1996 HONDA CIVIC Ignition rotor
[x] Cancel search: Ignition rotorPage 441 of 2189

PGM-FI System
tFos3sl
tFffi6l
tPr361 I
fPfi62l
fFr38il
tF13s2-l
Crankshaft Position/Top Dead Genter/Gylinder Position (CKP/TDC/CYP) Sensor
('96 - 98 Models, '!n - 00 D16Y5 engine with M/Tl
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0335: A malfunction in the Crankshaft position (CKp)
sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336: A range/performance problem in the CrankshaftPosition (CKP) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1361: Intermittent interruotion in the Too Dead Center(TDC) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code {DTC) P1362: No signal in the Top Dead Center (TDC} sensorcircuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1381: Intermittent interruption in the Cvlinder Position{CYP) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code {DTC) Pl382: No signal in the Cylinder Position (CYP} sensorcircuit.
Description
The CKP Sensor determines timing for fuel injection and ignition of each cylinder and also detects engine speed. The TDCSensor determines ignition timing at start-up (cranking) and when crank angle is abnormal. The Cyp Sensor detects theposition of No. 1 cylinder for sequential fuel injection to each cylinder. The CKP/TDC/CYP Sensor is built into the distribu-ror.
NOTE: lf DTC P1359 is stored atthesametime as DTC P0335. P0336, P1361, Pl362, P1381 and/or P1382, troubteshoor DTCP1359 first, then recheck for those DTCS. Ot6y5 6ngine: Dt6y7, ot6y8 enqin6s:
SENSORBOTOR
TDCSENSORCKPSENSORSENSORROTORSENSORROTORSENSORROTORROTORROTOR
DISTRIBUTOR 1OPcoNNECTOR tC120tTDC P
- The MIL hrs been reported on.- DTC P0335, P0336, P1361,P1362, P1381 and/or Pl382 6restored,
Problem verification:1. Do the ECM/PCM Reset Proce-dure.2. Stan the engine.
Intermittent hilu.e, system b OKat this time. Check tor poor con-n€ctions or 10036 wiros at C120{distributor} and ECM/PCM.
ls DTC P0335, P0336, P1361, P1362,P1381 and/or P'l382 indicated?
Check for an open in the CKP/TDC/CYP sensor:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the distributor 10P
3. Measure resistance betweenthe terminals of the indicatedsensor (*see table).
Replace the distributor ignitionhousing (soe section 23).ls there 350 - 700 0?
CYP M {BLK}
SENSORDTCSENSORIERMINATECMfCMTERMINATCOLOR
CKPP033s
m336
2c2BLU
6c12
TDCP1361
P1362
3GRN
7cl3RED
CYPP!381
P't382
c4YEL
8c148LK11-172
Page 443 of 2189

PGM-FI System
l-Fos3sl
tFos36l
tF1361 l
Fr362-1
tF13sil
Crankshaft Position/Top Dead Center/Cylinder Position (CKP/TDC/CYPI Sensor
f99 - 00 Models except D16Y5 engine with M/T)
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0335: A malfunction in the Crankshaft Position (CKP)
sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336: A range/performance problem in the Crankshaft
Position (CKP) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1361: Intermittent interruption in the Top Dead Center
{TDC) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code {DTC) P1362: No signal in the Top Dead Center (TDC) sensor
circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1381: Intermittent interruption in the Cylinder Position(CYP) sensor circuit.
lTiaSt The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1382; No signal in the Cylinder Position (CYP) sensor: circuil.
DoscriDtion
The CKP Sensor determines timing for fuel injection and ignition of each cylinder and also detects engine speed. The TDC
Sensor determines ignition timing at start-up (cranking) and when crank angle is abnormal. The CYP Sensor detects the
position of No. 1 cylinder for sequential fuel injection to each cylinder. The CKP/TDC/CYP Sensor is built into the distribu-
tor.
NOTE; lf DTC P1359 is stored at the same time as DTC P0335, P0336, P1361. P1362, P1381 and/or P1382, troubleshoot DTC
P1359 first, then recheck for those DTCS. D16Y5 engino:
SENSORROTOR
TDGSENSORCKPSENSOBTDCSENSOBCKPSENSOBCYPs€NsonBOTORROTORBOTONROTOR ROTOR
D16Y7, D16Y8 ongine:
(To page 11-175)
1-174
- The MIL has been reportod on.- DTC P0335, P0336. P1361,P1362, P1381 rnd/or P1382.restored.
Problem verific{tion:1. Do the ECM/PCM Reset Proce-dure.2. Start the engine.
Intormittcnt failure, systom b OKat thb time. Check to. poor con-nections or loose wires at C120(dktributorl and ECM/PCM.
ls DTC P0335, P0336, P1361, P1362,P1381 and/or Pl382 indicated?
Check tor an open in the CKP/TDC/CYP 3enior:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the distributor 10Pconnector,3. Measure resistance betweenthe terminals of the indicatedsensor (*see table).
Replrce the distributor ignitionhou3ing (!ee section 231.ls there 350 700 0?
SENSORDTCSENSORTEBMINAIECM/PCMTERI\,4INAICOLOR
CKPP0335
P0336
2c88LU
6c9
TDCP1361
P1362
3c20GRN
7c21BED
CYPP1381
P1342
c29YEL
Ic30BLK
Page 452 of 2189

\Crankshaft Speed Fluctuation (GKFI Sensor .
firC- 48 Models, '99 - 00 D16Y5 engine with M/Tl
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1336; Intermiftent interruption in the Crankshaft Speed
Fluctuation (CKF) sensor circuit.
ThescantooIindicatesDiagnosticTroub|ecode{DTC)P1337:NosignaIinthecrankshaftspeedF|uctuation(cKF}
sensor circuit.
D6scription
Thediagnosticsystemhasapu|serrotoronthecrankshaftandapu|sepick-upsensorontheengineblock.TheEcM/PcM
monitors the crankshaft speed ftuctuation based on the cKF sensor signal, and judges that 8n engine misfire occurred if
the fluctuation goes beyond a predetermined limit'
I
fPrk6l
lFr3g7-l
CKF SENSOR 3P CONNECTOR
L:l.)l l.' -Ir-T--T---.]l1 l2l3llL-''---r
CKFM I I CKFP
twrfit 1,.^ | lsLul\.7
Terminal side of male terminals
CKF MIWHT}
CKF PIBLUI
I(cont'd)
- The MtL hds been reported on.- DTC P1336 and/or P1337 a.e
stored.
P.oblem v€rific.tion:1. Do the ECM/PCM Reset Proce-
dure.2. Stan the enginelntormittont lailur6, tY3tom b OK
at thit tima. Chock tor Poor con'
nactions or loota wito! at C102
IC-KF son$rl .nd ECt /PCM, and
mrka suro CKF tonaor mounting
boh ittigM.
Chock for .n open in tho CKF aen-
30t:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF
2. Disconnect the CKF sensor 3P
connector,3. Measure the resista nce
between the CKF sensor 3P
connector terminals No. 1 and
No.3.
ls there 1.6- 3.2 kO?
Ch€ck tor a short in the CKF son'
30tiCheck {or continuitY between
body ground and the CKF sensor
3P connector termin6ls No. 1 and
No.3 individuallY.
(To page 11 184)
1 1-183
Page 454 of 2189
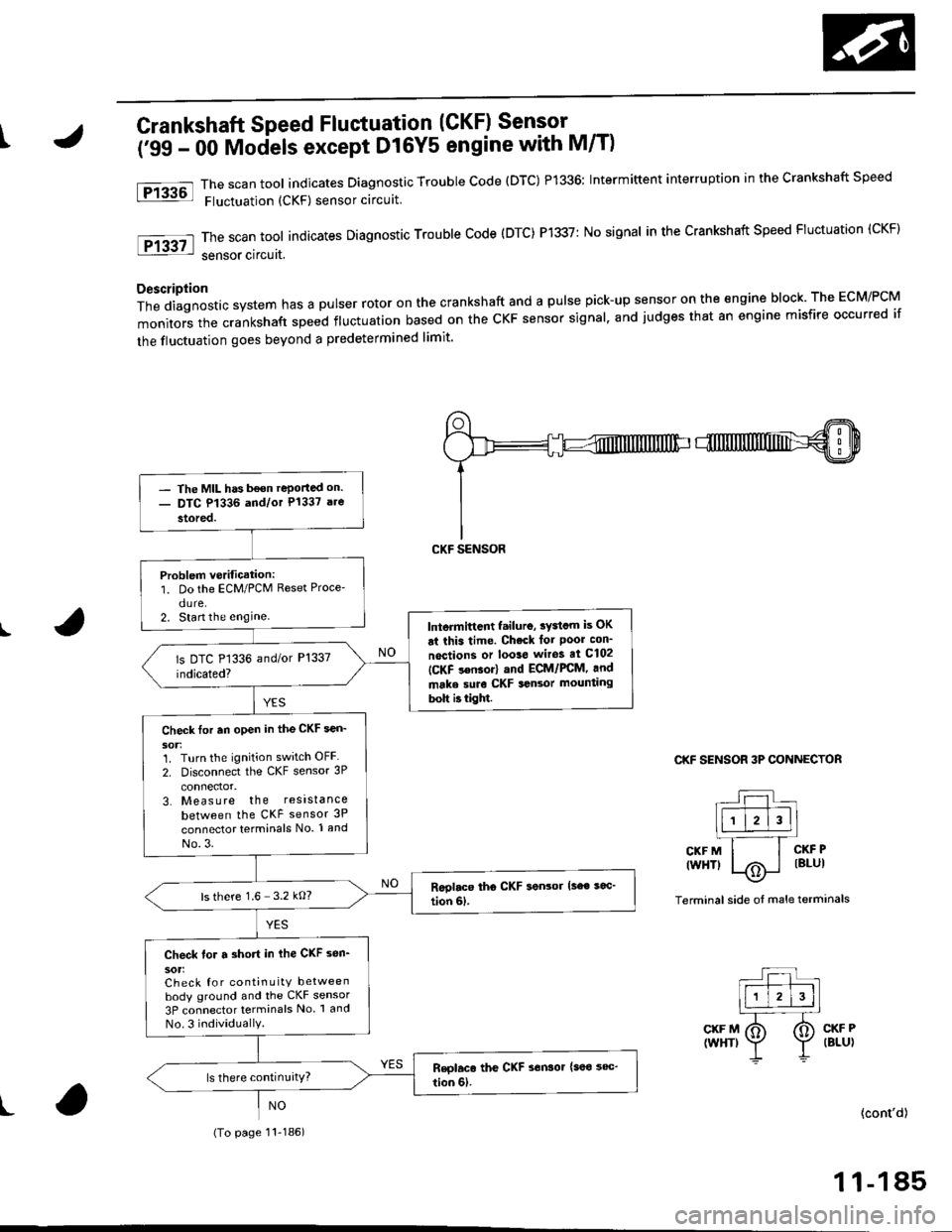
tCrankshaft Speed Fluctuation (CKF) Sensor -
('99 - 00 Mociels except D16Y5 engine with M/T)
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble code (DTC) P1336: Intermittent interruption in the crankshaft speed
Fluctuation (CKF) sensor circuit
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1337: No signal in the Crankshaft Speed Fluctuation (CKF)
sensor circuat,
Description
Thediagnosticsystemhasapulserrotoronthecrankshaftandapu|sepick-upsensorontheengineb|ock.TheEcM/PcM
monitors the crankshaft speed fluctuation based on the cKF sensor signal. and judges that an engine misfire occurred if
the fluctuation goes beyond a predetermined limit'
I
Ftu6l
tF13g7l
CKF SENSOR 3P CONNECTOR
r--r t|-.r-r'--]llll l2l3ll.l---'.-T_
CKFM I I CKFP
twHTl |/Ai i lBlul--\9-
Terminal side oI male terminals
CKF M(WHT)CKF P(BLU)
t(cont'd)
1 1-185
- The MIL has b€on reportad on.- DTC P1336 and/or P1337 are
stored.
Problem verification:1. Do the ECM/PCM Reset Proce'
dure.2. Start the enginelntermittcnt failuro, sydcm is OK
ai this time. Check lot Poor con_
noctions or loo3e wiros at C102
ICKF s€nsor) and ECM/FCM, and
make suro CKF sansor mounting
bolt b tight.
Check tor an open in the CKF sen_
1. Turn the ignition switch OFF
2. Disconnect the CKF sensor 3P
3. Measure the resistance
between the CKF sensor 3P
connector terminals No. 1 and
No.3.
ls there 1.6 3.2 kO?
Check for a short in ihe CKF sen_
sot:Check for continuity betweenbody ground and the CKF sensor
3P connector terminals No 1 and
No.3 individuallY.
(To page 11-186)
Page 1579 of 2189
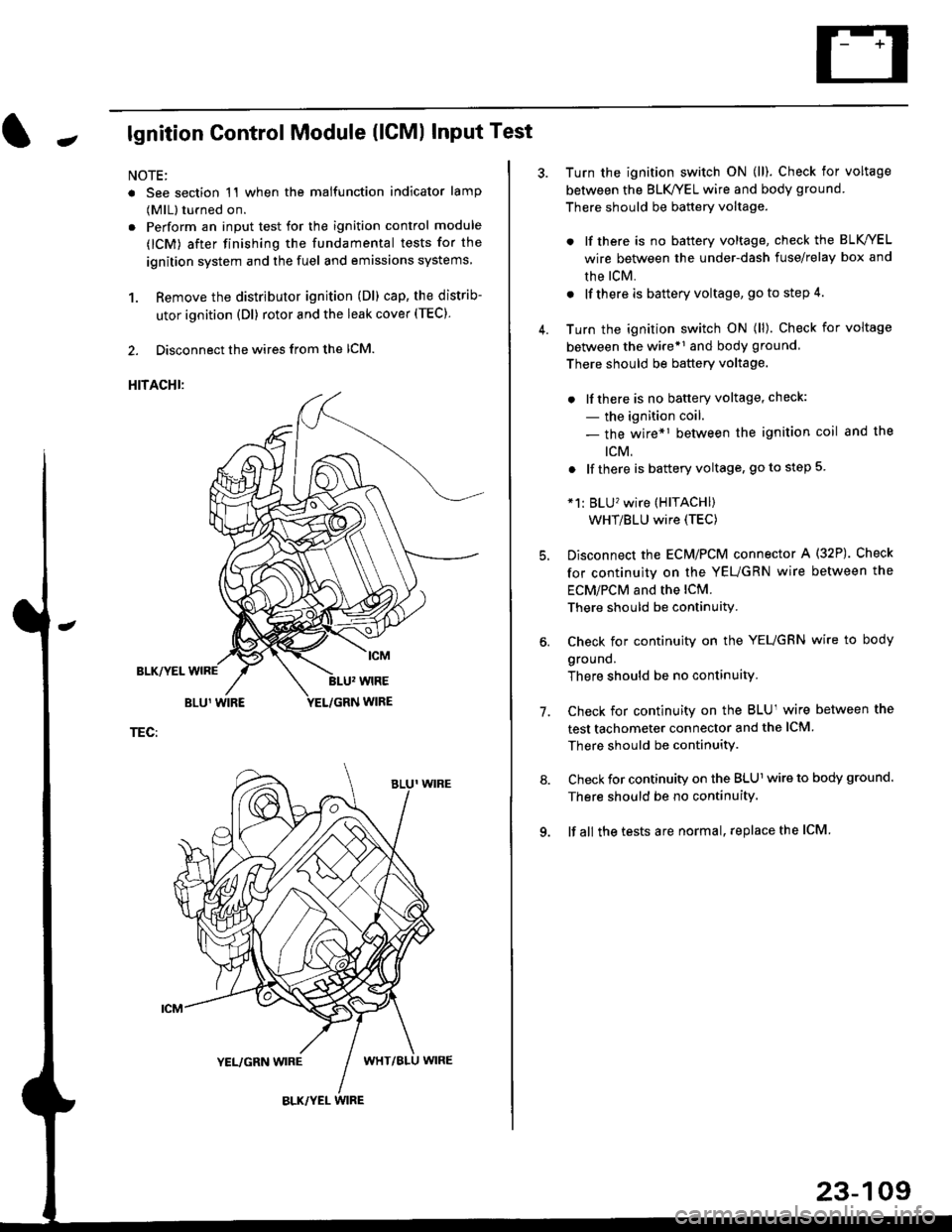
Jlgnition Control Module (lCMl Input Test
NOTE:
. See section 1'l when the malfunction indicator lamp
(MlL) turned on.
. Perform an input test for the ignition control module
(lCM) after finishing the fundamental tests for the
ignition system and the fuel and emissions systems
1. Remove the distributor ignition (Dl) cap, the distrib-
utor ignition (Dl) rotor and the leak cover (TEC).
2. Disconnect the wires from the lCM.
HITACHI:
BLK/YEL
TEC:
Turn the ignition switch ON (ll). Check for voltage
between the BLK/YEL wire and body ground.
There should be battery voltage.
. lf there is no battery voltage, check the BLK/YEL
wire between the under-dash fuse/relay box and
rhe lcM.
. lf there is battery voltage, go to step 4.
Turn the ignition switch ON (ll). Check for voltage
between the wire*r and body ground
There should be battery voltage.
. lfthere is no battery voltage, check:
- the ignition coil.
- the wire*1 between the ignition coil and the
tcM.
. lf there is battery voltage, go to step 5
*1: BLU'�wire (HITACHI)
WHT/BLU wire (TEC)
Disconnect the EcM/PCM connector A (32P). Check
for continuity on the YEUGRN wire between the
ECM/PCM and the lCM.
There should be continuity.
Check for continuity on the YEUGRN wire to body
ground.
There should be no continuity.
Check for continuity on the BLUl wire between the
test tachometer connector and the ICM
There should be continuitY.
Check for continuity on the BLUl wire to body ground.
There should be no continuity.
lf all the tests are normal, replace the ICM
7.
23-109
Page 1980 of 2189

Gauges (cont'd)
- How the Gircuit Works
When the ignition switch is in ON (ll) or START (lll),
battery voltage is supplied through fuse 25 to the
gauges in the gauge assembly.
Speedometer and Odometer
The odometer and soeedometer drive circuits
receive pulses from the vehicle speed sensor
(VSS). The pulse rate increases as the car
accelerates. The frequency and duration of these
input pulses are measured and displayed by the
speedometer, odometer and tripmeter.
Tachometer
The tachometer drive circuit receives pulses from
the ignition control module (lCM) in the distributor
assembly or the ECM/PCM. The solid-state
lachometer then displays these pulses as engine
speed. For each 200 pulses per minute from the
ignition control modul€ (lCM) or the ECM/PCM, the
tachometer displays 100 RPM.
Engine Coolant Temperature Gauge
The engine coolant temperature gauge has two
intersecting coils wound around a permanent
magnet rotor. Voltage applied to the coils, through
fuse 25, generates a magnetic lield. The magnetic
field, controlled by the coolant temperature sending
unit, causes the rotor to rotate and the gauge
needle to move. As the resistance in the sending
unit varies, current through the gauge coils
changes. The gauge needle moves toward the coil
with the strongest magnetic field.
The 6ngine coolant temperature sending unit's
resistance varies from about 137 ohms at low
engine temperature to between 3H6 ohms at high
temperature (radiator fan running).
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
81-2
(
Fuel Gauge (All except cX)
The fuel gauge has two intersecting coils wound
around a permanent magnet rotor. Voltage applied
to the coils, through tuse 25, generates a magnetic
field. The magnetic field, controlled by the fuel
gauge sending unit, causes the rotor to rotate and
the gauge needle to move. As the resislance in the
sending unit varies, current through the gauge coils
changes. The gauge needle moves toward the coil
with the strongest magnetic field.
The fuel gauge sending unit's resistance varies
from about 2-5 ohms at full, to about 110 ohms at
empty. When you turn the ignition switch off, the
gauge remains at the last reading until you turn the
ignition switch to ON (ll) or START (lll) again,
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
Fuel Gauge (GX)
The fuel gauge has two intersecting coils wound
around a permanent magnet rotor. Voltage applied
to the coils, through fuse 25, generates a magnetic
field. The magnetic field, controlled by the PCM,
causes the rotor to rotate and the gauge needle to
move. The PCM calculates the gas quantity in the
fuel tank by using the fuel pressure value detected
by the tuel tank pressure sensor and the fuel
temperature value detected by the fuel tank
temperalure sensor, and outputs the signal to the
gauge assembly. The gauge needle moves toward
the coil with the strongest magnetic field.
When you turn the ignition switch off , the gauge
remains at the last reading until you turn the ignition
switch to ON (ll) or START (lll) again. When the
PCM detects a malfunction with the fuel pressure or
temperature, or detects a gas leak, the PCM
reduces the fuel meter to 0.
Refer to the Service Manual GX Supplement
(Section 11 , Fuel and Emissions) for specific tests
or troubleshooting procedures.
a
a