1995 PONTIAC PONTIAC tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 11 of 354

Head Restraints
Slide the head restraint up or down so that the top of the
restraint is closest to the top of your ears. This position
reduces
the chance of a neck injury in a crash.
Seatback Latches (2-Door Models)
The front seat folds forward
to let people get into the
back seat. Your seatback
will move back and forth
freely, unless you come to a
sudden stop. Then
it will
lock in place.
~r your vehicle is parked going down a fairly steep hill,
the seatback may not fold without some help from you.
To fold the locked seatback forward, push the seatback
toward the rear as you
lift this latch. Then the seatback
will fold forward. The latch must be down for the seat to
work properly.
1-4
ProCarManuals.com
Page 33 of 354

When should an air bag inflate?
The air bag is designed to inflate in moderate to severe
frontal or near-frontal crashes. The air bag will inflate
only if the impact speed is above the system’s designed
“threshold level.”
If your vehicle goes straight into a
wall that doesn’t move or deform, the threshold level is
about
9 to 15 mph (14 to 24 lufl/h). The threshold level
can vary, however, with specific vehicle design,
so that
it can be somewhat above or below this range. If your
vehicle strikes something that will move or deform, such
as a parked car, the threshold level will be higher. The
air bag is not designed to inflate in rollovers, side
impacts, or rear impacts, because inflation would not
help the occupant. In any particular crash,
no one
can say whether an air
bag should have inflated simply because of the damage
to
a vehicle or because of what the repair costs were.
Inflation is determined by the angle of the impact and
the vehicle’s deceleration. Vehicle damage is only one
indication of this.
What makes an air bag inflate?
In a frontal or near-frontal impact of sufficient severity,
the air bag sensing system detects that the vehicle is
suddenly stopping as a result of a crash. The sensing
system triggers
a chemical reaction of the sodium azide
sealed in the inflator. The reaction produces nitrogen
gas, which inflates the air bag. The inflator,
air bag, and
related hardware
are all part of the air bag modules
packed inside the steering wheel and in the instrument
panel in front of the right front passenger.
How does an air bag restrain?
In moderate to severe frontal or near-frontal collisions,
even belted occupants can contact the steering wheel or
the instrument panel. The air bag supplements the
protection provided by safety belts. Air bags distribute
the force
of the impact more evenly over the occupant’s
upper body, stopping the occupant more gradually. But air bags would not help you in many types of collisions,
including rollovers and rear and side impacts, primarily
because an occupant’s motion
is not toward the air bag.
1-26 ,
ProCarManuals.com
Page 59 of 354

Q: What if a child is wearing a lap-shoulder belt,
but the child
is BO small that the shoulder belt is
very close to
the child’s face or neck?
A: Move the child toward the center of the vehicle, but
be sure that the shoulder belt still
is on the child’s
shoulder,
so that in a crash the child’s upper body
would have the restraint that belts provide.
If the
child is sitting in a rear seat outside position, see
“Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides” in the Index.
If the child is so small that the shoulder belt is still
very close to the child’s face or neck,
you might
want to place the child in the center seat position,
the one that has only a
lap belt.
1-52
ProCarManuals.com
Page 73 of 354
New Vehicle “Break-In”
NOTICE:
Your modern Pontiac doesn’t need an elaborate
“break-in.” But it will perform better in the long
run if you follow these guidelines:
Don’t drive at any one speed -- fast or
slow
-- for the first 500 miles (804 km).
Don’t make full-throttle starts.
200 miles (322 km) or so. During this time
your new brake linings aren’t yet broken
in. Hard stops with new linings can mean
premature wear and earlier replacement.
Follow
this “breaking-in” guideline every
time you get new brake linings.
Don’t tow a trailer during “break-in.” See
“Towing
a ”railer’’ in the Index for more
information.
Avoid making hard stops for the first
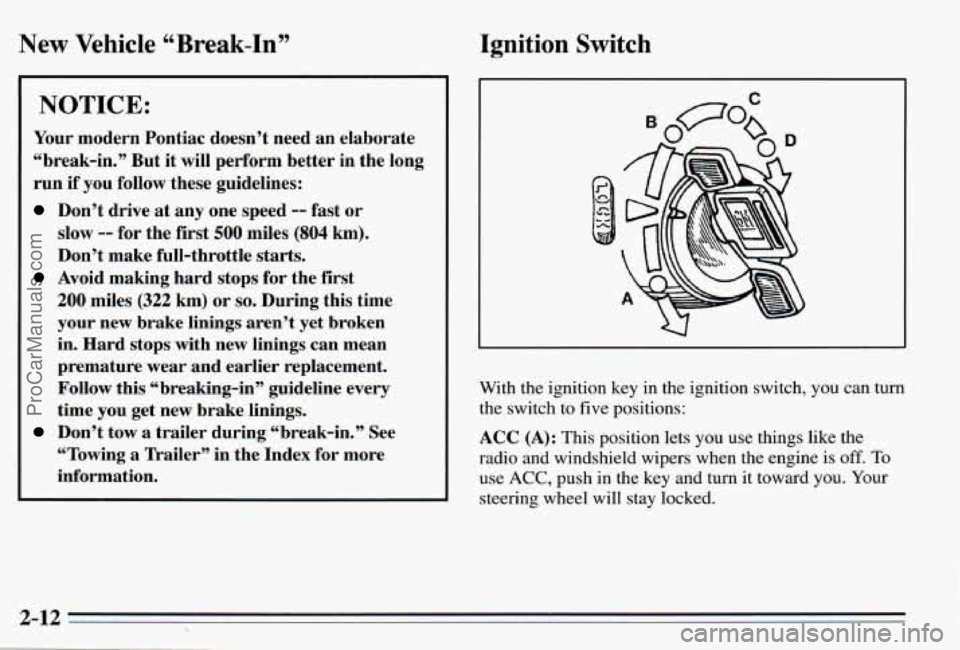
Ignition Switch
With the ignition key in the ignition switch, you can turn
the switch to five positions:
ACC (A): This position lets you use things like the
radio and windshield wipers when the engine is
off. To
use ACC, push in the key and turn it toward you. Your
steering wheel will stay locked.
2-12
ProCarManuals.com
Page 74 of 354

LOCK: Before you put the key into the ignition switch,
the switch is in
LOCK. It’s also the only position in
which you can remove
your key. This position locks
your ignition, steering wheel and transaxle. It’s a
theft-deterrent feature.
OFF (B): This position lets you turn off the engine but
still turn the steering wheel. It doesn’t lock the steering
wheel like LOCK. Use
OFF if you must have your
vehicle pushed or towed.
RUN (C): This position is where the key returns after
you start your vehicle. With the engine
off, you can use
RUN to display some of your warning and indicator
lights.
START
(D): This position starts your engine.
A warning chime will sound if you open the driver’s
door when the ignition is in
OFF, LOCK or ACC and
the key is in the ignition.
NOTICE:
If your key seems stuck in LOCK and you can’t
turn it, be sure it is all the way in.
If it is, then
turn the steering wheel left and right while you
turn the key hard. But turn the key only with
your hand. Using
a tool to force it could break
the key or the ignition switch.
If none of this
works, then your vehicle needs service.
Starting Your Engine
Move your shift lever to PARK (P) or NEUTRAL (N).
Your engine won’t start in any other position
-- that’s a
safety feature. To restart when you’re already moving,
use NEUTRAL (N) only.
NOTICE:
Don’t try to shift to PARK (P) if your Pontiac is
moving.
If you do, you could damage the
transaxle. Shift to PARK
(P) only when your
vehicle is stopped.
2-13
ProCarManuals.com
Page 75 of 354

To start your engine:
1. Without pushing the accelerator pedal, turn your
ignition
key to START. When the engine starts, let
go of the key. The idle speed will
go down as your
engine gets warm.
NOTICE:
Holding your key in START for longer than
15 seconds at a time will cause your battery to
be drained much sooner. And the excessive heat
can damage your starter motor.
2. If your engine won’t start (or starts but then stops),
it could be flooded with too much gasoline. Try
pushing your accelerator pedal all the way to the
floor and holding it there as you hold the key in
START for about three seconds. If the vehicle starts
briefly but then stops again, do the same thing, but
this time keep the pedal down for five or six seconds.
This clears the extra gasoline from the engine. Your
engine
is designed to work with the
electronics
in your vehicle. If’ you add electrical
parts or accessories, you could change the way the
fuel injection system operates. Before adding
electrical equipment, check with your dealer.
If you
don’t, your engine might not perform properly.
If you ever have to have your vehicle towed, see
the part of this manual that tells how to do it
Driving Through Deep Standing
Water
NOTICE:
If you drive too quickly through deep puddles
or standing water, water can come
in through
your engine’s
air intake and badly damage your
engine. Never drive through water that is slightly
lower than the underbody
of your vehicle. If you
can’t avoid deep puddles or standing water, drive
through them very slowly.
2-14
ProCarManuals.com
Page 78 of 354

Make sure the shift lever is fully into PARK Cp)
range before starting the engine. Your Pontiac has a
brake-transaxle sWt interlock. You must
fully apply
your regular brakes before you can shift from PARK
‘(I?)
when the ignition is in RUN. If you cannot shift out of
PARK (P), ease pressure on the shift lever by pushing it
all the way into PARK (9) while keeping the brake pedal
pushed down. Release the shift lever button if you have
a
console shift. Then move the shift lever out of PARK (P),
being sure to press the shift lever button if you have a
console shift. See “Shifting Out of
PARK (P)” in
the Index.
REVERSE (R): Use this gear to back up.
NOTICE:
Shifting to REVERSE (R) while your vehicle is
moving forward could damage your transaxle.
Shift to
REVERSE (R) only after your vehicle is
stopped.
To rock your vehicle back and forth to get out of snow,
ice or sand without damaging your transaxle, see
“Stuck: In Sand, Mud, Ice
or Snow” in the Index.
NEUTRAL (N): In this position, your engine
doesn’t connect with the wheels. To restart when you’re
already moving, use NEUTRAL
(N) only. Also, use
NEUTRAL
(N) when your vehicle is being towed.
NOTICE:
Damage to your transaxle caused by shifting out
of
PARK (P) or NEUTRAL (N) with the engine
racing isn’t covered by your warranty.
2-17
ProCarManuals.com
Page 79 of 354

DRIVE 0): This position is for normal driving.
If you vehicle has overdrive,
DRIVE (D) is the
overdrive position.
If you need more power for passing,
and you’re:
Going less than 35 mph (55 km/h), push your
accelerator pedal about halfway down.
Going about 35 mph (55 km/h) or more, push the
accelerator pedal all the way down.
You’ll shift down to the next gear and have more
power.
I NOTICE:
If your vehicle seems to start up rather slowly, or
if
it seems not to shift gears as you go faster,
something may be wrong with
a transaxle system
sensor. If you drive very far that way, your
vehicle can be damaged.
So, if this happens, have
your vehicle serviced right away. Until then, you
can use
SECOND (2) when you are driving less
than
35 mph (55 km/h) and DRIVE (D) for
higher speeds.
THIRD (3): You have this position if your vehicle has
overdrive.
THIRD (3) is like DRIVE (D), but you never
go into overdrive.
Here are some times you might choose
THIRD (3)
instead of DRIVE (D):
0 When driving on hilly, winding roads.
When towing a trailer, so there is less shifting
When going down a steep hill.
between gears.
2-18
ProCarManuals.com