Page 260 of 873
19FUEL SYSTEM
14
REPAIR RAM HOUSING
Service repair no - 19.70.04
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Remove plenum chamber.
See Plenum
Chamber
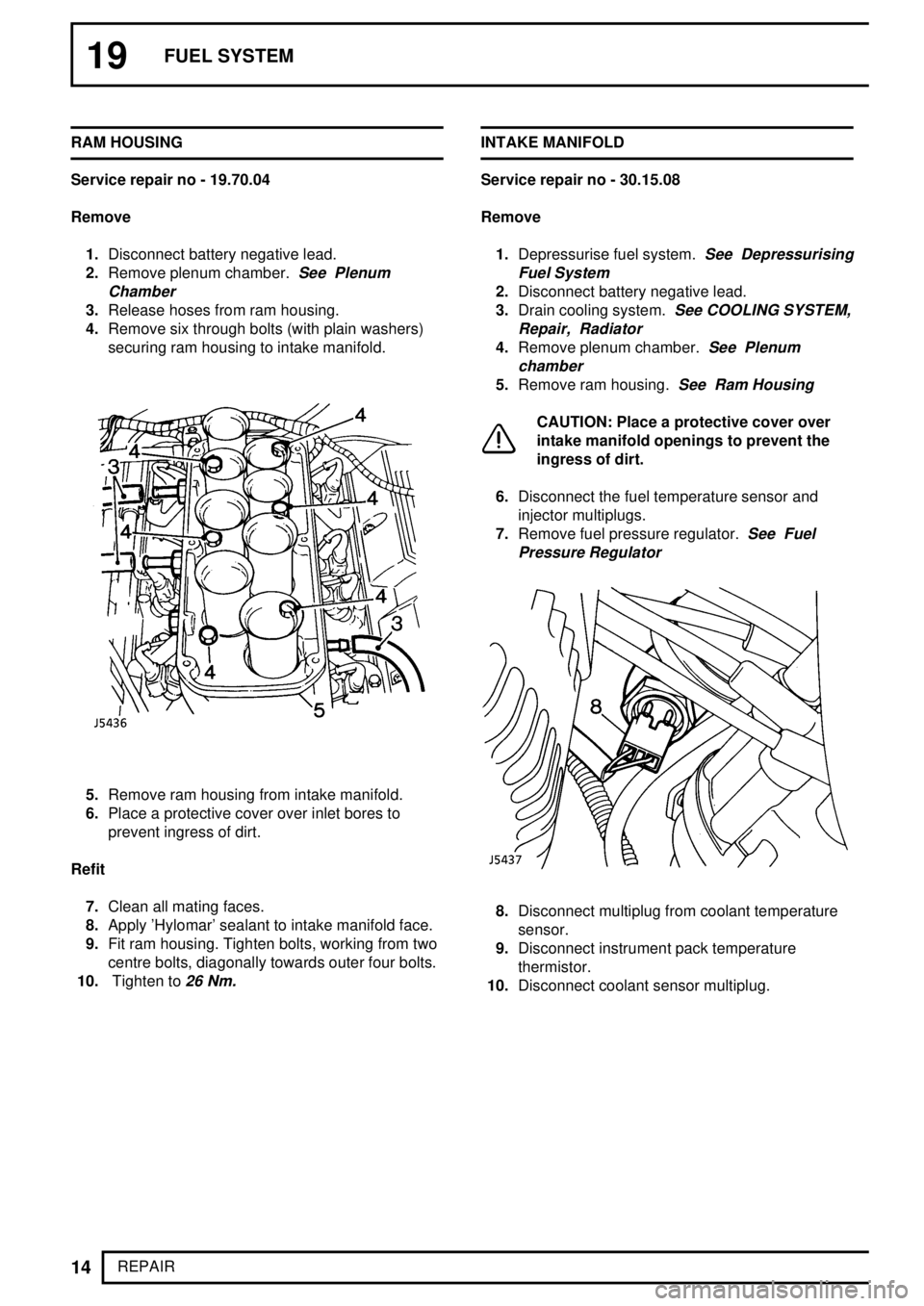
3.Release hoses from ram housing.
4.Remove six through bolts (with plain washers)
securing ram housing to intake manifold.
5.Remove ram housing from intake manifold.
6.Place a protective cover over inlet bores to
prevent ingress of dirt.
Refit
7.Clean all mating faces.
8.Apply 'Hylomar' sealant to intake manifold face.
9.Fit ram housing. Tighten bolts, working from two
centre bolts, diagonally towards outer four bolts.
10.Tighten to
26 Nm.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
Service repair no - 30.15.08
Remove
1.Depressurise fuel system.
See Depressurising
Fuel System
2.Disconnect battery negative lead.
3.Drain cooling system.
See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair, Radiator
4.Remove plenum chamber.See Plenum
chamber
5.Remove ram housing.See Ram Housing
CAUTION: Place a protective cover over
intake manifold openings to prevent the
ingress of dirt.
6.Disconnect the fuel temperature sensor and
injector multiplugs.
7.Remove fuel pressure regulator.
See Fuel
Pressure Regulator
8.Disconnect multiplug from coolant temperature
sensor.
9.Disconnect instrument pack temperature
thermistor.
10.Disconnect coolant sensor multiplug.
Page 271 of 873
MFI
1
SERVICE TOOLS FUEL SYSTEM
LRT-19-004 Test equipment fuel pressure
18G 500
LRT-19-003 MFI pressure test adaptor
LST 143
LRT-19-002 Connector splitter
LST 144
LRT-19-001 Fuel pump remover
LST 131
Page 273 of 873
19FUEL SYSTEM
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION REV: 09/95 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM COMPONENT
LOCATION - PRE ADVANCED EVAPS
1. Engine control module
2. Ignition coils
3. Fuel pressure regulator
4. Mass air flow sensor
5. Relay module
- Main relay
- Fuel pump relay
6. Engine coolant temperature sensor
7. Camshaft position sensor
8. Throttle position sensor
Page 276 of 873

SFI
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION REV: 09/95 Engine fuel temperature sensor (EFT Sensor)
This is another resistive sensor. Located on the fuel
rail it measures temperature of the rail rather than the
fuel. The resistance varies with changes in
temperature. The signal is used to increase the
injection pulse time when undergoing hot restarts.
When the fuel is hot, vapourisation occurs in the rail
and bubbles can occur in the injectors. Increasing the
pulse time flushes the bubbles away, and cools the
fuel rail with fuel from the tank. The fault may not be
evident to the driver, there may be a hot restart
problem. The fault is indicated by illumination of the
malfunction indicator light (MIL) on North American
specification vehicles.
Knock sensors
The knock sensor produces an output voltage in
proportion to mechanical vibration caused by the
engine. A sensor is located in each cylinder bank
between 2/4 and 3/5 cylinders. The ECM calculates if
the engine is knocking due to camshaft and
crankshaft sensor signals regarding the position of the
engine in the cycle. The ECM can also work out
exactly which cylinder is knocking and retards the
ignition on that particular cylinder until the knock
disappears. It then advances the ignition to find the
optimum ignition timing for that cylinder. The ECM can
adjust the timing of each cylinder for knock
simultaneously. It is possible that all eight cylinders
could have different advance angles at the same time.
If the camshaft sensor fails, the knock sensor will
continue to work, but as the engine may be running
one revolution out of sychronisation the ECM may
retard the wrong cylinder of the pair e.g. 1 instead of
6. If the knock sensor fails engine knock will not be
detected and corrected. The fault is indicated by
illumination of the malfunction indicator light (MIL) on
North American specification vehicles.Ignition coils
The electronic ignition system uses four double ended
coils. They are mounted on a bracket fitted to the rear
of the engine. The circuit to each coil is completed by
switching within the ECM, allowing each coil to charge
up and fire. Sparks are produced in two cylinders
simultaneously, one on compression stroke, the other
on exhaust stroke. Note that coil 1 feeds cylinders 1
and 6, coil 2 feeds cylinders 5 and 8, coil 3 feeds
cylinders 4 and 7, and coil 4 feeds cylinders 2 and 3.
Due to the ease of combustion in the cylinder on the
compression stroke, more energy is dissipated in that
cylinder. Coil failure will result in a lack of sparks and
misfire in the affected cylinders. The fault is indicated
by illumination of the malfunction indicator light (MIL)
on North American specification vehicles.
Injectors
A multiport fuel injection system (MFI) is used, one
injector per cylinder. Each injector consists of a small
solenoid which is activated by the ECM to allow a
metered amount of fuel to pass into the combustion
chamber. Due to the pressure in the fuel rail and the
shape of the injector orifice, the fuel squirts into the
cylinder in a fine spray to aid combustion. In the
unlikely event of injector failure a misfire will occur as
there will be no fuel to the affected cylinder. The fault
is indicated by illumination of the malfunction indicator
light (MIL) on North American specification vehicles.
Page 278 of 873

SFI
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION REV: 09/95 Fuel pressure regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is located at the rear of
the engine in the fuel rail. It consists of a fuel inlet,
outlet, vacuum port and internal diaphragm.
When the engine is under high manifold depression,
the applied vacuum sucks the diaphragm of its seat,
allowing fuel to return to the tank, resulting in a lower
fuel pressure. This is necessary because the high
depression will try to suck the fuel from the injector,
resulting in overfuelling if the pressure remained
constant. Failure will result in a rich mixture at idle but
normal at full load, or a rich mixture resulting in engine
flooding, or a weak mixture. Although the fault will not
illuminate the MIL, faults caused by the failure may be
indicated.Relay module
The engine management system employs a relay
module, which houses the main relay and the fuel
pump relay.
Main relay
The main relay supplies the power feed to the ECM
with a tap off to feed the fuel injectors (8 amps) and
air flow sensor (4 amps). This relay is controlled by
the engine management ECM. This enables the ECM
to remain powered up after ignition is switched off.
During this 'ECM power down routine' the ECM
records all temperature readings and powers the
stepper motor to the fully open position. Failure of this
relay will result in the engine management ECM not
being switched on resulting in engine not starting due
to absence of fuel and ignition.
Fuel pump relay
The fuel pump relay is fed from the ignition relay and
controlled by the engine management ECM. The relay
is activated in ignition key position 2 to prime the fuel
system for a period of time controlled by the ECM.
Failure of this relay will result in no fuel pressure.
Inertia switch
The inertia switch isolates the power supply to the fuel
pump in the event of sudden deceleration. The inertia
switch is located in the engine compartment. It is reset
by depressing the central plunger at the top of the
switch.
Page 279 of 873
19FUEL SYSTEM
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ADD: 09/95 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM COMPONENT
LOCATION - ADVANCED EVAPS
1.Engine control module (ECM)
2.Ignition coils
3.Fuel pressure regulator
4.Mass air flow (MAF) sensor
5.Relay module
- Main relay
- Fuel pump relay
6.Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
7.Camshaft position (CMP) sensor
8.Throttle position (TP) sensor
Page 281 of 873
19FUEL SYSTEM
10
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ADD: 09/95 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION - ADVANCED
EVAPS
1.Fuel filter
2.Fuel pump and gauge sender unit
3.Fuel feed hose
4.Fuel return hose
5.Fuel filler neck assembly
Fuel Tank Assembly
The fuel tank consists of a moulded High Density
Polyethylene (HDPE) fuel cell into which is fitted an
electric fuel pump and four roll-over valves. The pump
is a self priming ñwet" type where the motor is
immersed in fuel. The pump assembly is sealed to the
tank with a rubber seal and secured in place using a
coated steel locking ring. The pump also incorporates
a fuel tank pressure sensor in the top flange.
NOTE: If the pump is removed, a new seal
must always be fitted.
Page 286 of 873
SFI
3
REPAIR FUEL SYSTEM - DEPRESSURISE
WARNING: Fuel pressure of up to 2.5 bar
will be present in the system, even if the
engine has not been run for some time.
Always depressurise the system before
disconnecting any components in the fuel feed
line (between fuel pump and pressure regulator).
The spilling of fuel is unavoidable during this
operation. Ensure that all necessary precautions
are taken to prevent fire and explosion.
NOTE: Fuel pressure can be relieved at
fuel rail feed union or fuel filter unions.
1.Position cloth around relevant union to protect
against fuel spray.
2.Carefully slacken union.
3.Tighten union to correct torque once pressure
has relieved.