1994 BMW 750IL wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 13 of 80

13
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Principle of Operation
The optical infra red portion of the sensor operates by the principle of refraction (bending
of a light ray). The rain sensor control module activates the emitter diode which sends a
beam of infra red light through the windshield on an angle. The set angle is important
because it provides the beam with a calculated reflective path back to the detector diode.
The beam is reflected back into the windshield due to the density difference of the glass
compared with the ambient air on the outside surface of the glass. When the windshield is
clean (no rain drops, moisture or dirt) the detector diode receives 100% of the infra red light
that the was sent by the emitter. With this condition, the rain sensor evaluation electronics
determines the windshield is free of rain drops.
The density of water is closer to that of glass than air. When rain starts to accumulate in
the sensor monitoring area, it causes part of the infra red beam to extend past the outside
surface of the glass and into the rain drop. When this occurs, the beam is refracted and
only part of the beam returns to the detector diode.
The rain sensor evaluation elec-
tronics determines the windshield
has a few rain drops (or dirt) on it.
The intensity of the returned infra red beam diminishes proportionally with an increase of
water droplets. The rain sensor control module generates a signal proportionate to the
amount of rain on the windshield and broadcasts it to the GM via the K bus.
The GM activates the intermittent wipe cycle if the windshield wiper stalk switch is in the
intermittent position. It also adjusts the frequency of wiping the windshield depending on
the four position thumb wheel.
12510114.eps
12510115.eps
Page 14 of 80

14
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Rain Sensor Function
The rain sensor is online as soon as it receives KLR operating power.
• When the windshield wiper stalk switch is placed in the intermittent position the GM sig-
nals the rain sensor control module via the K-Bus of the request for intermittent wiping
and the position of the knurled wheel (sensitivity).
• As an acknowledgement, the rain sensor sends a command via the K Bus to activate the
wiper motor. If more than 12 seconds pass before the GM receives the acknowledge-
ment, the GM concludes the rain sensor has a defect and operates the intermittent wipe
function as a system not equipped with a rain sensor. The wiper intermittent cycling is
based solely on the knurled wheel setting.
• The rain sensor continuously monitors the windshield for rain accumulation and signals
the GM to activate the wipers based on the knurled wheel position and how fast the rain
accumulates on the windshield.
• The knurled wheel position signal (1-4) via the K bus informs the rain sensor of the select-
ed level of sensitivity.
- Position 1 (least sensitive) delays the wiper activation signal.
- Position 4 (most sensitive) sends the wiper activation signal to the GM sooner.
• When the wiper motor park contacts signal the GM of the wiper arm position, the signal
is simultaneously sent to the rain sensor as an indication that the windshield has been
cleared of water drops and causes the rain sensor to reset the sensitivity delay timer back
to 0.
• If night time driving is detected via the integral photocell, the sensitivity to water droplets
is increased causeing a shorter delay than day time driving.
• Depending on the intensity of the rain the wipers will be operated continuously as if set in
the normal wiper stalk switch position regardless of the knurled wheel setting. For this
reason, the vehicle speed signal on the K bus is not utilized on rain sensor equipped wiper
systems.
Page 15 of 80

• If the ignition switch is turned off with the wiper switch in the intermittent position, the rain
sensor will only become active after the ignition is switched back on and one of the fol-
lowing occurs:
- The stalk switch is moved from the intermittent position and then back.
- The knurled wheel setting is adjusted.
- or the wash function is activated.
The reasoning behind this switching strategy is to have the driver make a conscious deci-
sion to activate the system themselves.
Rain Sensor Control Module Adaptation
The rain sensor control module adapts to the optics system environment as follows:
Windshield Aging:As the vehicle ages the possibility of stone chipping in the rain sensors
monitoring area may occur which will cause a loss of light in the optics system.
The control module adapts for loss of light based on the intensity of the detected infra red
light with a cleared windshield (wiper motor park signal). Therefore, the rain sensors func-
tion is not adversely affected due to windshield aging.
Dirty Windows:The rain sensor adaptation reacts less sensitively to a dirty windshield
(dirt, road salt, wax residue) after a completed wipe cycle. A dirty windshield has a film on
it that diminishes the ability of the infra red to refract into present water droplets. This caus-
es a delay in the rain sensor detection capabilities which lengthens the time intervals on an
intermittent wipe.
Windshield Wiper System Failsafe Operation
The GM provides failsafe operation of the wiper system if faults are detected with any of the
following input signals:
15
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Function Faulted Input Detected Failsafe Function
Intermittent Wipe
Short or open circuit of
the knurled wheel signalDelay value for
setting 3 used.
Intermittent wipe
with Rain SensorFaulted Rain Sensor or
K-Bus Signal corruptNormal Intermittent
wipe implemented
Wiper Motor not
Functional MovingPark contact feedback
signal takes longer than
16 secondsWiper motor control
deactivated for 3
minutes
Page 18 of 80

• A remote luggage compartment button is installed in the left kick panel (center console
in the E53) to open the luggage compartment from inside the vehicle.
• The EWS is interfaced for double lock monitoring and unlock function. With the presence
of an accepted EWS key in the ignition, the vehicle will be unlocked and disarm DWA.
• The automatic locking feature (> 99 MY) activates the door locks when a road speed
signal of 5 MPH and engine RPM is detected via the K-Bus. The factory default setting
of this feature is off (can be encoded on for individual users with Key Memory function).
• In the event of an accident (ignition on), the GM will be signalled to unlock all doors.
Hardware Features:
• The external lock cylinders are located in the
driver’s door and luggage compartment lid
(E53/E39 Sport Wagon does not have a tail-
gate lock cylinder).
• The driver’s door and luggage compartment
incorporates an overrunning lock cylinder. The
lock cylinder will free wheel or spin If any key
other than the vehicle key or tool, such as a
screw driver, is inserted into the cylinder. The
lock cylinders can be manually locked/un-
locked by turning the key “past” lock/unlock.
• The door lock buttons are mechanically uncoupled from the
lock actuators when locked.
The door lock buttons “mechanically” lock the individual
doors. This provides manual locking in the event of a central
locking malfunction.
• Child safety locks (located in
the rear doors) are actuated
by inserting a key in the slot on
the door latch or by sliding a
lever (dependent on model).
The door can now only be
opened from outside.
18
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Door
Button
Lock
12520117.eps
12520119.eps
12510121.eps
12520120.eps
Page 37 of 80

• Signal "NG"; switched ground output signal provided to the GM. The signal is used for
two purposes,
1. As a momentary acknowledgment that the tilt sensor received STDWA and is cur-
rently monitoring the vehicle angle.
2. If the tilt sensor detects a change in the vehicle's angle when DWA is armed, signal
NG is switched to inform the GM to activate the siren.
When the tilt sensor receives the STDWA signal from the GM it memorizes the vehicle's
parked angle. The angle of the vehicle is monitored by the solid state electronics. Once
armed, if the angle changes, the tilt sensor provides a switched ground signal to the GM
to activate DWA.
As with the interior sensor, the tilt sensor is also switched OFF when the vehicle is locked
two times within ten seconds. The LED will flash one time for confirmation. This allows the
sensor to be switched OFF for transportation purposes.
Glass Breakage Sensors (Early E38 - before FIS Sensor): The door windows (includ-
ing the rear quarter glass wire loop) are monitored by inductive sensors mounted on the
inside of the door behind the trim panel. A closed window is recognized by a magnetic plate
on the glass lining up with the sensor.
If the glass is broken, the plate falls away and the signal from the sensor changes and the
GM will activate the alarm.
Alarm Siren: The alarm siren is mounted in the rear wheel well, behind the inner wheel
housing cover (early E38 used an alarm horn). The E53 alarm siren is located in the left side
of the engine compartment.
The siren contains electronic circuitry for producing the warn-
ing tone when the alarm is triggered. The siren also contains a
rechargeable battery that is used to power the siren when the
alarm is triggered.
The rechargeable battery will allow the siren to sound if it or the
vehicle’s battery is disconnected. The siren battery is
recharged, from the vehicle’s battery, when the alarm is not in
the armed state.
37
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
625200108.eps
Page 72 of 80
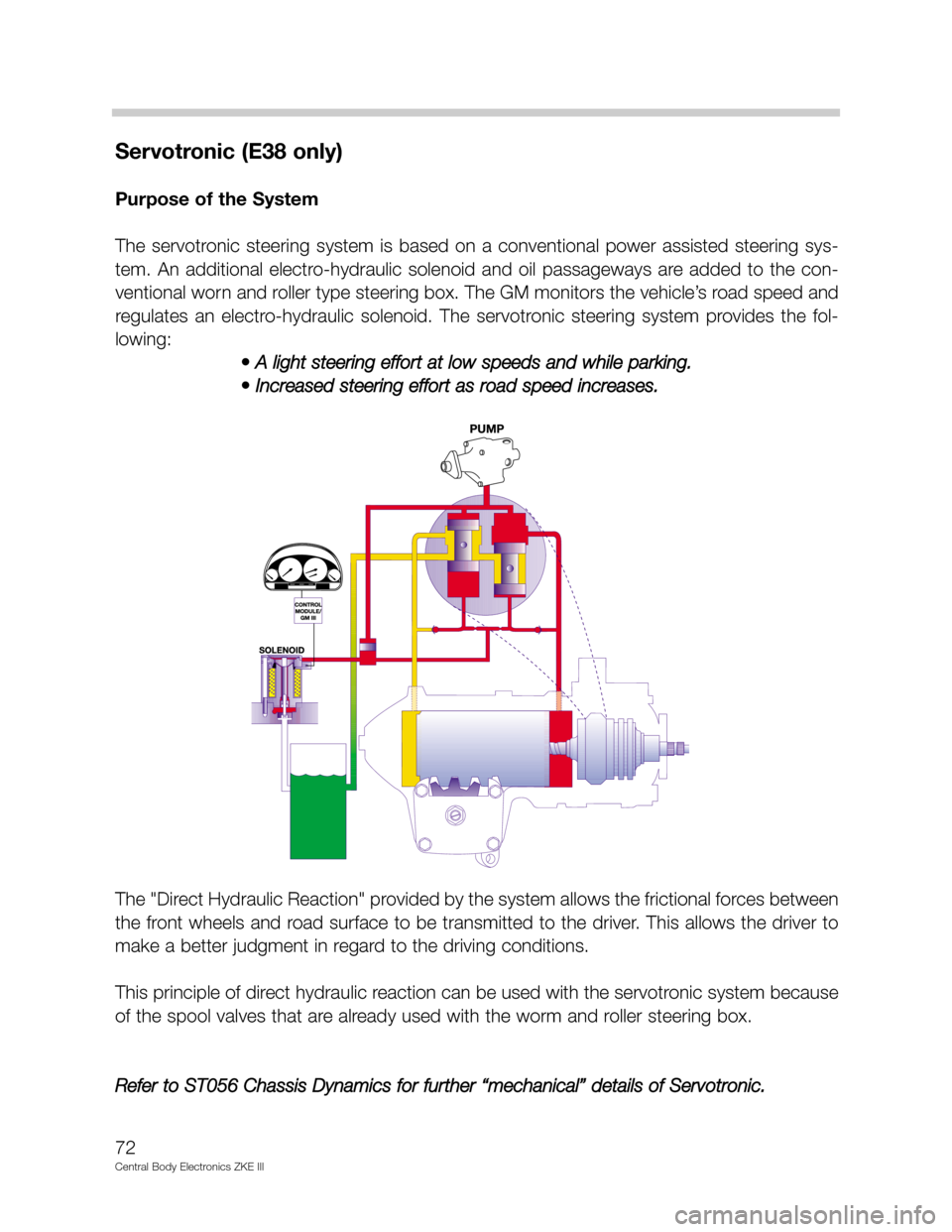
Servotronic (E38 only)
Purpose of the System
The servotronic steering system is based on a conventional power assisted steering sys-
tem. An additional electro-hydraulic solenoid and oil passageways are added to the con-
ventional worn and roller type steering box. The GM monitors the vehicle’s road speed and
regulates an electro-hydraulic solenoid. The servotronic steering system provides the fol-
lowing:
• A light steering effort at low speeds and while parking.
• Increased steering effort as road speed increases.
The "Direct Hydraulic Reaction" provided by the system allows the frictional forces between
the front wheels and road surface to be transmitted to the driver. This allows the driver to
make a better judgment in regard to the driving conditions.
This principle of direct hydraulic reaction can be used with the servotronic system because
of the spool valves that are already used with the worm and roller steering box.
Refer to ST056 Chassis Dynamics for further “mechanical” details of Servotronic.
72
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 80 of 80

9. What type of sensor is used to detect the position of a seat with Memory? What type
of signal does it produce?__________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
10. How does the Seat Module communicate a request for a stored memory position with
the mirror modules?_______________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
11. On an E38 with Servotronic, why is the speed signal provided to the GM from both
the IKE “A” signal and the K-Bus?___________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
12. An E38 customer complains that when exiting the vehicle the steering wheel moves
up. What is the cause of this?______________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
13. How does the SZM monitor the Seat Heating temperature?_____________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
14. What circuits are controlled by Consumer Cut Off? ____________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
15. If a technician double locked a 2000 MY E39 while still inside the vehicle, how could
he/she exit the vehicle?____________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
16. How is the MY 2000 key charged?__________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
17. How is the DWA Disarmed (emergency)?_____________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
18. What functions will deactivate the exterior door handle lighting? _________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
80
Central Body Electronics ZKE III