1995 JEEP CHEROKEE spark plug
[x] Cancel search: spark plugPage 249 of 2198

CAUTION: Do not operate the engine with a spark
plug shorted for more than a minute. The catalytic
converter may be damaged.
Isolate the compression leak by shorting each
spark plug to the cylinder block. The gauge pointer
should stop or decrease vibration when spark plug
for leaking cylinder is shorted. This happens because
of the absence of combustion pressure.
COMBUSTION LEAKAGE TEST (WITHOUT
PRESSURE TESTER)
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
Drain sufficient coolant to allow for thermostat re-
moval. Refer to Thermostat Replacement. Disconnect
the water pump drive belt.
Disconnect the upper radiator hose from the ther-
mostat housing. Remove the housing and thermostat.
Install the thermostat housing.
Add coolant to the radiator to bring the level to
within 6.3 mm (1/4 in) of the top of the thermostat
housing.
CAUTION: Avoid overheating. Do not operate the
engine for an excessive period of time. Open the
draincock immediately after the test to eliminate
boil over of coolant.
Start the engine and accelerate rapidly three times
(to approximately 3000 rpm) while observing the
coolant. If internal engine combustion gases are leak-
ing into the cooling system, bubbles will appear in
the coolant. If bubbles do not appear, there is no in-
ternal combustion gas leakage.
COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW SYSTEM
The system works along with the radiator pressure
cap. This is done by using thermal expansion and
contraction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. It provides:
²A volume for coolant expansion and contraction.
²A convenient and safe method for checking/adjust-
ing coolant level at atmospheric pressure. This is
done without removing the radiator pressure cap.
²Some reserve coolant to the radiator to cover mi-
nor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses.
As the engine cools, a vacuum is formed in the
cooling system of both the radiator and engine. Cool-ant will then be drawn from the coolant tank and re-
turned to a proper level in the radiator.
The coolant reserve/overflow system consists of a
radiator mounted pressurized cap, a plastic reserve/
overflow tank (Figs. 22, 23 or 24), a tube (hose) con-
necting the radiator and tank, and an overflow tube
on the side of the tank.
Fig. 22 Reserve/Overflow TankÐYJ Models
Fig. 23 Reserve/Overflow TankÐXJ ModelsÐExcept
Right Hand Drive
7 - 24 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 312 of 2198

IGNITION SYSTEMS
CONTENTS
page page
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION/SYSTEM
OPERATION........................... 1
COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION...... 17
DIAGNOSTICS/SERVICE PROCEDURES....... 6IGNITION SWITCHÐXJ MODELS........... 26
IGNITION SWITCHÐYJ MODELS........... 29
SPECIFICATIONS........................ 32
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION/SYSTEM OPERATION
INDEX
page page
Automatic Shutdown (ASD) Relay.............. 1
Camshaft Position Sensor.................... 2
Crankshaft Position Sensor................... 3
Distributors............................... 4
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor............ 5
General Information........................ 1Ignition Coil.............................. 4
Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor.......... 5
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor........ 5
Oxygen (O2S) Sensor....................... 5
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).............. 5
Throttle Position Sensor..................... 5
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references are made to par-
ticular vehicle models by alphabetical designation
(XJ or YJ) or by the particular vehicle nameplate. A
chart showing a breakdown of alphabetical designa-
tions is included in the Introduction group at the be-
ginning of this manual.
This section of the group, Component Identifica-
tion/System Operation, will discuss ignition system
operation and will identify ignition system compo-
nents.
For diagnostic procedures and adjustments, refer to
the Diagnostics/Service Procedures section of this
group.
For removal and installation of ignition system
components, refer to the Component Removal/Instal-
lation section of this group.
For other useful information, refer to On-Board Di-
agnostics in the General Diagnosis sections of Group
14, Fuel System in this manual.
For operation of the DRB Scan Tool, refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures ser-
vice manual.
An Ignition specifications section is included at the
end of this group. A general Maintenance Schedule
(mileage intervals) for ignition related items can be
found in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. This
schedule can also be found in the Owners Manual.
IGNITION SYSTEMS
A multi-port, fuel injected engine is used on all
models. The ignition system is controlled by the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) on all engines. The
PCM was formerly referred to as the SBEC or engine
controller.
The ignition system consists of:
²Spark plugs
²Ignition coil
²Secondary ignition cables
²Distributor (contains rotor and camshaft position
sensor)
²Powertrain control module (PCM)
²Crankshaft position sensor
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY
The automatic shutdown (ASD) relay is located in
the power distribution center (PDC) near the battery
(Fig. 1 or 2). As one of its functions, it will supply
battery voltage to the ignition coil.
The ground circuit for the ASD relay is controlled
by the powertrain control module (PCM). This is
done through pin/cavity number 51 of the PCM 60-
way connector. The PCM then regulates ASD relay
operation by switching this ground circuit on-and-off.
Also refer to Ignition Coil for additional informa-
tion.
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 1
Page 317 of 2198

DIAGNOSTICS/SERVICE PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Automatic Shutdown (ASD) Relay Test.......... 6
Camshaft Position Sensor Test................ 6
Crankshaft Position Sensor Test............... 7
Distributor Cap............................ 7
Distributor Rotor........................... 8
DRB Scan Tool............................ 8
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Test........ 9
General Information........................ 6
Ignition Coil.............................. 9
Ignition Secondary Circuit Diagnosis........... 10Ignition Timing............................ 11
Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor Test..... 11
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Test . . . 11
On-Board Diagnostics...................... 15
Oxygen (O2S) Sensor Tests................. 15
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)............. 11
Spark Plug Secondary Cables................ 14
Spark Plugs............................. 12
Throttle Position Sensor Test................. 15
GENERAL INFORMATION
This section of the group, Diagnostics/Service Pro-
cedures, will discuss basic ignition system diagnostics
and service adjustments.
For system operation and component identification,
refer to the Component Identification/System Opera-
tion section of this group.
For removal or installation of ignition system com-
ponents, refer to the Component Removal/Installa-
tion section of this group.
For other useful information, refer to the On-Board
Diagnostics section.
For operation of the DRB Scan Tool, refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures ser-
vice manual.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY TEST
To perform a complete test of this relay and its cir-
cuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the relay only, refer to RelaysÐOpera-
tion/Testing in the Group 14, Fuel Systems section.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the sensor only, refer to the following:
The camshaft position sensor is located in the dis-
tributor (Fig. 1).
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the sensor only, refer to the following:
For this test, an analog (non-digital) voltme-
ter is needed.Do not remove the distributor connec-
tor from the distributor. Using small paper clips,
insert them into the backside of the distributor wire
harness connector to make contact with the termi-nals. Be sure that the connector is not damaged
when inserting the paper clips. Attach voltmeter
leads to these paper clips.
(1) Connect the positive (+) voltmeter lead into the
sensor output wire. This is at done the distributor
wire harness connector. For wire identification, refer
to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
(2) Connect the negative (-) voltmeter lead into the
ground wire. For wire identification, refer to Group
8W, Wiring Diagrams.
(3) Set the voltmeter to the 15 Volt DC scale.
(4) Remove distributor cap from distributor (two
screws). Rotate (crank) the engine until the distribu-
tor rotor is pointed to approximately the 11 o'clock
position. The movable pulse ring should now be
within the sensor pickup.
(5) Turn ignition key to ON position. The voltmeter
should read approximately 5.0 volts.
(6) If voltage is not present, check the voltmeter
leads for a good connection.
(7) If voltage is still not present, check for voltage
at the supply wire. For wire identification, refer to
Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
Fig. 1 Camshaft Position SensorÐTypical
8D - 6 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 318 of 2198

(8) If voltage is not present at supply wire, check
for voltage at pin-7 of powertrain control module
(PCM) 60-way connector. Leave the PCM connector
connected for this test.
(9) If voltage is still not present, perform vehicle
test using the DRB scan tool.
(10) If voltage is present at pin-7, but not at the
supply wire:
(a) Check continuity between the supply wire.
This is checked between the distributor connector
and pin-7 at the PCM. If continuity is not present,
repair the harness as necessary.
(b) Check for continuity between the camshaft
position sensor output wire and pin-44 at the PCM.
If continuity is not present, repair the harness as
necessary.
(c) Check for continuity between the ground cir-
cuit wire at the distributor connector and ground.
If continuity is not present, repair the harness as
necessary.
(11) While observing the voltmeter, crank the en-
gine with ignition switch. The voltmeter needle
should fluctuate between 0 and 5 volts while the en-
gine is cranking. This verifies that the camshaft po-
sition sensor in the distributor is operating properly
and a sync pulse signal is being generated.
If sync pulse signal is not present, replacement of
the camshaft position sensor is necessary.
For removal or installation of ignition system com-
ponents, refer to the Component Removal/Installa-
tion section of this group.
For system operation and component identification,
refer to the Component Identification/System Opera-
tion section of this group.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the sensor only, refer to the following:
The sensor is located on the transmission bellhous-
ing at the left/rear side of the engine block (Figs. 2, 3
or 4).
(1) Near the rear of the intake manifold, discon-
nect sensor pigtail harness connector from main wir-
ing harness.
(2) Place an ohmmeter across terminals B and C
(Fig. 5). Ohmmeter should be set to 1K-to-10K scale
for this test. The meter reading should be open (no
resistance). Replace sensor if a low resistance is indi-
cated.
For removal or installation of ignition system com-
ponents, refer to the Component Removal/Installa-
tion section of this group.DISTRIBUTOR CAP
INSPECTION
Remove the distributor cap and wipe it clean with
a dry lint free cloth. Visually inspect the cap for
cracks, carbon paths, broken towers, or damaged ro-
tor button (Figs. 6 and 7). Also check for white depos-
its on the inside (caused by condensation entering
the cap through cracks). Replace any cap that dis-
plays charred or eroded terminals. The inside flat
surface of a terminal end (faces toward rotor) will in-
dicate some evidence of erosion from normal opera-
tion. Examine the terminal ends for evidence of
mechanical interference with the rotor tip.
If replacement of the distributor cap is necessary,
transfer spark plug cables from the original cap to
the new cap. This should be done one cable at a time.
Each cable is installed onto the tower of the new cap
that corresponds to its tower position on the original
Fig. 2 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ2.5L 4-Cyl.
EngineÐTypical
Fig. 3 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.0L 6-Cyl.
EngineÐAll Except YJ models With Auto. Trans.
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 7
Page 320 of 2198

IGNITION COIL
To perform a complete test of the ignition coil and
its circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer tothe appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures
manual. To test the coil only, refer to the following:
The ignition coil (Fig. 11) is designed to operate
without an external ballast resistor.
Inspect the ignition coil for arcing. Test the coil ac-
cording to coil tester manufacturer's instructions.
Test the coil primary and secondary resistance. Re-
place any coil that does not meet specifications. Refer
to the Ignition Coil Resistance chart.
If the ignition coil is being replaced, the secondary
spark plug cable must also be checked. Replace cable
if it has been burned or damaged.
Arcing at the tower will carbonize the cable nipple,
which if it is connected to a new ignition coil, will
cause the coil to fail.
If the secondary coil cable shows any signs of dam-
age, it should be replaced with a new cable and new
terminal. Carbon tracking on the old cable can cause
arcing and the failure of a new ignition coil.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR TEST
For an operational description, diagnosis and re-
moval/installation procedures, refer to Group 14,
Fuel System.
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE
Fig. 9 Firing OrderÐ4.0L 6-Cylinder Engine
Fig. 10 Rotor InspectionÐTypical
Fig. 11 Ignition CoilÐTypical (4.0L Shown)
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 9
Page 321 of 2198

IGNITION SECONDARY CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS
CHECKING FOR SPARK
CAUTION: When disconnecting a high voltage cable
from a spark plug or from the distributor cap, twist
the rubber boot slightly (1/2 turn) to break it loose
(Fig. 12). Grasp the boot (not the cable) and pull it
off with a steady, even force.
(1) Disconnect the ignition coil secondary cable
from center tower of the distributor cap. Hold the ca-
ble terminal approximately 12 mm (1/2 in.) from a
good engine ground (Fig. 13).
WARNING: BE VERY CAREFUL WHEN THE ENGINE
IS CRANKING. DO NOT PUT YOUR HANDS NEAR
THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN. DO NOT WEAR
LOOSE FITTING CLOTHING.
(2) Rotate (crank) the engine with the starter mo-
tor and observe the cable terminal for a steady arc. If
steady arcing does not occur, inspect the secondary
coil cable. Refer to Spark Plug Cables in this group.
Also inspect the distributor cap and rotor for cracksor burn marks. Repair as necessary. If steady arcing
occurs, connect ignition coil cable to the distributor
cap.
(3) Remove a cable from one spark plug.
(4) Using insulated pliers, hold the cable terminal
approximately 12 mm (1/2 in.) from the engine cylin-
der head or block while rotating the engine with the
starter motor. Observe the spark plug cable terminal
for an arc. If steady arcing occurs, it can be expected
that the ignition secondary system is operating cor-
rectly.(note that if the ignition coil cable is re-
moved for this test, instead of a spark plug
cable, the spark intensity will be much higher.)
If steady arcing occurs at the spark plug cables, but
the engine will not start, connect the DRB scan tool.
Refer to the Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures ser-
vice manual.
FAILURE TO START TEST
To prevent unnecessary diagnostic time and wrong
test results, the previous Checking For Spark test
should be performed prior to this test.
WARNING: SET PARKING BRAKE OR BLOCK THE
DRIVE WHEELS BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH THIS
TEST.
(1) Unplug the ignition coil harness connector at
the coil (Fig. 14).
(2) Connect a set of small jumper wires (18 gauge
or smaller) between the disconnected harness termi-
nals and the ignition coil terminals. To determine po-
larity at connector and coil, refer to the Wiring
Diagrams section.
(3) Attach one lead of a voltmeter to the positive
(12 volt) jumper wire. Attach the negative side of
voltmeter to a good ground. Determine that sufficient
battery voltage (12.4 volts) is present for the starting
and ignition systems.
Fig. 12 Cable Removal
Fig. 13 Checking for SparkÐTypical
Fig. 14 Coil Harness ConnectorÐTypical (4.0L
Shown)
8D - 10 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 323 of 2198

For diagnostics, refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures service manual for operation
of the DRB scan tool.
SPARK PLUGS
For spark plug removal, cleaning, gap adjustment
and installation, refer to the Component Removal/In-
stallation section of this group.
Faulty carbon and/or gas fouled plugs generally
cause hard starting, but they will clean up at higher
engine speeds. Faulty plugs can be identified in a
number of ways: poor fuel economy, power loss, de-
crease in engine speed, hard starting and, in general,
poor engine performance.
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. For identification, keep plugs ar-
ranged in the order in which they were removed from
the engine. An isolated plug displaying an abnormal
condition indicates that a problem exists in the cor-
responding cylinder. Replace spark plugs at the inter-
vals recommended in the maintenance chart in
Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective. Refer to the
following Spark Plug Condition section of this group.
CONDITION
NORMAL OPERATING
The few deposits present on the spark plug will
probably be light tan or slightly gray in color. This is
evident with most grades of commercial gasoline
(Fig. 19). There will not be evidence of electrode
burning. Gap growth will not average more than ap-
proximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 1600 km (1000
miles) of operation. Spark plugs that have normal
wear can usually be cleaned, have the electrodes
filed, have the gap set and then be installed.Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United
States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT)
for unleaded fuel. During combustion, fuel with MMT
causes the entire tip of the spark plug to be coated
with a rust colored deposit. This rust color can be
misdiagnosed as being caused by coolant in the com-
bustion chamber. Spark plug performance is not af-
fected by MMT deposits.
COLD FOULING/CARBON FOULING
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon
fouling. The deposits that cause cold fouling are ba-
sically carbon (Fig. 19). A dry, black deposit on one or
two plugs in a set may be caused by sticking valves
or defective spark plug cables. Cold (carbon) fouling
of the entire set of spark plugs may be caused by a
clogged air cleaner element or repeated short operat-
ing times (short trips).
WET FOULING OR GAS FOULING
A spark plug coated with excessive wet fuel or oil is
wet fouled. In older engines, worn piston rings, leak-
ing valve guide seals or excessive cylinder wear can
cause wet fouling. In new or recently overhauled en-
gines, wet fouling may occur before break-in (normal
oil control) is achieved. This condition can usually be
resolved by cleaning and reinstalling the fouled
plugs.
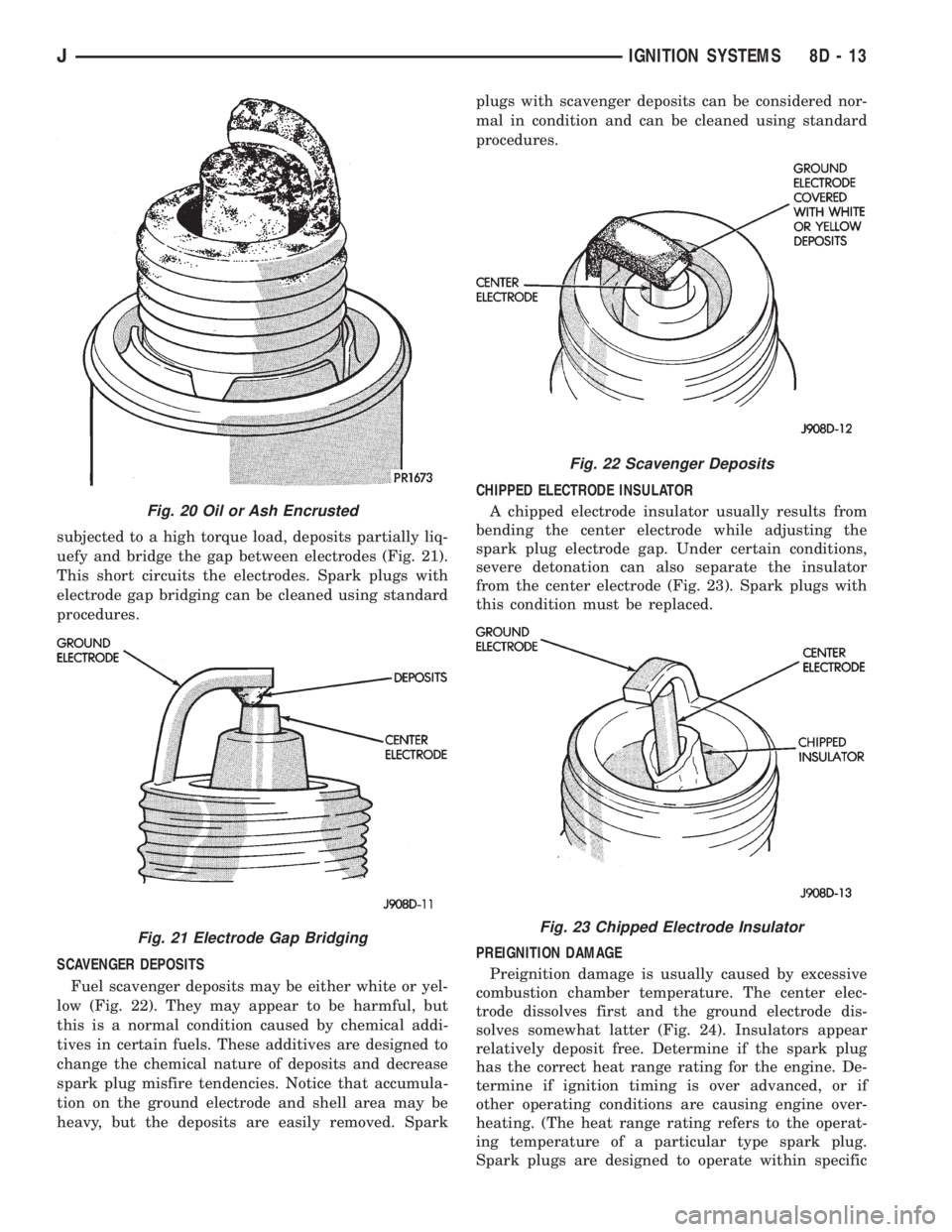
OIL OR ASH ENCRUSTED
If one or more spark plugs are oil or oil ash en-
crusted (Fig. 20), evaluate engine condition for the
cause of oil entry into that particular combustion
chamber.
ELECTRODE GAP BRIDGING
Electrode gap bridging may be traced to loose de-
posits in the combustion chamber. These deposits ac-
cumulate on the spark plugs during continuous stop-
and-go driving. When the engine is suddenly
Fig. 18 PCM LocationÐXJ ModelsFig. 19 Normal Operation and Cold (Carbon) Fouling
8D - 12 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 324 of 2198
subjected to a high torque load, deposits partially liq-
uefy and bridge the gap between electrodes (Fig. 21).
This short circuits the electrodes. Spark plugs with
electrode gap bridging can be cleaned using standard
procedures.
SCAVENGER DEPOSITS
Fuel scavenger deposits may be either white or yel-
low (Fig. 22). They may appear to be harmful, but
this is a normal condition caused by chemical addi-
tives in certain fuels. These additives are designed to
change the chemical nature of deposits and decrease
spark plug misfire tendencies. Notice that accumula-
tion on the ground electrode and shell area may be
heavy, but the deposits are easily removed. Sparkplugs with scavenger deposits can be considered nor-
mal in condition and can be cleaned using standard
procedures.
CHIPPED ELECTRODE INSULATOR
A chipped electrode insulator usually results from
bending the center electrode while adjusting the
spark plug electrode gap. Under certain conditions,
severe detonation can also separate the insulator
from the center electrode (Fig. 23). Spark plugs with
this condition must be replaced.
PREIGNITION DAMAGE
Preignition damage is usually caused by excessive
combustion chamber temperature. The center elec-
trode dissolves first and the ground electrode dis-
solves somewhat latter (Fig. 24). Insulators appear
relatively deposit free. Determine if the spark plug
has the correct heat range rating for the engine. De-
termine if ignition timing is over advanced, or if
other operating conditions are causing engine over-
heating. (The heat range rating refers to the operat-
ing temperature of a particular type spark plug.
Spark plugs are designed to operate within specific
Fig. 20 Oil or Ash Encrusted
Fig. 21 Electrode Gap Bridging
Fig. 22 Scavenger Deposits
Fig. 23 Chipped Electrode Insulator
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 13