1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 2047 of 2438

OPERATION
The 41TE transaxle provides forward ratios of 2.84,
1.57, 1.00, and 0.69 with torque converter clutch
available in 2nd, direct, or overdrive gear; the Re-
verse ratio is 2.21. The shift lever is conventional
with six positions: P, R, N, OD, 3, and L. When OD
is selected the transaxle shifts normally through all
four speeds with torque converter clutch available in
overdrive; this position is recommended for most
driving. The 3 position is tailored for use in hilly or
mountainous driving. When 3 is selected, the trans-
mission uses only 1st, 2nd, and direct gears with
2nd-direct shift delayed to 40 mph or greater. When
operating in 3 or L positions torque converter clutch
application occurs in direct gear for improved trans-
mission cooling under heavy loads. If high engine
coolant temperature occurs, the torque converter
clutch will also engage in 2nd gear. The L position
provides maximum engine braking for descending
steep grades. Unlike most current transaxles, up-
shifts are provided to 2nd or direct gear at peak en-
gine speeds if the accelerator is depressed. This
provides engine over-speed protection and maximum
performance.
CLUTCH AND GEAR
The transaxle consists of:
² Three multiple disc input clutches
² Two multiple disc grounded clutches
² Four hydraulic accumulators
² Two planetary gear sets
This provides four forward ratios and a reverse ra-
tio. The clutch-apply pistons were designed with cen-
trifugally balanced oil cavities so that quick response
and good control can be achieved at any speed. A
push/pull piston is incorporated for two of the three
input clutches.
CAUTION: Some clutch packs appear similar, but
they are not the same. Do not interchange clutch
components as they might fail.
HYDRAULICS
The hydraulics of the transaxle provide the manual
shift lever select function, main line pressure regula-
tion, and torque converter and cooler flow control.
Oil flow to the friction elements is controlled directly
by four solenoid valves. The hydraulics also include a
unique logic-controlled ``solenoid torque converter
clutch control valve''. This valve locks out the 1st
gear reaction element with the application of 2nd, di-
rect, or overdrive gear elements. It also redirects the
1st gear solenoid output so that it can control torque
converter clutch operation. To regain access to 1st
gear, a special sequence of solenoid commands must
be used to unlock and move the solenoid torque con-
verter clutch control valve. This precludes any appli- cation of the 1st gear reaction element with other
elements applied. It also allows one solenoid to con-
trol two friction elements.
Small, high-rate accumulators are provided in each
controlled friction element circuit. These serve to ab-
sorb the pressure responses, and allow the controls to
read and respond to changes that are occurring.
SOLENOIDS
Since the solenoid valves perform virtually all con-
trol functions, these valves must be extremely dura-
ble and tolerant of normal dirt particles. For that
reason hardened-steel poppet and ball valves are
used. These are free from any close operating clear-
ances, and the solenoids operate the valves directly
without any intermediate element. Direct operation
means that these units must have very high output
so that they can close against the sizeable flow areas
and high line pressures. Fast response is also re-
quired to meet the control requirements. Two of the solenoids are normally-venting and two
are normally-applying; this was done to provide a de-
fault mode of operation. With no electrical power, the
transmission provides 2nd gear in OD, 3,orLshift
lever positions. All other transmission lever positions
will operate normally. The choice of 2nd gear was
made to provide adequate breakaway performance
while still accommodating highway speeds.
SENSORS
There are three pressure switches to identify sole-
noid application and two speed sensors to read input
(torque converter turbine) and output (parking sprag)
speeds. There is also a position switch to indicate the
manual shift lever position. The pressure switches
are incorporated in an assembly with the solenoids.
Engine speed, throttle position, temperature, etc., are
also observed. Some of these signals are read directly
from the engine control sensors; others are read from
a multiplex circuit with the powertrain control mod-
ule.
ELECTRONICS
The 41TE transmission control module is located
underhood in a potted, die-cast aluminum housing
with a sealed, 60-way connector.
ELECTRONIC MODULATED CONVERTER CLUTCH (EMCC)
The EMCC enables the torque converter clutch to
partially engage between 23 to 47 MPH before full
engagement at about 50 MPH and beyond. This fea-
ture is on all vehicles equipped with the 41TE tran-
saxle.
ADAPTIVE CONTROLS
These controls function by reading the input and
output speeds over 140 times a second and respond-
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 87
Page 2048 of 2438

ing to each new reading. This provides the precise
and sophisticated friction element control needed to
make smooth clutch-to-clutch shifts for all gear
changes. The use of overrunning clutches or other
shift quality aids are not required. As with most au-
tomatic transaxles, all shifts involve releasing one el-
ement and applying a different element. In simplified
terms, the upshift logic allows the releasing element
to slip back wards slightly to ensure that it does not
have excess capacity; the apply element is filled until
it begins to make the speed change to the higher
gear; its apply pressure is then controlled to main-
tain the desired rate of speed change until the shift
is complete. The key to providing excellent shift
quality is precision; for example, as mentioned, the
release element for upshifts is allowed to slip back-
wards slightly; the amount of that slip is typically
less than a total of 20 degrees. To achieve that pre-
cision, the transmission control module learns the
characteristics of the particular transaxle that it is
controlling. It learns the release rate of the releasing
element and the apply time of the applying element.
It also learns the rate at which the apply element
builds pressure sufficient to begin making the speed
change. This method achieves more precision than
would be possible with exacting tolerances. It can
also adapt to any changes that occur with age or en-
vironment, for example, altitude, temperature, en-
gine output, etc. For kickdown shifts, the control logic allows the re-
leasing element to slip and then controls the rate at
which the input (and engine) accelerate; when the
lower gear speed is achieved, the releasing element
reapplies to maintain that speed until the apply ele-
ment is filled. This provides quick response since the
engine begins to accelerate immediately and a
smooth torque exchange since the release element
can control the rate of torque increase. This control
can make any powertrain feel more responsive with-
out in creasing harshness. Adaptive controls respond to input speed changes. They compensate for changes in engine or friction el-
ement torque and provide good, consistent shift qual-
ity for the life of the transaxle.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
These controls provide comprehensive, on-board
transaxle diagnostics. The information available can
aid in transaxle diagnosis. For example, apply ele-
ment buildup rate indicates solenoid performance.
Also included are self diagnostic functions. Self diag-
nostics allow the technician to test the condition of
the electronic controls. The transmission control
module continuously monitors its critical functions.
It also records any malfunctions, and the number of
engine starts since the last malfunction. This allows
the technician to use the information in the event of
a customer complaint.
41TE TRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a 41TE
four speed automatic transaxle, check for diagnos-
tic trouble codes with the DRB II scan tool. Always
use the Powertrain Diagnostic Test Procedure Man-
ual.
Transaxle malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
² Poor engine performance
² Improper adjustments
² Hydraulic malfunctions
² Mechanical malfunctions
² Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid
level and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then
perform a road test to determine if the problem has
been corrected or that more diagnosis is necessary. If
the problem exists after the preliminary tests and
corrections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
21 - 88 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 2055 of 2438

(5) This test checks pump output, pressure regula-
tion and condition of the low/reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit and shift schedule.
TEST TWO-SELECTOR IN DRIVE 2ND GEAR
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the 3position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle
speed of 30 mph. (4) Underdrive clutch pressure should read 110 to
145 psi. (5) This test checks the underdrive clutch hydrau-
lic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
TEST THREE-OVERDRIVE CLUTCH CHECK
(1) Attach gauge to the overdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the circle Dposition.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle
speed of 20 mph. (4) Overdrive clutch pressure should read 74 to 95
psi. (5) Move selector lever to the 3position and in-
crease indicated vehicle speed to 30 mph. (6) The vehicle should be in second gear and over-
drive clutch pressure should be less than 5 psi. (7) This test checks the overdrive clutch hydraulic
circuit as well as the shift schedule.
TEST FOUR-SELECTOR IN CIRCLE DRIVE, OVERDRIVE GEAR
(1) Attach gauge to the 2/4 clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the circle Dposition.
(3) Allow vehicle front wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle
speed of 30 mph. (4) The 2/4 clutch pressure should read 75 to 95
psi. (5) This test checks the 2/4 clutch hydraulic circuit.
TEST FIVE-SELECTOR IN CIRCLE DRIVE,
OVERDRIVE
(1) Attach gauge to the torque converter clutch off
pressure tap. (2) Move selector lever to the circle Dposition.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 50 mph.
CAUTION: Both wheels must turn at the same speed. (4) Torque converter clutch off pressure should be
less than 5 psi. (5) This test checks the torque converter clutch
hydraulic circuit.
TEST SIX-SELECTOR IN REVERSE
(1) Attach gauge to the reverse clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the reverse position.
(3) Read reverse clutch pressure with output sta-
tionary (foot on brake) and throttle opened to achieve
1500 rpm. (4) Reverse clutch pressure should read 165 to 235
psi. (5) This test checks the reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit.
TEST RESULT INDICATIONS
(1) If proper line pressure is found in any one test,
the pump and pressure regulator are working properly. (2) Low pressure in all positions indicates a defec-
tive pump, a clogged filter, or a stuck pressure regula-
tor valve. (3) Clutch circuit leaks are indicated if pressures do
not fall within the specified pressure range. (4) If the overdrive clutch pressure is greater than 5
psi in step (6) of Test Three, a worn reaction shaft seal
ring is indicated.
CLUTCH AIR PRESSURE TESTS
Inoperative clutches can be located using a series of
tests by substituting air pressure for fluid pressure
(Figs. 2 and 3). The clutches may be tested by applying
air pressure to their respective passages after the valve
body has been removed and Tool 6056 has been in-
stalled. To make air pressure tests, proceed as follows: The compressed air supply must be free of all
dirt and moisture. Use a pressure of 30 psi. Remove oil pan and valve body. See Valve body
removal.
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the overdrive clutch apply
passage and watch for the push/pull piston to move
Fig. 1 Pressure Taps
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 95
Page 2105 of 2438

41TE ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS INDEX
page page
CCD Bus .............................. 145
Diagnostic Trouble Code Charts ............ 146
Diagnostic Trouble Codes ................. 145
DRB II Scan Tool ....................... 146 General Information
...................... 145
Limp-In Mode .......................... 145
On-Board Diagnostics Information ........... 145
GENERAL INFORMATION
The information in this manual is designed to help
the technician understand and repair the transaxle
with the aid of the built in on-board diagnostics. Chrysler Corporation has developed a com-
plete set of diagnostic manuals which cover the
diagnosis of the 41TE transaxle. They have been
designed to make transaxle diagnosis accurate
and simple. Use these manuals with the DRB II
scan tool and the latest cartridge, when diagnos-
ing transaxle problems.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS INFORMATION
The 41TE transaxle is controlled and monitored by
the transmission control module. The transmission
control module monitors critical input and output
circuits within the transaxle. Some circuits are tested continuously; others are
checked only under certain conditions. Each circuit
monitored by the transmission control module has a
corresponding fault message assigned to it that can be
read with the DRB II scan tool. If the on-board diagnostic system senses that one of
the circuits is malfunctioning, the corresponding code
is stored in memory. If the malfunction goes away after
the code is stored, the transmission control module will
erase the code after 75 key cycles.
CCD BUS
In order to diagnose the 41TE transaxle, diagnostic
trouble codes in the transmission control module's
memory should be read. Use the Diagnostic Readout
Box (DRB II) scan tool to read codes. If more than one
diagnostic trouble code exists, diagnostic priority
should be given to the most recent code. With CCD bus
bias and communication problems, the DRB II scan
tool displays an appropriate message. Diagnostic
trouble codes might not be accessible until the bus
problem is fixed. The following is a list of probable
causes for a bus problem:
² Open or short to ground/battery in either or both
CCD bus wires (pins 4 and 43).
² Open or short to ground/battery in either or both
41TE transaxle's bias wires (pin 5 and 44) on vehicles
requiring the transaxle to bias the bus.
² Open or short to ground/battery in the diagnostic
connector bus wire. ²
Internal failure of any module connected to the bus.
The CCD bus should have 2.5 volts (+2.5 volts on
CCD+ and -2.5 volts on CCD-). The bus error message displayed by the DRB II scan
tool should be helpful in diagnosing the CCD bus. For more information on diagnosing CCD bus prob-
lems, refer to the 1993 Diagnostic Procedures Manual
(non-communication with the CCD bus). All other
problems refer to the 1993 Body Vehicle Communica-
tions Diagnostic Procedures Manual.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Diagnostic Trouble Codes are two-digit numbers that
identify which circuit is malfunctioning. A code can be
set for hydraulic and mechanical reasons as well as for
electrical problems. In most cases, codes do not pin-
point which specific component is defective. Diagnostic trouble codes can only be read with
the use of the DRB II scan tool or equivalent.
HARD FAULTS
Any Diagnostic trouble code that comes back within
3 engine starts (reset count 3 or less) is a ``Hard Fault''.
This means that the defect is there every time the
transmission control module checks that circuit.
SOFT FAULTS
A ``Soft Fault'' is one that occurs intermittently. It is
not there every time the transmission control module
checks the circuit. Most soft faults are caused by wiring
or connector problems. Intermittent defects must be
looked for under the specific conditions that caused
them.
LIMP-IN MODE
The transmission control module continuously
checks for electrical and internal transaxle problems.
When a problem is sensed, the transmission control
module stores a diagnostic trouble code. All but twelve
of these codes cause the transaxle to go into the
``Limp-in mode''. While in this mode, electrical power is
taken away from the transaxle. When this happens,
the only transaxle ranges that will function are:
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 145
Page 2375 of 2438
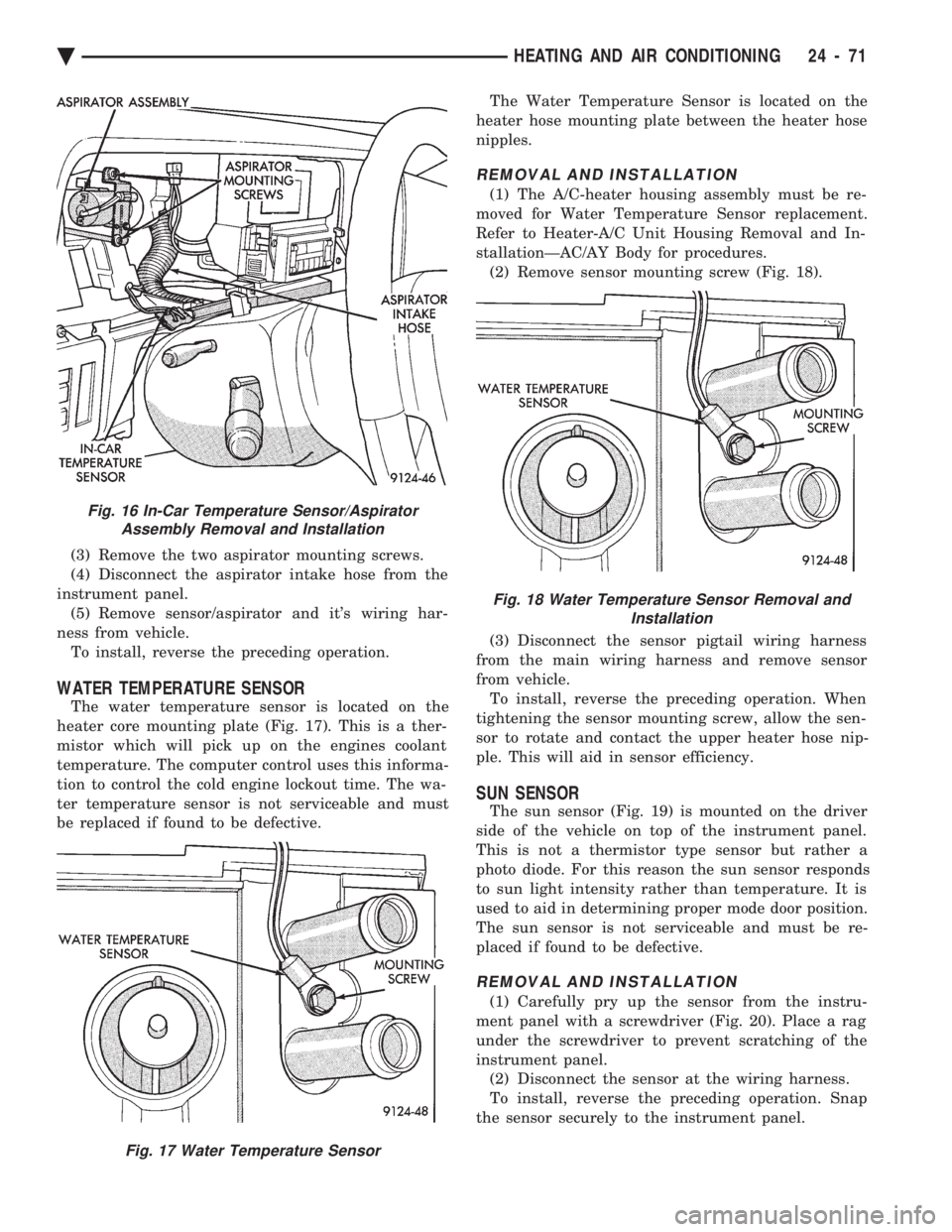
(3) Remove the two aspirator mounting screws.
(4) Disconnect the aspirator intake hose from the
instrument panel. (5) Remove sensor/aspirator and it's wiring har-
ness from vehicle. To install, reverse the preceding operation.
WATER TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The water temperature sensor is located on the
heater core mounting plate (Fig. 17). This is a ther-
mistor which will pick up on the engines coolant
temperature. The computer control uses this informa-
tion to control the cold engine lockout time. The wa-
ter temperature sensor is not serviceable and must
be replaced if found to be defective. The Water Temperature Sensor is located on the
heater hose mounting plate between the heater hose
nipples.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
(1) The A/C-heater housing assembly must be re-
moved for Water Temperature Sensor replacement.
Refer to Heater-A/C Unit Housing Removal and In-
stallationÐAC/AY Body for procedures. (2) Remove sensor mounting screw (Fig. 18).
(3) Disconnect the sensor pigtail wiring harness
from the main wiring harness and remove sensor
from vehicle. To install, reverse the preceding operation. When
tightening the sensor mounting screw, allow the sen-
sor to rotate and contact the upper heater hose nip-
ple. This will aid in sensor efficiency.
SUN SENSOR
The sun sensor (Fig. 19) is mounted on the driver
side of the vehicle on top of the instrument panel.
This is not a thermistor type sensor but rather a
photo diode. For this reason the sun sensor responds
to sun light intensity rather than temperature. It is
used to aid in determining proper mode door position.
The sun sensor is not serviceable and must be re-
placed if found to be defective.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
(1) Carefully pry up the sensor from the instru-
ment panel with a screwdriver (Fig. 20). Place a rag
under the screwdriver to prevent scratching of the
instrument panel. (2) Disconnect the sensor at the wiring harness.
To install, reverse the preceding operation. Snap
the sensor securely to the instrument panel.
Fig. 16 In-Car Temperature Sensor/Aspirator Assembly Removal and Installation
Fig. 17 Water Temperature Sensor
Fig. 18 Water Temperature Sensor Removal and Installation
Ä HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 71
Page 2421 of 2438

TORQUE REFERENCES
Individual Torque Charts appear at the end of many
Groups. Refer to the Standard Torque Specifications
and Bolt Identification Chart in this Group for torques
not listed in the individual torque charts (Fig. 4).
Torque specifications on the Bolt Torque chart are
based on the use of clean and dry threads. Reduce the
torque by 10% when the threads are lubricated with
engine oil and by 20% if new plated bolts are used. Various sizes of Torx head fasteners are used to
secure numerous components to assemblies. Due
to ever changing usage of fasteners, Torx head
fasteners may not be identified in art or text .
METRIC THREAD AND GRADE IDENTIFICATION
Metric and SAE thread notations differ slightly. The
difference is illustrated in Figure 5. Common metric fastener strength classes are 9.8
and 12.9 with the class identification embossed on
the head of each bolt (Fig. 6). Some metric nuts will
be marked with a single digit strength number on
the nut face.
SAE strength classes range from grade 2 to 8 with
line identification embossed on each bolt head. Mark-
ings corresponding to two lines less than the actual
grade (Fig. 7). For Example: Grade 7 bolt will exhibit
5 embossed lines on the bolt head.
METRIC SYSTEM
Figure art, specifications, and tightening references
in this Service Manual are identified in the metric
system and in the SAE system. During any maintenance or repair procedures, it is
important to salvage metric fasteners (nuts, bolts,
etc.) for reassembly. If the fastener is not salvage-
able, a fastener of equivalent specification should be
used.
Fig. 6 Metric Bolt Identification
Fig. 7 SAE Bolt Identification
Fig. 4 Grade 5 and 8 Standard Torque Specifica- tions
Fig. 5 Thread Notation (Metric and SAE)
6 INTRODUCTION Ä