1990 MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE crank
[x] Cancel search: crankPage 161 of 391

FUEL SYSTEM -Idle Speed Control14-49
Servo ControlServo control includes feedback control and position
ontrol. In feedback control, the engine control uniti;onstantly calculates the actual idle speed, and if
the
value differs from the target idle speed, the unit
drives the stepper motor to adjust actual speed to
Feedback ControlWhile the engine runs at idle speed, the stepper
motor is activated to keep the engine speed at the
preset target idle speed by controlling the bypass air
volume.
The target idle speed that is optimum for each
operating condition (including air conditioner switch
ON/OFF) has been preset. This engine speed
feedback control is provided under stabilized idling
conditions and not when any of the following
conditions occur.
l When the vehicle is moving at 2.5 km/h (1.6
mph) or more.the target value. In position control, the idle speed
control
is adjusted to the target position to cope
with air conditioner and other load changes. Position
control is also performed when cranking the engine
and decelerating.
lWhen the idle switch is turned from OFF to ON,
and while the idle switch is in the OFF position.
lWhen the air conditioner switch is turned from
ON to OFF, or vice versa.
l When power steering oil pressure switch is
turned from ON to OFF, or vice versa.
l When the ignition switch is turned from ST to
IG, or vice versa.
l While the dash pot control is in operation.
lWhen the inhibitor switch is switched from “N”
range to “D” range or vice versa.
If-1Air conditioner switch
Idle speed
control servo
r------ -- -‘,
(N range)4* I-I
BI
8
IL -L
- !5ysr motor 1I
zIdle upIStepper motor 7Engine
PII2. I.1Coolant temperature
tL.---m--v--JJ
Engine speed
I6Fuo6oo
Servo Drive Steps
(1) If there is a difference between the target and actual idle
speeds, the servo is activated the number of angular steps
corresponding to the difference, thereby extending or
.retracting the pintle to control the amount of bypass air, and
adjusts the actual idle speed to the target value.
Difference between the target
and actual idle speed fpm6FUO699I
Time sec.
c
6FUO76!The sewo drive steps during idle speed feedback Control
van/ as shown at the left.
Page 162 of 391

14-50FUEL SYSTEM- Idle Speed Control
SDeed adiustina screwI -Throttle valve
Lw-3O(-22) 0132) 30(86! 601140) 9ofl94)Coolant temperature
“C (OF)6FUO641
E94
72--2--I
Q--.-.-z
3201.000 --4-\-\
5P9.o%IIIaI L-2O(-41 Of3214Of104)801176)Coolant temperature
“C VF)6FU028E
-201-4) Of3214OI104180(176(2) When the engine coolant temperature is low, the fast idle
air valve together with the idle speed control
servoperated to supply an adequate volume of bypass
,.raccording to the engine coolant temperature.
Feedback Control at
Idle(1) Basic target idle speed
The basic target idle’ speed is preset as a map value
optimized according to the engine coolant temperature.
This speed is maintained to ensure stabilized idle speed.
(2) Idle speed while the air conditioner is being operated
When the engine coolant temperature is high with the air
conditioner switch in the ON position, the idle speed is set
higher than the basic idle speed.
,
ICoolant temperature “C VF)6FUO28:Position Control
When the steering wheel is turned or the air
conditioner switch is operated while idling, theachieve the target position, thus controlling the
engine load changes and consequently the idlebypass air volume and suppressing engine speed
changes. The engine control unit also activates the
speed changes sharply. Therefore, immediately
after detection of such a load signal, the engine
control unit activates the idle speed control servo toidle speed control servo to achieve the optimum
target position while cranking, driving and decelerat-
ing, according to the operating conditions.
Power steering oil
pressure switchIInhibitor
switch
IDash pot
concjition“D”
xl
rangeposition-
UP W-U
IAlPower
steeringposition-
UP.4~i~hnditioner
IIdle speed
control servor”--““IiiI
I
c
IEngine
I
I
1wuosu
-
Page 164 of 391

--
14-52FUEL SYSTEM - Idle Speed Control
4
Start of deceleration
DLhq ON
position
I*2 to 6
Time sec.6FUO295
II)
0(32180(176)Temperature “C 1°F)6FUO29t
CONTROL WHEN THE ENGINE SPEED IS UNUSUALLY LOWThe followi
gcontrols are provided when the engine speecfalls below
i5;D rpm after the engine has been fully warmed-up
[with engine coolant temperature more than
55°C (131”F)].
(1) During feedback control
The idle speed control servo is activated immediately by a
particular number of angular steps which represent the
feedback correction.
(2) During servo position control
The idle speed control servo is activated to conform to
aposition corresponding to an increased number of steps
(46
steps).DASH POT CONTROL
Control is provided to dampen the extending motion of the
pintle from a certain opening degree, thereby absorbing
deceleration shocks.
(1) Control while cruising
While cruising or racing, the idle speed control servo is
activated to further open the bypass air path corresponding
to the dash pot position which is more open than the idle
position.The idle speed control servo is activated in this way when
the following conditions are met.
l Engine speed 500 rpm or higher
l Idle position switch in the OFF position
The dash pot position is dependent on the throttle valve
opening map value.,
(2) Control during deceleration
When the vehicle is decelerated from a cruising or racing
speed, the idle speed control servo is activated to close the
bypass air path gradually from the dash pot position so that
the intake air volume is not abruptly reduced, thereby
dampening deceleration shocks.
The idle speed control servo is activated when either one of
the following conditions are met.
lWhen the throttle position sensor output voltage drops
l When the idle switch is turned on.
CONTROL WHEN STARTING
While the engine is being cranked, the idle speed control servo
is controlled to provide optimum bypass air volume for starting.
Immediately after the ignition switch is turned on, idle speed
servo position control is provided to achieve the optimum
_
position.
Page 166 of 391

FUEL SYSTEM- Power Supply Control
Battery
L11The engine control unit controls the power
suv ’tcthe sensors, engine control unit and
actuate,A;the control relay.
-P
.
-p.Ignition switch
Inn yr
To air flow sensor,crank angle sensor,idle speed controlsetvo. injectors
Control relay
Relay controlFuel pump
controlIgnitionswitch signal
Enginecontrol
unit
I6FUOl’
Power Supply ControlWhen the ignition switch on signal is input, the
engine control unit energizes the control relay coil
L3to turn on the
S2 switch, thus supplying power to the
injectors, air flow sensor, idle speed control servo,
Fuel Pump ControlWhen cranking the’engine (ignition switch at the ST
position), the engine control unit energizes the
Lcoil to turn on the
S switch, thus activating the fuel
pump.While operating the engine (ignition switch at the
IGposition), the crank angle sensor signal is input to
the engine control unit, which energizes the
L,
etc.Approximately seven seconds after input of
theignition switch off signal, the unit turns off the
Sswitch.
control relay coil to keep the
SI switch on, thus
continuing to activate the fuel pump.
When the crank angle sensor signal fails to be
inputfor 0.6 second or longer due to engine stalling,
.,the engine control unit immediately turns
thz. 5switch off to stop the fuel pump as a safet)
precaution.
Page 169 of 391

FUEL SYSTEMAir Flow Sensor (AFSI Filter Reset Control
AIR FLOW SENSOR (AFS) FILTER RESET CONTROL
I1Air flow sensor
Crank-angle sensorIdle position switch
Throttle position sensor
4Air flow sensor
//\\ -
\Reset terminal
RllruAs
6FlJo664I11When the idle switch is ON, or when the throttleWhen these Signals are input. the air flow sensor
position sensor output voltage is low, the engineresets the modulator. There is a switch to the circuit
control unit functions to switch ON the powerthat lessens turbo noise. This eliminates any error in
transistor, and, as a result, air flow sensor resetmeasuring the
.amount of intake air when there is a
signals are sent to the air flow sensor.change from high speed, high load driving to
deceleration.
TURBO METER CONTROL
Air flow sensor
(AFSI ’
Crank angle sensorEngine control unit
BT
Rl4QAAATurbo meterControl relay
The turbo meter is a current type meter. The engine
control unit receives the intake air volume signal
from the air flow sensor and the rpm
signal from the
crank angle sensor and calculates the engine load.Then, the unit determines the duty ratio according
to the load and drives the turbo meter.
Intake air volume
Duty ratio
it Load 0:rwDuty ratio
The duty ratio is defined as ON time ratio
TJT, of 33.3 Hz pulse.
When the duty ratio increases, average current that flows to
the turbo meter also increases
so that the turbo meter
indicates higher value.
When the duty ratio is decreased, the turbo meter indicates
smaller value.
cI30
msec. 30 msec.1621cm:
Page 246 of 391

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Torque Converter
TORQUE CONVERTER
Lock
ring
I
Damper
F
clutch-
B-.Turbine
.AA
/:ront cover
h,Impeller
AStartorWhen damper clutch is
I\When damper
aInput shaftactivated
clutch isactivated
175202The torque-converter is composed of the impeller
(rear cover), turbine,
stator, damper clutch, one-way
clutch, front cover, etc.Furthermore. the torque-converter cannot be dis-
assembled because the outer circumference of the
shell
(front cover and rear cover) is sealed by
welding.
Because the torque-converter is coupled to the
engine’s crankshaft (via the drive plate). the shell
(front cover and impeller) always turns in the same
way when the engine is running.
As a result, the oil pump is also caused to rotate (by
the hub welded to the center part of the rear of the
shell) at the same speed as the engine.
The boss at the front part of the shell is inserted in
the hole at the rear part of the crankshaft. thus
providing support of the torque-converter.
A facing like that attached to the transaxle’s clutch
disc is attached to the damper clutch, and the
damper clutch and the turbine are connected by the
tabs (of the lock ring on the outer circumference of
the turbine shell) that fit into the groove on the outer
circumference of the damper clutch.
The torque-converter actuation hydraulic pressure,at the damper clutch activation area, passes be-
tween the torque-converter’s hub and the reaction
shaft, and enters the torque-converter.
When this happens, the hydraulic pressure acts
upon the A part (between the damper clutch and the
turbine), with the result that the damper clutch is
pressed against the front cover, and the damper
clutch, with a slight slip (as described later) becom-
es connected.
In this manner, the amount of slippage of the
torque-convener is reduced, without a damper
spring, to far below at even the low-speed level,
thus making a practical improvement of fuel con-
sumption.
At the damper clutch non-activation area, because
the torque-converter actuation hydraulic pressure
passes through the input shaft oil passage
-1enters the torque-converter from the
B part &-tween the damper clutch and the front cover). the
damper clutch moves away from the front
cover,thus releasing the damper clutch.
In this condition, operation is as an ordinary torque-
converter.
Page 373 of 391

25-1
EMISSION
CONTROL SYSTEMSCONTENTS
RZSA---AIR-FUEL MIXTURE
RATIOCONTROL SYSTEM
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .._.................9CATALYTIC CONVERTER
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .._............9CRANKCASE VENTlLATlON SYSTEM
. . . . . . . . . . . .10EVAPORATIVE EMISSION
CONTROL SYSTEM
: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..-.........11Canister
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..~...................._._...__..12
FuelCheck Valve. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .._.........14
FuelFiller Cap. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..__....._..14Overfill Limiter (Two-way Valve)
_................... 14
Purge Control Solenoid Valve
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13Purge Control Solenoid Valve
. . . . . . . . . . . _ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13Purge Control Valve
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
(EGR) SYSTEM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..-......5
EGR Control Solenoid Valve
..,.........................................7EGR Temperature Sensor
. . . . . . . .8Operation
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Operation
Therm0 Valve
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Page 374 of 391
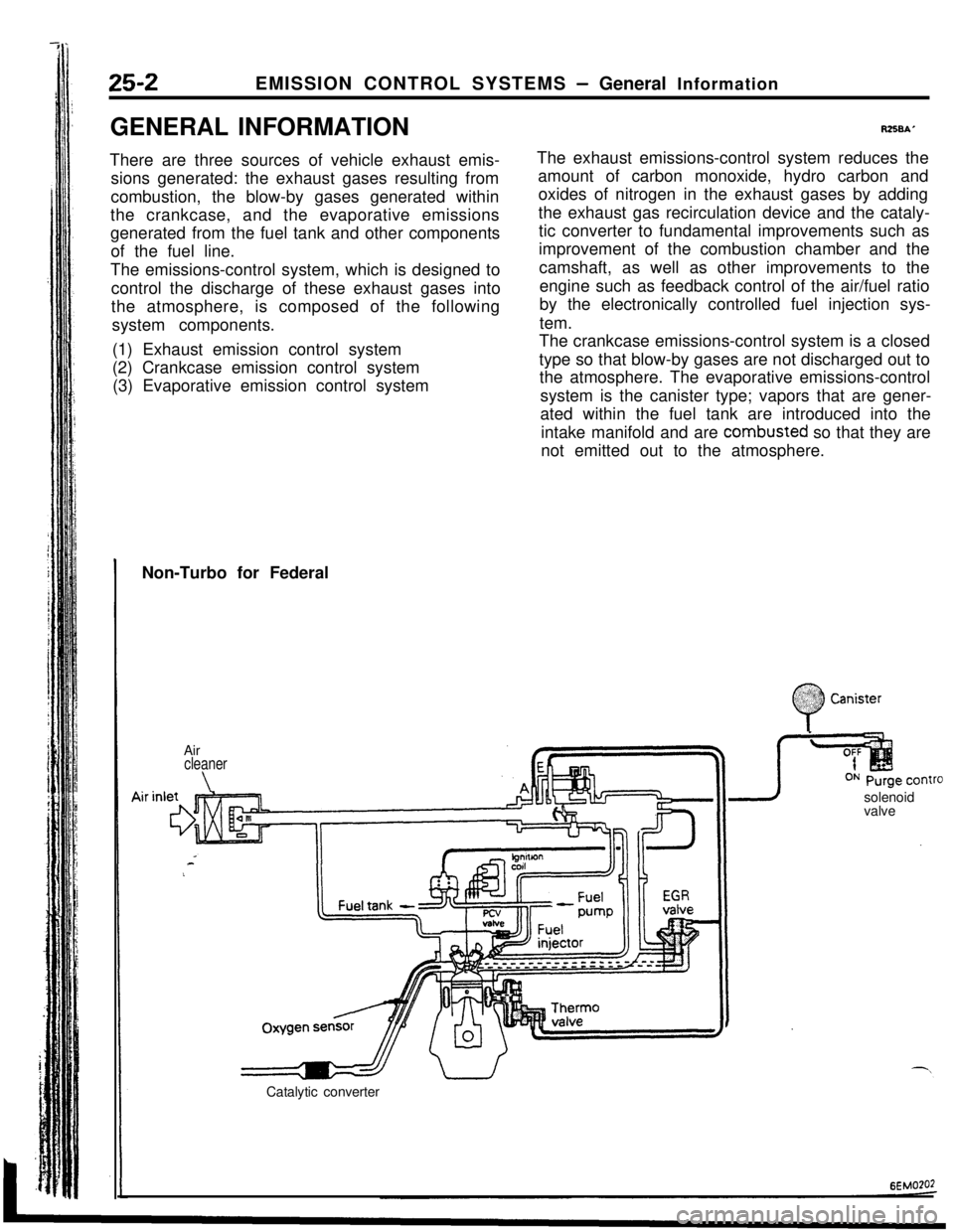
25-2EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS - General Information
GENERAL INFORMATION
There are three sources of vehicle exhaust emis-
sions generated: the exhaust gases resulting from
combustion, the blow-by gases generated within
the crankcase, and the evaporative emissions
generated from the fuel tank and other components
of the fuel line.
The emissions-control system, which is designed to
control the discharge of these exhaust gases into
the atmosphere, is composed of the following
system components.
(1) Exhaust emission control system
(2) Crankcase emission control system
(3) Evaporative emission control system
R258A’The exhaust emissions-control system reduces the
amount of carbon monoxide, hydro carbon and
oxides of nitrogen in the exhaust gases by adding
the exhaust gas recirculation device and the cataly-
tic converter to fundamental improvements such as
improvement of the combustion chamber and the
camshaft, as well as other improvements to the
engine such as feedback control of the air/fuel ratio
by the electronically controlled fuel injection sys-
tem.
The crankcase emissions-control system is a closed
type so that blow-by gases are not discharged out to
the atmosphere. The evaporative emissions-control
system is the canister type; vapors that are gener-
ated within the fuel tank are introduced into the
intake manifold and are combusted so that they are
not emitted out to the atmosphere.
Non-Turbo for Federal
Air
cleaner
\solenoid
valve
Catalytic converter
:
0
$2:) Canister:.: