Page 689 of 2189
4th cear lE position)
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 4th clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, causing the mainshaft 4th
gear to rotate.
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 4th gear' which drives the countershaft'
3. Power is transmitted to the final drive gear, which drives the final driven gear'
NOTE: Hvdraulic pressure is also applied to the lst clutch, but since the rotation speed of 4th gear exceeds that of 1st
gear, power from 1st gear is cut off at the one-way clutch
TOROUE
MAINSHAFT 4TH GEAR
COUNTERSHAFT
FINAL ORIVEN GEAR
14-11
Page 690 of 2189
Description
Power Flow (cont'd)
El Po3ition
1, Hydraulic pressure is switched by the manual valve to the servo valve, which moves the reverse shift fork to thereverse position. The reverse shift fork engages with the reverse selector, reverse selector hub, and the countershaftreverse gear.
Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 4th clutch. Power is transmitt€d from the mainshaft reverse gear via thereverse idler gear to the countershaft reverse gear.
The rotation direction of the countershaft reverse gear is changed via the reverse idler gear,
Power is transmitted to the final drive gear, which drives the final driven gear.
TOROUE
MAINSHAFT
COU TERSHAFT
REVERSE SELECTORHUBREVERSE SETICTOR
REVERSE SHIFTFORK
REVERSE IDLER
14-12
FINAL ON|VEN GEAR
Page 697 of 2189
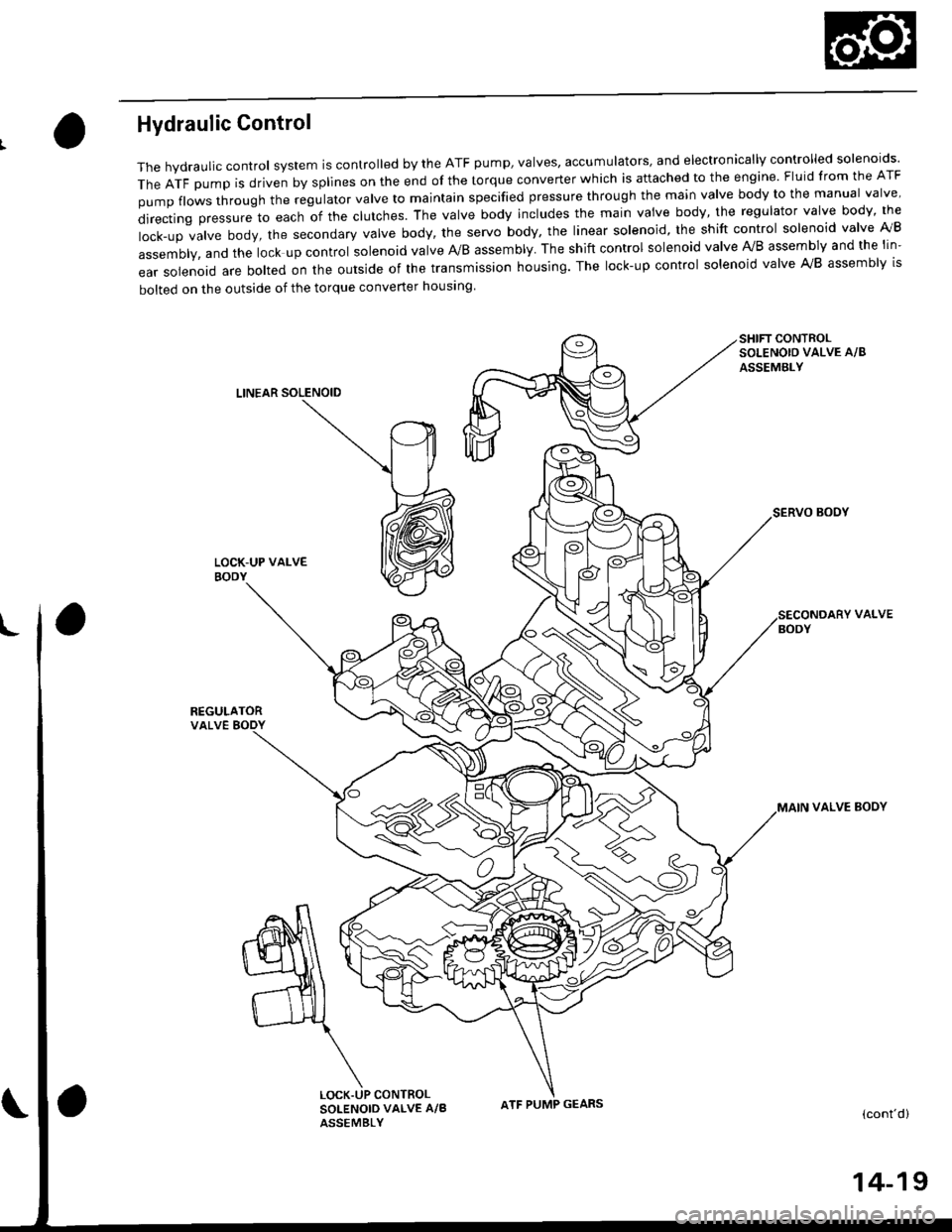
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, accumulators, and electronically controlled solenoids'
TheATFpUmpisdrivenbysp||nesontheendofthetorqueconverterWhichisattachedtotheengine.F|uidfromtheATF
pumpf|owsthroughtheregu|atorva|vetomajntainspecifiedpressurethroughthemainva|vebodytothemanuaIva|ve'
directingpressuretoeachofthec|utches.Theva|vebodyinc|udesthemainvaivebody,theregu|atorvalvebody,the
|ock-upva|vebody,thesecondaryVa|vebody,theservobody,theIinearso|enoid,theshiftcontro|so|enoidva|velVB
assembly, and the lock up control solenoid valve A/B assembly. The shift control solenoid valve Ay'B assembly and the lin-
ear solenoid are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing. The lock-up control solenoid valve A,/B assembly is
bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing
SHIFT CONTROLSOLENOIO VALVE A/8
ASSEMBLY
LINEAR SOLENOID
SERVO BOOY
REGULATORVALVE BODY
VALVE
VALVE BOOY
(cont'd)
CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMBLY
ATF PUMP GEARS
14-19
Page 698 of 2189
Description
Hydraulic Control (cont'dl
Msin Valve Body
The main valve body houses the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve, the 2nd orifice control valve, the cpB valve, the modu-lator valve' the servo control valve, and the relief valve. The primary functions of the main valve body are to swatch fluidpressure on and off and to control the hydraulic pressure going to the hydraulic control svstem.
2ND ORIFICE CONTROTVALVE
1-2 SHIFT VALVE
RELIEF VALVE
CPC VAL
3-4 SHTFT V
VALVE
Socondary Valve Body
The secondary valve body is located on the main valve body. The secondary valve body houses the 2-3 shift vatve, the 3-4shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve, and the CpC valve.
CONTROL
2.3 SHIFT VALVE
4TH EXHAUST VALV€
VALVE
14-20
VALVE
Page 700 of 2189

Description
Hydraulic Control (cont'dl
Regulator Valve
The regulator valve maintains a constant hydraulic pressure from the ATF pump to the hydraulic control system, whitealso furnishing fluid to the lubricating system and torque converter. The fluid from the ATF pump flows through B and 8,.The regulator valve has a valve orifice. The fluid entering from B flows through the orifice to the A cavity. This pressure ofthe A cavity pushes the regulator valve to the right side, and this movement of the regulator valve uncovers the fluid portto the torque converter and the relief valve. The fluid flows out to the torque converter, and the relief valve and regulatorvalve moves to the left side. According to the level of the hydraulic pressure through B, the position of the regutator vatvechanges and the amount of the fluid from B' through D and c also changes. This operation is continued. maantaining theline pressure,
NOTE: When used. "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on the illustration betow.
ENGINE NOT RUNNING
TOROUE CONVERTER
ENGINE RUNNING
To TOROUE CONVERTER Lubrication
Stator Roaction Hydraulic Prossur6 Control
Hydraulic pressure increases according to torque, are performed by the regulator valve using the stator torque reaction.The stator shaft is splined with the stator in the torque converter, and its arm end contacts the regulator sprang cap. whenthe vehicle is accelerating or climbing (Torque Convert€r Range), the stator torque reaction acts on the stator shaft, andthe stator arm pushes the regulator spring cap in the direction of the arrow in proponion to the reaction. Jne stator reac-tion spring compresses, and th€ reoulator valve moves to increase the line pressure which is regulated by the regulatorvalve. The line pressure reaches its maximum when the stator torque reaction reaches its maximum.
STATOR SHAFT ARM
REGULATOR VALVE
14-22
STATORATOR SHAFT ARM
SPRING CAP
Page 702 of 2189

Description
Hydraulic Flow
General Chart ol Hydraulic PressureATF Pump- pegurator varve -_l- Line pressure -f- Modurator pressure - Linear sorenoid
| -Clutch pressure
-Torque Converter pressure
t-Lubrication Pressure
Distribution of Hydraulic Pressur€. Regulator Valve -]- Torque Converter pressure
F_ Lubrication pressure
i- To regulate Line pressure
. Manual valve _ To select Line pressure _ clutch pressure
' Modulator Valve i/odulator pressure _ ___f_ Shift Control Solenoid Valves
F_ Lock_up Control Solenoid ValvesL_ Linear Solenoid
. 1-2 Shift Valve - l. 2-3 Shift Valve - 1- Ctutch pressure. 3-4 Shift Valve
lra
PORT NO.DESCRIPTION OF PRESSUREPORT NO.DESCRIPTION OF PRESSUREPORT NO.DESCRIPTION OF PRESSURE
1LINE6B
MODULATE(SHIFT CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE B)
414TH CLUTCH
LINEMODULATE(LOCK-UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE A)
56LINEAR SOLENOID
LINE6D
MODULATE(LOCK-UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE B)
90TOROUE CONVEBTER
2LINE6D'
MODULATE
(LOCK-UP CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE B)
91TOROUE CONVERTER
LINE7LINE92TOROUE CONVERTERLINE8LINE/CPC93ATF COOLER3"LINE9LINE94TOROUE CONVERTER4LIN E'101ST CLUTCH95LUBRICATION
LINE202ND CLUTCHYOTOROUE CONVERTERLINE20A2ND ACCUMULATOR97TOROUE CONVERTER5LINE99SUCTION
MODULATE303RD CLUTCHXDRAIN
6A
MODULATE(SHIFT CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE A)
404TH CLUTCH
14-24
Page 703 of 2189
\
@ Position
As the engine turns, the ATF pump also starts to operate, Automatic transmission fluid (ATF) is drawn from (99) and dis-
charged into (1). Then, ATF flowing from the ATF pump becomes the line pressure (1). The line pressure (1) is regulated
by the regulator valve. The torque conv€rter inlet pressure (92) enters (94) of the torque converter through the lock-up
shift valve and discharges into (901. The torque converter ch€ck valve prevents the torque converter pressure from rising'
Under this condition, the hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches'
NOTE: When used, "1eft" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit'
14-25
Page 704 of 2189

Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'd)
L?j Position
The line pressure (1) flows to the manual valve and the modulator valve. The line pressure (1) changes the trne pressure(4) and (25) at the manual valve. and changes to the modulator pressure at the modulator valve. But the moourator pres-sure (6) does not flow to each shift valve because shift control solenoid valves A and B are turned oN by the pcM. Theline pressure (4) passes through the cPB valve and the cPc valve. and changes to the line pressure (s), th;n flows to the1-2 shift valve. The line pressure {S) from the l-2 shift valve changes to the 2nd clutch pressure (20) at the 2-3 shift valve.The 2nd clutch pressure (20) is applied to the 2nd clutch. and the 2nd clutch is engaged. The line pressure (4) passesthrough the 1-2 shift valve and the orifice, and changes the lst clutch pressure, The 1st clutch pressure (10) atso flows tothe 1st clutch. However, no power is transmitted because of the one_way clutch.
NOTE: When used, "Ieft" or "right" indicates direction on the hvdraulic circuit.
14-26