1994 JAGUAR XJ diagram
[x] Cancel search: diagramPage 2 of 74

ZF Automatic Transmissions Service Manual
CON TENTS
Section Title SRO Page
Foreword ........................................................................\
... ii
I ................ Service Tools & Equipment ........................................................... iii
I1 ................ Torque Tightening Specifications ....................................................... iii
111 ............... Service Materials .................................................................... iii
IV ............... Service Data ....................................................................... \
iii
1.1 .......................................... 1
1.1.7 ............. Torqueconverter .................................................................... 1
1.1.2 ............. Four-speed Epicyclic Gear Train ........................................................ 2
1.1.3
............. Operation Of Gear Train Clutches ...................................................... 3
1.1.4
............. Transmission Output Shaft Extension Housing ............................................ 4
1.1.5.
............ Transmission Control Unit ............................................................. 4
1.1.6 ............. Gearshift Selection ................................................................... 8
1.1.7. ............ Throttle Valve Mechanism (kickdown) ................................................. 8
1.1.8
............. Starter Inhibit Switch ................................................................. 8
1.1.9
............. Gearshift Interlock ................................................................... 8
1.2
.............. Hydraulic Circuit Diagrams ........................................................... 9
1.3
.............. Fault Diagnosis ..................................................................... 33
1.3.1
............. Initial Checks ...................................................................... 33
1.3.2
............. Engine Tune ........................................................................\
33
1.3.3
............. Stall Test ........................................................................\
.. 33
1.3.4
............. Road Test ........................................................................\
.. 33
1.3.5
............. Electrical Checks ................................................................... 33
1.3.6
............. Fault Finding Chart .................................................................. 34
2.1
.............. ZF 4 HP 24 E Transmission - General Description ........................................ 39
2.1.1
............. Torqueconverter ................................................................... 39
2.1.2
............. Four-speed Epicyclic Gear Train ....................................................... 40
2.1.3
............. Operation Of Gear Train Clutches ..................................................... 41
2.1.4
............. Transmission Control Unit ............................................................ 42
2.1.5
............. Transmission Control Module (TCM) ................................................... 46
2.1.6
............. Transmission Rotary Switch ........................................................... 47
2.1.7
............. Decoder Module .................................................................... 47
2.1.8 ............. Performance Modeswitch ............................................................ 47
2.1.9
............. 'Kick-down' Mechanism ............................................................. 47
2.1.10.
........... Reverse Safety Inhibit ................................................................ 47
2.1.11
............ Gearshift Interlock .................................................................. 47
2.1.12.
........... Starter Inhibit Switch ................................................................ 47
2.1.13 ............ Harness Connections ................................................................ 48
2.1.14. ........... Rotary Switch Harness ............................................................... 49
2.1.15 ............ Main Harness Connectors- 12 wayand8 way .......................................... 50
2.2
.............. Hydraulic Circuit Diagrams .......................................................... 51
2.3
.............. Fault Diagnosis ..................................................................... 60
2.3.1 ............. Initial Checks ...................................................................... 60
2.3.2 ............. Engine Tune ........................................................................\
60
2.3.3 ............. Stall Test ........................................................................\
.. 60
2.3.4 ............. Road Test ........................................................................\
.. 61
2.3.5 ............. Electrical Checks ................................................................... 61
2.3.6 ............. Fault Finding Chart .................................................................. 61
2.4
.............. Service Operations ................................................................. 68
............... ZF 4 HP 22 Transmission . General Description
i Issue 1 August 1994
Page 3 of 74

ZF Automatic Transmissions Service Manual
FORE WORD
This manual provides information relevant to the servicing of ZF Automatic Transmission Units 4 HP 22 and 4 HP 24 E (irrespective of the vehicle range to which the unit is fitted). The manual should be used in conjunction with the rel- evant Vehicle Service Manual (VSM) and Electrical Diagnostic Manual (EDM).
It assumes that the transmission has been removed from the vehicle, in accordance with the Vehicle Service Manual,
and is
in a clean condition and all service tools and materials are available.
The manual is divided into two sections covering the ZF
4 HP 22 and ZF 4 HP 24 E and each section is divided into sub- sections covering:
0 Service Information
0 General Description
0 Hydraulic Circuit Diagrams
0 Fault Diagnosis
o Service Repair Operations.
An index can be found at the rear of the manual.
Ne@: For information relating to in-vehicle operations, refer to the Vehicle Service Manual.
ii Issue 1 August 1994
Page 10 of 74

1.1.6 Gearshift Selection
Gearshift selection is by movement of the shift lever which through a selector cable causes repositioning ofthe manual
(selector) valve to direct oil pressure to the required shift valve. The automatic shift points are determined by acceler- ator position and road speed: throttle movement moves a cam on the throttle valve, directing oil pressure to the shift
valves and modulator valve, road speed modulates hydraulic pressure through a centrifugal governor driven by the
transmission output shaft. Operation
of the hydraulic control system is shown diagrammatically in the circuit dia
-
grams on the following pages.
I I
I
I
2 -3- I
I I
I
I
- I
I I 1 4 -5 - - -
+ ! + I I 'I 10 I I
I
I 1
1, 1-Y I
I I
I
I
1. Engine 8. Pump regulator valve 2. Torque converter 9. Damper
3. Pump 10. Governor valve 4. Clutch & gears 11. Shift valve 5. Governor 12. Kickdown cable &throttle cam 6. Shift 13. Throttle / modulator valves 7. Solenoid valve 14. Transmission housing
Fig.
1 Schematic Diagram of Hydraulic Control
I. 1.7 Throttle Valve Mechanism (kick-down)
The throttlevalve or 'kick-down' mechanism comprises a cable connected between throttle body pedal and the throttle
valve cam/ quadrant located on the selector valve shaft; the cam operates the throttle valve housed within the throttle
valve block. The travel of the valve is proportional to throttle positions and alters shift speeds and pressures during
gearshifts to take account of throttle position. The mechanism also provides for immediate selection of a lower
ratio (eg when overtaking) by depressing the accelerator beyond the normal full
-throttle position. 'Kick-down' is oper- ated by movement of the throttle cable into the 'kick-down' position causing full movement of the throttle valve and
directing oil flow to the shift valves.
1.1.8 Starter Inhibit Switch
The starter inhibit switch prevents the starter motor from being operated when the shift lever is not in position 'P' - Park or position 'N'- Neutral. The switch is located in the gear selector housing.
I. I. 9 Gearshift Interlock
A brake pedal /shift lever interlock is incorporated in the gearselector mechanism. Theshift lever may only be moved
from the 'P'- Park position if the ignition key switch is in position '11', and the foot brake pedal is applied. The ignition
key cannot be removed from the ignition switch unless the shift lever is in the 'P' -Park position. Once the ignition key
has been removed, the shift lever is locked in the park position.
The gearshift interlock is operated by an electrical solenoid located adjacent to the selector; an override latch is incorpo
- rated into the mechanism to enable the gearshift interlock to be manually overridden in the event of electrical failure
or when towing.
8 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 14 of 74

ZF Automatic Transmissions Service Manual
1.2 HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS
Key To Hydraulic Circuit Diagrams (commencing on page IO)
1. Governor 16. 1 - 2
Shift Valve
2. Torque Converter 17.
Clutch
'C' Valve
3. Sump
18. Clutch 'C" Damper
4. Pump 19.
Clutch
'C" Valve
5. Pressure Regulating Valve 20.
2
- 3 Shift Valve
6. Clutch
'B' Valve And Damper 21.
2nd Gear Inhibit
7. Clutch 'D' Valve And Damper 22.
Throttle Valve
8. Reverse Gear Inhibit 23. Converter Clutch Lock-up Control Valve
9. Manual Valve 24.
Converter Clutch Hysteresis Valve
IO. Oil Cooler 25. 3 - 4 Shift
Valve
11. Converter And Reversing Valve 26.
Clutch 'F' Valve And Damper
12. Converter Clutch Damper 27.
Clutch
'A' Damper
13. One
-way Valve
14. Modulator Valve
15. 1st Gear Inhibit
A Clutch'A'
B Clutch'B'
C Clutch'C'
C1 Clutch 'C"
D Clutch'D'
E Clutch'E'
F Clutch'F'
Exhaust
Throttle
Orifice Branch
Main Pressure
Converter Pressure
Throttle Pressure
28. Clutch 'E' Damper
29. Clutch 'F' Inhibit Valve (Reverse)
Vlll HII Governor Pressure
IX - Locking Pressure
X -1- Modulation Pressure
XI - Pump Pressure
XI1 Lubrication Pressure
issue 1 August 1994 9
Page 45 of 74

ZF Automatic Transmissions Service Manual
The torque converter acts in all four forward gears and in reverse. The converter lock-up clutch closes in 4th gear at
a point depending on road speed and accelerator position; engine power is then transmitted
by purely mechanical
means.
A low
-loss oil pump in the front of the transmission housing supplies the converter, the automatic gear shift and the
lubrication circuit; oil is drawn from a sump in the bottom of the gear train housing through a filter. The pump drive
gear is keyed to the converter impeller hub and therefore turns when the engine is running, thereby pressurizing the
oil.
2.1.2 Four-speed Epicyclic Gear Train
The torque converter drives a mechanical epicyclic gear train providing four forward ratios and reverse. Individual ra-
tios are obtained by coupling together the various parts of the gear train by means of solenoid-operated, hydraulically
actuated multi-disc clutches and brakes; built in freewheels permit gear shifts without any interruption of the power
flow.
For information on the operation of the solenoids, clutches, brakes and freewheels, refer to the table below and the
schematic diagrams shown overleaf.
A parking lock pawl is provided at the rear of the gear train, operating on a toothed wheel attached to the output shaft;
the parking lock is operated from the selector (position
'P) by actuator rod.
An electro
-magnetic sensor detects output shaft revolutions by means of a toothed disc attached to the shaft; one rev- olution of the shaft is equal to 36 pulses. The electrical signal from the sensor is passed, via a screened cable, to the
TCM.
R
Park,
Neutral
Solenoid ~
MV2
MVI, MV2
MVI, MV3
MV2
-
MV2
OWC
= one way clutch
Resulting clutch operation
A Clutch drives annulus clockwise
D Clutch OWC holds F carrier against shaft clockwise
E Clutch & OWC drives output shaft clockwise
A Clutch drives annulus clockwise
C1 Clutch holds sungear against anti-clockwise
C Clutch
& OWC holds sungear against anti-clockwise
A Clutch drives annulus clockwise
B Clutch drives sungear clockwise
C Clutch
& OWC holds sungear against anti-clockwise
A Clutch drives annulus clockwise
B Clutch drives sungear clockwise
C Clutch
& OWC holds sungear against anti-clockwise
B Clutch drives sungear clockwise
D Clutch holds carrier against clockwise
E Clutch & OWC drives output shaft anti-clockwise
E Clutch & OWC applied (hydraulics)
40
Issue 1 August 1994
Page 47 of 74

ZF Automatic Transmissions Service Manual
Reverse Gear
Clutches 'B','D' and 'E' are engaged.
As the front planet gear carrier of epicyclic gear SE '9' is
locked, the direction of output shafgt rotation is reversed.
Epicyclic gear set '10' also rotates as a solid block. I
~~~-698
Fig. 1
2.1.4 Transmission Control Unit
The electronichydrauliccontrol unit comprising a series of valve blocks housing a cable-operated manual valve, con- trol pistons and pressure valves is attached to the underside of the transmission housing; the unit controls the oper- ation of the gear train clutches and directs oil pressure to the appropriate system components (refer to illustrations,
pages 43 to 46) to operate the transmission.
The four valve blocks in which the control valves, pistons etc are located, are mounted and connected through a main
gallery plate. The three solenoid valves
MVI, MV2 and MV3 and the pressure regulator operating solenoid are located
on the upper surface of the plate; electrical connections between the solenoids and the transmission and transmission
control unit are via cable harnesses (refer to relevant diagrams and tables for details of the various pin connections).
Operation of the transmission control unit is through an electronic Transmission Control Module
(TCM) which on re-
ceipt of electrical signalsfrom transmission and engine management sources, activates the hydraulic pressure regulat- ing and shift valves via solenoid valves located on the valve block. The gearshift selector transmits movement, via the
selector cable, to the selector lever on the side of the gearbox; this rotates the selector shaft which controls the manual
selector valve. The rotary position of the shaft is monitored by the rotary switch.
42 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 56 of 74
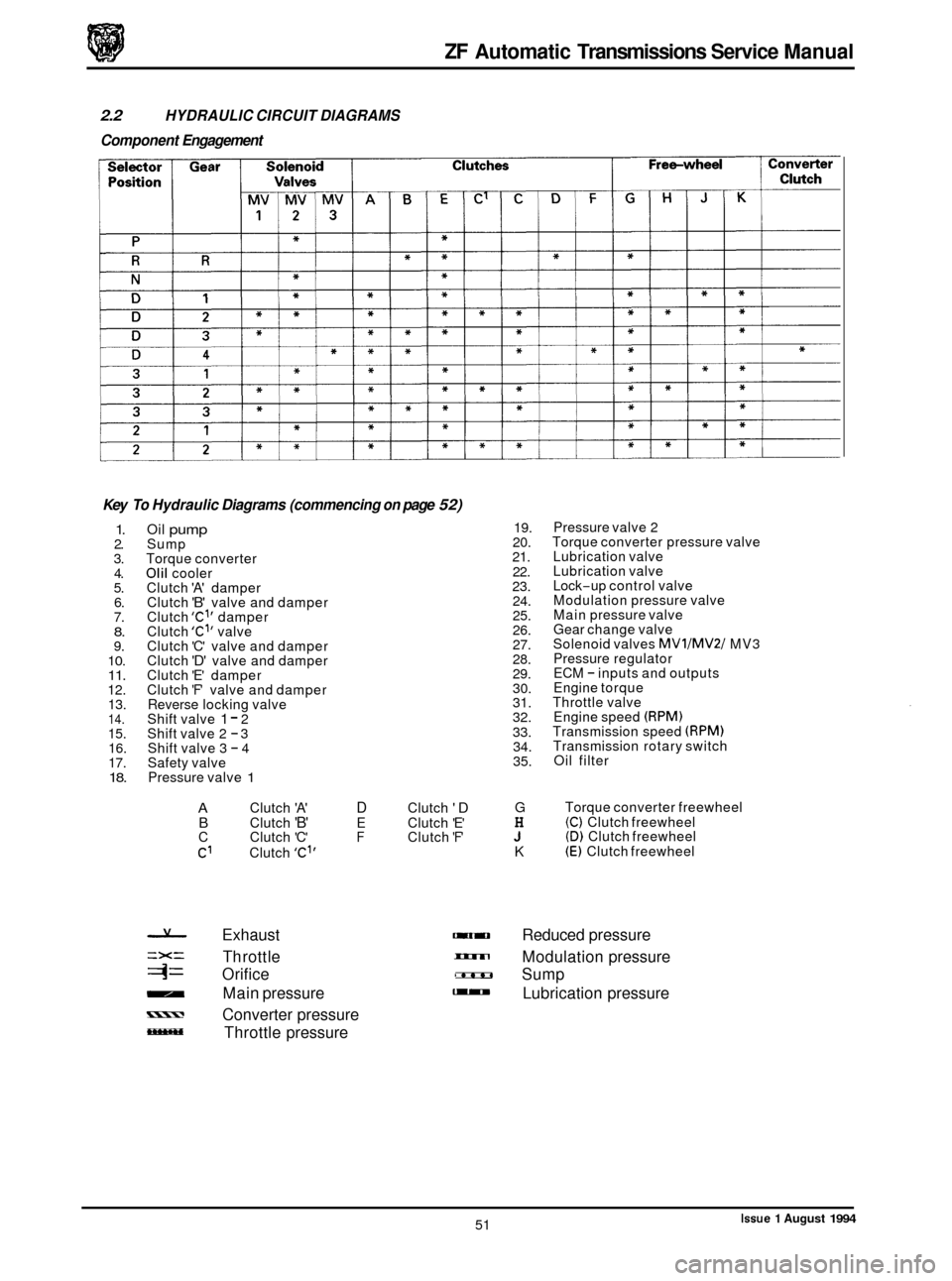
ZF Automatic Transmissions Service Manual
2.2 HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS
Component Engagement
Key
To Hydraulic Diagrams (commencing on page 52)
1. 2.
3. 4.
5. 6.
7.
8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13.
14. 15. 16.
17.
18.
Oil pump Sump
Torque converter
Olil cooler
Clutch 'A' damper
Clutch 'B' valve and damper
Clutch 'Cl' damper
Clutch 'Cl' valve
Clutch 'C' valve and damper
Clutch
'D' valve and damper
Clutch 'E' damper
Clutch
'F' valve and damper
Reverse locking valve
Shift valve
1 - 2
Shift valve 2 - 3
Shift valve 3 - 4
Safety valve
Pressure valve
1
A Clutch 'A' D Clutch 'D B Clutch 'B' E Clutch 'E'
C Clutch 'C' F Clutch 'F'
C1 Clutch 'C"
19.
20.
21.
22.
23. 24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33. 34.
35.
G
H J K
Pressure valve 2
Torque converter pressure valve
Lubrication valve
Lubrication valve
Lock
-up control valve
Modulation pressure valve
Main pressure valve
Gear change valve
Solenoid valves
MVllMV2l MV3
Pressure regulator
ECM
- inputs and outputs
Engine torque
Throttle valve Engine speed
(RPM) Transmission speed (RPM) Transmission rotary switch
Oil filter
Torque converter freewheel
(C) Clutch freewheel (D) Clutch freewheel (E) Clutch freewheel
Exhaust - Reduced pressure
=X= Th rott le - Modulation pressure
4= Orifice 2- Sump
- Main pressure - Lubrication pressure
- Converter pressure
Throttle pressure
Issue 1 August 1994 51
Page 74 of 74

E
Fau;t diagnosis
ZF 4HP 22
Electrical checks,
33
Engine tune, 33
Fault finding chart, 34
Initial checks, 33
Road test, 33
Stall test, 33
Electrical tests, 61
Engine tune, 60
Fault finding chart, 61
Initial checks, 60
Road test, 61
Stall test, 60
ZF 4HP 24 E
Foreword, ii
G
General description
ZF4HP22
Epicyclic gear train, 2
Gear train clutches operation, 3
Gearshift interlock, 8
Gearshift selection, 8
Output shaft extension housing, 4
Starter inhibit switch, 8
Throttle valve mechanism, 8
Torque converter, 1
Transmission control unit, 4
Control layout schematic illustration, 46
Decoder module, 47
Epicyclic gear train, 40
Gear train clutches operation, 41
Gearshift interlock, 47
Harness connections, 48
Kick-down mechanism, 47
Main harness connector
ZF
4HP 24 E
12-way, 50
Sway, 50
Performance mode switch, 47
Reverse safety inhibit, 47
Rotary switch connector pins, 49
Rotary switch harness, 49
Starter inhibit switch, 47
TCM connector pins, 48
Torque converter, 39
Transmission control module, 46
Transmission control unit, 42
Transmission rotary switch, 47
H
Hydraulic circuit diagrams
‘1 ’ - 1 st, full throttle, 32
‘1’ - 21-14 idling, 31
‘1 ’ - 3rd, idling, 30
‘2’ - 2nd, full throttle, 29
‘2’ - 3rd, idling, 28
‘3’ - 3rd, full throttle, 26
‘3’ - 3rd, kickdown, 27
‘3’ - 3rd, part throttle, 25
ID’- drive, Ist, full throttle, 14
ZF 4HP 22
‘D’ - drive, lst, idle, 13
‘D’ - drive, lst, kickdown, 15
‘D’ -drive, 2nd, full throttle, 17
‘D’ - drive, 2nd, idle, 16
‘D’ - drive, 2nd, kickdown, 18
‘D’ -drive, 3rd, full throttle, 20
‘D’ - drive, 3rd, kickdown, 21
‘D’ -drive, 3rd, part throttle, 19
‘D’ -drive, 4th, full throttle lock-up, 24
‘D’ -drive, 4th, part throttle, 22
‘D’ - drive, 4th, part throttle lock-up, 23
‘N’ - neutral, 12
‘P’ - park, 10
‘R‘ - reverse, 11
Key, 9
‘1’ - Ist, 59
‘D’ - drive, 1 st, 55
‘D’ - drive, 2nd, 56
‘D’ - drive, 3rd, 57
‘D’ - drive, 4th, lock-up, 58
‘N’ - neutral, 54
‘P’ - park, 52
‘R‘ - reverse, 53
Key, 51
ZF 4HP 24 E
S
Service data, iii
Service materials, iii
Service operations
ZF 4HP 22, Not yet available, 68
ZF 4HP 24 E, Not yet available, 68
Service tools & equipment, iii
T
Torque tightening specifications, iii