicle with the hoist.
However, storing it that way
for an extended
period could damage the wheel.
To avoid this,
have the wheel repaired as soon as possible.
5-32
Page 254 of 410
Follow this diagram to store the llnderbody-mounted spare.
A. Retainer
B. Valve Stem
(Pointed
Down)
C. Spare 01- Flat Tire
D. Spring
E. Wheel Wrench
F. Lower
G. Raise
H. Hoist
Arm
1. Put the tire on the gro~~nd at the rear of the vehicle,
with the valve stem pointed down and to the rear.
2. Pull the retainer t11ro~1sh the wheel.
3. Put the chisel end of the wheel wrench, on an angle,
through
the hole in the rear bllmper and into the hoist
shaft. Turn the wheel wrench clockwise until the tire
is raised against the underside
of the vehicle.
You will hear two "clicks" when the tire is secure.
but p~111 on the tire to make SLII-e.
5-33
Page 255 of 410
Follow this diagram for the inside-mounted spare.
D f
A. Spare or Flat Tire
B. Retainer (Two-Wheel Drive)
C. Nut
D. Retainer (Four-Wheel DI-~LT)
E. Wheel Can-ier
E Hook
A. Wheel Carrier
C.
Wheel Nut and Locking Nut Cylinder
5-34
Page 256 of 410

Return the jack, wheel wrench and wheel blocks to the
proper location in your vehicle’s rear area. Secure the
items and replace the jack cover.
I /-A
I L
A. Retainer E Wheel Blocks
B. Rubber Band
G. Hub Cap Removal
(Some Models) Tool (Some Models)
C. Work Gloves
H. Wheel Wrench
D. Mat I. Jack
E. Jack Storage Cover J. Jacking Instructions
Make sure the tire and carrier are secure.
Driving with the tire or carrier unlatched could
injure pedestrians or damage the vehicle.
Compact Spare Tire (If Equipped)
Although the compact spare tire was fully inflated when
your vehicle was new, it can lose air after a time. Check
the inflation pressure regularly. It should be
60 psi
(420 Wa).
After installing the compact spare on your vehicle,
you should stop as soon as possible and make sure
your spare tire is correctly inflated. The compact
spare is made to perform well at speeds up to
65 mph
(105 km/h) for distances up to 3,000 miles (5 000 km),
so you can finish your trip and have your full-size tire
repaired or replaced where
you want. Of course, it’s best
to replace your spare with a full-size tire as
soon as you
can. Your spare will last longer and be in good shape in
case you need it again.
5-35
Page 300 of 410

A CAUTION:
Poorly maintained and improperly used tires
are dangerous.
0
0
0
0
Overloading your tires can cause
overheating
as a result of too much friction.
You could have an air-out and a serious
accident. See “1,oading Your Vehicle” in
the Index.
Underinflated tires pose the same danger as
overloaded tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury. Check
all tires
frequently to maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure should be checked
when your tires are cold.
Overinflated tires are more likely to be
cut, punctured or broken by a sudden
impact
-- such as when you hit a pothole.
Keep tires at the recommended pressure.
Worn, old tires can cause accidents. If your
tread
is badly worn, or if‘ your tires have
been damaged, replace them.
Inflation -- Tire Pressure
The Cel-tification/Tire label. which is 011 the driver‘s
door edge, above the door latch. shows the correct
inflation
pressures for your tires when they’re cold.
“Cold“ lneans your vehicle has been sitting for at least
three hours or driven no more than 1 mile ( 1 .6 km).
NOTICE:
Don’t let anyone tell you that underinflation or
overinflation is all right. It’s not.
If‘ your tires
don’t have enough air (underinflation), you can
get the following:
Too much flexing
Too much heat
0 Tire overloading
Bad wear
0 Bad handling
0 Bad fuel economy.
NOTICE: (Continued)
6-4 1
Page 301 of 410
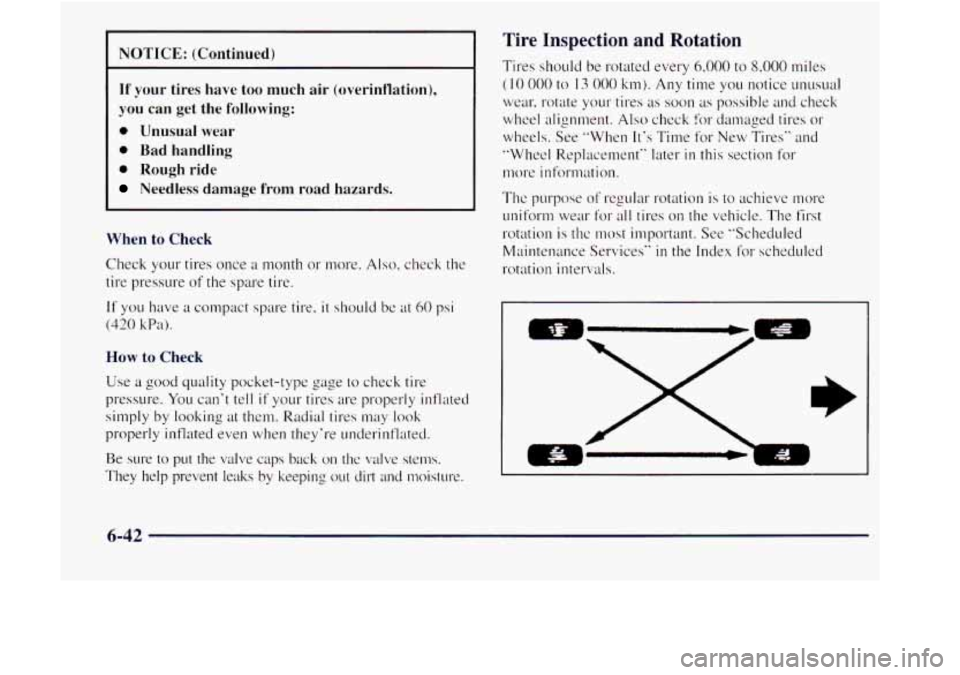
I NOTICE: (Continued) I
If your tires have too much air (overinflation),
you
can get the following:
0 Unusual wear
0 Bad handling
0 Rough ride
Needless damage from road hazards.
When to Check
Check your tires once a month or n101-e. Also. check the
tire pressure
of the spare tire.
I! you have a compact spare tire. it should be at 60 psi
(420
k Pa).
How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type gage to check tire
pressure. You can't tell
if your tires are properly inflated
simply
by looking at thcm. Radial tires may look
properly inflated even when they're underintlatecl.
Be sure to put the valve caps back on the valve stems.
They help prevent leaks
by keeping out dirt and moisture.
Tire Inspection and Rotation
Tires s11o111d be rotated every 6,000 to 8,000 miles
( IO 000 to 13 000 km). Any time you notice unusual
we;^. rotate your tires as soon as possible and check
wheel alignment.
Also check for damaged tires or
wheels. See "When 1t.s Time for New Tires" and
"Wheel Replacement" later
in this section for
more information.
Thc purpose
of' reg~~lar rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear
fur all tires on the vehicle. The first
rotation
is thu most important. See "Schecluled
Maintenance Services"
in the Index for scheduled
rotation intervals.
r --
6-42