1988 OPEL CALIBRA coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 156 of 525

4B
cruising and accelerating. The injector earth is
also switched off on the overrun to improve
fuel economy and reduce exhaust emissions.
Additionally, on the X16 SZ engine, the ECU
also controls the operation of the charcoal
canister purge valve in the evaporative
emission control system.
10The oxygen sensor screwed into the
exhaust manifold provides the ECU with a
constant feedback signal. This enables it to
adjust the mixture (closed-loop control) to
provide the best possible conditions for the
catalytic converter to operate effectively.
11Until the oxygen sensor is fully warmed up
it gives no feedback so the ECU uses
pre-programmed values (open-loop control) to
determine the correct injector pulse width.
When the sensor reaches its normal operating
temperature, its tip (which is sensitive to
oxygen) sends the ECU a varying voltage
depending on the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gases. If the inlet air/fuel mixture is too
rich, the exhaust gases are low in oxygen so the
sensor sends a low-voltage signal. The voltage
rises as the mixture weakens and the amount of
oxygen rises in the exhaust gases. Peak
conversion efficiency of all major pollutants
occurs if the inlet air/fuel mixture is maintained
at the chemically correct ratio for the complete
combustion of petrol of 14.7 parts (by weight) of
air to 1 part of fuel (the “stoichiometric” ratio).
The sensor output voltage alters in a large step
at this point, the ECU using the signal change
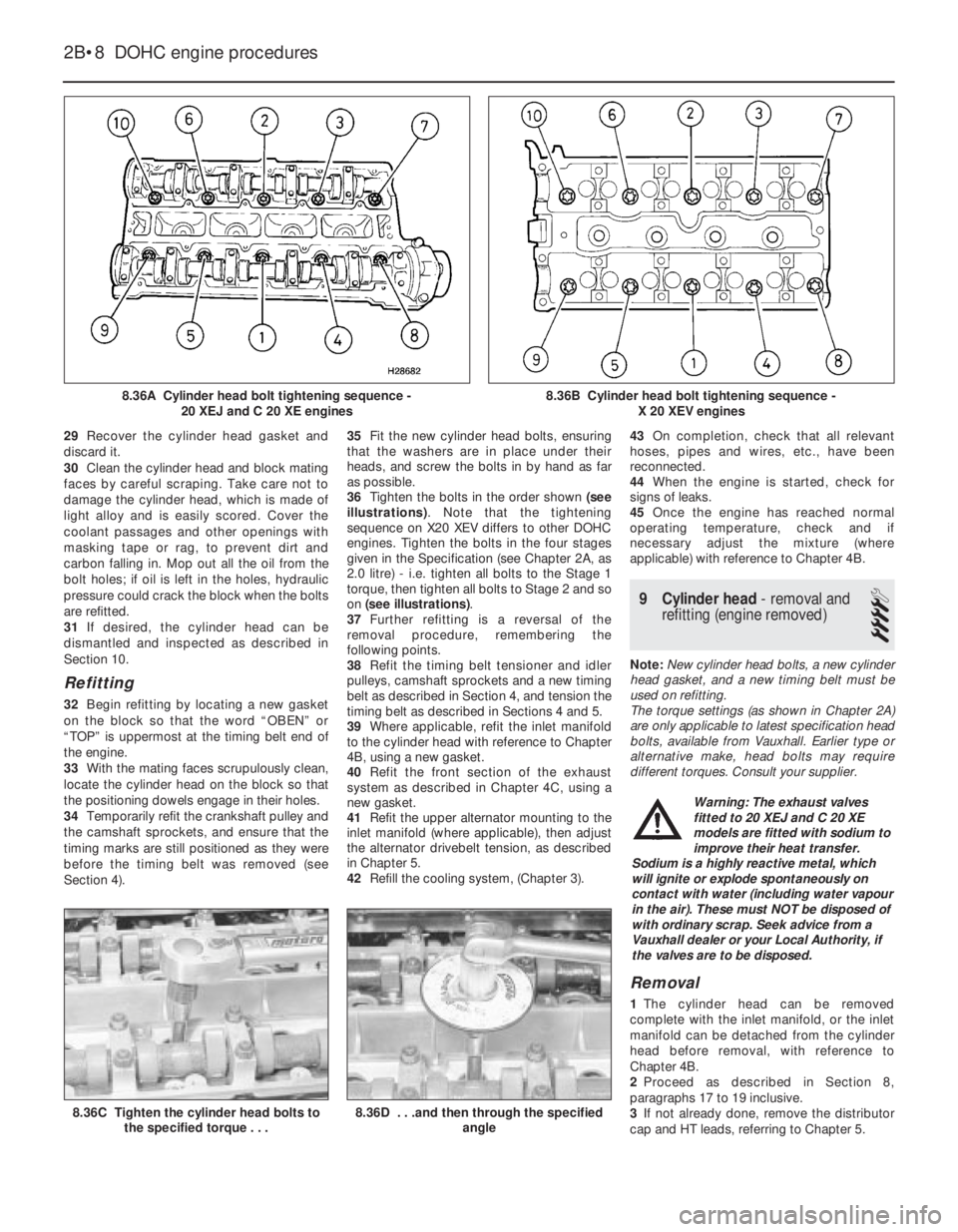
as a reference point and correcting the inlet
air/fuel mixture accordingly by altering the fuel
injector pulse width.
12In addition, the ECU senses battery
voltage, incorporates diagnostic capabilities,
and can both receive and transmit information
by way of the diagnostic connector, thus
permitting engine diagnosis and tuning by
Vauxhall’s TECH1, test equipment.
Motronic system
13The Motronic type is available in several
different versions, depending on model. The
system is under the overall control of the
Motronic engine management system (Chapter
5), which also controls the ignition timing.
14Fuel is supplied from the rear-mounted
fuel tank by an electric fuel pump mounted
under the rear of the vehicle, through a
pressure regulator, to the fuel rail. The fuel rail
acts as a reservoir for the four fuel injectors,
which inject fuel into the cylinder inlet tracts,
upstream of the inlet valves. On SOHC
engines, the fuel injectors receive an electrical
pulse once per crankshaft revolution, which
operates all four injectors simultaneously. On
DOHC engines, sequential fuel injection is
used, whereby each injector receives an
individual electrical pulse allowing the four
injectors to operate independently, which
enables finer control of the fuel supply to each
cylinder. The duration of the electrical pulse
determines the quantity of fuel-injected, and
pulse duration is computed by the Motronic
module, based on the information received
from the various sensors.15On SOHC engines, inlet air passes from
the air cleaner through a vane type airflow
meter, before passing to the cylinder inlet
tracts through the throttle valve. A flap in the
vane airflow meter is deflected in proportion
to the airflow; this deflection is converted into
an electrical signal, and passed to the
Motronic module. A potentiometer screw
located on the airflow meter provides the
means of idle mixture adjustment, by altering
the reference voltage supplied to the Motronic
module.
16On DOHC engines, inlet air passes from
the air cleaner through a hot wire type air
mass meter, before passing to the cylinder
inlet tracts through a two-stage throttle body
assembly. The electrical current required to
maintain the temperature of the hot wire in the
air mass meter is directly proportional to the
mass flow rate of the air trying to cool it. The
current is converted into a signal, which is
passed to the Motronic module. The throttle
body contains two throttle valves that open
progressively, allowing high torque at part
throttle, and full-throttle, high-speed
“breathing” capacity. A potentiometer screw
located on the air mass meter provides the
means of idle mixture adjustment, by altering
the reference voltage supplied to the Motronic
module.
17A throttle position sensor enables the
Motronic module to compute the throttle
position, and on certain models, its rate of
change. Extra fuel can thus be provided for
acceleration when the throttle is opened
suddenly. Information from the throttle
position sensor is also used to cut off the fuel
supply on the overrun, thus improving fuel
economy and reducing exhaust gas
emissions.
18Idle speed is controlled by a variable-
orifice solenoid valve, which regulates the
amount of air bypassing the throttle valve. The
valve is controlled by the Motronic module;
there is no provision for direct adjustment of
the idle speed.
19Additional sensors inform the Motronic
module of engine coolant temperature, air
temperature, and on models fitted with a
catalytic converter, exhaust gas oxygen
content.
20A fuel filter is incorporated in the fuel
supply line, to ensure that the fuel supplied to
the injectors is clean.
21A fuel pump cut-off relay is controlled by
the Motronic module, which cuts the power to
the fuel pump should the engine stop with the
ignition switched on, if there is an accident. All
1993-onwards models equipped with
Motronic systems, have their fuel pump
located inside the fuel tank.
22The later M2.8 system is basically the
same as the earlier M2.5 system apart from
the following:
a)Hot Film Mass Airflow Meter - The hot
wire type unit used previously is replaced
on the M2.8 system by a hot film mass
airflow meter. The operation is the sameexcept that a thin, electrically heated plate
rather than a wire is used. The plate is
maintained at a constant temperature by
electric current as the inlet air mass
passing over the plate tries to cool it. The
current required to maintain the
temperature of the plate is directly
proportional to the mass flow rate of the
inlet air. The current is converted to a
signal that is passed to the Motronic
module.
b)Inlet Air Temperature Sensor -The sensor
is located in the hose between the hot
film mass airflow meter and the air cleaner
for precise monitoring of inlet air
temperature. Signals from the sensor are
used in conjunction with other sensors to
indicate the occurrence of a hot start
condition. The Motronic module then
interprets these signals to alter injector
duration accordingly.
c)Throttle Valve Potentiometer -On the
M2.8 system a throttle valve
potentiometer replaces the throttle valve
switch used previously.
Simtec system
23An increased amount of electronic
components are used instead of mechanical
parts as sensors and actuators with the
Simtec engine management system. This
provides more precise operating data as well
as greater problem free motoring.
24The control unit is equipped with
electronic ignition control. Called ‘Micropro-
cessor Spark Timing System, inductive
triggered’, (or MSTS-i), and means that the
mechanical high voltage distributor is no
longer needed. It is located behind the trim
panel, on the right-hand side footwell (door
pillar).
25The ignition coil is replaced by a dual
spark ignition coil, which is switched directly
by the output stages in the control unit.
26A camshaft sensor will maintain
emergency operation, should the crankshaft
inductive pulse pick-up, malfunction. These
sense TDC (‘Top Dead Centre’), crankshaft
angle and engine speed. The signals are used
by the control unit to calculate ignition point
and for fuel injection.
27The ‘hot film airflow meter’ determines the
mass of air taken in by the engine. The system
uses this information to calculate the correct
amount of fuel needed for injection in the
engine.
28The air inlet temperature sensor (NTC), is
fitted in the air inlet duct between the air
cleaner and the hot mass air flow meter.
29A controlled canister purge valve is
actuated by the system. The tank ventilation is
monitored closely with the Lambda control (or
oxygen sensor) and adaptation by the
computer within the control unit.
30A knock control system is also fitted. This
eliminates the need for octane number
adjustment, as it is performed automatically
through the control unit.
Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models 4B•3
Page 170 of 525

Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, ensuring that the wiring plugs are
correctly reconnected and that the unit is
located securely.
36Knock sensor and module
(X16 SZ models) - removal
and refitting
3
Removal
1The knock sensor fitted to the X16 SZ
engine is located on the cylinder block below
the inlet manifold, between cylinders 2 and 3.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Remove the wiring and unscrew the unit
from the block.
4The module and control unit are located on
the left-hand side of the engine compartment
behind the battery. To remove, disconnect the
wiring multiplug and remove the retaining
bolts (see illustration).
5There is no provision for testing the knock
sensor or module without dedicated Vauxhall
test equipment. Check for external damage
and replace if necessary.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, ensuring that the wiring plugs are
correctly reconnected and that the units are
located securely.
37Knock sensor (Simtec
system) - removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect wiring harness plug, from inlet
air temperature sensor and wiring harness
plug, from hot mass air flow meter.
3Remove crankcase ventilation hoses.
4Remove coolant hoses from air inlet hoses,
hot film mass air flow meter complete with air
inlet hoses, from upper part of air cleaner and
throttle body.5Press retaining clip for 1st and 4th cylinder
injectors in plug strip (with screwdriver)
towards fuel distributor pipe - lifting plug strip
at the same time. On the underside of the plug
strip there are a total of 6 plug connections, 4
of which are for the injectors.
6Disconnect wiring harness plug for knock
sensor from the plug strip.
7Connect a 1 metre length of separate cable
to knock sensor wiring harness plug (note
routing).
8Remove knock sensor from cylinder block
(see illustration).
9Disconnect knock sensor cable from
separately attached cable, separate cable
remains in engine compartment.
Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of removal, but note
the following.
11Before refitting ensure that the sensor is
spotlessly clean. Clean the entire contact
surface of the sensor must lie directly on the
cylinder block. Do not use any form of
washers.
12Carefully refit sensor into the block.
Tighten to the correct torque.
13Guide knock sensor cable between ridges
on inlet manifold using separate cable -
ensure correct routing.
14Remove the cable.
15Insert the wiring harness plug for the
knock sensor, into the plug strip.
16Correctly align the spring clips for theinjectors as they may prevent engagement of
the plug strip. Correct contact between the
plug strip and the injector is essential.
17When connecting plug strip, an audible
‘click’ should be heard.
18Ensure that hoses are in good condition
and installed securely with the two clamps.
38Inlet manifold (SOHC without
Multec) - removal and refitting
3
Note:Refer to warning in Section 2, before
proceeding. Use a new gaskets when refitting.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the idle speed adjuster and its
hoses, referring to Section 22, if necessary.
3Release the securing clip, then disconnect
the throttle cable and balljoint from the throttle
valve lever. Slide the throttle cable grommet
from the bracket on the inlet manifold, and
move the throttle cable to one side out of the
way.
4Loosen the clamp screw and disconnect
the air trunking from the throttle body.
5Unscrew the union nut and disconnect the
brake servo vacuum hose from the inlet
manifold(see illustration).
6Disconnect the camshaft cover breather
hose from the throttle body.
7Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
throttle body. Be prepared for coolant
spillage, and clamp or plug the open ends of
the hoses, to prevent further coolant loss.
8Disconnect the wiring plug from the throttle
position sensor.
9Disconnect the vacuum pipe from the top
of the fuel pressure regulator.
10Disconnect the wiring harness housing
from the fuel injectors and move it to one side,
taking care not to strain the wiring. Pull up on
the wiring harness housing, and compress the
wiring plug retaining clips to release the
harness housing from the injectors.
11Disconnect the fuel hoses from the fuel
rail. Be prepared for fuel spillage, and take
adequate fire precautions. Clamp or plug the
open ends of the hoses, to prevent dirt
ingress and further fuel leakage.
Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models 4B•17
38.5 Disconnecting the brake servo
vacuum hose -
SOHC models37.8 Knock sensor and wiring
(Simtec system)
1 Sensor2 Securing bolt
36.4 Knock sensor and module (X16 SZ models)
1 Sensor2 Module3 Sensor securing bolt
4B
Page 172 of 525

1
Chapter 1
Routine maintenance and servicing
Air cleaner element - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Air inlet temperature control check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Alternator V-belt check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Automatic transmission check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Automatic transmission fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Automatic transmission fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Bodywork check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Brake fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Brake pad check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Brake shoe check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Clutch cable check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Coolant renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Distributor and HT lead check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Door lock key battery - replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Driveshaft gaiter check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Engine oil and filter - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Fuel filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Handbrake linkage check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16Headlamp alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Hose and fluid leak check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Idle speed and mixture - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Ignition timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Intensive maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Lock and hinge check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Manual transmission fluid check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Power steering fluid check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Power steering pump drivebelt check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Radiator inspection and cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Rear suspension level control system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Road test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Spark plug renewal (SOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Spark plug renewal (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Steering and suspension check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Throttle linkage maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Timing belt renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Wiring check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
1•1
Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 175 of 525

1•4Maintenance schedule
Every 250 miles (400 km) or weekly
MRefer to “Weekly checks”
Basic service, every 9000 miles
(15 000 km) or 12 months -
whichever comes sooner
Along with the items in “Weekly checks”, carry out the
following:
MRenew the engine oil and oil filter (Section 3).
MCheck all hoses and other components for fluid
leaks (Section 4).
MCheck the steering and suspension components
(Section 5).
MCheck the condition of the driveshaft rubber
gaiters (Section 6).
MCheck the automatic transmission fluid level (if
applicable), (Section 7).
MCheck the radiator for blockage (e.g. dead insects)
and clean as necessary (Section 8).
MCheck and adjust the idle speed and mixture (if
applicable), (Section 9).
MCheck the throttle linkage and lubricate if
necessary (Section 10).
MCheck the exhaust system for corrosion, leaks and
security (Section 11).
MCheck all wiring for condition and security
(Section 12).
MCheck and adjust the ignition timing (if applicable),
(Section 13).
MRenew the brake fluid (Section 14).
MCheck the brake pad friction material for wear
(Section 15).
MCheck the handbrake linkage (Section 16).
MCheck the power steering fluid level (if applicable),
(Section 17).
MCheck the power steering pump drivebelt (if
applicable), (Section 18).
MCheck the rear suspension level control system
height, if fitted (Section 19).
MCheck the bodywork (Section 20).
MLubricate all locks and hinges (Section 21).
MCheck the alternator V-belt (Section 22).
MCheck the headlamp alignment (Section 23).
MReplace battery in the door-lock key (if applicable),
(Section 24).
MCarry out a road test (Section 25).
Note: Vauxhall specify that an Exhaust Emissions Test should be
carried out at least annually. However, this requires special
equipment, and is performed as part of the MOT test (refer to the
end of the manual).
Full service, every 18 000 miles
(30 000 km) or 24 months -
whichever comes sooner
Along with the ‘basic service’, carry out the following:
MRenew the coolant (Section 26).
MRenew the air cleaner element (Section 27).
MCheck the operation of the air cleaner air inlet
temperature control (carburettor models only),
(Section 28).
MRenew the fuel filter (Section 29).
MRenew the spark plugs (SOHC only), (Section 30) *.
MInspect and clean the distributor cap and HT leads
(Section 31).
MCheck the clutch cable adjustment (Section 32).
MCheck the manual transmission oil level (Section 33).
MCheck the automatic transmission (Section 34).
MCheck the brake drum shoe for wear (Section 35).
Major service, every 36 000 miles
(60 000 km) or 48 months -
whichever comes sooner
Along with the ‘full service’, carry out the following:
MRenew timing belt (Section 36).
MRenew the spark plugs (DOHC models only),
(Section 37).
MRenew automatic transmission fluid (Section 38) *.
* Note: If a vehicle is used for heavy-duty work (e.g. taxi work,
caravan/trailer towing, mostly short-distance, stop-start city driving)
the fluid must be changed every 36 months or 27 000 miles (45 000
km), whichever occurs first.
Page 190 of 525

Torque wrench settings (continued)Nmlbf ft
Starter to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Starter support to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Temperature regulator plug (M20) * . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Timing belt cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Timing belt drive gear to crankshaft: *
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .250184
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by between 40°and 50°
Timing belt guide roller bracket to block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Timing belt guide roller to bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Timing belt guide roller to cylinder block:
Engines up to 1993
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 45°
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15°
1993-on engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Transfer box bracket to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Transmission to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
1General
This part of Chapter 2 describes
procedures that are specific to the DOHC
engine. It should be read in conjunction with
Part A.
The lower engine is basically the same as
the 2.0 litre SOHC. However the pistons are
attached to the connecting rods by gudgeon
pins, which are fully floating, and are secured
by circlips.
Both camshafts on these engines are driven
from the crankshaft by one toothed
composite rubber belt. Each cylinder has four
valves (two inlet and two exhaust), operated
directly from the camshafts by hydraulic
self-adjusting valve lifters. One camshaft
operates the inlet valves, and the other
operates the exhaust valves.
DOHC models are fitted with a remotely
mounted oil cooler.
The distributor is driven directly from the
exhaust camshaft.
2Engine - removal and refitting
4
Removal
1Carry out procedure in Chapter 2A, noting
the following differences.
2With the car safely raised, remove the
engine undershield.
3The fuel hoses need to be disconnected
from the fuel rail.
4Disconnect coolant hoses from the cylinder
block and cylinder head. Also disconnect the
oil cooler pipe unions from the oil pump.
5Unbolt the right-hand driveshaft centre
bearing support bracket from the rear of the
cylinder block.
Refitting
6Refitting the engine is similar to theprocedure in Chapter 2A. The exceptions
being, replacement of the right-hand
driveshaft centre bearing support bracket at
the rear of the cylinder block and retightening
the securing bolts.
7Replace the undershield.
3Engine/transmission
mountings- renewal
3
The procedure for replacing the engine/
transmission is similar to SOHC models, see
Chapter 2A. However this engine is fitted with
an undershield that needs to be removed
before replacing the mounts. Do not forget to
replace the undershield before lowering the
car.
4Timing belt, sprockets and belt
tensioner and idler pulleys-
removal, refitting and adjustment
3
Note: The timing belt should be renewed on
refitting. A two-legged puller may be required
to remove the crankshaft sprocket
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.2Disconnect the air cleaner trunking from the
airflow meter, then remove the cover and the
air cleaner element from the air cleaner. If
desired, for improved access, the complete
air cleaner assembly can be removed, as
described in Chapter 4B.
3Remove the power steering pump drivebelt,
as described in Chapter 10.
4Remove the alternator drivebelt, as
described in Chapter 5.
5Remove the three securing screws, and
withdraw the outer timing belt cover. Recover
the rubber grommets from the screw holes in
the cover if they are loose.
6Turn the crankshaft using a Torx socket on
the crankshaft sprocket bolt, until the timing
marks on the camshaft sprockets are aligned
with the notches in the camshaft cover. The
notch in the crankshaft pulley should also be
aligned with the pointer on the rear timing belt
cover (see illustrations).
7Extract the six securing bolts using a
splined bit, and withdraw the crankshaft
pulley (see illustration). If necessary,
counterhold the crankshaft using a socket on
the crankshaft sprocket bolt. If the engine is in
the vehicle, the crankshaft can be prevented
from turning by having an assistant engage
first gear and depress the brake pedal.
Alternatively, the flywheel ring gear teeth can
be jammed using a large screwdriver or
similar tool. Before removing the pulley, check
that the timing marks are still aligned.
DOHC engine procedures 2B•3
4.6B . . .and notch in crankshaft pulley
aligned with pointer on rear timing belt
cover (circled)4.6A Camshaft sprocket TDC mark
aligned with notch in camshaft cover
2B
Page 194 of 525

pitting. If evident, the cylinder head and all
bearing caps must be renewed as a matched
set, as there is no provision for refacing if the
bearing caps cannot be renewed individually.
8The camshaft(s) should show no marks or
scoring on the journal or cam lobe surfaces. if
evident, renew the camshaft(s).
9It is advisable to renew the camshaft front
oil seal(s) as a matter of course. Prise the old
seal(s) from the front of the camshaft(s) and
discard them.
Refitting
10Begin refitting by liberally coating the
contact faces of the hydraulic valve lifters and
the camshaft(s) with molybdenum disulphide
paste.
11Coat the mating faces of the front and
rear bearing caps with sealing compound and
refit the bearing caps in their original positions
as noted during removal.
12Tighten the camshaft bearing cap nuts to
the specified torque in half-turn stages, as
when loosening the nuts. Note that when
refitting the exhaust camshaft, the two smaller
rear bearing cap securing nuts should be
tightened after all the main camshaft bearing
cap nuts have been tightened. Note also that
the two smaller nuts should be tightened to a
lower torque wrench setting than the main
nuts.
13Turn the camshaft until the locating peg
for the camshaft sprocket is uppermost, then
lubricate the lips of a rear camshaft front oil
seal with a little grease, and fit the oil seal,
using a tube or socket of similar diameter with
a washer and the camshaft sprocket bolt.
Screw the camshaft sprocket bolt into the end
of the camshaft to draw the oil seal into
position on its shoulder.
14Repeat the procedure for the remaining
camshaft.
15Refit the distributor with reference to
Chapter 5. Fit a new timing belt and the
camshaft sprockets, then adjust the timing
belt as described in Section 4 or 5, as
applicable.
8Cylinder head -removal and
refitting (engine in vehicle)
4
Note: The engine must be cold when the
cylinder head is removed. Do not remove the
cylinder head from a hot engine. New cylinder
head bolts, a new cylinder head gasket and a
new timing belt must be used on refitting.
The torque settings (as shown in Chapter 2A)
are only applicable to latest specification head
bolts, available from Vauxhall. Earlier type or
alternative make, head bolts may require
different torques. Consult your supplier
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Drain the cooling system, as described in
Chapter 3.3Remove the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
4The cylinder head can be removed
complete with the inlet manifold, or the inlet
manifold can be detached from the cylinder
head before removal, with reference to
Chapter 4B. If no work is to be carried out on
the inlet manifold, it can be unbolted from the
cylinder head and supported to one side out
of the way, thus avoiding the need to
disconnect the relevant hoses, pipes and
wiring.
5If the cylinder head is to be removed
complete with the inlet manifold, disconnect
all relevant hoses, pipes and wiring from the
inlet manifold and associated components,
referring to Chapter 4B, and unbolt the
manifold support bracket from the manifold.
Loosen the alternator mountings with
reference to Chapter 5, then unbolt the upper
alternator mounting from the inlet manifold.
6If the inlet manifold is to be left in the engine
compartment, continue as follows, otherwise
go on to paragraph 17.
7Disconnect the wiring plug from the airflow
meter, and the breather hose from the air box
on the throttle body. Disconnect the air
cleaner trunking and remove the airflow
meter/air box assembly from the throttle
body. Refer to Chapter 4B if necessary.
8Disconnect the end of the throttle cable
from the throttle valve lever, then unbolt the
throttle cable support bracket and remove it
from the inlet manifold.
9Unscrew the two earth lead securing nuts
from the fuel rail (one at each end of the rail)
and disconnect the three earth leads.
10Disconnect the wiring plug from the
throttle position switch.
11Pull up on the wiring harness housing, and
disconnect the wiring plugs from the fuel
injectors by compressing the retaining clips.
Move the wiring harness housing to one side.
12Disconnect the two breather hoses from
the rear of the camshaft cover.
13Loosen the alternator mountings, with
reference to Chapter 5, then unbolt the upper
alternator mounting from the inlet manifold.
14Unbolt the manifold support bracket from
the manifold.15Make a final check to ensure that all
necessary hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected, then unscrew the securing nuts
and lift the inlet manifold from the cylinder
head. Ensure that the manifold is properly
supported, taking care not to strain any of the
hoses, pipes and wires, etc., which are still
connected.
16Recover the manifold gasket from the
cylinder head.
17Remove the timing belt, camshaft
sprockets, and timing belt tensioner and idler
pulleys, as described in Section 4.
18Unscrew the upper and middle studs for
the timing belt outer cover screws. Note that
the upper stud simply unscrews from the
cylinder head, but the middle stud is secured
by a bolt.
19Unscrew the two upper rear timing belt
cover securing bolts from the cylinder head.
20Remove the distributor cap and HT leads
with reference to Chapter 5.
21Disconnect the distributor wiring plug.
22Disconnect the coolant hose from the
left-hand end of the cylinder head.
23Unscrew the bolt securing the crankcase
breather tube bracket to the end of the
cylinder head.
24Disconnect the radiator top hose from the
thermostat housing, and disconnect the
wiring plugs from the temperature gauge
sender and the coolant temperature sensor
(both situated in the thermostat housing).
25Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected.
26On X20 XEV models, remove the
camshaft, as described in Section 7.
27Using a Torx socket, and working in the
order shown (see illustrations), loosen all the
cylinder head bolts by a quarter of a turn, then
loosen all the bolts by half a turn, and finally
loosen and remove the bolts. Recover the
washers. Note that the loosening sequence
on X20 XEV differs to other DOHC engines.
28Lift the cylinder head from the cylinder
block. If necessary, tap the cylinder head
gently with a soft-faced mallet to free it from
the block, but do not lever at the mating
faces. Note that the cylinder head is located
on dowels.
DOHC engine procedures 2B•7
8.27B Cylinder head bolt loosening
sequence - (X 20 XEV engines)8.27A Cylinder head bolt loosening
sequence - (20 XEJ and C 20 XE engines)
2B
Page 195 of 525
29Recover the cylinder head gasket and
discard it.
30Clean the cylinder head and block mating
faces by careful scraping. Take care not to
damage the cylinder head, which is made of
light alloy and is easily scored. Cover the
coolant passages and other openings with
masking tape or rag, to prevent dirt and
carbon falling in. Mop out all the oil from the
bolt holes; if oil is left in the holes, hydraulic
pressure could crack the block when the bolts
are refitted.
31If desired, the cylinder head can be
dismantled and inspected as described in
Section 10.
Refitting
32Begin refitting by locating a new gasket
on the block so that the word “OBEN” or
“TOP” is uppermost at the timing belt end of
the engine.
33With the mating faces scrupulously clean,
locate the cylinder head on the block so that
the positioning dowels engage in their holes.
34Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley and
the camshaft sprockets, and ensure that the
timing marks are still positioned as they were
before the timing belt was removed (see
Section 4).35Fit the new cylinder head bolts, ensuring
that the washers are in place under their
heads, and screw the bolts in by hand as far
as possible.
36Tighten the bolts in the order shown (see
illustrations). Note that the tightening
sequence on X20 XEV differs to other DOHC
engines. Tighten the bolts in the four stages
given in the Specification (see Chapter 2A, as
2.0 litre) - i.e. tighten all bolts to the Stage 1
torque, then tighten all bolts to Stage 2 and so
on (see illustrations).
37Further refitting is a reversal of the
removal procedure, remembering the
following points.
38Refit the timing belt tensioner and idler
pulleys, camshaft sprockets and a new timing
belt as described in Section 4, and tension the
timing belt as described in Sections 4 and 5.
39Where applicable, refit the inlet manifold
to the cylinder head with reference to Chapter
4B, using a new gasket.
40Refit the front section of the exhaust
system as described in Chapter 4C, using a
new gasket.
41Refit the upper alternator mounting to the
inlet manifold (where applicable), then adjust
the alternator drivebelt tension, as described
in Chapter 5.
42Refill the cooling system, (Chapter 3).43On completion, check that all relevant
hoses, pipes and wires, etc., have been
reconnected.
44When the engine is started, check for
signs of leaks.
45Once the engine has reached normal
operating temperature, check and if
necessary adjust the mixture (where
applicable) with reference to Chapter 4B.
9Cylinder head -removal and
refitting (engine removed)
4
Note: New cylinder head bolts, a new cylinder
head gasket, and a new timing belt must be
used on refitting.
The torque settings (as shown in Chapter 2A)
are only applicable to latest specification head
bolts, available from Vauxhall. Earlier type or
alternative make, head bolts may require
different torques. Consult your supplier.
Removal
1The cylinder head can be removed
complete with the inlet manifold, or the inlet
manifold can be detached from the cylinder
head before removal, with reference to
Chapter 4B.
2Proceed as described in Section 8,
paragraphs 17 to 19 inclusive.
3If not already done, remove the distributor
cap and HT leads, referring to Chapter 5.
2B•8DOHC engine procedures
8.36A Cylinder head bolt tightening sequence -
20 XEJ and C 20 XE engines
8.36C Tighten the cylinder head bolts to
the specified torque . . .8.36D . . .and then through the specified
angle
8.36B Cylinder head bolt tightening sequence -
X 20 XEV engines
Warning: The exhaust valves
fitted to 20 XEJ and C 20 XE
models are fitted with sodium to
improve their heat transfer.
Sodium is a highly reactive metal, which
will ignite or explode spontaneously on
contact with water (including water vapour
in the air). These must NOT be disposed of
with ordinary scrap. Seek advice from a
Vauxhall dealer or your Local Authority, if
the valves are to be disposed.
Page 204 of 525

Oil pick-up pipe bracket to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Oil pick-up pipe to oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Oil pipes to radiator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Oil pressure switch to oil pump:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4030
Oil pressure relief valve to oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Oil pump cover to oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Oil pump to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Oxygen sensor to exhaust manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Power steering pump bracket to support:
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1813
Power steering pump to support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Right engine mounting to subframe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6548
Shackle to alternator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Starter to cylinder block (M10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Starter to cylinder block (M12) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Sump:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
Sump drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5541
Support to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3526
Temperature sender to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Thermostat housing:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
Timing belt tensioner to oil pump:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5541
Timing belt cover to oil pump/camshaft housing:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .129
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Timing belt drive gear to crankshaft:
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13096
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by between 40º to 50º
Transmission to engine (M10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Transmission to engine (M12) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
1General description
General
The engine is of four-cylinder, in-line single
or double overhead camshaft type (depending
on model), mounted transversely at the front
of the vehicle.
The crankshaft runs in five shell-type
bearings, and the centre bearing incorporates
a thrust bearing shell to control crankshaft
endfloat.
The connecting rods are attached to the
crankshaft by horizontally split shell-type
big-end bearings. On single overhead
camshaft (SOHC) models, the pistons are
attached to the connecting rods by gudgeon
pins, which are an interference fit in the
connecting rod small-end bore. The
aluminium alloy pistons are fitted with three
piston rings: two compression rings and an oil
control ring.
The camshaft on SOHC engines is driven
from the crankshaft by a toothed composite
rubber belt. Each cylinder has two valves (oneinlet and one exhaust), operated through
rocker arms that are supported at their pivot
ends by hydraulic self-adjusting valve lifters
(tappets).
The inlet and exhaust valves are each
closed by a single valve spring, and operate in
guides pressed into the cylinder head.
A gear-type oil pump is located in a housing
attached to the front of the cylinder block, and
is driven directly from the crankshaft. A
full-flow type oil filter is fitted.
The distributor is driven directly from the
end of the camshaft. On carburettor models,
the mechanical fuel pump is operated from
the front end of the camshaft. The coolant
pump is located at the front of the cylinder
block, and is driven by the timing belt.
Chapter 2A describes the SOHC engine
repair procedures. Many repairs and specifi-
cations to the DOHC engine are similar to the
2.0 litre SOHC. However where they differ,
details can be found in Chapter 2B.
Engine identification codes -
general
Before ordering spare parts, or carrying out
any repair or overhaul operations on the
engine, it is essential to identify the exactengine type being worked on. Later engines,
although outwardly similar in appearance,
often have significant differences in repair
procedures, even though they may be of the
same displacement and model year.
The following sub-Sections in this Chapter
are mainly specific to engine type, as will be
noted from the sub-Section headings. Check
the engine identification code first, which is
located on a horizontal surface on the exhaust
manifold side of the cylinder block, at the
distributor end. On later engines, the code is
on the cylinder block-to-transmission flange,
next to the engine oil dipstick.
2Crankcase ventilation
system - description and
maintenance
2
Description
1A crankcase ventilation system is fitted to
all models, but the systems differ in detail
depending on the model concerned.
2Oil fumes and blow-by gases (combustion
gases that have passed by the piston rings)
are drawn from the crankcase into the area of
SOHC engine procedures 2A•7
2A