1996 BMW 323i starter motor
[x] Cancel search: starter motorPage 356 of 759

515-8
CENTRAL
LOCKING
AND
ANTI-THEFT
Central
Body
Electronics
(ZKE
IV)
Electronic
Immobilization
System
(EWS)
Beginning
withvehicles
produced
9193
(model
year
1994),
The
electronic
anti-theft
system
known
as
EWS
was
first
in-
the
centrallocking
system
was
integrated
with
sunroof
and
troduced
in
January
1994
.
The
early
version
of
the
system
window
closure
into
the
Central
Body
Electronics
(ZKE
IV)
uses
a
starting
inhibition
module
to
interrupt
the
ignition,
the
(generation
four)
system
.
The
control
module
for
this
system
fuel
injection
and
the
starter
motor
.
This
system
is
activated
ís
mounted
in
front
of
the
glove
compartment
.
and
deactivated
by
the
centrallockíng
system
.
The
control
module
for
the
system
is
installed
under
the
left
side
of
the
Inthis
system
two
microswítches
are
operated
viathe
door
dashboard
.
lock
cylinder
at
both
front
doors
.
Turning
the
key
approximate-
ly
45°
(position
1)
operates
the
door
locking
microswitch
and
Startingwith
modeis
built
since
January
1995,
E36
cars
activates
the
alarm
system
.
Holding
the
key
in
thatposition
come
equipped
with
a
sophisticated
coded
electronic
immobi
also
closes
any
open
windows
and
the
sunroof
.
lization
system
called
EWS
II
.
Foraschematic
of
the
system,
refer
to
Fig
.
21
.
Turning
the
key
approximately
45°
in
the
opposite
direction
through
position
0
actuates
theunlocking
microswitch
and
de-
activates
the
alarm
system
(position
2)
.
See
Fig
.
20
.
NOTE
-
The
EWS
11
system
is
also
sometimes
referred
to
as
the
Driveaway
Protection
System
or
the
electronic
immobi-
lization
system
.
On
EWS
II
equipped
cars,
the
ignition
key
is
embedded
with
a
computer
chip
and
permanently
encoded
.
A
primary
code
is
programmed
into
the
keyand
finto
the
vehicle
itself
.
A
second-
ary
code
is
changed
every
time
the
vehicle
is
started
.
If
thekey
code
and
EWS
II
control
module
code
do
notmatch,
the
en-
gine
management
control
module
and
the
starter
are
dis-
abled
.
EWS
II
ignition
keyscannot
be
duplicated
.
The
system
is
designed
to
have
up
to
ten
keys
and
only
an
authorized
BMW
dealer
can
provide
replacement
keys
.
j
NOTE-
0011762a
ft
is
possible
to
damage
the
electronic
circuítry
in
the
Fig
.
20
.
ZKE
IV
door
lock
cylinder
positions
.
key,
rendering
if
unusable
.
In
that
case,
a
new
key
shouldbe
purchased
and
initialized
byan
authorized
BMW
dealer
.
LOCKING
SYSTEM
AND
ELECTRONIC
IMM081LIZATION
Page 383 of 759

NOTE
-
Sometimes
the
color
of
en
installed
wire
may
be
differ-
ent
than
the
one
on
the
wiring
diagram
.
Don't
be
con-
cerned
.
Just
be
sure
lo
confirm
that
the
wire
connects
lo
the
proper
terminals
.
Wire
color
codes
"
BLU
.........
.
..
..
...
.
.................
Blue
"
BRN
....:....
.
..
..
...
..
...............
Brown
"
YEL
.........
.
..
..
...................
.Yellow
"
GRN
.........
.
..
..
...
.
................
creen
"
G
RY
.......
.
.
.
..
..
.....................
G
ray
"
ORG
.........
.
..
..
...
.
..............
.Orange
"
RED
......
...
.
.
..
.....................
.Red
"
BLK
.........
.
..
..
...
.
................
Black
"
VIO
..........
.
..
...
..
..
.......
.
.......
Violet
"
WHT
.........
.
.
....
.
...
:..............
White
Table
a
.
Terminal
and
Circuit
Numbers
Number
1
Circuít
description
1
j
Low
voltage
switched
terminal
of
coi¡
4
1
High
voltage
center
termina¡
of
coi¡
+x
Originates
atignition
switch
.
Supplies
powerwhen
the
ignition
switch
is
in
the
PARK,
RUN,
or
START
position
15
Originates
atignition
switch
.
Supplies
powerwhen
ignition
switch
is
in
RUN
or
START
position
30
Battery
positive
(+)
voltage
.
Supplies
power
whenever
battery
is
connected
.
(Not
dependent
on
ignition
switch
position,
unfused)
31
1
Ground,
battery
negative
(-)
terminal
50
Supplies
power
from
battery
to
starter
solenoid
when
ignition
switch
isin
START
position
only
+54
Originates
atignition
switch
.
Supplies
power
when
ignition
switch
isin
the
RUN
position
only
85
1
Ground
side
(-)
ofrelay
coil
86
1
Power-in
side
(+)
ofrelay
coil
87
1
Relay
actuatedcontact
D
Alternator
warning
light
and
field
energizing
circuit
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM-GENERAL
600-
3
Additional
abbreviations
shown
in
the
wiring
diagrams
are
given
below
.
Abbreviations
"
ABS
........
.
...
.
...
.
..........
antilock
brakes
"
A/C
........
.
...
..
..
.
.........
.airconditioning
"
AST/ASC+T
.......
...
.
.
.......
al¡
season
traction
"
CONV
.......
.
.
...
.................
convertible
"
DME
........
.
.
...
.......
digital
motor
electronics
"
ECM
.......
.
...
..
..
.
..
electronic
control
module
"
EWS/EWS
II
......
...
.
.
coded
driveaway
protection
"
SRS
........
.
supplemental
restraint
system-airbag
"
TCM
........
.
..
....
.
transmission
control
module
"
ZKE
(94-98
models)
..
..
.
...
central
body
electronics
"
ZVM
(92-93
models)
...
.
.
..
.
.......
central
locking
ELECTRICAL
TROUBLESHOOTING
Most
terminals
are
identified
by
numbers
on
the
compo-
nents
and
harness
connectors
.
The
terminal
numbers
for
ma-
Four
things
are
required
for
current
toflow
in
any
electrical
jor
electrical
connections
are
shown
in
the
diagrams
.
Though
circuit
:
a
voltagesource,
wires
or
connections
to
transport
the
many
terminal
numbers
appear
only
once,
severa¡other
num-
voltage,
a
load
or
device
that
uses
the
electricity,
and
a
con-
bers
appear
in
numerous
places
throughout
the
electrical
sys-
nection
to
ground
.
Most
problemscanbefound
using
a
digital
tem
and
identify
certain
types
ofcircuits
.
Some
of
the
most
multimeter
(volt/ohm/amp
meter)to
check
for
voltage
supply,
common
circuit
numbers
are
listed
below
in
Table
a
.
for
breaks
in
the
wiring
(infinite
resistance/no
continuity),
orfor
a
path
to
ground
that
completesthe
circuit
.
Electric
current
is
logical
in
its
flow,
always
moving
from
the
voltage
sourcetoward
ground
.
Electricalfaults
can
usually
be
located
through
a
process
of
elimination
.
When
troubleshoot-
ing
a
complex
circuit,
separate
the
circuit
into
smaller
parts
.
The
general
testsoutlined
below
may
be
helpful
in
finding
electrical
problems
.
The
information
is
most
helpful
when
used
with
the
wiring
diagrams
.
Be
sure
to
analyze
the
problem
.
Use
the
wiring
diagrams
to
determine
the
most
likely
cause
.
Getan
understanding
of
how
the
circuit
works
by
following
the
circuit
from
groundback
to
the
power
source
.
When
making
test
connections
at
connectors
andcompo-
nents,
use
care
to
avoidspreading
or
damaging
the
connec-
tors
or
terminals
.
Some
tests
may
require
jumper
wires
to
bypass
components
or
connections
in
the
wiring
harness
.
When
connecting
jumper
wires,
use
bladeconnectors
at
the
wire
ends
that
match
the
size
of
the
terminal
being
tested
.
The
small
interna¡
contacts
are
easily
spread
apart,
and
this
can
cause
intermittent
or
faultyconnections
that
can
leadto
more
problems
.
ELECTRICAL
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 384 of 759

600-
4
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM-GENERAL
Voltage
and
Voltage
Drops
The
wires,
connectors,
and
switches
that
carry
current
are
designed
with
very
low
resistance
so
that
current
flows
with
a
minimum
loss
of
voltage
.
A
voltage
drop
is
caused
by
higher
than
normal
resistance
in
a
circuit
.
This
additional
resistance
actually
decreases
or
stops
the
flow
of
current
.
A
voltage
drop
can
be
noticed
byproblems
ranging
fromdim
headlights
to
sluggish
wipers
.
Some
common
sources
of
voltage
drops
are
corroded
or
dirty
switches,
dirty
or
corroded
connections
or
contacts,
and
loose
or
corroded
ground
wires
and
ground
con-
nections
.
A
voltage
drop
test
is
a
good
test
to
make
if
current
is
flowing
through
the
circuit,
butthe
circuit
is
not
operating
correctly
.
A
voltage
drop
test
will
help
to
pinpoint
a
corroded
ground
strap
or
a
faulty
switch
.
Normally,
there
should
be
less
than
1
volt
drop
across
most
wires
or
closed
switches
.
A
voltage
drop
across
a
connector
or
short
cable
shouldnot
exceed
0
.5
volts
.
Voltage,
measuring
1
.
Connect
digital
multimeternegative
lead
to
a
reliable
ground
point
oncar
.
NOTE-
The
negative
(-)
battery
terminal
is
alwaysa
good
ground
point
.
2
.
Connect
digital
multimeter
positive
lead
to
point
incir-
cuit
you
wish
to
measure
.
See
Fig
.
1
.
If
a
reading
is
ob-
tained,
current
is
flowing
through
circuit
.
NOTE-
The
voltage
reading
shouldnot
deviate
more
than
1
volt
from
the
voltage
at
the
battery
.
If
the
voltage
drop
is
more
than
this,
check
for
acorroded
connector
or
cose
ground
wire
.
ELECTRICAL
TROLIBLESHOOTING
from
Battery
Fig
.
1
.
Digital
multimeterbeing
used
to
test
voltage
.
No
voltage
r_l
-1
Load
LJ
Switch
NOTE-
The
maximum
voltage
drop
in
an
automotive
circuit,
as
recommended
by
the
Society
of
AutomotiveEngineers
(SAE),
is
as
follows
:
0
voltsfor
small
vire
connections
;
0
.1
Volts
for
high
current
connections
;
0
.2
volts
for
high
current
cables
;
and
0
.3volts
for
switch
or
solenoidcon-
tacts
.
On
longer
wires
or
cables,
the
drop
may
be
slight-ly
higher
.
In
any
case,
a
voltage
drop
of
more
than
1.0volt
usually
indicates
a
problem
.
0013238
NOTE-
"
A
voltage
drop
test
is
generally
more
accuratethan
a
Voltage
drop,
testing
simple
resistance
check
because
the
resistances
in-
volvedare
often
too
small
to
measure
with
most
ohm-
Voltage
drop
can
only
be
checked
when
current
is
running
meters
.
For
example,
a
resistance
as
small
as0
.02
through
the
circuit,
suchasby
operating
the
starter
motor
or
ohms
would
results
in
a
3
volt
drop
in
a
typical
150
turning
onthe
headlights
.
A
digital
multimeter
should
beused
amp
starter
circuit
.
(150
amps
x
0
.02
ohms
=3
volts)
.
lo
ensure
accurate
readings
.
"
Keep
in
mind
that
voltage
with
the
key
on
and
voltage
with
the
engine
running
arenotthe
same
.
With
the
ig-
1
.
Connect
digital
multimeter
positive
lead
to
positive
(+)
nition
on
and
the
engine
off
(battery
voltage),
voltage
battery
terminalor
a
positive
power
supply
close
lo
bat
should
be
approximately
12
.6volts
.
With
the
engine
tery
source
.
running
(charging
voltage),
voltage
should
be
approx-
imately
14
.0
volts
.
Measure
voltage
at
the
battery
with
2
.
Connect
digital
multimeter
negativelead
to
other
end
of
the
ignition
on
and
then
with
the
engine
running
to
get
cable
orswitch
being
tested
.
See
Fig
.
2
.
exact
measurements
.
3
.
With
power
on
and
circuit
working,
meter
shows
volt-
age
drop
(difference
between
two
points)
.
This
value
should
not
exceed
1
volt
.
Page 389 of 759

Fig
.
5
.
Splice
panel
under
left
side
of
dash
.
SplicePanel,
Right
ir1!
1,
111lí~lll
.
'
ELECTRICAL
COMPONENT
LOCATIONS
610-3
0013091
1
.
Unloader
relay
4
.
Starter
immobilization
2
.
Wiper
relay
relay
(1994
only)
3
.
Wiper
motor
relay
F47
&
F50
Fuses47
and
50
The
right
splice
panel
contains
three
relay
positions
.
It
is
lo-
cated
under
the
right
side
of
the
dashboard
.
To
access
the
panel,
remove
theglove
compartment
as
de-
scribed
in
513
Interior
Trim
.
See
Fig
.
6
.
Fig
.
6
.
Splice
panel
under
right
side
of
dash
(arrow)
.
Glove
compart-
ment
and
right
side
vents
shown
removed
.
COMPONENT
LOCATIONS
On
the
following
pages
are
illustrations
and
photos
showing
the
location
of
major
electrical
components
in
E36
vehicles
.
NOTE-
-
Every
component
is
not
installed
in
everycar
.
"
Due
to
changes
in
production,
component
locations
may
vary
from
what
is
illustrated
.
Consult
your
BMW
dealer
for
the
latest
information
.
"
The
gear-position/neutral
safety
switch
ís
also
some-
times
referred
to
as
the
automatic
transmission
range
switch
.
"
The
EWS
11
system
is
also
sometimes
referred
to
as
the
Driveaway
Protection
System
or
the
electronic
im-
mobilization
system
.
"
All-Season
Traction
(AST)
is
also
sometimes
referred
to
as
ASC
or
ASC+T
.
COMPONENT
LOCATIONS
Page 403 of 759

Tablea
.
E36
Component
Locations
Component
Model
Year
Location
Refer
to
Rollover
Sensor
1994-1998
In
lower
left
C-pillar
behind
trim
panel
(Convertible)
Seat
Belt
Switch
1992-1998
In
front
seat
belt
buckle
SeatCushion
Tilt
Motor
1992-1998
Under
front
seat
Seat
Heater
1993-1998
Under
front
seat
Seat
Height
Motor
Front
1992-1998
Under
front
seat
Seat
Movement
Motor
1992-1998
Under
front
seat
Seatback
Heater
1993-1998
In
upper
front
seatback
Seatback
Recliner
Motor
1993-1998
Under
front
seat
Seat
Occupancy
Detector
1994-1998
Under
rightfront
seat
Secondary
Air
Pump
(4-cyl
.)
1997
1
/2
-
1998
Left
engine
compartment,
belowpower
distribution
box
(M44
engine)
Secondary
Air
Pump
(6-cyl
.)
1996-1998
Front
of
engine
compartment
(M52/S52US
engine)
Secondary
Air
Pump
Relay
1996-1998
Power
distribution
box
Fig
.
2
.
Secondary
Air
Pump
Valve
1996-1998
Right
sideof
engine
Side
Impact
Air
Bag
Right/Left
1997-1998
Behind
right/left
door
trim
panel
Síde
Impact
Airbag
Crash
Sensor,
1997-1998
Right/left
door
si¡¡
behind
front
seat
Right/Left
Shift
Interlock
1992-1998
Center
console
beside
shift
selector
Slip
Control
Module
(ABS/AST)
1992-1998
Behind
glove
compartment
Fig
.
8
.
Fig
.
9
.
Splice
Panel,
Left
Side
1992-1998
Behind
footwell
speaker
grill
Fig
.
5
.
SplicePanel,
Right
Side
1992-1998
Behind
glove
compartment
Fig
.
6
.
Starter
1992-1998
Leftrear
of
engine
Starter
Immobilization
Relay
1994-1998
In
left
splice
panelbehind
footwell
speaker
grill
Starter
Relay
1992-1993
Below
left
side
of
dash
Starter
Relay
1994-1998
Behind
left
footwell
speaker
grill
Sunroof
Control
Assembly
1992-1998
In
roof
center
panel
Supplemental
Restraint
System
11992-1993
I
Behind
glove
compartment
I
Fig
.
8
.
(Airbag)
Control
Module
Fig
.
9
.
Supplemental
Restraint
System
1994-1998
1
Under
center
of
rear
seat
(Airbag
ZAE)
Control
Module
Switch,
Power
Window
1
1992-1998
1
Center
console
Telephone
Eject
Box
1
1994-1996
1
Center
console
ELECTRICAL
COMPONENT
LOCATIONS
610-17
Telephone
Transceiver
1992-1992
In
luggage
compartment
Throttle
Flap
Heater
1994-1996
Left
sideof
engine
Throttle
Position
Sensor
1992-1998
I
Left
sideof
engine
inthrottle
housing
I
Fig
.
7
.
Fig
.
15
.
Fig
.
21
.
Continued
COMPONENT
LOCATIONS
Page 495 of 759
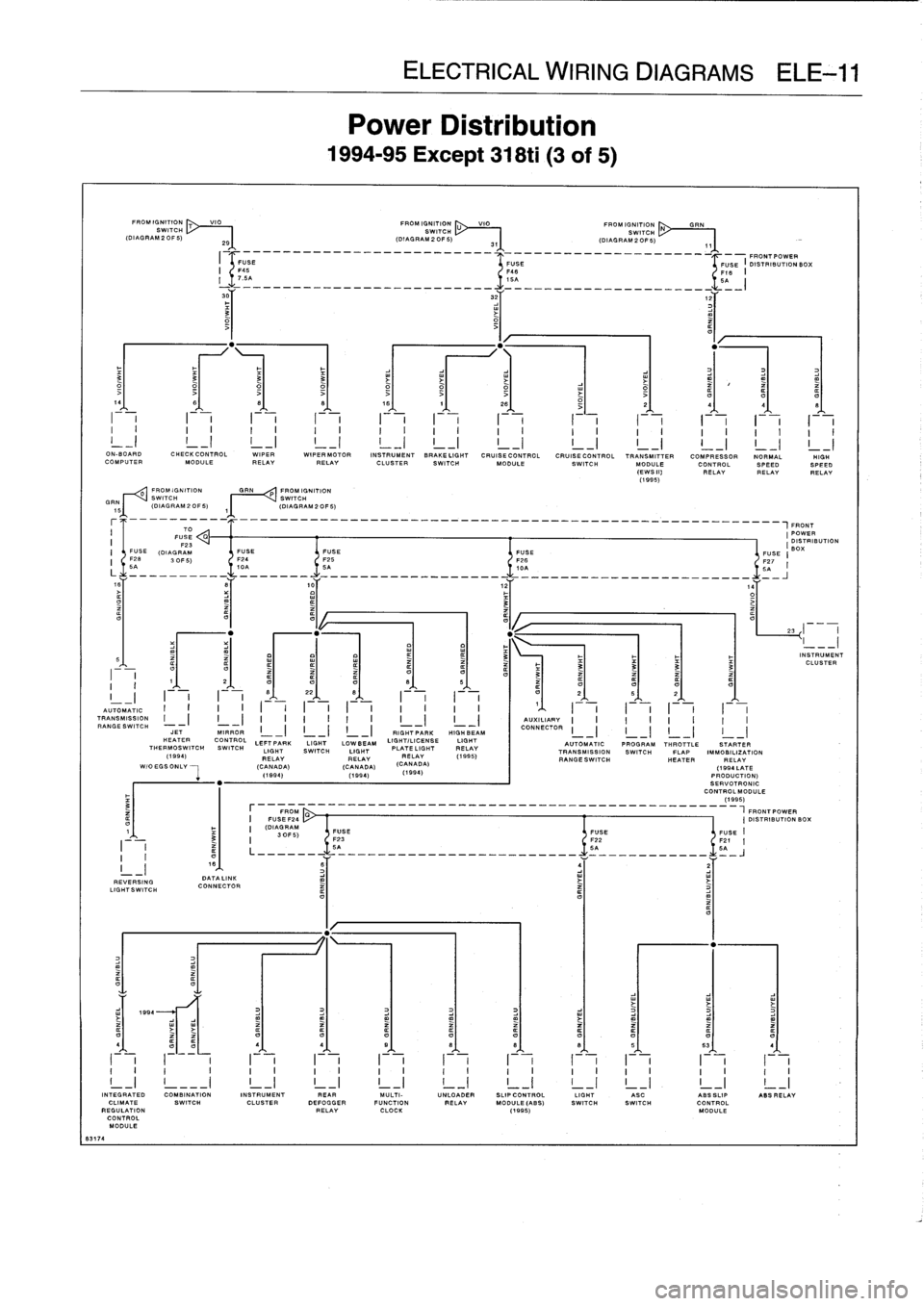
8317
4
FROMIGNITION
T
VIO
FROM
IGNITION
U
VIO
"I"
IGNITION
SWITCH
SWITCH
SWITCH
(DIAGRAM2OF5)
29
(DIAGRAM20F5)
31
(DIAGRAM20F5)
FROMIGNITION
GRIN
PROMIGNITION
SWITCH
SWITCH
(DIAGRAM20F5)
~(DIAGRAM20F5)
REVERSING
LIGHT
SW
TO
DATA
LINK
CONNECTOR
Power
Distribution
1994-95
Except
318ti
(3
of
5)
______________________________________________
-_-
FRONTPOWER
ELECTRICAL
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
ELE-11
3
FUSE
FUSE
I
DISTRIBUTION
BOX
F46
F18
I
L
>
t
141
6'
81
81
16/
11
261
j
2
4
q
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
i
I
Jll~~~
i
I
It
i
I
JJJ
...
i
-
i
-
i
-
i
-
i
--
I
I
I
1
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
ON-BOARD
CHECKCONTROL
WIPER
WIPERMOTOR
INSTRUMENT
BRAKELIGHT
CRUISE
CONTROL
CRUISECONTROL
TRANSMITTER
COMPRESSOR
NORMAL
HIGH
COMPUTERMODULE
RELAY
RELAY
CLUSTER
SWITCH
MODULE
SWITCH
MODULE
CONTROL
SPEEDSPEED
(EWSIN
RELAYRELAYRELAY
(1995)
,FRONT
(POWER
DISTRIBUTION
FUSE
FUSE
FUSE
(BOX
FUSE
I
F24
F25
F26
F27
10A
5A
10A
5q
I
------------------
-
-------
-
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
'
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
AUTOMATIC
"1"
TRANSMISSION
I
-
I
I
_
I
I
_
I
I
I
I
I
I
-)
I
_
I
AUXILIARY
RANGESWITCH
JETMIRROR
L
II
CONNECTORCONNECTOR
RIG
H7
PARK
HIGH
BEAM
I
I
I
I
HEATER
CONTROL
LEFT
PARK
LIGHT
LOWBEAM
LIGHT/LICENSE
LIGHT
AUTOMAT
IC
PROGRAM
THROTTLE
SWITCH
LIGHT
SWITCH
LIGHT
PLATE
LIGHT
RELAY
HROTTLE
STARTER
(
(1995)
TRANSMISSIONSWITCH
FLAP
IMMOBILIZATION
994)
RELAY
RELAYRELAY
A)
RANGESWITCH
HEATER
RELAY
WIOEGSONLV
--
I
-
(CANADA)
(CANADA)
(CANAD
(1994
LATE
(1894)
(1994)
(1
994
)
PRODUCTION)
SERVOTRONIC
CONTROLMODULE
(1995)
FROM
FRONTPOWER
I
FU
SEF24
I
DISTRIBUTIONBOX
I
(DIAGRAM
30F5)
FUSE
FUSE
FUSE
II
F23
F22
F21
I
5A
5A
5A
61
_I-
=
L
41
4,
1
91
8t
el
8),
51
531
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
i
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
_I
!
---
I
!
_I
!
_I
23
INTEGRATED
COMBINATION
INSTRUMENT
PEAR
MULTI-
UNLOADER
SLIP
CONTROL
LIGHT
ASC
ABSSLIP
ASS
RELAY
CLIMATE
SWITCH
CLUSTER
DEFOGGER
FUNCTION
RELAY
MODULE
(AB
S)
SWITCH
SWITCH
CONTROL
REGULATION
RELAY
CLOCK
(1995)
MODULE
CONTROL
MODULE
INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER
Page 500 of 759

ELE-16
ELECTRICAL
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
88978
TO
FUSE
F16
yDIAGRAM
4
OF
5)
70FU
SEF28
K
GRN
(DIAGRAM
4OF5)
___
--------
_---------------------
______________
I
IGNITION
I
SWITCH
I
_
_
_-_-__-
-----------
I
OFF
START
OFF
START
OFF
START
F,
START
FROM
FRONT
POWER
r
<
DISTRIBUTION
BOX
(DIAGRAM
2OF5)
=OC---U-
-_-_---_-__-ACC--RU=
____CC_CC--R=N-
CC-PUN
Power
Distribution
1996-97
Except
318ti
(3
of
5)
ELECTRONICIMMOBLIZER
CONTROL
MODULE
(EWS11)
NOTUSED
2_
.
15
t
I
I
II
II
F-,
II
II
I
I
II
I
I
I
I
I
-I
L-1
INSTRUMENT
HORN
RELAY
ENGINECONTROL
UN
LOADER
INSTRUMENT
BLOWERRELAY
CLUSTER
No
DULE(DME)
RELAY
CLUSTER
°_
(1996)
-----
-------
1
1'
--
FRONTPOWER
I
M
TO
1111111
IDISDISTRIBUTION
BOX
(DIAGRAM
3
OF5)
II
FUSE
FUSE
USE
I
1'44
F43
42
I
!
'________________________________
5A
~
_________________
5=
el
231
51
41
51
51
41
1
J
1
2
J
1
2
J
1
5~
1),
1
I
.+
.
1
1
1
CE
.N+
TER
I
I
.+
.
i
I
.
1
I
.
1
I
.
1
1
1
1
1
I
I
II
II
I
I
I
I
CONSOLE
TELEPHONE
GLOVE
BOX
I
-
.
I
I
-
I
I
-)
I
-
I
I
-
I
CONNECTOR
LIGHT
(1987)
WIPER/
WIPER/
RADIO
TWIN
RELAY
WASHERWASHER
WASHER
MODULE
PUMPMODULE
MODULE
(1996
CANADA)
(1996
CANADA)
SEAT
RIGHTSIDE
LEFT
SIDE
SRS
ROLLOVER
OCCUPANCY
IMPACTIMPACT
CONTROLSENSOR
DETECTOR
SENSORSENSOR
MODULE
(1997)(1997)(1997)
O~
31
1~
~
1
31
11
51
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
LUG
AGE
I
I
II
II
I
I
II
I
I
II
II
I
I
COMPARTMENT
TELEPHONE
CONNECTOR
LEF7MAKEUP
CONVERTIBLETOP
TELEPHONE
SEAT
SWITCH
FRONTDOME/
ANTI-THEFT
RIGHTMAKEUP
REAR
(1997)
MI
PROFLIGHT
CONTROLMODULE
TRANSCEIVER
OCCUPANCY
SPATIALSOUND
MAPLIGHT
CONTROLMODULE
MIRROR
LIGHT
INTERIOR
(1996)
DETECTOR
ASSEMBLY
(199fi)
FROMFISE
141
---
(DIAGRAM
30F5)
M
________--_--_________________-_----------------
FRONTPOWER
DISTRIBUTIONBOX
(
FUSE
FUSE
1I
F45
F4fi
I
'S
7
.5A--______________-________________-______
___
30Y
32Y
I
i
F-
,I
iF-
,I
i
I
-
F
-
,
I-
ON-BOAR
CHECK
WIPER
WIPER
STARTER
TRANSMITTER
INSTRUMENT
BRAKELIGHT
CRUISECONTROL
CRUISECONTROL
TRANSMITTER
COMPUTER
CONTROL
RELAY
MOTOR
IMMOBILIZATION
MODULE
CLUSTER
SWITCH
MODULE
SWITCH
MODULE
MODULE
(1996)
RELAY
SWITCH
(1996)
(1998)
(1997)
0
TALINK
CONNECTOR
Page 524 of 759

ELE-40
ELECTRICAL
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
RIGHTHEADLIGHT/
RIGHT
I
FRONT
I
FOG
LIGHT
I
HIGH
I
TURN
I
I
WASHER
I
I
BEAM
LIGHT
I
(PUMP
I
(LIGHT
,
L-
1
1
1
I
(POWER
I
(DOOR
I
]CONTROL
_
_
_-1
WINDOW
I
(
(CONSOLE)
I
(
(CONSOLE)
WASHER
RIGHT
WASHER
PRESSURE
m
ANTI-
--
SWITCH
--
POWER
--
(L
DOOR)
I
(FLUID
I
LOW
I
(PUMP
I
SWITCH
(-
IITHEFT
S
(CONVERTIBLE)
S
SWWINDOW
ITCH
3
I
(LEVEL
I
(BEAM
I
I(CANADA)
m
II
I
IIHORN
WSWITCH
I
SWITCH
I
(
LIGHT
I
I
I
I
I
(1995)
(4
DOOR)
I7
IT
~
~T
I
(
)
PARK
I
-
LIGHT
I
I
'DRIVERS
(
(PASSENGERS
I
(CENTRAL
LEFT
,
JI
I
(WINDOW
I(
POWER
]
(POWER
AUXILIARY
LEFT
I
FRONT
I
RIGHT
WINDOW
WINDOW
I
,
_
_
_
FAN
I
(
HIGH
(-
TURN
I
-
(
HORN
LEFT
I
(
SWITCH
I
(SWITCH
I
(
SWITCH
I
(
MOTOR
LIGHT
I--
I
LIGHT
LIGHT
¢~
¢~
¢~
(CONVERTIBLE)
I
I,
-I
I
-(
---
-
84318
ENGINE
LEFT
LEFT
CRUISE
I
I
I
rII
I
I
COOLANT
m
LOW
HORN
CONTROL
I
(LEVEL
I
(BEAM
I
II
I
(ACTUATOR
I
_I
SWITCH
I
-
(LIGHT
I
I_
-I
1
1
1
8
BRN
LEFT
LEFT
LEFT
I
I
I
I
I
I
REAR
REAR
REAR
RIGHT
I
I
(
POWER
I
(
DOOR
I
(
WINDOW
I
PARK
I
I
(WINDOW
I
((CONSOLE)
I
SWITCH
I
l,
LIGHT
I
--
SWITCH
--
POWER
-
r
-
(6
DOOR)
(CONVERTIBLE(
/A
BF.
T
BRN
Ground
Distribution
1994-95
Except
318ti
(1
of
5)
I
(TEMPERATURE
-
RIGHT
I
SWITCH
)FOG
51
¢1
WINDOW
SWITCH
(C
DOOR)
I
I
REAAT
I
,
FEAR'
I
,
PCHILD
ROTECTION
LEFT
FRONT
BRAKE
WIPER
THROTTLE
OW
WIPER/
LEFT
I
,
WASHER
I
(
FOG
I
(
FLUID
I
(
MOTOR
I
(FLAP
I
(LBEAM
I
(
WASHER
(
)
FRONT
I
(JET
I
[LIGHT
I
(LEVEL
I
I
I
(HEATER
I
(LIGHT
I
MODULE
_
AUXILIARY
_
_
_
(HEATER
I
-(RELAY
I
_(
SWITCH
I
I
I
SWITCH
I
-
IRELAY
I
(LOW
11)
TURN
LIGHT
_
a
_
2
1
s
RIGHT
ASS
COMPRESSOR
t
WIPER
HIGH
BLOWER
HAZARD
I
WASHER
I
RELAY
I
]CONTROL
I
RELAY
I
(BEAM
II
RELAY
I
(FLASHER
I
(JET
II
I
IRELAY
I
((CANADA)
m
I
,LIGHT
II
I
IRELAY
I
(HEATER
i
v
I
I
v
(SWITCH
I
v
I
I
v
IRELAV
I
v
I
,
v
I
BR
I
LIGHT
LEFT
IGNITION
CHIME
DRIVERS
DIMMER
RIGHT
,SWITCH
I(
PARK
I
SWITCH
I
MODULE
I
SEAT
.
BEAT
I
,
(
)
FRONT
I
I
I
(LIGHT
]
II
_
_I
,
,
HEATER
I
I
-
AUXILIARY
I
-I
I
-I
RELAY
I
I
I
-I
I
-I
SWITCH
I
-I
TURN
LIGHT
7
91
6
6
INSTRUMENT
STARTER
WIPER/
HORN
UNLOADER
BRAKE
PASSENGERS
,
CLUSTER
I
,RELAY
I
WASHER
I
,
SWITCH
I
,RELAY
I
LIGHT
I
,SEAT,SEAT
II
I
I
I
SWITCH
I
II
I
I
(
SWITCH
I
(
HEATER
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
"T
I
I
^T
I
I
°T
SWITCH
3
`
T
T
BRN
G302
-
I
-
.
LIGHT
-
1_
G302