Page 383 of 4087
7. REMOVE 4 SOLENOID VALVES
(a) Remove the No. 1 and No.2 solenoid valves.
(b) Remove the O±rings from the No. 1 and No.2 solenoidvalves.
(c) Remove the lock plate and No.3 and No.4 solenoid valves.
8. REMOVE THROTTLE CABLE Disconnect the throttle cable from the cam.
9. REMOVE VALVE BODY
(a) Remove the 20 bolts.
(b) Remove the valve body.
NOTICE: Do not drop the check ball body and spring.
10. INSPECT VALVE BODY Refer to `94 A340E and A341E Automatic Transmission Re-
pair Manual (for LEXUS SC400)
AT±20
±
A304E (1UZ±FE) AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 384 of 4087
VALVE BODY INSTALLATION
AT0GH±02
1. INSTALL 4 SOLENOID VALVES
2. INSTALL CHECK BALL BODY AND SPRING AND HOLDIT
3. INSTALL VALVE BODY
(a) Align the groove of the manual valve to the pin of the lever.
(b) Install the 20 bolts and clamp.
Torque: 10 N Vm (100 kgf Vcm, 7 ft Vlbf)
(c) Connect the throttle cable to the cam.
±
A304E (1UZ±FE) AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION VALVE BODYAT±21
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 395 of 4087

HOW TO PROCEED WITH TROUBLESHOOTING
AT09N±0D
1. CUSTOMER PROBLEM ANALYSISUsing the customer problem analysis check sheet for reference, ask the c\
ustomer in as much detail as
possible about the problem.
2. CHECK AND CLEAR THE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (PRECHECK) Before confirming the problem symptom, first check if there are any diagnostic\
trouble malfunction codes
stored in memory. When there are malfunction codes, make a note of them, then clear them\
and proceed
to ª3. Problem Symptom Confirmationº.
3. PROBLEM SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION Confirm the problem symptoms.
4. SYMPTOM SIMULATION If the problem does not reappear, be sure to simulate the problem by mainly checking the circuits indica\
ted
by the diagnostic trouble code in step 2., using ªProblem Simulation me\
thodº.
5. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHECK Check the diagnostic trouble codes. Check if there is abnormality in the\
sensors or the wire harness.
If a malfunction code is output, proceed to ª6. Diagnostic Trouble Code Chartº.
If the normal code is output, proceed to ª11. Matrix Chart of Problem Symptomsº.
Be sure to proceed to ª6. Diagnostic Trouble Code Chartº after the steps 2. and 3. are completed.
If troubleshooting is attempted only by following the malfunction code sto\
red in the memory is output, errors
could be made in the diagnosis.
6. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART If a malfunction code is confirmed in the diagnostic trouble code check, p\
roceed to the inspection proce-
dure indicated by the matrix chart for each diagnostic trouble code.
7. PRELIMINARY CHECK Carry out a preliminary check of the transmission oil level, throttle ca\
ble adjustment, etc.
8. SHIFT POSITION SIGNAL CHECK
Carry out the shift position signal check when the transmission gears do\
not up±shift, down±shift or lock±
up. This is to check the output condition from the ECM to each solenoid. If the r\
esults are NG, then it is
likely that the trouble is in the electrical system (particularly in th\
e sensors or the ECM).
Proceed to Part 1 (Electrical System) under ª11. Matrix Chart of Problem Symptomsº. If all the circuits speci-
fied in Part 1 are OK, check the ECM and replace it.
9. MECHANICAL SYSTEM TEST (Stall Test, Time Lag Test, Line Pressure Test, Accumulator Back Pressure Test)
If the malfunction is found in the stall test, time lag test, line press\
ure test or accumulator back pressure
test, check the parts indicated in the respective tests. If the problem is th\
at ªshift shock is largeº, perform
the accumulator back pressure test.
10. MANUAL SHIFTING TEST If the results of the manual driving test are NG, it is likely that the trouble is in the mechanical system or
hydraulic system. Proceed to Part 2 (Mechanical System) under the Matrix Chart \
of Problem Symptoms.
AT±32
±
A304E (1UZ±FE) AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION TROUBLESHOOTING
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 396 of 4087

11. MATRIX CHART OF PROBLEM SYMPTOMSIf the normal code is confirmed in the diagnostic trouble code check, perform inspection according to the
inspection order in the matrix chart of problem symptoms. Perform diagno\
sis of each circuit or part in the
order shown in the Matrix Chart. The Matrix Chart contains 3 chapters, Electronically Controlled Circuits
in Chapter 1, On±vehicle Inspection in Chapter 2 and Off±vehicle Inspection in Chapter 3. If all the circuits
indicated in Chapter 1 are normal, proceed to Chapter 2. If all the parts indicated i\
n Chapter 2 are normal,
proceed to Chapter 3. If all the circuits and parts in Chapter 1±Chapter 3 are normal and the trouble still
occurs, check and replace the ECM.
12. CIRCUIT INSPECTION Perform diagnosis of each circuit in accordance with the inspection order confirmed in 6. and 11. Judge
whether the cause of the problem is in the sensor, actuators, wire harness and connectors, or the ECM.
In some cases, the Flow Chart instructs that a throttle signal check, brak\
e signal check or kick down signal
check (in test mode) be performed. These are diagnosis functions used \
to check if signals are being input
correctly to the ECM.
13. PARTS INSPECTION Check the individual parts of the mechanical system and hydraulic system in t\
he order of the numbers indi-
cated in the Matrix Chart.
14. REPAIRS After the cause of the problem is located, perform repairs by following the i\
nspection and replacement pro-
cedures in this manual or '94 A340E and A341E Automatic Transmission Repair Manual (for LEXUS
SC400).
15. CONFIRMATION TEST
After completing repairs, confirm not only that the malfunction is eliminated\
, but also conduct a test drive,
etc., to make sure the entire electronically controlled transmission system i\
s operating correctly.
±
A304E (1UZ±FE) AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION TROUBLESHOOTINGAT±33
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1153 of 4087
ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL
For convenience, the following abbreviations are used in this
manual.
ABS Antilock Brake System
assy assembly
ECT Electronic Controlled Transmission
ECU Electronic Control Unit
e.g. Exempi Gratia (For Example)
Ex. Except
in. inch
LH Left-hand
MIG Metal Inert Gas
M/Y Model Year
PPS Progressive Power Steering
RH Right-hand
w/ with
w/o without
INTRODUCTIONIN-16
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3826 of 4087
15
ABBREVIATIONS
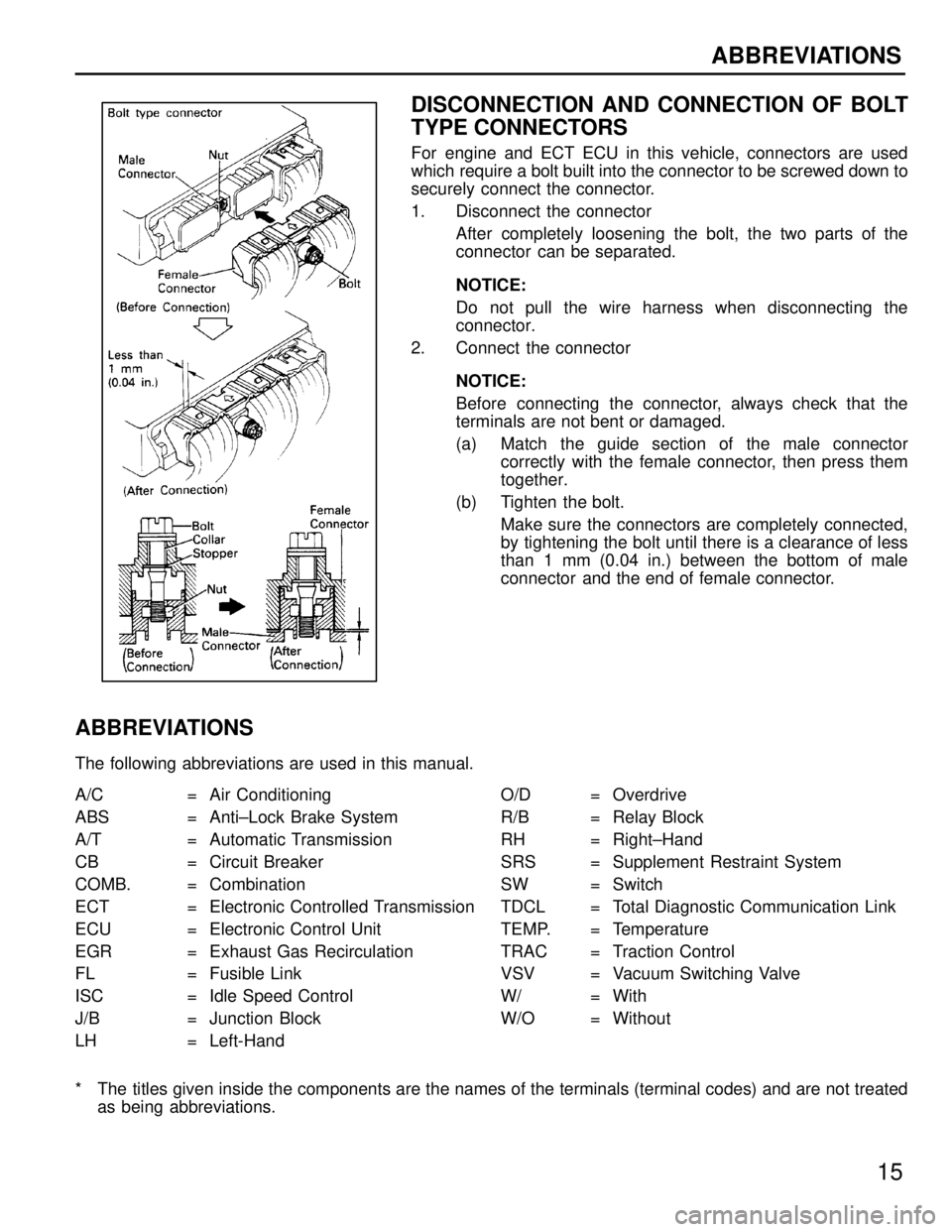
DISCONNECTION AND CONNECTION OF BOLT
TYPE CONNECTORS
For engine and ECT ECU in this vehicle, connectors are used
which require a bolt built into the connector to be screwed down to
securely connect the connector.
1. Disconnect the connectorAfter completely loosening the bolt, the two parts of the
connector can be separated.
NOTICE:
Do not pull the wire harness when disconnecting the
connector.
2. Connect the connector
NOTICE:
Before connecting the connector, always check that the
terminals are not bent or damaged.
(a) Match the guide section of the male connectorcorrectly with the female connector, then press them
together.
(b) Tighten the bolt. Make sure the connectors are completely connected,
by tightening the bolt until there is a clearance of less
than 1 mm (0.04 in.) between the bottom of male
connector and the end of female connector.
ABBREVIATIONS
The following abbreviations are used in this manual.
A/C = Air Conditioning O/D = Overdrive
ABS = Anti±Lock Brake System R/B = Relay Block
A/T = Automatic Transmission RH = Right±Hand
CB = Circuit Breaker SRS = Supplement Restraint System
COMB. = Combination SW = Switch
ECT = Electronic Controlled Transmission TDCL = Total Diagnostic Communication Link
ECU = Electronic Control Unit TEMP. = Temperature
EGR = Exhaust Gas Recirculation TRAC = Traction Control
FL = Fusible Link VSV = Vacuum Switching Valve
ISC = Idle Speed Control W/ = With
J/B = Junction Block W/O = Without
LH = Left-Hand
* The titles given inside the components are the names of the terminals (ter\
minal codes) and are not treatedas being abbreviations.
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 4081 of 4087
15
ABBREVIATIONS
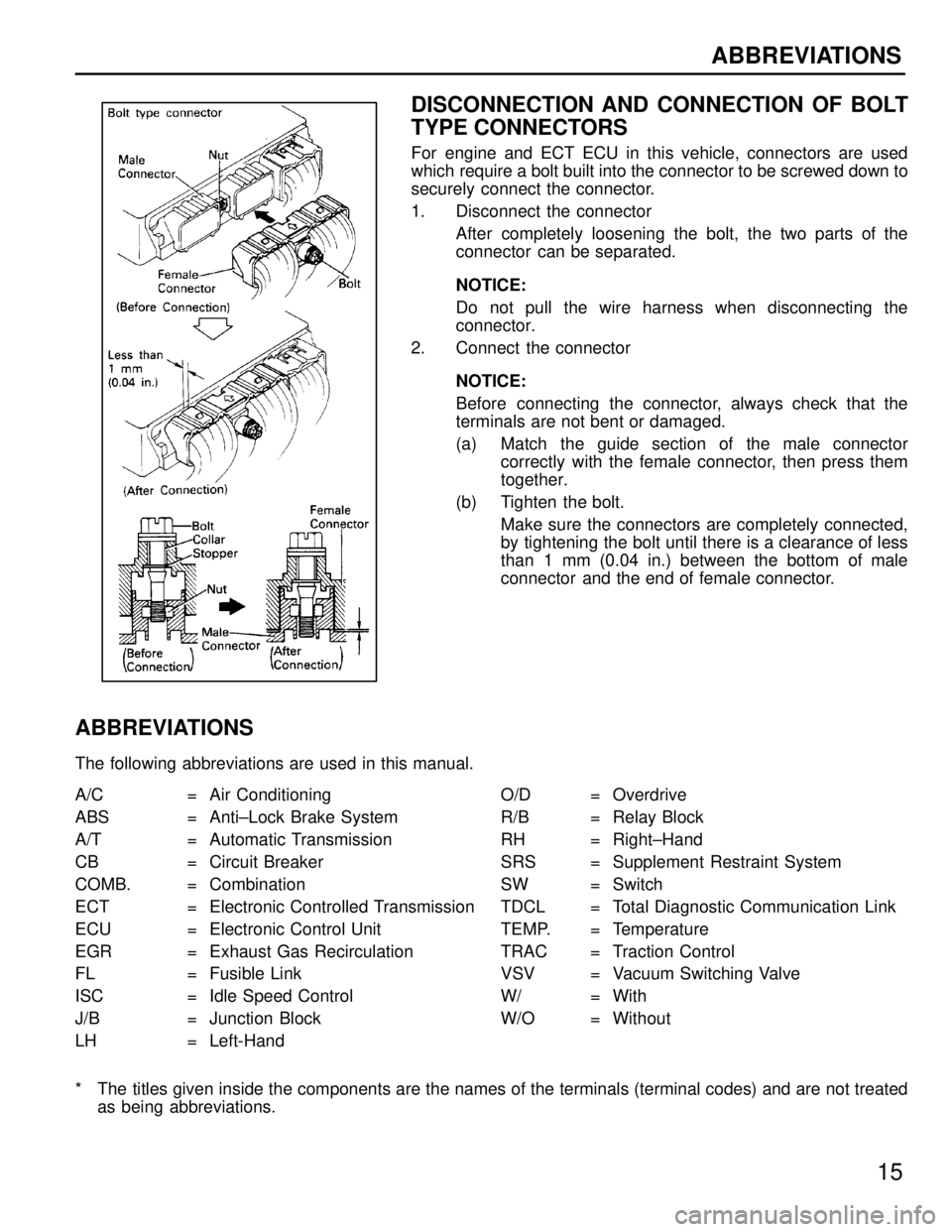
DISCONNECTION AND CONNECTION OF BOLT
TYPE CONNECTORS
For engine and ECT ECU in this vehicle, connectors are used
which require a bolt built into the connector to be screwed down to
securely connect the connector.
1. Disconnect the connectorAfter completely loosening the bolt, the two parts of the
connector can be separated.
NOTICE:
Do not pull the wire harness when disconnecting the
connector.
2. Connect the connector
NOTICE:
Before connecting the connector, always check that the
terminals are not bent or damaged.
(a) Match the guide section of the male connectorcorrectly with the female connector, then press them
together.
(b) Tighten the bolt. Make sure the connectors are completely connected,
by tightening the bolt until there is a clearance of less
than 1 mm (0.04 in.) between the bottom of male
connector and the end of female connector.
ABBREVIATIONS
The following abbreviations are used in this manual.
A/C = Air Conditioning O/D = Overdrive
ABS = Anti±Lock Brake System R/B = Relay Block
A/T = Automatic Transmission RH = Right±Hand
CB = Circuit Breaker SRS = Supplement Restraint System
COMB. = Combination SW = Switch
ECT = Electronic Controlled Transmission TDCL = Total Diagnostic Communication Link
ECU = Electronic Control Unit TEMP. = Temperature
EGR = Exhaust Gas Recirculation TRAC = Traction Control
FL = Fusible Link VSV = Vacuum Switching Valve
ISC = Idle Speed Control W/ = With
J/B = Junction Block W/O = Without
LH = Left-Hand
* The titles given inside the components are the names of the terminals (ter\
minal codes) and are not treatedas being abbreviations.
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName