1995 JEEP CHEROKEE reset
[x] Cancel search: resetPage 1133 of 2198

SIDE CLEARANCE MEASUREMENT
Slide snug-fitting feeler gauge between the connect-
ing rod and crankshaft journal flange. Refer to En-
gine Specifications for the proper clearance. Replace
the connecting rod if the side clearance is not within
specification.
PISTON FITTING
BORE GAUGE METHOD
(1) To correctly select the proper size piston, a cyl-
inder bore gauge, Special Tool 6879 or equivalent, ca-
pable of reading in .00019INCREMENTS with gauge
ring Special Tool 6884 is required. If a bore gauge is
not available, do not use an inside micrometer.
(2) Set the bore gauge to the gauge ring and zero
gauge.
(3) Remove gauge from ring and check cylinder as
shown in (Fig. 8) bore and record reading.
(4) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at a point 58.725 mm (2-5/16 inches) below top
of bore. Start perpendicular (across or at 90 degrees)
to the axis of the crankshaft at point B and then take
an additional bore reading 90 degrees to that at point A.
(5) Recheck bore gauge in gauge ring, bore gauge
should read zero. If gauge does not read zero, reset
gauge and start over with procedure.
The coated pistons will be serviced with the piston
pin and connecting rod pre-assembled.The coated
piston connecting rod assembly can be used to
service previous built engines and MUST be re-
placed as complete sets.Tin coated pistons should
not be used as replacements for the new coated pistons.
The coating material is applied to the piston after
the final piston machining process. Measuring the
outside diameter of a coated piston will not provide
accurate results. Therefore, measuring the inside di-
ameter of the cylinder bore with a dial Bore Gauge is
MANDATORY. To correctly select the proper size
piston, a cylinder bore gauge capable of reading in.00019increments is required.
Piston installation into the cylinder bore requires
slightly more pressure than that required for non-
coated pistons. The bonded coating on the piston will
give the appearance of a line-to-line fit with the cyl-
inder bore.
PISTON PIN
Piston pins are press-fitted into the connecting rods
and require no locking device. The piston, piston pin
and connecting rod are replaced as an assembly.
PISTON RING FITTING
(1) Carefully clean the carbon from all ring
grooves. Oil drain openings in the oil ring groove and
pin boss must be clear. DO NOT remove metal from
the grooves or lands. This will change ring-to-groove
clearances and will damage the ring-to-land seating.
(2) Be sure the piston ring grooves are free of nicks
and burrs.
(3) Measure the ring side clearance with a feeler
gauge fitted snugly between the ring land and ring
(Fig. 10). Rotate the ring in the groove. It must move
freely around circumference of the groove.
(4) Place ring in the cylinder bore and push down
with inverted piston to position near lower end of the
ring travel. Measure ring gap with a feeler gauge fit-
ting snugly between ring ends (Fig. 12). The correct
compression ring end gap is 0.25-0.51 mm (0.010-
0.020 inch). The correct oil control ring end gap is
0.381-1.397 mm (0.015-0.055 inch).
Fig. 8 Bore Gauge
Fig. 9 Piston Size Chart
Fig. 10 Piston Dimensions
9 - 42 2.5L ENGINEJ
Page 1175 of 2198
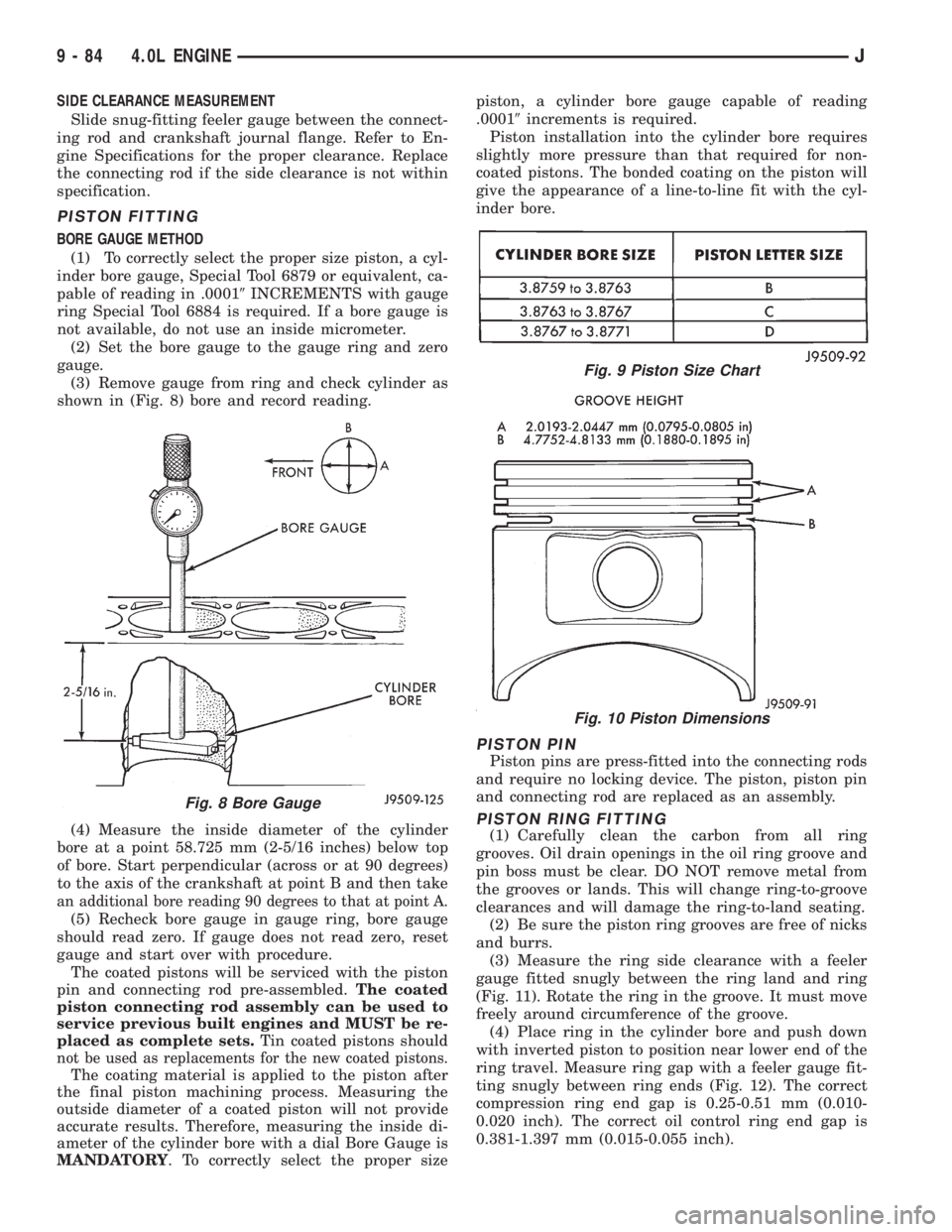
SIDE CLEARANCE MEASUREMENT
Slide snug-fitting feeler gauge between the connect-
ing rod and crankshaft journal flange. Refer to En-
gine Specifications for the proper clearance. Replace
the connecting rod if the side clearance is not within
specification.
PISTON FITTING
BORE GAUGE METHOD
(1) To correctly select the proper size piston, a cyl-
inder bore gauge, Special Tool 6879 or equivalent, ca-
pable of reading in .00019INCREMENTS with gauge
ring Special Tool 6884 is required. If a bore gauge is
not available, do not use an inside micrometer.
(2) Set the bore gauge to the gauge ring and zero
gauge.
(3) Remove gauge from ring and check cylinder as
shown in (Fig. 8) bore and record reading.
(4) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at a point 58.725 mm (2-5/16 inches) below top
of bore. Start perpendicular (across or at 90 degrees)
to the axis of the crankshaft at point B and then take
an additional bore reading 90 degrees to that at point A.
(5) Recheck bore gauge in gauge ring, bore gauge
should read zero. If gauge does not read zero, reset
gauge and start over with procedure.
The coated pistons will be serviced with the piston
pin and connecting rod pre-assembled.The coated
piston connecting rod assembly can be used to
service previous built engines and MUST be re-
placed as complete sets.Tin coated pistons should
not be used as replacements for the new coated pistons.
The coating material is applied to the piston after
the final piston machining process. Measuring the
outside diameter of a coated piston will not provide
accurate results. Therefore, measuring the inside di-
ameter of the cylinder bore with a dial Bore Gauge is
MANDATORY. To correctly select the proper sizepiston, a cylinder bore gauge capable of reading
.00019increments is required.
Piston installation into the cylinder bore requires
slightly more pressure than that required for non-
coated pistons. The bonded coating on the piston will
give the appearance of a line-to-line fit with the cyl-
inder bore.
PISTON PIN
Piston pins are press-fitted into the connecting rods
and require no locking device. The piston, piston pin
and connecting rod are replaced as an assembly.
PISTON RING FITTING
(1) Carefully clean the carbon from all ring
grooves. Oil drain openings in the oil ring groove and
pin boss must be clear. DO NOT remove metal from
the grooves or lands. This will change ring-to-groove
clearances and will damage the ring-to-land seating.
(2) Be sure the piston ring grooves are free of nicks
and burrs.
(3) Measure the ring side clearance with a feeler
gauge fitted snugly between the ring land and ring
(Fig. 11). Rotate the ring in the groove. It must move
freely around circumference of the groove.
(4) Place ring in the cylinder bore and push down
with inverted piston to position near lower end of the
ring travel. Measure ring gap with a feeler gauge fit-
ting snugly between ring ends (Fig. 12). The correct
compression ring end gap is 0.25-0.51 mm (0.010-
0.020 inch). The correct oil control ring end gap is
0.381-1.397 mm (0.015-0.055 inch).
Fig. 8 Bore Gauge
Fig. 9 Piston Size Chart
Fig. 10 Piston Dimensions
9 - 84 4.0L ENGINEJ
Page 1245 of 2198

The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors air
temperature in the intake manifold through the in-
take manifold air temperature sensor. The PCM ad-
justs injector pulse width and ignition timing to
compensate for intake manifold air temperature. Re-
fer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) for more in-
formation.
For removal and installation procedures of both the
air cleaner housing and the air cleaner element, refer
to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group
OPEN LOOP/CLOSED LOOP MODES OF
OPERATION
As input signals to the powertrain control module
(PCM) change, the PCM adjusts its response to the
output devices. For example, the PCM must calculate
different injector pulse width and ignition timing for
idle than it does for wide open throttle (WOT). There
are several different modes of operation that deter-
mine how the PCM responds to the various input sig-
nals.
MODES
²Open Loop
²Closed Loop
During Open Loop modes, the powertrain control
module (PCM) receives input signals and respondsonly according to preset PCM programming. Input
from the oxygen (O2S) sensor is not monitored dur-
ing Open Loop modes.
During Closed Loop modes, the PCM will monitor
the oxygen (O2S) sensor input. This input indicates
to the PCM whether or not the calculated injector
pulse width results in the ideal air-fuel ratio. This
ratio is 14.7 parts air-to-1 part fuel. By monitoring
the exhaust oxygen content through the O2S sensor,
the PCM can fine tune the injector pulse width. This
is done to achieve optimum fuel economy combined
with low emission engine performance.
The fuel injection system has the following modes
of operation:
²Ignition switch ON
²Engine start-up (crank)
²Engine warm-up
²Idle
²Cruise
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide open throttle (WOT)
²Ignition switch OFF
The ignition switch On, engine start-up (crank), en-
gine warm-up, acceleration, deceleration and wide
open throttle modes are Open Loop modes. The idle
and cruise modes, (with the engine at operating tem-
perature) are Closed Loop modes.IGNITION SWITCH (KEY-ON) MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. When the fuel system
is activated by the ignition switch, the following ac-
tions occur:
Fig. 27 Air CleanerÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
Fig. 28 Air CleanerÐYJ ModelsÐTypical
14 - 30 FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENT DESCRIPTION/SYSTEM OPERATIONJ
Page 1364 of 2198
(6) Position the turn signal switch and wire har-
ness in the cylinder housing. Fold the wires against
the connector. Route the connector down through the
steering column jacket.
(7) Install the windshield wiper wire harness and
switch. Route the wire harness down through steer-
ing column jacket.
(8) Align the turn signal switch in the housing and
secure the switch with the attaching screws. Tighten
the screws to 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the dimmer switch actuator arm.
Tighten the attaching screws to 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.)
torque.
(10) If equipped, install the cruise control wire har-
ness. Install the turn signal stalk by pushing it
straight into the column.
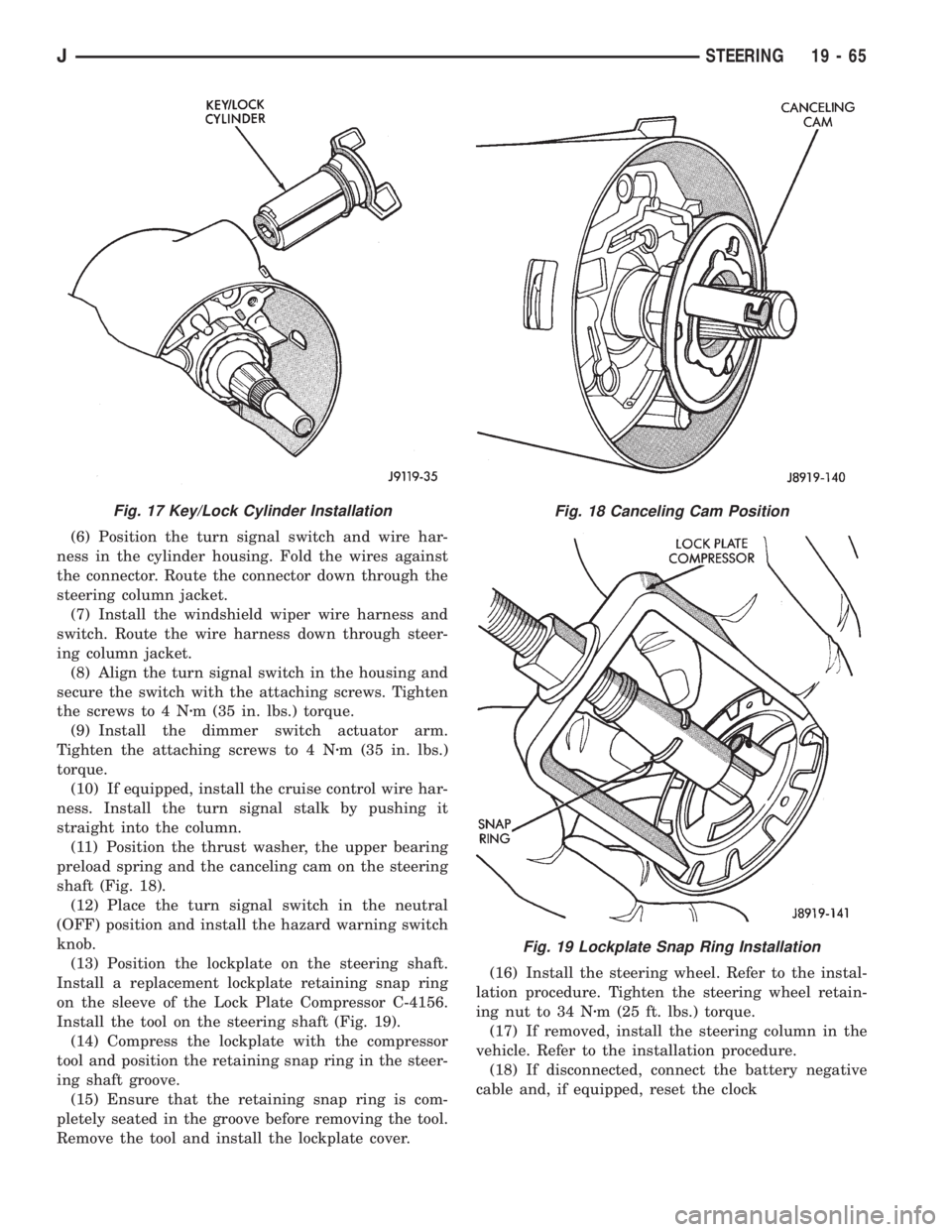
(11) Position the thrust washer, the upper bearing
preload spring and the canceling cam on the steering
shaft (Fig. 18).
(12) Place the turn signal switch in the neutral
(OFF) position and install the hazard warning switch
knob.
(13) Position the lockplate on the steering shaft.
Install a replacement lockplate retaining snap ring
on the sleeve of the Lock Plate Compressor C-4156.
Install the tool on the steering shaft (Fig. 19).
(14) Compress the lockplate with the compressor
tool and position the retaining snap ring in the steer-
ing shaft groove.
(15) Ensure that the retaining snap ring is com-
pletely seated in the groove before removing the tool.
Remove the tool and install the lockplate cover.(16) Install the steering wheel. Refer to the instal-
lation procedure. Tighten the steering wheel retain-
ing nut to 34 Nzm (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(17) If removed, install the steering column in the
vehicle. Refer to the installation procedure.
(18) If disconnected, connect the battery negative
cable and, if equipped, reset the clock
Fig. 17 Key/Lock Cylinder InstallationFig. 18 Canceling Cam Position
Fig. 19 Lockplate Snap Ring Installation
JSTEERING 19 - 65
Page 1556 of 2198

(3) Apply parking brakes and turn off air condi-
tioning unit.
(4) Shift transfer case into 2H range.
(5) Start engine and check curb idle speed. Adjust
speed if necessary. Curb idle must be correct to en-
sure accurate test results.
(6) Shift transmission into Neutral and set stop
watch.
(7) During following test steps, start stop watch as
soon as shift lever reaches D and Reverse ranges.
(8) Shift transmission into D range and record
time it takes for engagement. Repeat test two more
times.
(9) Reset stop watch and shift transmission back to
Neutral.
(10) Shift transmission into Reverse and record
time it takes for engagement. Repeat test two more
times.(11) Engagement time in D range should be a max-
imum of 1.2 seconds. Engagement time for Reverse
should be a maximum of 1.5 seconds.
TIME LAG TEST ANALYSIS
If engagement time is longer than specified for D
range, check for the following:
²shift cable misadjusted
²line pressure low
²forward clutch worn
²overdrive clutch worn or damaged
If engagement time is longer than specified for Re-
verse, check for the following:
²shift cable misadjusted
²line pressure low
²direct clutch worn
²first/reverse brake worn
²overdrive clutch worn or damaged
JAW-4 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 179
Page 1810 of 2198
TRAILER HITCH
TRAILER HITCHÐXJ
CLASS III HITCH
A class III weight-distributing/equalizer type hitch
can be used to tow a trailer:
²Having a maximum gross weight of 5,000 lbs/2250
kg.
²Having a maximum tongue weight of 750 lbs/332
kg).
The following vehicle basic equipment is required
for class III trailer towing:
²P205/75R15 or larger tires.
²Full size spare tire.
²Trailer sway control.
²Trailer tow wire harness and connector.
²Heavy duty turn signal flasher element.
²Heavy duty axle (with synthetic lubricant).
²Heavy duty cooling system.
²Heavy duty generator/battery.
²Auxiliary automatic transmission fluid cooler.
²I-6, 4.0L engine.
Wide-angle type door mirrors are recommended but
not required.
WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
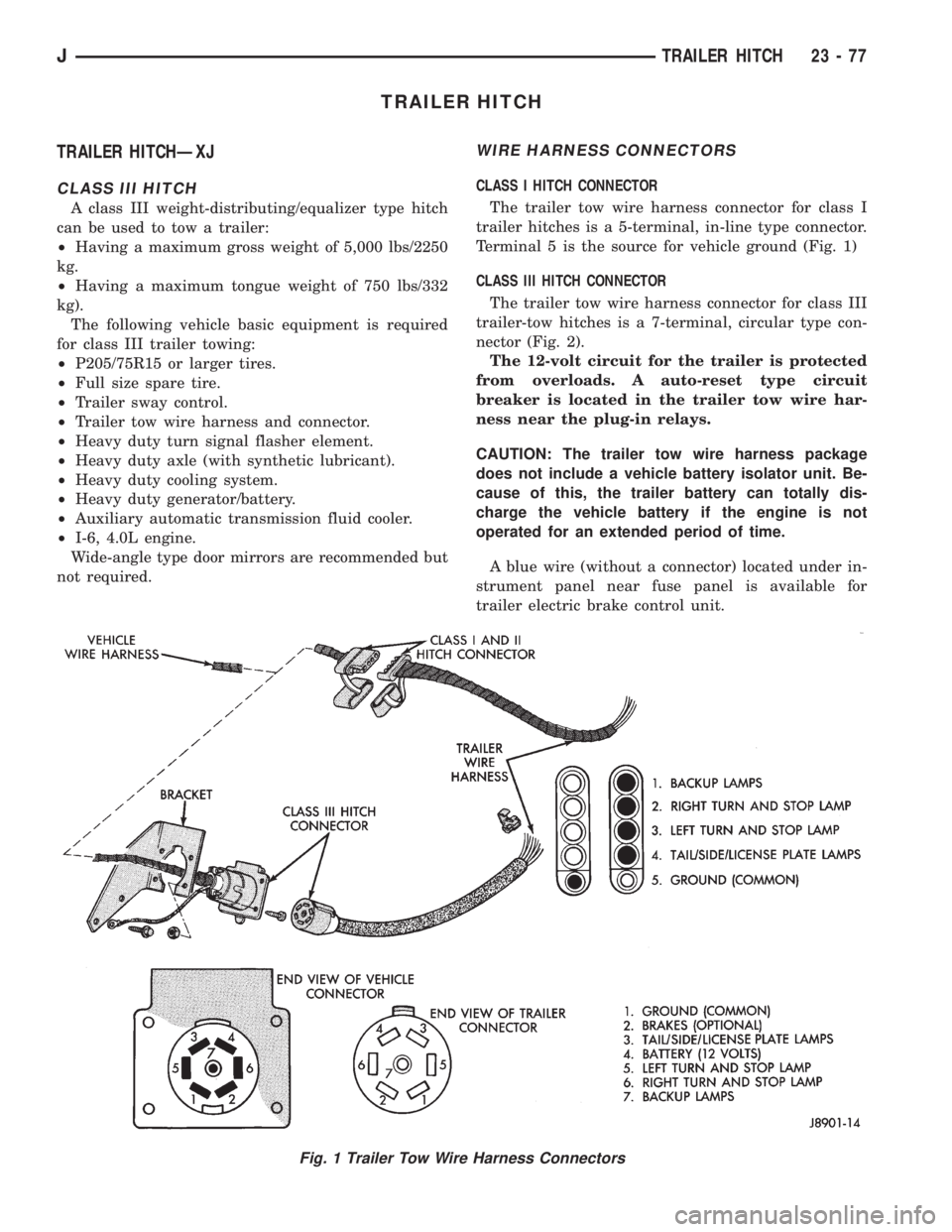
CLASS I HITCH CONNECTOR
The trailer tow wire harness connector for class I
trailer hitches is a 5-terminal, in-line type connector.
Terminal 5 is the source for vehicle ground (Fig. 1)
CLASS III HITCH CONNECTOR
The trailer tow wire harness connector for class III
trailer-tow hitches is a 7-terminal, circular type con-
nector (Fig. 2).
The 12-volt circuit for the trailer is protected
from overloads. A auto-reset type circuit
breaker is located in the trailer tow wire har-
ness near the plug-in relays.
CAUTION: The trailer tow wire harness package
does not include a vehicle battery isolator unit. Be-
cause of this, the trailer battery can totally dis-
charge the vehicle battery if the engine is not
operated for an extended period of time.
A blue wire (without a connector) located under in-
strument panel near fuse panel is available for
trailer electric brake control unit.
Fig. 1 Trailer Tow Wire Harness Connectors
JTRAILER HITCH 23 - 77