1995 JEEP YJ check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 161 of 2158

(7) Wait a minimum of 90 seconds and try brake
action again. Booster should provide two or more vac-
uum assisted pedal applications. If vacuum assist is
not provided, perform booster and check valve vac-
uum tests.
POWER BOOSTER CHECK VALVE TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose from check valve.
(2) Remove check valve and seal from booster (Fig.
1).
(3) Hand operated vacuum pump can be used for
test (Fig. 2).
(4) Apply 15-20 inches vacuum at large end of
check valve (Fig. 1).
(5) Vacuum should hold steady. If gauge on pump
indicates any vacuum loss, valve is faulty and must
be replaced.
POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST
(1) Connect a vacuum gauge to the booster check
valve with a short length of hose and tee fitting (Fig.
3).(2) Start and run engine at idle speed for one
minute.
(3) Pinch hose shut between vacuum source and
check valve (Fig. 3).
(4) Stop engine and observe vacuum gauge.
(5) If vacuum drops more than one inch HG (33
millibars) within 15 seconds, booster diaphragm or
check valve is faulty.
Fig. 1 Typical Vacuum Check Valve And Seal
Fig. 2 Typical Hand Operated Vacuum Pump
Fig. 3 Booster Vacuum Test Connections
JSERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSIS 5 - 9
Page 175 of 2158
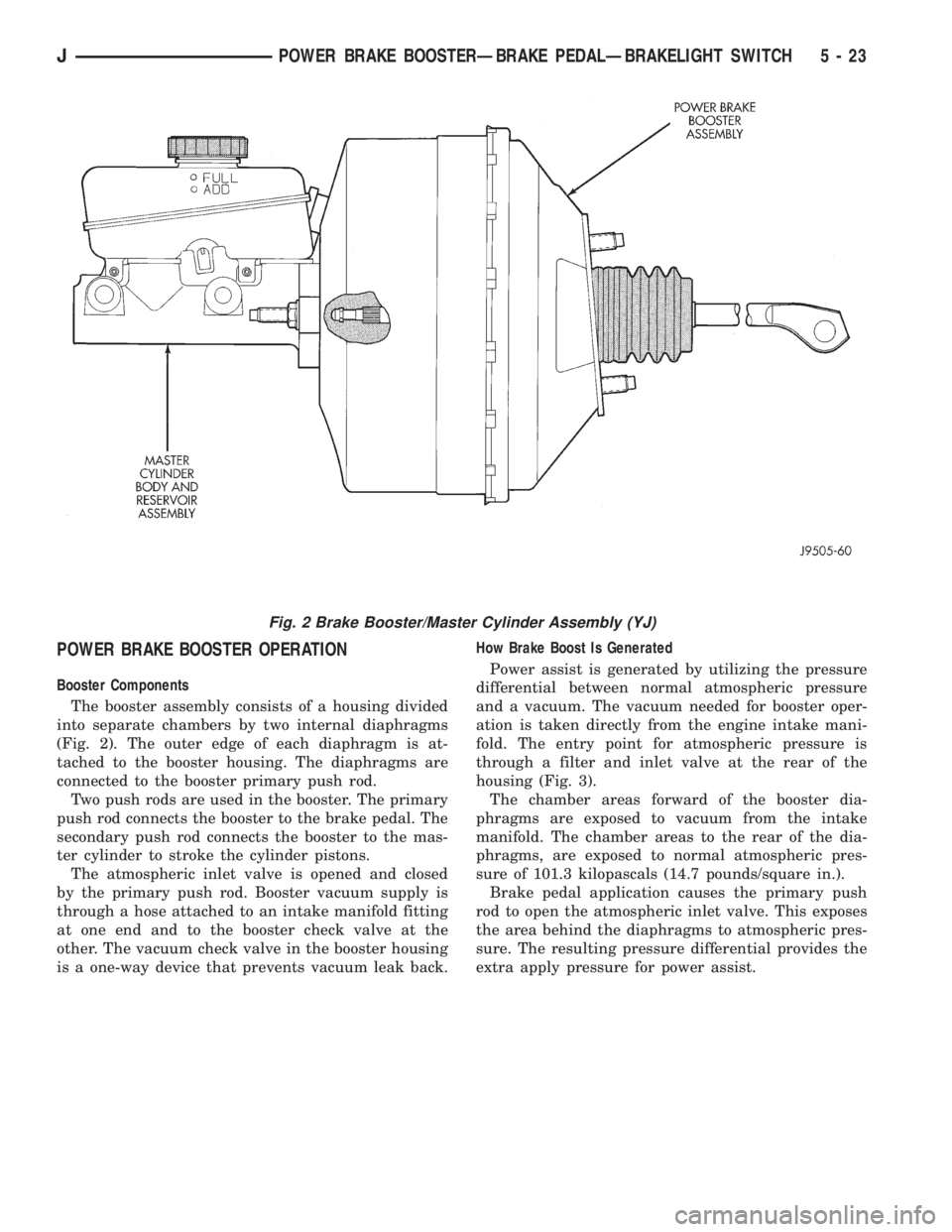
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER OPERATION
Booster Components
The booster assembly consists of a housing divided
into separate chambers by two internal diaphragms
(Fig. 2). The outer edge of each diaphragm is at-
tached to the booster housing. The diaphragms are
connected to the booster primary push rod.
Two push rods are used in the booster. The primary
push rod connects the booster to the brake pedal. The
secondary push rod connects the booster to the mas-
ter cylinder to stroke the cylinder pistons.
The atmospheric inlet valve is opened and closed
by the primary push rod. Booster vacuum supply is
through a hose attached to an intake manifold fitting
at one end and to the booster check valve at the
other. The vacuum check valve in the booster housing
is a one-way device that prevents vacuum leak back.How Brake Boost Is Generated
Power assist is generated by utilizing the pressure
differential between normal atmospheric pressure
and a vacuum. The vacuum needed for booster oper-
ation is taken directly from the engine intake mani-
fold. The entry point for atmospheric pressure is
through a filter and inlet valve at the rear of the
housing (Fig. 3).
The chamber areas forward of the booster dia-
phragms are exposed to vacuum from the intake
manifold. The chamber areas to the rear of the dia-
phragms, are exposed to normal atmospheric pres-
sure of 101.3 kilopascals (14.7 pounds/square in.).
Brake pedal application causes the primary push
rod to open the atmospheric inlet valve. This exposes
the area behind the diaphragms to atmospheric pres-
sure. The resulting pressure differential provides the
extra apply pressure for power assist.
Fig. 2 Brake Booster/Master Cylinder Assembly (YJ)
JPOWER BRAKE BOOSTERÐBRAKE PEDALÐBRAKELIGHT SWITCH 5 - 23
Page 181 of 2158

(16) Install combination valve as follows:
(a) Work combination valve and brakelines into
position.
(b) Slide combination valve bracket onto booster
stud closest to driver side fender (Fig. 25). Then in-
stall bracket attaching nut but do not fully tighten
nut at this time.
(c) Connect flex lines to HCU. Start lines by
hand to avoid cross threading.
(17) Swing rear brakeline around and connect it to
master cylinder. Then install and connect front
brakeline to combination valve and master cylinder.
Start brakelines by hand to avoid cross threading.
(18) Tighten combination valve bracket attaching
nut to 25 Nzm (220 in. lbs.) torque.
(19) Install clip on lines from master cylinder to
combination valve.
(20) Connect wire to pressure differential switch
on combination valve.
(21) Connect flex lines to HCU (Fig. 10). Start line
fittings by hand to avoid cross threading. Then
tighten fittings snug but not to required torque at
this time.(22) Bleed brakes. Refer to procedure in Brake
Fluid-Brake Bleeding-Brakelines And Hoses section.
(23) Tighten brakeline fittings to 15-18 Nzm (130-
160 in. lbs.) at HCU and master cylinder, and 18-24
Nzm (160-210 in. lbs.) at combination valve.
(24) Install air cleaner assembly.
(25) Connect vacuum lines to manifold fittings.
(26) Check brake pedal action before moving vehi-
cle. Bleed brakes again if pedal is not firm (feels soft/
spongy).POWER BRAKE BOOSTER REMOVAL (XJ WITHOUT
ABS)
(1) Disconnect vent and vacuum hose from engine
air cleaner cover.
(2) Remove engine air cleaner cover, filter, housing
and hoses (Fig. 4).
(3) Disconnect brakelines at master cylinder.
(4) Disconnect wire at combination valve differen-
tial pressure switch.
(5) If combination valve does not have an integral
bracket, disconnect brakelines at combination valve
and remove valve.
(6) If combination valve has integral bracket, re-
move nut attaching valve bracket to booster studs
and remove valve.
(7) Remove nuts attaching master cylinder to
booster studs and remove cylinder.
(8) Disconnect vacuum hose from booster check
valve.
(9) In passenger compartment, remove instrument
panel lower trim cover.
(10) Remove retaining clip that secures booster
push rod to brake pedal (Fig. 5).
Fig. 23 HCU And Bracket Mounting (RHD Models)
Fig. 24 Starting Brakelines In HCU
Fig. 25 Combination Valve Installation
JPOWER BRAKE BOOSTERÐBRAKE PEDALÐBRAKELIGHT SWITCH 5 - 29
Page 182 of 2158

(11) Remove nuts attaching booster to passenger
compartment side of dash panel.
(12) In engine compartment, slide booster studs
out of dash panel, tilt booster upward, and remove
booster from engine compartment.
(13) Remove dash seal from booster.
(14) If booster is only being removed for access to
other components, cover booster front opening with
clean shop towel.
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER INSTALLATION (XJ
WITHOUT ABS)
(1) If original booster is being installed, test check
valve with vacuum tool before booster installation.
Replace check valve if it will not hold vacuum.
(2) Install dash seal on booster.
(3) Align and position booster on dash panel (Fig.
17).
(4) In passenger compartment, install nuts that at-
tach booster to dash panel. Tighten nuts just enough
to hold booster in place.
(5) Slide booster push rod onto brake pedal. Then
secure push rod to pedal pin with retaining clip.
(6) Tighten booster attaching nuts to 41 Nzm (30 ft.
lbs.) on XJ and 34 Nzm (25 ft. lbs.) on YJ.
(7) Install instrument panel lower trim cover.
(8) If original master cylinder is being installed,
check condition of seal at rear of master cylinder
(Fig. 18). Clean and reposition seal if dislodged. Re-
place seal if cut, or torn.
(9) Clean cylinder mounting surface of brake
booster. Use shop towel wetted with brake cleaner for
this purpose. Dirt, grease, or similar materials will
prevent proper cylinder seating and could result in
vacuum leak.
(10) Align and install master cylinder on booster
studs. Tighten cylinder attaching nuts to 13-25 Nzm
(115-220 in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Connect vacuum hose to booster check valve.
(12) Connect and secure brakelines to combination
valve and master cylinder. Start all brakeline fittings
by hand to avoid cross threading.
(13) If combination valve has integral bracket, po-
sition bracket on booster studs. Then install and
tighten bracket attaching nuts to 13-25 Nzm (115-220
in. lbs.) torque.
(14) Connect wire to combination valve switch.
(15) Top off master cylinder fluid level.
(16) Bleed brakes. Refer to procedures in section
on brake bleeding.
(17) Install engine air cleaner and hoses.
(18) Verify proper brake operation before moving
vehicle.
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER REMOVAL (YJ)
(1) Disconnect brakelines at master cylinder. Then
loosen lines at combination valve and move lines
away from cylinder.
(2) Remove nuts master cylinder to booster studs.
(3) If combination valve has integral bracket, slide
bracket off studs and move valve aside.
(4) Remove master cylinder. Slide cylinder off
studs and remove it from engine compartment.
(5) Working under instrument panel, remove re-
tainer clip that secures booster push rod to brake
pedal.
(6) Disconnect vacuum hose at booster check valve.
(7) On non-ABS models, remove nuts attaching
brake booster spacer to dash panel and remove
booster (Fig. 26).
(8) On ABS models, remove nuts attaching booster
to spacer and remove booster (Fig. 27).
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER INSTALLATION (YJ)
(1) Install seal on booster spacer, if equipped.
(2) Position booster on dash panel, or on spacer.
(3) Secure booster push rod to brake pedal with re-
taining clip.
(4) Install and tighten booster attaching nuts to
27-47 Nzm (20-35 ft. lbs.) torque. Nut torque applies
to both styles of booster.
Fig. 26 Booster Mounting (4-Cyl. Models)
Fig. 27 Booster Mounting (With ABS)
5 - 30 POWER BRAKE BOOSTERÐBRAKE PEDALÐBRAKELIGHT SWITCHJ
Page 190 of 2158

air gap should be 0.40 to 1.3 mm (0.0157 to 0.051
in.). If gap is incorrect, the sensor is either loose, or
damaged.
A rear sensor air gap adjustment is only needed
when reinstalling an original sensor. Replacement
sensors have an air gap spacer attached to the sensor
pickup face. The spacer establishes correct air gap
when pressed against the tone ring during installa-
tion. As the tone ring rotates, it peels the spacer off
the sensor to create the required air gap. Rear sensor
air gap is 0.92-1.45 mm (0.036-0.057 in.).
Sensor air gap measurement, or adjustment proce-
dures are provided in this section. Refer to the front,
or rear sensor removal and installation procedures as
required.
FRONT WHEEL SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and turn wheel outward for easier
access to sensor.
(2) Remove sensor wire from mounting brackets.
(3) Clean sensor and surrounding area with shop
towel before removal.
(4) Remove bolt attaching sensor to steering
knuckle and remove sensor.
(5) remove sensor wire from brackets on body and
steering knuckle.
(6) Unseat sensor wire grommet in wheel house
panel.
(7) In engine compartment, disconnect sensor wire
connector at harness plug. Then remove sensor and
wire.
FRONT WHEEL SENSOR INSTALLATION
(1) Iforiginalsensor will be installed, wipe all
traces of old spacer material off sensor pickup face.
Use a dry shop towel for this purpose.
(2) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctite 242 to bolt
that secures sensor in steering knuckle. Use new
sensor bolt if original bolt is worn or damaged.
(3) Position sensor on steering knuckle. Seat sen-
sor locating tab in hole in knuckle and install sensor
attaching bolt finger tight.
(4) Tighten sensor attaching bolt to 14 Nzm (11 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(5) If original sensor has been installed, check sen-
sor air gap. Air gap should be 0.40 to 1.3 mm (0.0157
to 0.051 in.). If gap is incorrect, sensor is either loose,
or damaged.
(6) Secure sensor wire to steering knuckle and
body brackets.
(7) Route sensor wire forward and behind shock
absorber. Then attach sensor wire to spring seat
bracket with grommets on sensor wire.
(8) Route sensor wire to outer sill bracket. Remove
all twists or kinks from wire.
(9) Attach sensor wire to sill bracket with grom-
met. Be sure wire is free of twists and kinks.(10) Verify sensor wire routing. Wire should loop
forward and above sill bracket. Loose end of wire
should be below sill bracket and towards brake hose.
(11) Seat sensor wire grommet in body panel and
clip wire to brake line at grommet location.
(12) Connect sensor wire to harness in engine com-
partment.
REAR WHEEL SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) On XJ models, raise and fold rear seat forward
for access to rear sensor connectors (Fig. 9).
(2) Disconnect sensors at rear harness connectors.
(3) Push sensor grommets and sensor wires
through floorpan.
(4) Raise vehicle.
(5) Disconnect sensor wires at rear axle connectors.
(6) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(7) Remove brake drum.
(8) Remove clips securing sensor wires to brake-
lines, rear axle and, brake hose.
(9) Unseat sensor wire support plate grommet.
(10) Remove bolt attaching sensor to bracket and
remove sensor.
REAR WHEEL SENSOR INSTALLATION AND
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Iforiginal sensoris being installed, remove
any remaining pieces of cardboard spacer from sen-
sor pickup face. Use dry shop towel only to remove
old spacer material.
(2) Insert sensor wire through support plate hole.
Then seat sensor grommet in support plate.
(3) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctite 242 to
Fig. 9 Acceleration Switch And Rear Sensor
Connections (XJ)
5 - 38 ABS OPERATION AND SERVICEJ
Page 195 of 2158

HCU INSTALLATION (XJ)
(1) Install HCU as follows:
(a) If only the HCU was removed, position HCU
in mounting bracket. Then install and tighten
three shoulder bolts that attach HCU to bracket
(Figs. 23 and 24). One bolt is used at forward end
of bracket and two at rear as shown.
(b) If HCU and bracket were removed as assem-
bly, position bracket on studs and install attaching
nuts. Tighten nuts to 10-13 Nzm (92-112 in. lbs.)
torque.
(c) On right hand drive models, If brackets were
removed, assemble brackets. Then position lower
bracket on body studs and install attaching nuts
and the one attaching bolt (Fig. 25).
(2) If HCU mounting bracket was not removed,
press solenoid harness connecter fasteners into
mounting bracket.
(3) Connect HCU pump motor and solenoid har-
nesses (Figs. 19 and 20).
(4) Connect brakelines from front/rear brakes to
HCU. Start brakeline fittings in HCU ports by handto avoid cross threading (Fig. 26). Then tighten line
fittings snug but not to required torque at this time.
(5) Connect flex lines to HCU (Fig. 18). Start
brakeline fittings in flex line ports by hand to avoid
cross threading. Then tighten line fittings snug but
not to required torque at this time.
(6) Bleed brakes. Refer to procedure in Brake Flu-
id-Brake Bleeding-Brakelines And Hoses section.
(7) Tighten brakeline fittings to following torques
after brake bleeding: 15- 18 Nzm (130-160 in. lbs.) at
HCU and master cylinder and 18-24 Nzm (160-210 in.
lbs.) at combination valve.
(8) Install engine air cleaner assembly and hoses.
(9) Connect vacuum lines to manifold fittings.
(10) Check brake pedal action before moving vehi-
cle. Bleed brakes again if pedal is not firm (feels soft/
spongy).
Fig. 23 Installing HCU Front Shoulder Bolt
Fig. 24 Installing HCU Rear Shoulder Bolts
Fig. 25 HCU And Bracket Mounting (RHD Models)
Fig. 26 Starting Brakelines In HCU (By Hand)
JABS OPERATION AND SERVICE 5 - 43
Page 226 of 2158

when handling the cover and disc. Impact can distort
the cover, diaphragm spring, release fingers and the
hub of the clutch disc.
Use an alignment tool when positioning the disc on
the flywheel. The tool prevents accidental misalign-
ment which could result in cover distortion and disc
damage.
A frequent cause of clutch cover distortion (and
consequent misalignment) is improper bolt tighten-
ing. To avoid warping the cover, the bolts must tight-
ened alternately (diagonal pattern) and evenly (2-3
threads at a time) to specified torque.
CLUTCH HOUSING MISALIGNMENT
Clutch housing alignment is important to proper
clutch operation. The housing maintains alignment
between the crankshaft and transmission input
shaft. Misalignment can cause clutch noise, hard
shifting, incomplete release and chatter. It can also
result in premature wear of the pilot bearing, cover
release fingers and clutch disc. In severe cases, mis-
alignment can also cause premature wear of the
transmission input shaft and front bearing.
Housing misalignment is generally caused by incor-
rect seating on the engine or transmission, loose
housing bolts, missing alignment dowels, or housing
damage. Infrequently, misalignment may also be
caused by housing mounting surfaces that are not
completely parallel. Misalignment can be corrected
with shims.
INSTALLATION METHODS AND PARTS USAGE
Distortion of clutch components during installation
and the use of non-standard components are addi-
tional causes of clutch malfunction.Improper clutch cover bolt tightening can distort
the cover. The usual result is clutch grab, chatter
and rapid wear. Tighten the cover bolts as described
in Clutch Service section.
An improperly seated flywheel and/or clutch hous-
ing are additional causes of clutch failure. Improper
seating will produce misalignment and additional
clutch problems.
The use of non-standard or low quality parts will
also lead to problems and wear. Use recommended
factory quality parts to avoid comebacks.
A cocked pilot bearing is another cause of clutch
noise, drag, and hard shifting, and rapid bearing
wear. Always use an alignment tool to install a new
bearing. This practice helps avoid cocking the bear-
ing during installation.
INSPECTION AND DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
The clutch inspection chart (Fig. 1) outlines items
to be checked before and during clutch installation.
Use the chart as a check list to help avoid overlook-
ing potential problem sources during service opera-
tions.
The diagnosis charts describe common clutch prob-
lems, causes and correction. Fault conditions are
listed at the top of each chart. Conditions, causes and
corrective action are outlined in the indicated col-
umns.
The charts are provided as a convenient reference
when diagnosing faulty clutch operation.
6 - 4 CLUTCH DIAGNOSISJ
Page 233 of 2158

(4) Position clutch disc on flywheel. Be sure side of
disc marked flywheel side is positioned against fly-
wheel (Fig. 2). If disc is not marked, be sure flat side
of disc hub is toward flywheel.
(5) Inspect condition of pressure plate surface of
clutch cover (Fig. 2). Replace cover if this surface is
worn, heat checked, cracked, or scored.
(6) Insert clutch alignment tool in clutch disc (Fig.
3).
(7) Insert alignment tool in pilot bearing and posi-
tion disc on flywheel. Be sure disc hub is positioned
correctly. Side of hub marked Flywheel Side should
face flywheel (Fig. 2). If disc is not marked, place flat
side of disc against flywheel.
(8) Position clutch cover over disc and on flywheel
(Fig. 3).
(9) Install clutch cover bolts finger tight.(10) Tighten cover bolts evenly and in rotation a
few threads at a time.Cover bolts must be tight-
ened evenly and to specified torque to avoid
distorting cover. Tightening torques are 31 Nzm
(23 ft. lbs.) on 2.5L engines and 54 Nzm (40 ft.
lbs.) on 4.0L engines.
(11) Apply light coat of Mopar high temperature
bearing grease to pilot bearing hub and splines of
transmission input shaft.Do not overlubricate
shaft splines. This will result in grease contam-
ination of disc.
(12) Install transmission (Figs. 4 and 5). Refer to
procedures in Group 21.
RELEASE BEARING REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove transmission as described in Group 21.
Fig. 2 Clutch Disc And Pressure Plate InspectionFig. 3 Typical Method Of Aligning Clutch Disc
Fig. 4 Manual Transmission Mounting (4.0L)
JCLUTCH SERVICE 6 - 11