1995 JEEP CHEROKEE engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 1210 of 2198

The frame is constructed of high-strength channel
steel siderails and crossmembers. The crossmembers
join the siderails and retain them in alignment in re-
lation to each other. This provides resistance to
frame twists and strains.
FRAME STRAIGHTENING
When necessary, a conventional frame that is bent
or twisted can be straightened by application of heat.
The temperature must not exceed 566ÉC (1050ÉF).
The use of a specially designed heat crayon can de-
termine the desired temperature. Excessive heat will
decrease the strength of the metal and result in a
weakened frame.
Welding the joints around riveted cross members
and frame side rails is not recommended.
A straightening repair process should be limited to
frame members that are not severely damaged.
FRAME REPAIRS
DRILLING HOLES
Do not drill holes in frame side rail top and bottom
flanges, metal fatigue can result causing frame fail-
ure. Holes drilled in the side of the frame rail must
be at least 38 mm (1.5 in.) from the top and bottom
flanges.
Additional drill holes should be located away from
existing holes.
WELDING
Use MIG, TIG or arc welding equipment to repair
welded frame components.
Frame components that have been damaged should
be inspected for cracks before returning the vehicle
to use. If cracks are found in accessible frame com-
ponents perform the following procedures.
(1) Drill a hole at each end of the crack with a 3
mm (O.125 in.) diameter drill bit.
(2) Using a suitable die grinder with 3 inch cut off
wheel, V-groove the crack to allow 100% weld pene-
tration.
(3) Weld the crack.
(4) If necessary when a side rail is repaired, grind
the weld smooth and install a reinforcement channel
(Fig. 4) over the repaired area.
If a reinforcement channel is required, the
top and bottom flanges should be 0.250 inches
narrower than the side rail flanges. Weld only
in the areas indicated (Fig. 4).
FRAME FASTENERS
Bolts, nuts and rivets can be used to repair frames
or to install a reinforcement section on the frame.
Bolts can be used in place of rivets. When replacing
rivets with bolts, install the next larger size diameter
bolt to assure proper fit. If necessary, drill the hole
out just enough to receive the bolt.Conical-type washers are preferred over the split-
ring type lock washers. Normally, grade-5 bolts are
adequate for frame repair.Grade-3 bolts or softer
should not be used.Tightening bolts/nuts with the
correct torque, refer to the Introduction Group at the
front of this manual for tightening information.
FRAME DIMENSIONS
Frame dimensions are listed in millimeter scale.
All dimensions are from center to center of Principal
Locating Point (PLP), or from center to center of PLP
and fastener location (Fig. 5).
TOW HOOKS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the two bolts that attach the tow hook
to the bumper rail and to the frame rail.
(2) Remove the tow hook.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the tow hook on the bumper rail and
frame rail.
(2) Install the attaching bolts. Tighten the bolts to
102 Nzm (75 ft. lbs.) torque.
GENERATOR SPLASH SHIELD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the shield retaining nut and washer
(Fig. 6) from the engine oil pan stud (2.5L engines
only).
(2) Pry the serrated retainers from the frame rail
holes at each side of the vehicle.
(3) Pry the serrated retainers from the fan shroud
holes (Fig. 6).
(4) Remove the shield from the vehicle.
Fig. 4 Frame Reinforcement
JYJÐFRAME 13 - 13
Page 1216 of 2198

FUEL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
ACCELERATOR PEDAL AND THROTTLE CABLE.17
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM.................. 3
FUEL TANKS........................... 13
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)Ð
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEMOPERATION.......................... 19
MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)Ð
COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.... 58
MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)Ð
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS.................. 35
SPECIFICATIONS........................ 67
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references are made to par-
ticular vehicle models by alphabetical designation
(XJ or YJ) or by the particular vehicle nameplate. A
chart showing a breakdown of the alphabetical desig-
nations is included in the Introduction section at the
beginning of this manual.
TheFuel Systemconsists of: the fuel tank, an
electric (fuel tank mounted) fuel pump and a fuel fil-
ter. It also consists of fuel tubes/lines/hoses, vacuum
hoses, throttle body and fuel injectors.
TheFuel Delivery Systemconsists of: the electric
fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel tubes/lines/hoses, fuel rail,
fuel injectors and fuel pressure regulator.
AFuel Return Systemis used on all vehicles.
The system consists of: the fuel tubes/lines/hoses that
route fuel back to the fuel tank.
TheFuel Tank Assemblyconsists of: the fuel
tank, filler tube, fuel fill and vent hoses, fuel gauge
sending unit/electric fuel pump module, a pressure
relief/rollover valve and a pressure-vacuum filler cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
Evaporation Control System.This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in Group 25, Emission
Control Systems.
FUEL USAGE STATEMENT
Your vehicle was designed to meet all emission reg-
ulations and provide excellent fuel economy using
high quality unleaded gasoline. Only use unleaded
gasolines having a minimum posted octane of 87.
If your vehicle develops occasional light spark
knock (ping) at low engine speeds, this is not harm-
ful. However,continued heavy knock at high
speeds can cause damage and should be re-
ported to your dealer immediately.Engine dam-
age as a result of heavy knock operation may not becovered by the new vehicle warranty.
In addition to using unleaded gasoline with the
proper octane rating,those that contain deter-
gents, corrosion and stability additives are rec-
ommended.Using gasolines that have these
additives will help improve fuel economy, reduce
emissions and maintain vehicle performance.
Poor quality gasolinecan cause problems such
as hard starting, stalling and stumble. If you experi-
ence these problems, use another brand of gasoline
before considering service for the vehicle.
GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS
Some fuel suppliers blend unleaded gasoline with
materials that contain oxygen such as alcohol, MTBE
and ETBE. The type and amount of oxygenate used
in the blend is important. The following are generally
used in gasoline blends:
ETHANOL
Ethanol (Ethyl or Grain Alcohol) properly blended,
is used as a mixture of 10 percent ethanol and 90
percent gasoline.Gasoline with ethanol may be
used in your vehicle.
METHANOL
CAUTION: DO NOT USE GASOLINES CONTAINING
METHANOL.Use of methanol/gasoline blends may re-
sult in starting and driveability problems. In addition,
damage may be done to critical fuel system compo-
nents.
Methanol (Methyl or Wood Alcohol) is used in a va-
riety of concentrations blended with unleaded gaso-
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1
Page 1218 of 2198

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
INDEX
page page
Fuel Filter................................ 9
Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test................ 8
Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.............. 6
Fuel Pump Capacity Test.................... 7
Fuel Pump Electrical Control.................. 5Fuel Pump Module......................... 3
Fuel System Pressure Test................... 6
Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps............ 9
Quick-Connect Fittings..................... 10
FUEL PUMP MODULE
The fuel pump module is installed in the top of the
fuel tank. The fuel pump module contains the follow-
ing components:
²Electric fuel pump
²Fuel pump reservoir
²In-tank fuel filter
²Fuel gauge sending unit
²Fuel supply and return tube connections
The fuel pump used on all vehicles is a turbine
type pump. It is driven by a permanent magnet 12
volt electric motor that is immersed in the fuel tank.
The electrical pump is integral with the fuel sender
unit. The pump/sender assembly is installed inside
the fuel tank.
The fuel pump has a check valve at the outlet end
that consists of a ball held against a seat by force ap-
plied from a spring. When the pump is operating,
fuel pressure overcomes spring pressure and forces
the ball off its seat, allowing fuel to flow. When the
pump is not operating, spring pressure forces the ball
back against the seat preventing fuel backflow
through the pump.
Fuel system pressure is maintained at approxi-
mately 214 kPa (31 psi). This is when the pump is
operating and vacuum is supplied to the fuel pres-
sure regulator. If vacuum is not supplied to the pres-
sure regulator, fuel pressure will be approximately
55-69 kPa (8-10 psi) higher. This may be due to a
broken or clogged vacuum line. When the fuel pump
is not operating, fuel system pressure of 131-269 kPa
(19-39 psi) is maintained for approximately 2 to 6
hours. This is done by the fuel pump outlet check
valve and the vacuum assisted fuel pressure regula-
tor.
REMOVALÐXJ MODELS
The fuel pump/gauge sender unit assembly can be
removed from the fuel tank without removing the
tank from the vehicle.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP MODULE,
THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RE-LEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RE-
LEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
WARNING: EXTINGUISH ALL TOBACCO SMOKING
PRODUCTS BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL SYS-
TEM. KEEP OPEN FLAME AWAY FROM FUEL SYS-
TEM COMPONENTS.
(1) Remove fuel filler cap. Perform the Fuel Pres-
sure Release Procedure as outlined in this group.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(3) Using an approved portable gasoline siphon/
storage tank, drain fuel tank until fuel level is below
one quarter (1/4) full.
(4) Raise and support vehicle.
WARNING: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND FUEL
HOSES TO ABSORB ANY FUEL SPILLAGE DURING
FUEL TANK REMOVAL.
(5) Disconnect fuel vent supply and return tubes
from fittings on fuel pump module.
(6) Disconnect fuel pump module electrical harness
connector from main harness.
(7) Using a brass punch and hammer, remove fuel
pump module lock ring by carefully tapping it coun-
terclockwise (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Removing Lock RingÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
JFUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM 14 - 3
Page 1219 of 2198
(8) Remove fuel pump module and O-ring seal.
Discard old O-ring and fuel pump module inlet filter.
DISASSEMBLYÐXJ MODELS
(1) Remove and discard fuel pump inlet filter.
The wire terminals to the fuel pump motor are dif-
ferent in size and cannot be connected to the wrong
terminal.
(2) Disconnect fuel pump terminal wires.
(3) Remove fuel pump outlet hose and clamp. Re-
place the hose if it shows any signs of fatigue or fail-
ure.
(4) Remove fuel pump top mounting bracket nut.
Remove fuel pump (Fig. 2).
ASSEMBLYÐXJ MODELS
Whenever the fuel pump is replaced, the fuel pump
inlet filter (sock) must also be replaced.
(1) Place fuel pump top mounting bracket over top
of pump.
(2) Position fuel pump into lower bracket. Slide
stud of top bracket through hole in fuel pump side
bracket. Tighten fuel pump top mounting nut.
(3) Install new fuel pump outlet hose. Secure with
new clamps.
(4) Connect wire terminals to motor.
(5) Install new fuel pump inlet filter.
INSTALLATIONÐXJ MODELS
Whenever the fuel pump is replaced, the fuel
pump inlet filter must also be replaced.
(1) Install new fuel pump inlet filter onto fuel
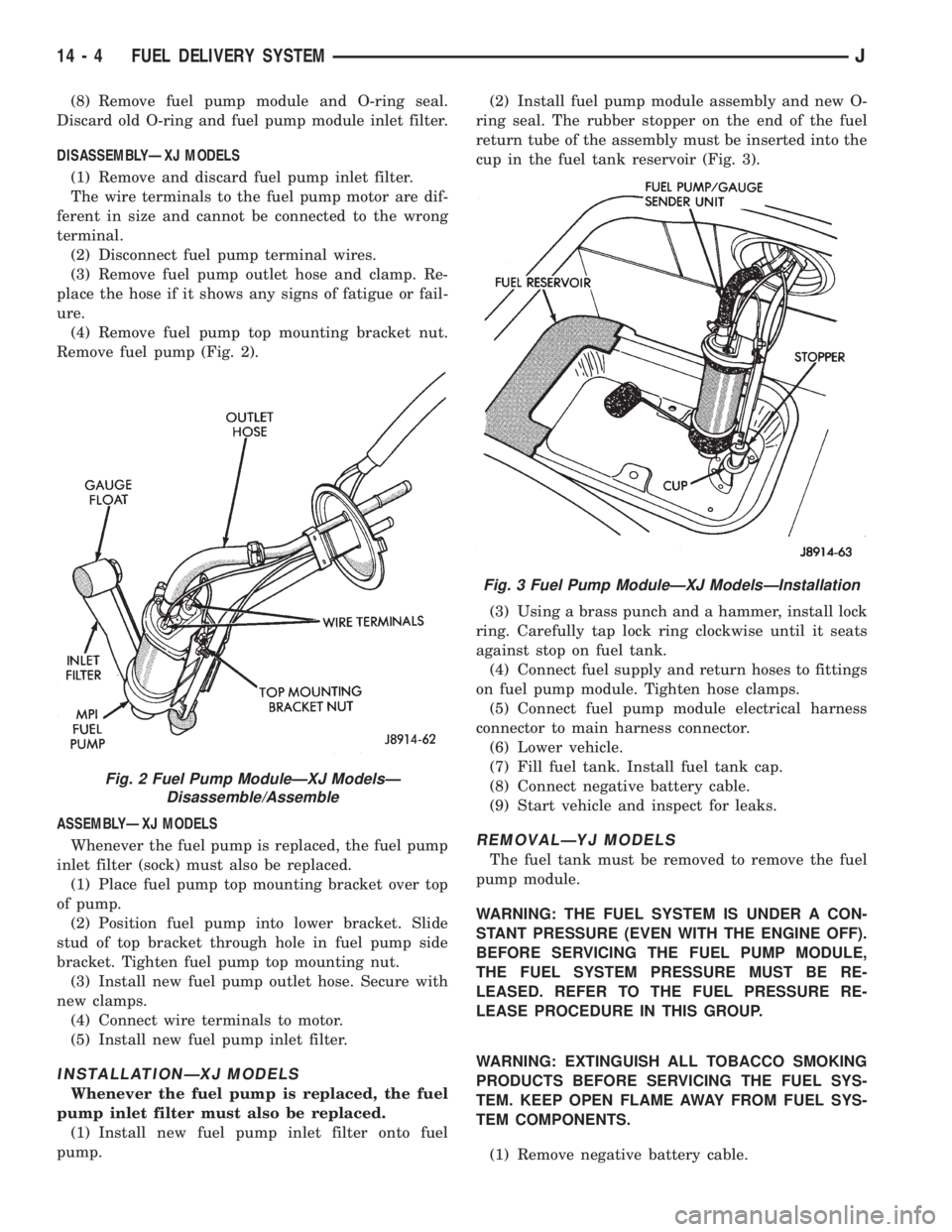
pump.(2) Install fuel pump module assembly and new O-
ring seal. The rubber stopper on the end of the fuel
return tube of the assembly must be inserted into the
cup in the fuel tank reservoir (Fig. 3).
(3) Using a brass punch and a hammer, install lock
ring. Carefully tap lock ring clockwise until it seats
against stop on fuel tank.
(4) Connect fuel supply and return hoses to fittings
on fuel pump module. Tighten hose clamps.
(5) Connect fuel pump module electrical harness
connector to main harness connector.
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Fill fuel tank. Install fuel tank cap.
(8) Connect negative battery cable.
(9) Start vehicle and inspect for leaks.
REMOVALÐYJ MODELS
The fuel tank must be removed to remove the fuel
pump module.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP MODULE,
THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RE-
LEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RE-
LEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
WARNING: EXTINGUISH ALL TOBACCO SMOKING
PRODUCTS BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL SYS-
TEM. KEEP OPEN FLAME AWAY FROM FUEL SYS-
TEM COMPONENTS.
(1) Remove negative battery cable.
Fig. 2 Fuel Pump ModuleÐXJ ModelsÐ
Disassemble/Assemble
Fig. 3 Fuel Pump ModuleÐXJ ModelsÐInstallation
14 - 4 FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEMJ
Page 1221 of 2198

FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF) OF APPROXIMATELY 131-269 KPA (19-39 PSI).
THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED BEFORE
SERVICING ANY FUEL SUPPLY OR FUEL RETURN
SYSTEM COMPONENT.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove fuel tank filler neck cap to release fuel
tank pressure.
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW FUEL TO SPILL ONTO
THE ENGINE INTAKE OR EXHAUST MANIFOLDS.
PLACE SHOP TOWELS UNDER AND AROUND THE
PRESSURE PORT TO ABSORB FUEL WHEN THE
PRESSURE IS RELEASED FROM THE FUEL RAIL.
WARNING: WEAR PROPER EYE PROTECTION
WHEN RELEASING FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE.
(3) Remove protective cap from pressure test port
on the fuel rail (Fig. 7).
(4) Obtain the fuel pressure gauge/hose assembly
from fuel pressure gauge tool set 5069. Remove the
gauge from the hose.
(5) Place one end of hose (gauge end) into an ap-
proved gasoline container.
(6) Place a shop towel under the test port.
(7) To release fuel pressure, screw the other end of
hose onto the fuel pressure test port.
(8) After fuel pressure has been released, remove
the hose from the test port.
(9) Install protective cap to fuel test port.
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE TEST
The fuel system is equipped with a vacuum as-
sisted fuel pressure regulator (Fig. 8). With engine atidle speed, system fuel pressure should be approxi-
mately 214 kPa (31 psi) with the vacuum line con-
nected to the regulator. With the vacuum line
disconnected from the regulator, fuel pressure should
be approximately 269 kPa (39 psi). This is 55-69 kPa
(8-10 psi) higher.
(1) Remove the protective cap at the fuel rail (Fig.
7). Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to test port pressure fit-
ting on fuel rail (Fig. 9).
(2) Note pressure gauge reading. Fuel pressure
should be approximately 214 kPa (31 psi) at idle.
(3) Disconnect vacuum line (hose) at fuel pressure
regulator (Fig. 8). Note gauge reading. With vacuum
line disconnected, fuel pressure should rise to ap-
proximately 269 kPa (39 psi).
Fuel pressure should be approximately 55-69 kPa
(8-10 psi) higher with vacuum line removed from reg-
ulator. If not, inspect pressure regulator vacuum line
for leaks, kinks or blockage. If vacuum line checks
Fig. 7 Pressure Test PortÐTypical
Fig. 8 Fuel Pressure RegulatorÐTypical
Fig. 9 Fuel Pressure Test ConnectionÐTypical
14 - 6 FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEMJ
Page 1223 of 2198

FUEL PRESSURE LEAK DOWN TEST
ENGINE OFF
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hot engine that has been shut down for a short pe-
riod of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past the fuel pressure reg-
ulator.
²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in the
outlet end of the fuel tank mounted fuel pump.
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s)
(1) Remove protective cap at fuel rail test port
(Fig. 11). With the engine off, connect the 0-414 kPa
(0-60 psi) fuel pressure gauge to the pressure test
port fitting on the fuel rail. The fitting on the pres-
sure tester must be in good condition and free of any
leaks before performing this test.
(2) Start the vehicle and let engine idle. Check fuel
pressure reading on gauge. Fuel pressure should be
within specifications. Refer to the previous Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Tests.
(3) Shut engine off. Observe and record fuel pres-
sure reading on gauge. Leave fuel pressure gauge
connected. Allow engine to set for 30 minutes and
then compare the fuel pressure reading on the gauge
with the reading taken when engine was shut down.
A pressure drop of up to 138 kPa (20 psi) within 30
minutes is within specifications.
(4) If the fuel pressure drop is within specifica-
tions, the fuel pump outlet check valve and fuel pres-
sure regulator are both operating normally.
(5) If fuel pressure drop is greater than 138 kPa
(20 psi), it must be determined if this drop is being
caused by (in-tank mounted) fuel pump outlet check
valve or fuel pressure regulator. Proceed to next step.
(6) Release the fuel system pressure from fuel sys-
tem. Refer to the previous Fuel Pressure Release
Procedure in this group.(7) Disconnect both fuel lines at fuel rail near fuel
pressure regulator. For procedures, refer to Fuel
Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps. Also refer to Quick-
Connect Fittings. These can be found in the Fuel De-
livery System section of this group.
(8) Connect Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter Tool
number 6631 (3/8 in.) between the disconnected fuel
supply line and fuel rail (Fig. 12).
(9) Connect Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter Tool
number 6539 (5/16 in.) between the disconnected fuel
return line and fuel rail (Fig. 12).
(10) Start engine. Observe and record fuel system
pressure.
(11) Shut engine off.
(12) Clamp off the rubber hose portion of adapter
tool number 6539 connected to the fuel return line.
Allow engine to set for 30 minutes. If pressure has
dropped more than 138 kPa (20 psi) in 30 minutes,
pressure is bleeding past the (in-tank mounted) fuel
pump outlet check valve. Replace Fuel Pump Module
assembly. Refer to Fuel Pump Module removal and
installation in this group. If pressure drop is within
specifications, proceed to next step.
(13) Clamp off the rubber hose portion of adapter
tool number 6631 connected to the fuel supply line.
Allow engine to set for 30 minutes. If pressure has
dropped more than 138 kPa (20 psi) in 30 minutes,
pressure is bleeding past the fuel pressure regulator.
Replace fuel pressure regulator. Refer to Fuel Rail re-
moval and installation in the Component Removal/
Installation section of this group.
MECHANICAL MALFUNCTIONS
Mechanical malfunctions are more difficult to diag-
nose with this system. The powertrain control mod-
ule (PCM) has been programmed to compensate for
some mechanical malfunctions such as incorrect cam
timing, vacuum leaks, etc. If engine performance
problems are encountered and diagnostic trouble
Fig. 11 Fuel Pressure Test PortÐTypical
Fig. 12 Adapter ToolsÐTypical Connections
14 - 8 FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEMJ
Page 1224 of 2198

codes are not displayed, the problem may be mechan-
ical rather than electronic.
FUEL FILTER
The fuel filter protects the fuel injectors and fuel
pressure regulator from dirt, water and other foreign
matter. The filter is located under the vehicle along
the frame rail (Figs. 13 or 14). Replace fuel filter at
intervals specified in the Lubrication and Mainte-
nance Schedule chart found in Group 0, Lubrication
and Maintenance.
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF) OF APPROXIMATELY 131-269 KPA (19-39 PSI).
THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED BEFORE
SERVICING THE FUEL FILTER.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove fuel
filler cap.
WARNING: FUEL PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED
BEFORE DISCONNECTING ANY FUEL SYSTEM
COMPONENT.
(2) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure in this group.
(3) Raise and support vehicle.
(4) On YJ models remove the fuel filter shield (Fig.
13).
(5) Remove hoses and clamps from inlet and outlet
sides of filter (Figs. 13 or 14). For procedures, refer to
Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps. Also refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. These can be found in the
Fuel Delivery System section of this group.
(6) Remove retaining strap bolt.
(7) Remove filter from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The ends of the fuel filter are marked for
correct installation. Install filter with the end marked
IN towards fuel tank and the end marked OUT to-
wards engine.
(1) Place fuel filter in retaining strap with the
marked ends in the correct position.
(2) Install retaining strap bolt and tighten to 12
Nzm (106 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install inlet and outlet hoses and hose clamps.
For procedures, refer to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and
Clamps. Also refer to Quick-Connect Fittings. These
can be found in the Fuel Delivery System section of
this group.
(4) On YJ models, install fuel filter shield (Fig. 13).
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Connect negative battery cable.
(7) Start engine and check for leaks.
FUEL TUBES/LINES/HOSES AND CLAMPS
Also refer to the proceeding section on Quick-Con-
nect Fittings.
Fig. 13 Fuel Filter and ShieldÐYJ Models
Fig. 14 Fuel FilterÐXJ Models
JFUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM 14 - 9
Page 1225 of 2198

WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS
GROUP.
Inspect all hose connections such as clamps, cou-
plings and fittings to make sure they are secure and
leaks are not present. The component should be re-
placed immediately if there is any evidence of degra-
dation that could result in failure.
Never attempt to repair a plastic fuel line/tube. Re-
place as necessary.
Avoid contact of any fuel tubes/hoses with other ve-
hicle components that could cause abrasions or scuff-
ing. Be sure that the plastic fuel lines/tubes are
properly routed to prevent pinching and to avoid heat
sources.
The lines/tubes/hoses used on fuel injected vehicles
are of a special construction. This is due to the
higher fuel pressures and the possibility of contami-
nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, only those marked EFM/EFI
may be used.
The hose clamps used to secure rubber hoses on
fuel injected vehicles are of a special rolled edge con-
struction. This construction is used to prevent the
edge of the clamp from cutting into the hose. Only
these rolled edge type clamps may be used in this
system. All other types of clamps may cut into the
hoses and cause high-pressure fuel leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
Tighten hose clamps to 1 Nzm (15 in. lbs.) torque.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
Also refer to the previous Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses
and Clamps section.
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components. These are: a
single-tab type, a two-tab type or a plastic retainer
ring type.
SINGLE-TAB TYPE
This type of fitting is equipped with a single pull
tab (Fig. 15). The tab is removable. After the tab is
removed, the quick-connect fitting can be separated
from the fuel system component.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers) of this type of quick-connect fitting are not ser-
viced separately, but new pull tabs are available. Do
not attempt to repair damaged fittings or fuel lines/
tubes. If repair is necessary, replace the complete
fuel tube assembly.WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS
GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Perform the fuel pressure release procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(3) Clean the fitting of any foreign material before
disassembly.
(4) Press the release tab on the side of fitting to re-
lease pull tab (Fig. 15).
CAUTION: If this release tab is not pressed prior to
releasing the pull tab, the pull tab will be damaged.
(5) While pressing the release tab on the side of
the fitting, use a screwdriver to pry up the pull tab
(Fig. 16).
(6) Raise the pull tab until it separates from the
quick-connect fitting (Fig. 17). Discard the old pull
tab.
(7) Disconnect the quick-connect fitting from the
fuel system component being serviced.
(8) Inspect the quick-connect fitting body and fuel
system component for damage. Replace as necessary.
(9) Prior to connecting the quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean the parts with a lint-free
cloth. Lubricate them with clean engine oil.
(10) Insert the quick-connect fitting into the fuel
tube or fuel system component until the built-on stop
on the fuel tube or component rests against back of
fitting.
Fig. 15 Single-Tab Type Fitting
14 - 10 FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEMJ