1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 727 of 1938
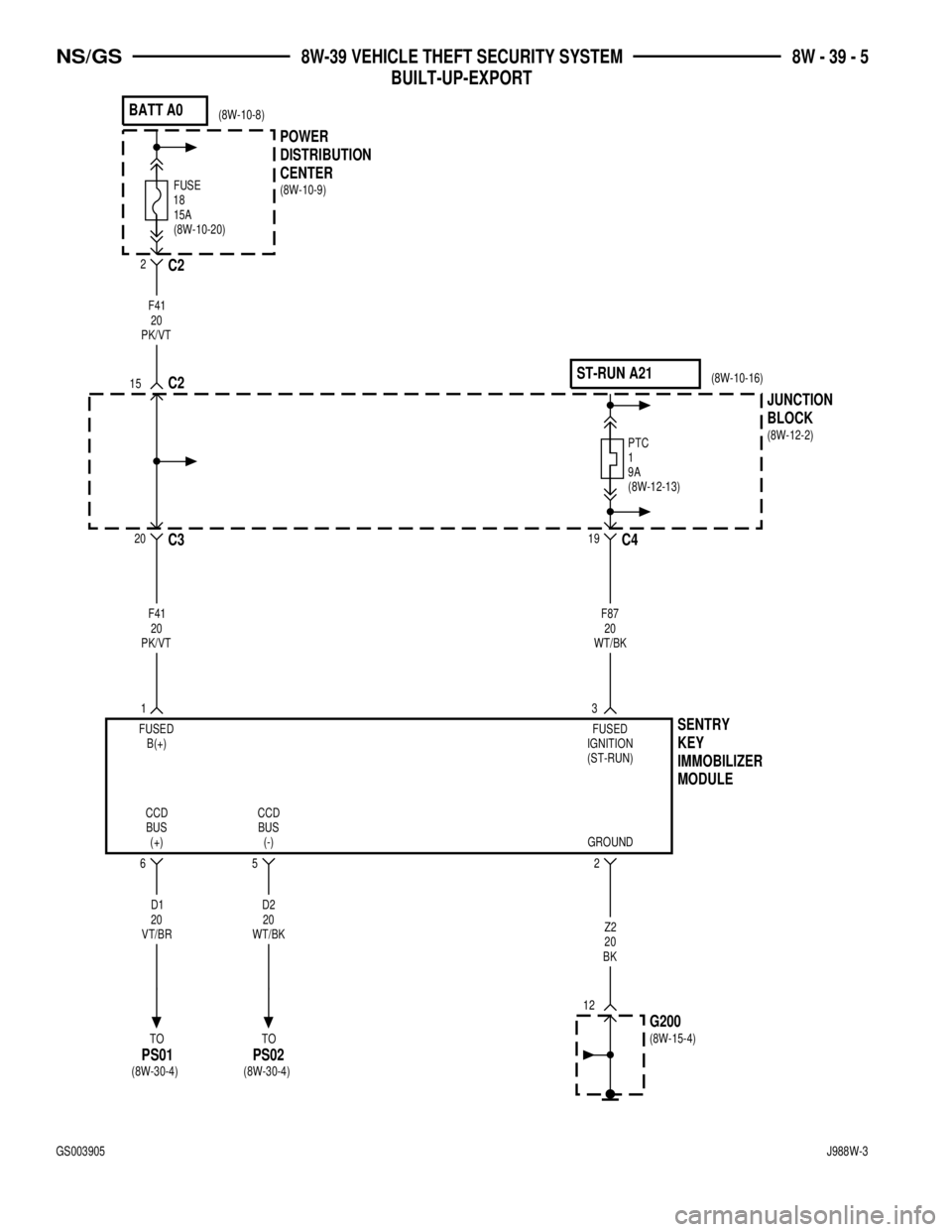
18FUSE15A
BATT A0
12
CENTER
DISTRIBUTION
POWER
2C2
15C2
F41
20
PK/VT
20C3
PTC
1
9A
ST-RUN A21
BLOCK JUNCTION
C4
19
MODULE IMMOBILIZER
KEY
SENTRY
1F41
20
PK/VT3
F87
20
WT/BK
FUSED
B(+)FUSED
IGNITION
(ST-RUN)
CCD
BUS
(+) (-)BUS CCD
GROUND
Z2
20
BK
G200
2 56
D1
20
VT/BR
D2
20
WT/BK
TO
PS01
TO
PS02
(8W-10-20)(8W-10-8)
(8W-10-9)
(8W-12-13)(8W-10-16)
(8W-12-2)
(8W-15-4)
(8W-30-4) (8W-30-4)
NS/GS8W-39 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY SYSTEM
BUILT-UP-EXPORT8W - 39 - 5
GS003905J988W-3
Page 1052 of 1938

made to seal the area between the bedplate and cyl-
inder block without disturbing the bearing clearance
or alignment of these components.
GASKET DISASSEMBLY
Parts assembled with form-in-place gaskets may be
disassembled without unusual effort. In some
instances, it may be necessary to lightly tap the part
with a mallet or other suitable tool to break the seal
between the mating surfaces. A flat gasket scraper
may also be lightly tapped into the joint but care
must be taken not to damage the mating surfaces.
SURFACE PREPARATION
Scrape clean or wire brush all gasket surfaces to
remove all loose material. Inspect stamped parts to
ensure gasket rails are flat. Gasket surfaces must be
free of oil and dirt. Make sure old gasket material is
removed from blind attaching holes.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing the material off location.
TheMopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant
gasket material or equivalent should be applied in a
continuous bead approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in
diameter. All mounting holes must be circled. For
corner sealing, a 3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop
is placed in the center of the gasket contact area.
Uncured sealant may be removed with a shop towels.
Components should be torqued in place while the
sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10 minutes).
The usage of a locating dowel is recommended during
assembly to prevent smearing of material off loca-
tion.
CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET BOLT ACCESS PLUG
An Access plug is located in the right inner fender
shield. Remove the plug and insert the proper size
socket, extension and ratchet, when crankshaft rota-
tion is necessary.
ENGINE CORE PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screwdriver
and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the cup
plug (Fig. 1). With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmlywith pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug
(Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting
as restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly remove all rust and clean inside of cup
plug hole in cylinder block or head. Be sure to
remove old sealer. Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole
with sealer. Make certain the new plug is cleaned of
all oil or grease. Using proper drive plug, drive plug
into hole so that the sharp edge of the plug is at
least 0.5 mm (0.020 inch.) inside the lead in chamfer
(Fig. 1).
It is in not necessary to wait for curing of the seal-
ant. The cooling system can be refilled and the vehi-
cle placed in service immediately.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
If a loss of performance is noticed, timing belt or
chain may have skipped one or two teeth. Camshaft
and crankshaft timing should be checked. Refer to
Group 9, Engine Timing belt or chain installation.
It is important that the vehicle is operating to its
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and lowest vehicle emissions. If vehicle is not operat-
ing to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis out-
lined is this section. The following procedures can
assist in achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Group
8B, Starting.
(2) Check intake manifold for vacuum leaks.
(3) Perform cylinder compression pressure test.
Refer to Engine Diagnosis, outlined in this section.
(4) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Group 8D, Ignition System.
Tighten to specifications.
Fig. 1 Core Hole Plug Removal
9 - 2 ENGINENS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1057 of 1938

ENGINE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CYLINDER COMBUSTION
PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST.............. 8
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST . . 7
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐMECHANICAL......... 12
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE...... 10GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 7
INSPECTION
(ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)......... 8
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS..... 7
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET)
NOISE DIAGNOSIS...................... 8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GENERAL INFORMATION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Service DiagnosisÐMechanical Chart
and the Service DiagnosisÐPerformance Chart, for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. Refer
to Group 14, Fuel System, for the fuel system diag-
nosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If a change in RPM'S, the area of the suspected
leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.
(4) Disconnect coil wire from distributor and
secure to good ground to prevent a spark from start-
ing a fire (Conventional Ignition System). For Direct
Ignition System DIS disconnect the coil connector.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gage adaptor into the #1
spark plug hole in cylinder head. Crank engine until
maximum pressure is reached on gage. Record this
pressure as #1 cylinder pressure.
(7) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(8) Compression should not be less than (689kPa)
100 psi and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(9) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(10) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
NSENGINE 9 - 7
Page 1145 of 1938

aligning yokes. The yokes are secured by an align-
ment yoke retainer (Fig. 4).
PRELIMINARY STEP TO CHECKING THE
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, read the oil pressure at the gauge.
Install a reliable gauge at pressure sending unit if
vehicle has no oil pressure gauge and check the oil
level in the oil pan. The pressure should be between
30 and 80 psi (206.8 to 551.6 kPa) at 2000 rpm.
The oil level in the pan should never be above the
MAX mark on dipstick, or below the MIN mark.
Either of these two conditions could be responsible
for noisy tappets.Oil Level Check: stop engineafter reaching normal operating temperature.
Allow 5 minutes to stabilize oil level, check dipstick.
OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the MAX mark on dip stick, it
is possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil
while engine is running and create foam. Foam in oil
pan would be fed to the hydraulic tappets by the oil
pump causing them to become soft and allow valves
to seat noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which
when fed to the tappets, causes them to become soft
and allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake
side of pump through which air can be drawn will
create the same tappet action. Check the lubrication
system from the intake strainer to the pump cover,
including the relief valve retainer cap. When tappet
noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent or
constant, and usually more than one tappet will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all of
the air inside of the tappets to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE DIAGNOSIS
To determine source of valve train noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and
listen for source of the noise.
Fig. 3 3.3/3.8L V-6 Engines
Fig. 4 Roller Tappets Aligning Yoke and Retainer
NS3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 95
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1221 of 1938

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT
CRANK OR CRANKS
SLOWLY1. Starting motor operating, but not cranking the
engine.1. Remove the starter motor. Check for broken
flywheel teeth or a broken starter motor spring.
2. Crankshaft rotation restricted. 2. Rotate the engine to check for rotational
resistance.
3. Starting circuit connections loose or corroded. 3. Clean and tighten connections.
4. Neutral safety or starter relay inoperative. 4. Check starter relay supply voltage and proper
operation of neutral safety switch (if equipped).
Replace defective parts.
5. Battery charge low. 5. Check Battery voltage. Replace battery if a
charge cannot be held.
6. No voltage to starter solenoid. 6. Check voltage to solenoid. If necessary, replace
the solenoid.
7. Solenoid or starter motor inoperative. 7. Replace starter motor.
ENGINE CRANKS, BUT
WILL NOT START, NO
SMOKE1. No fuel in supply tank. 1. Fill fuel supply.
2. Electrical fuel shutdown solenoid not operating. 2. Check for loose wires and verify that the fuel
shutdown solenoid is functioning. Check for fault
codes in the ECU.
3. Fuel injection system defective: Cranking speed
sensor. Loose connection between ECU and
harness. No power supply to the ECU. Loose
connection between injection pump and harness.3. Check for fault codes at ECU. Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System for repairs procedures.
4. Air intake or exhaust plugged. 4. Remove the obstruction.
5. Fuel filter plugged. 5. Drain fuel/water separator and replace fuel filter.
6. Excessive fuel inlet restriction. 6. Check for restriction. Correct cause.
7. Injection pump not getting fuel or fuel is aerated. 7. Check fuel flow/bleed fuel system.
8. One or more injectors worn or not operating
properly.8. Check/replace bad or improperly operating
injectors.
9. Camshaft out of time. 9. Check/correct timing chain sprocket alignment.
ENGINE HARD TO
START, OR WILL NOT
START, SMOKE FROM
EXHAUST1. Incorrect starting procedure. 1. The fuel shutoff solenoid control must be in the
run position. Ensure the proper procedure is being
used.
2. Cranking speed to slow. 2. Check the battery, starter motor and look for
loose or corroded wiring connections.
3. Cylinder head heater plugs defective. 3. Verify system is working. Verify connection
between heater plug relay and ECU. Repair/replace
inoperative parts.
4. Insufficient intake air 4. Inspect or replace air filter and check for
obstruction in air supply.
5. Air in fuel system or the fuel supply is
inadequate.5. Check the fuel flow through the filter and bleed
system. Locate and eliminate the air source.
6. Contaminated fuel. 6. Verify by operating the engine with clean fuel
from a temporary tank. Check for the presence of
gasoline. Drain and flush fuel supply tank. Replace
fuel/water separator filter.
7. Fuel screen plugged. 7. Check fuel screen.
8. One or more injectors worn or not operating
properly.8. Check/replace improperly operating injectors.
9. Injector pump out of time. 9. Check pump timing. Refer to Group 14, Fuel
System for procedure.
10. Engine compression low. 10. Check compression to identify the problem.
11. Fuel injection system defective. 11. Vacuum modulator defective causing EGR to
open in cold condition. Check for fault codes in the
ECU.
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 43
Page 1223 of 1938
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐMECHANICAL CONT.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
LUBRICATING OIL LOSS
(CONT.)6. Turbocharger leaking oil into the
air intake.6. Inspect air duct for evidence of oil
transfer.
7. Piston rings not sealing (oil being
consumed by the engine).7. Perform blow-by check. Repair as
required.
COMPRESSION KNOCKS 1. Air in fuel system. 1. Bleed the fuel system (refer to
Group 14, Fuel System).
2. Poor quality fuel or water/gasoline
contaminated fuel.2. Verify by operating from a
temporary tank with good fuel. Clean
and flush the fuel supply tank.
Replace fuel/water separator.
3. Engine Overloaded. 3. Verify the engine load rating is not
being exceeded.
4. Improperly operating injectors. 4. Check and replace injectors.
5. Fuel injection system defective. 5a. Instrumented injection. 5b. Timing
solenoid of the fuel pump. 5c. Pre
and post heat time of the glow plugs.
Check the fault codes in the ECU.
EXCESSIVE ENGINE NOISES 1. Drive belt squeal, insufficient
tension or abnormally high loading.1. Inspect the drive belts. Make sure
water pump pulley, generator and
power steering all turn freely.
2. Intake air and exhaust leak. 2. Refer to excessive exhaust smoke.
(Engine Diagnosis and Testing)
3. Excessive valve lash. 3. Make sure the rocker arms are not
bent. Defective hydraulic lash
adjuster.
4. Turbocharger noise. 4. Check turbocharger impeller and
turbine wheel for housing contact.
5. Power function knock. 5. Check and replace rod and main
bearings.
6. Fuel injection system defective. 6a. Instrumented injection. 6b. Timing
solenoid of the fuel pump. 6c. Pre
and post heat time of the glow plugs.
Check the fault codes in the ECU.
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 45
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1228 of 1938

VALVE STAND DOWN
Valve stand down is to maintain the adequate com-
pression ratio.
(1) Invert cylinder head.
(2) Fit each valve to its respective valve guide.
(3) Using a straight edge and feeler gauge (Fig. 9),
check valve head stand down: Inlet valve head stand
down .80 to 1.2 mm (.031 to .047 in.) and exhaust
valve stand down .79 to 1.19 mm (.031 to .047 in).
(4) If valve head stand down is not in accordance
with above, discard original valves, check stand down
with new valves and recut valve seat inserts to
obtain correct stand down.
VALVE GUIDE HEIGHT
(1) Valve Guides height requirement.
(2) Measurement A (Fig. 10): 13.50 - 14.00 mm.
VALVE STEM-TO-GUIDE CLEARANCE
MEASUREMENT
(1) Measure and record internal diameter of valve
guides. Valve guide internal diameter is 8.0 to 8.015
mm (.3149 to .3155 in.).
(2) Measure valve stems and record diameters.
Intake valve stem diameter 7.94 to 7.96 mm (.3125 to
.3133 in). Exhaust valve stem diameter 7.92 to 7.94
mm (.3118 to .31215 in).(3) Subtract diameter of valve stem from internal
diameter of its respective valve guide to obtain valve
stem clearance in valve guide. Clearance of inlet
valve stem in valve guide is .040 to .075 mm (.0015
to .0029 in). Clearance of exhaust valve stem in valve
guide is .060 to .095 mm (.0023 to .0037 in).
(4) If valve stem clearance in valve guide exceeds
tolerances, new valve guides must be installed.
FITTING PISTON RING
(1) Wipe cylinder bore clean. Insert ring and push
down with piston to ensure it is square in bore. The
ring gap measurement must be made with the ring
positioning at least 12 mm (0.50 in.) from bottom of
cylinder bore (Fig. 11). Check gap with feeler gauge.
Top compression ring gap .25 to .50mm (.0098 to
.0196 in.). Second compression ring gap .25 to .35mm
(.0098 to .0137 in.). Oil control ring gap .25 to .58mm
(.0098 to .0228 in.).
(2) If ring gaps exceed dimension given, new rings
or cylinder liners must be fitted. Keep piston rings in
piston sets.
(3) Check piston ring to groove clearance (Fig. 12).
Top compression ring gap .08 to .130mm (.0031 to
.0051 in.). Second compression ring gap .070 to
.102mm (.0027 to .0040 in.). Oil control ring gap .040
to .072mm (.0015 to .0028 in.).
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
(1) Attach dial indicator to engine block (Fig. 13).
(2) Move crankshaft toward front of engine and
zero indicator.
(3) Move crankshaft toward the rear of engine and
record measurement.
(4) Subtract specified crankshaft end float from
figure obtained. Crankshaft end float 0.08 to
0.21mm.
(5) Select thrust washer which will give correct
end float.
Fig. 9 Checking Valve Stand Down
Fig. 10 Valve Guide Height
Fig. 11 Ring Gap Measurement
9 - 50 ENGINENS/GS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1232 of 1938

(28) Remove radiator support bolts.It is neces-
sary to loosen the receiver/dryer to gain access
to the radiator bolts.
(29) Remove radiator and fans as an assembly.
(30) Remove accessory drive belt generator/power
steering. Refer to Group 7, for procedure.
(31) Remove both power steering lines at pump,
and cap both lines.
NOTE: It is not necessary to discharge A/C system
for engine removal.
(32) Remove A/C compressor. Secure compressor
away from engine for clearance during engine
removal.
(33) Remove Generator and adjusting bracket.
NOTE: Do not remove the mounting base from the
generator. It is aligned at the factory and cannot be
realigned in the field.
(34) Hoist vehicle.
(35) Remove exhaust pipe at turbo outlet.
(36) Remove connections at starter.
(37) Remove power steering high pressure line
bracket at rear of oil pan.
(38) Remove both driveshafts from transaxle. Refer
to Group 2, Suspension and Driveshafts.
(39) Disconnect clutch cable at transaxle.
(40) Remove reinforcement plate on lower cross-
member.
(41) Remove front and rear engine mounts. Refer
to procedure outlined in this section.
(42) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter if neces-
sary.
(43) Mount both special tool, engine support brack-
ets VM-1026 to cylinder block (Fig. 21).
(44) Using engine dolly and cradle assembly with
4 adjustable posts align posts with holes in the
engine support brackets.
(45) Lower vehicle so weight ofonly the engine
and transmissionis on the dolly and cradle assem-
bly.
(46) Remove left side splash shield to gain access
to thru bolt for left side mount.
(47) Remove right engine mount and left side
mount. Refer to procedure outlined in this section.
(48) Raise vehicle slowly. It may be necessary to
move the engine/transmission assembly on the dolly
to allow for removal around body.
(49) Reverse removal procedure for installation.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery cables.
(2) Remove generator bracket.(3) Remove breather hose.
(4) Remove coolant pressure tank.
(5) Remove cylinder head cover.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install cylinder head cover, torque nuts to 23.5
N´m (208 in. lbs.).
(2) Install coolant pressure tank.
(3) Install breather hose.
(4) Install generator bracket, tighten bolts to 7
N´m (4 ft. lbs.).
(5) Connect battery cable.
ROCKER ARMS AND PUSH RODS
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery cables.
(2) Remove generator bracket.
(3) Remove breather hose.
(4) Remove coolant pressure tank.
(5) Remove cylinder head cover.
(6) Remove rocker retaining nuts (Fig. 22).
(7) Remove rocker assembly. Place them on a
bench in the same order as removed.
(8) Remove the push rods and place them on a
bench in the same order as removed.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the push rods in the same order as
removed.
(2) Install rocker arm assemblies in the same
order as removed. Tighten the rocker arm nuts to
29.4 N´m (264 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 21 Engine Removal
9 - 54 ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)