1995 GMC SIERRA service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 311 of 488

Brake Adjustment
Every time you make a brake stop, your disc brakes adjust for wear.
If your brake pedal goes down farther than normal, your rear drum brakes
may need adjustment. Adjust them by backing
up and firmly applying the
brakes
a few times.
Replacing Brake System Parts
The braking system on a modeffl VEShicle is complex. Its many parts have to
be of top quality and work well together if the vehicle
is to have really good
braking. Vehicles we design and test have top-quality
GM brake parts in
them, as your vehicle does when it is new. When you replace parts of your
braking system
- for example, when your brake linings wear down and
you have to have new ones put
in - be sure you get new genuine GM
replacement parts. If you don't, your brakes may no longer work properly.
For example, if someone puts in brake linings that are wrong for your
vehicle, the balance between your front and rear brakes can change
- for
the worse. The braking performance you've come to expect can change
in
many other ways if someone puts in the wrong replacement brake parts.
Front Shock Absorbers
The front shock absorbers of your vehicle do many things. They help the
vehicle ride smoothly and
also control the travel of the suspension system.
When the shock absorbers are serviced, any replacement shock absorbers
must be the same as the original equipment shock absorbers
in both
extended length and strength.
I NOTICE:
If you use shock absorbers that are not the same as the original
shock absorbers, the shock absorbers
or suspension system
could be damaged.
6-45
ProCarManuals.com
Page 322 of 488

Rear Lamps - Chassis Cab Models
d
1. Using your
hands, peel the
rubber seal away
from the lens.
2. Lift the lens off
the lamp
assembly.
3. Slide the socket
out
of the lamp
assembly.
4. Push in gently on
the bulb, turn it to
the left and remove
it from
the socket.
5. Put in a new bulb
and, pushing
in
gently, turn it to
the right
until it is
tight.
6. Put the socket back in the lamp assembly and replace the lens and lens
seal.
Exhaust System
To help prevent damage to your exhaust system, do not continue to drive
your vehicle
if you notice:
0 Engine misfiring
0 Loss of performance
0 Exhaust system components hanging lower than normal
0 Loud exhaust system noises
0 Other unusual operating conditions
Have
your engine and exhaust system serviced regularly.
6-56
ProCarManuals.com
Page 323 of 488

Three- Way Catalytic Converter (Gasoline Engines)
Your vehicle’s three-way catalytic converter is designed to reduce the
pollutants
in your vehicle‘s exhaust. Use only unleaded fuel in your vehicle.
If you use leaded fuel, you could damage your three-way catalytic converter
and other engine components.
Oxidation Catalytic Converter (Diesel Engines)
Your vehicle’s oxidation catalytic converter is designed to reduce the
particulates
in your vehicle‘s exhaust. If your vehicle’s oxidation catalytic
converter ever needs to be replaced,
it must be replaced with an oxidation
converter intended for use
with diesel engines only.
Engine Control Module System
Gasoline Engines
This system has an oxygen sensor (OS) that helps keep your engine’s
air-fuel mixture at a proper level. Use only unleaded fuel in your vehicle. If
you use leaded fuel, you could damage your oxygen sensor
(OS) and
three-way catalytic converter.
Diesel Vehicles Below 8,500 (3 850 Kg) G VWR
This system monitors engine speed and throttle position. It adjusts exhaust
gas recirculation to limit emissions.
Malfunction Indicator (SERVICE ENGINE SOON)
Light
The Malfunction Indicator (SERVICE ENGINE SOON) Light on your
instrument panel lets you know when your emission system needs service.
The light will come on briefly when you start your engine to
let you know
that the system is working. If
it does not come on when you start your
engine, or
if it comes on and stays on while you’re driving, your system
may need service. Your vehicle should still be driveable, but you should
have your system serviced right away.
Secondary Air Injection Reaction (AIR) System
(Gasoline Engines)
You may have this system. It has a control valve that will direct air to where
it is needed. If the AIR system needs service, your Malfunction Indicator
(SERVICE ENGINE
SOON) Lamp on your instrument panel will come on.
6-57
ProCarManuals.com
Page 326 of 488
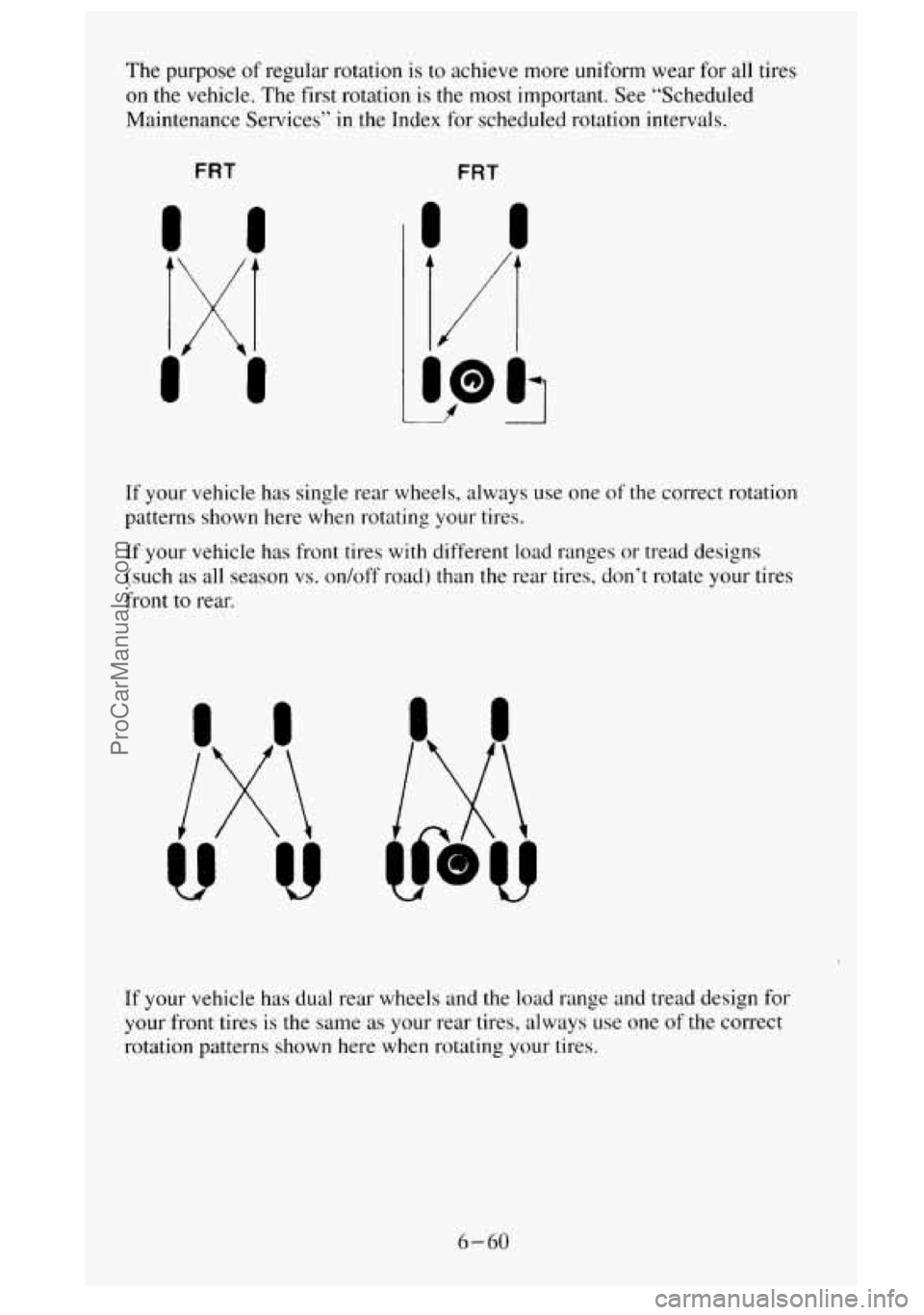
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more uniform wear for all tires
on the vehicle. The first rotation is the most important. See “Scheduled
Maintenance Services”
in the Index for scheduled rotation intervals.
FRT
I
II
FRT
If your vehicle has single rear wheels, always use one of the correct rotation
patterns shown here when rotating your tires.
If your vehicle has front tires with different load ranges
or tread designs
(such as all season vs. on/off road) than the rear tires. don‘t rotate your tires
front
to rear.
W v
If your vehicle has dual rear wheels and the load range and tread design for
your front tires
is the same as your rear tires, always use one of the correct
rotation patterns shown here when rotating your tires.
6-60
ProCarManuals.com
Page 329 of 488

A CAUTION:
If you operate your vehicle with a tire that is badly
underinflated, the tire can overheat. An overheated tire
can lose
air suddenly or catch fire. You or others could be injured. Be
sure all tires (including the spare, if any) are properly inflated.
Buying New Tires
To find out what kind and size of tires you need, look at the
CertificationRire label.
The tires installed on your vehicle when
it was new a Tire Performance
Criteria Specification (TPC Spec) number on each tire’s sidewall. When you
get new tires, get ones with that same TPC Spec number. That way, your
vehicle will continue to have tires that are designed to give proper
endurance, handling, speed rating, traction, ride and other things during
normal service on your vehicle.
If your tires have an all-season tread
design, the TPC number will be followed by an
“MS” (for mud and snow).
If you ever replace your tires with those not having a TPC Spec number,
make sure they are the same. size, load range, speed rating and construction
type (bias, bias-belted or radial) as your original tires.
I A CAUTION:
Mixing tires could cause you to lose control while driving. If you
mix tires of different sizes or types (radial and bias-belted tires),
the vehicle may not handle properly, and you could have
a crash.
Be sure to use the same size and type tires on all four wheels.
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
The following information relates to the system developed by the United
States National Highway Traffic Safety Administration which grades tires
by treadwear, traction and temperature performance.
(This applies only to
vehicles sold in the United States.)
6-63
ProCarManuals.com
Page 330 of 488

Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the
tire when tested under controlled conditions on
a specified government test
course. For example,
a tire graded 150 would wear one and a half (1 1/2)
times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. The relative
performance
of tires depends upon the actual conditions of their use,
however, and may depart significantly from the norm due to variations
in
driving habits, service practices and differences in road characteristics and
climate.
Traction - A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to lowest are: A, B, and C. They represent
the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement
as measured under controlled
conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete.
A
tire marked C may have poor traction performance.
Warning: The traction grade assigned to this tire
is based on braking
(straight-ahead) traction tests and does not include cornering (turning)
traction.
Temperature - A, B, C
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C, representing the tire’s
resistance to the generation
of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when
tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test
wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the material
of the tire to
degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead
to
sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a level of performance
which all passenger car tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle
Safety Standard
No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of
performance
on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by
law.
Warning: The temperature grade for this tire is established for a tire that is
properly inflated and
not overloaded. Excessive speed, underinflation, or
excessive loading, either separately or in combination, can cause heat
buildup and possible tire failure.
These grades are molded on the sidewalls of passenger car tires.
While the tires available as standard or optional equipment on General
Motors vehicles may vary with respect to these grades, all such tires meet
General Motors performance standards and have been approved for use on
General Motors vehicles.
All passenger type (P Metric) tires must conform
to Federal safety requirements in addition to these grades.
6-64
ProCarManuals.com
Page 340 of 488

Finish Damage
Any stone chips, fractures or deep scratches in the finish should be repaired
right away. Bare metal will corrode quickly and may develop into
a major
repair expense.
Minor chips and scratches can be repaired with touch-up materials available
from your dealer or other service outlets. Larger areas of finish damage can
be corrected in your dealer’s body and paint shop.
Underbody Maintenance
Chemicals used for ice and snow removal and dust control can collect on
the underbody. If these are not removed, accelerated corrosion (rust) can
occur
on the underbody parts such as fuel lines, frame, floor pan, and
exhaust system even though they have corrosion protection.
At least every spring, flush these materials from
the underbody with plain
water. Clean any areas where mud and other debris can collect. Dirt packed
in closed areas of the frame should be loosened before being flushed. Your
dealer or
an underbody vehicle washing system can do this for you.
Chemical Paint Spotting
Some weather and atmospheric conditions can create a chemical fallout.
Airborne pollutants can fall upon and attack painted surfaces on your
vehicle. This damage can take two forms: blotchy, ringlet-shaped
discolorations, and small irregular dark spots etched into the paint surface.
Although no defect
in the paint job causes this, GM will repair, at no charge
to
the owner, the surfaces of new vehicles damaged by this fallout condition
within
12 months or 12,000 miles (20 000 km) of purchase, whichever
comes first.
This applies only to materials manufactured and sold by General Motors.
Bodies, body conversions or equipment not made or sold by General Motors
are not covered.
6-74
ProCarManuals.com
Page 342 of 488
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
0 TESTVNXX3XXQ09696 G
This is the legal identifier for your vehicle. It appears on a plate in the front
corner
of the instrument panel, on the driver’s side. You can see it if you
look through the windshield from outside your vehicle. The
VIN also
appears
on the Vehicle Certification and Service Parts labels and the
certificates of title and registration.
Engine ldentificafion
The eighth character in your VIN is the engine code. This code will help
you identify your engine, specifications. and replacement parts.
6-76
ProCarManuals.com