1988 OPEL CALIBRA brakes
[x] Cancel search: brakesPage 149 of 525

8Disconnect the battery negative lead.
9Unclip the lid and open the relay box, then
pull out the relay (see illustration).
Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of removal, with
reference to paragraph 6.
24Rear brake pressure-
proportioning valves -
removal and refitting
4
Note: Refer to the note at the beginning of
Section 3 before proceeding. Note also that
the valve must only be renewed in pairs, and
both valves must be of the same calibration.
Ensure that correct type of valves are fitted.
The bodies have been stamped for easier
identification.
Master cylinder-mounted valves
Removal
1Remove the brake fluid reservoir cap, and
secure a piece of polythene over the filler
neck with a rubber band, or by refitting the
cap. This will reduce the loss of fluid during
the following procedure.
2Locate a container beneath the master
cylinder, to catch the brake fluid that will be
released.
3Identify the two lower brake pipes for
position, then unscrew the union nuts and
disconnect the pipes from the proportioning
valves in the base of the master cylinder. Plug
the open ends of the pipes to prevent dirt
ingress.
4Unscrew the proportioning valves from the
master cylinder, and plug the open ends of
the cylinder to prevent dirt ingress.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but on
completion, remove the polythene from the
brake fluid reservoir filler neck, and bleed the
complete hydraulic system, as described in
Section 3.
Rear underbody-mounted valves
Removal
6Proceed as described in paragraph 1.
7Chock the front wheels, then jack up the
rear of the vehicle, and support securely on
axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support”) positioned under the body side
members.
8Working under the rear of the vehicle,
unscrew the union nut and disconnect the
brake pipe from one of the valves. Be
prepared for fluid spillage, and plug the open
end of the pipe to prevent dirt ingress and
further fluid spillage.
9Similarly, disconnect the flexible hose from
the valve.
10Pull the valve retaining clip from the
bracket on the underbody, noting that on
certain models, the retaining clip also secures
the ABS sensor wiring, and withdraw the valve
(see illustration).
11Repeat the procedure for the other valve.
Refitting
12Proceed as described in paragraph 5.
25Brake fluid pipes and hoses
- general, removal and refitting
4
Note: Refer to the note at the beginning of
Section 3, before proceeding.
General
1When checking the condition of the
system’s pipes and/or hoses, carefully check
that they do not foul other components such
as the power steering gear pipes (where
applicable), so that there is no risk of the
pipes chafing. If necessary use clips or ties to
secure braking system pipes and hoses well
clear of other components.
Rigid pipes
Removal
2Some of the commonly used brake pipes
can be obtained from Vauxhall parts dealers,
ready-formed and complete with unions, but
other brake pipes must be prepared using
4.75 mm (0.19 in) diameter brake pipe. Kits for
making the brake pipes can be obtained from
certain motor accessory shops.
3Before removing a brake pipe, remove the
brake fluid reservoir cap, and secure a piece
of polythene over the filler neck with a rubber
band, or by refitting the cap. This will reduce
the loss of fluid when the pipe is
disconnected.4Jack up the vehicle, and support securely
on axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support”) positioned under the body side
members.
5To remove a brake pipe, unscrew the
unions at each end, and release the pipe from
the retaining clips.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, taking
care not to overtighten the unions.
7On completion, remove the polythene from
the brake fluid reservoir filler neck, and bleed
the relevant hydraulic circuit(s), as described
in Section 3.
Flexible hoses
Removal
8Proceed as described previously for the
rigid pipes, but note that a flexible pipe must
never be installed twisted, although a slight
“set” is permissible to give it clearance from
adjacent components.
Refitting
9When reconnecting a flexible hose to a
front brake caliper, note that the sealing rings
on the union bolt must be renewed.
26Handbrake - adjustment
2
Models with rear drum brakes
1The handbrake will normally be kept in
correct adjustment by the self-adjusting
action of the rear brake shoes. However, due
to cable stretch over a period of time, the
travel of the handbrake lever may become
excessive, in which case the following
operations should be carried out.
2Chock the front wheels, jack up the rear of
the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
3Fully release the handbrake.
4Turn the knurled nut on the cable adjuster
(mounted on the torsion beam), until the brake
shoes can just be heard to rub when the rear
wheels are turned by hand in the normal
direction of rotation (see illustration).
9•18Braking system
23.9 ABS surge arrester relay (arrowed)
26.4 Handbrake cable adjuster. Knurled
nut arrowed - all SOHC models24.10 Brake pressure-proportioning valve
on rear underbody - DOHC model
1 Valve 2 Retaining clip
Page 150 of 525
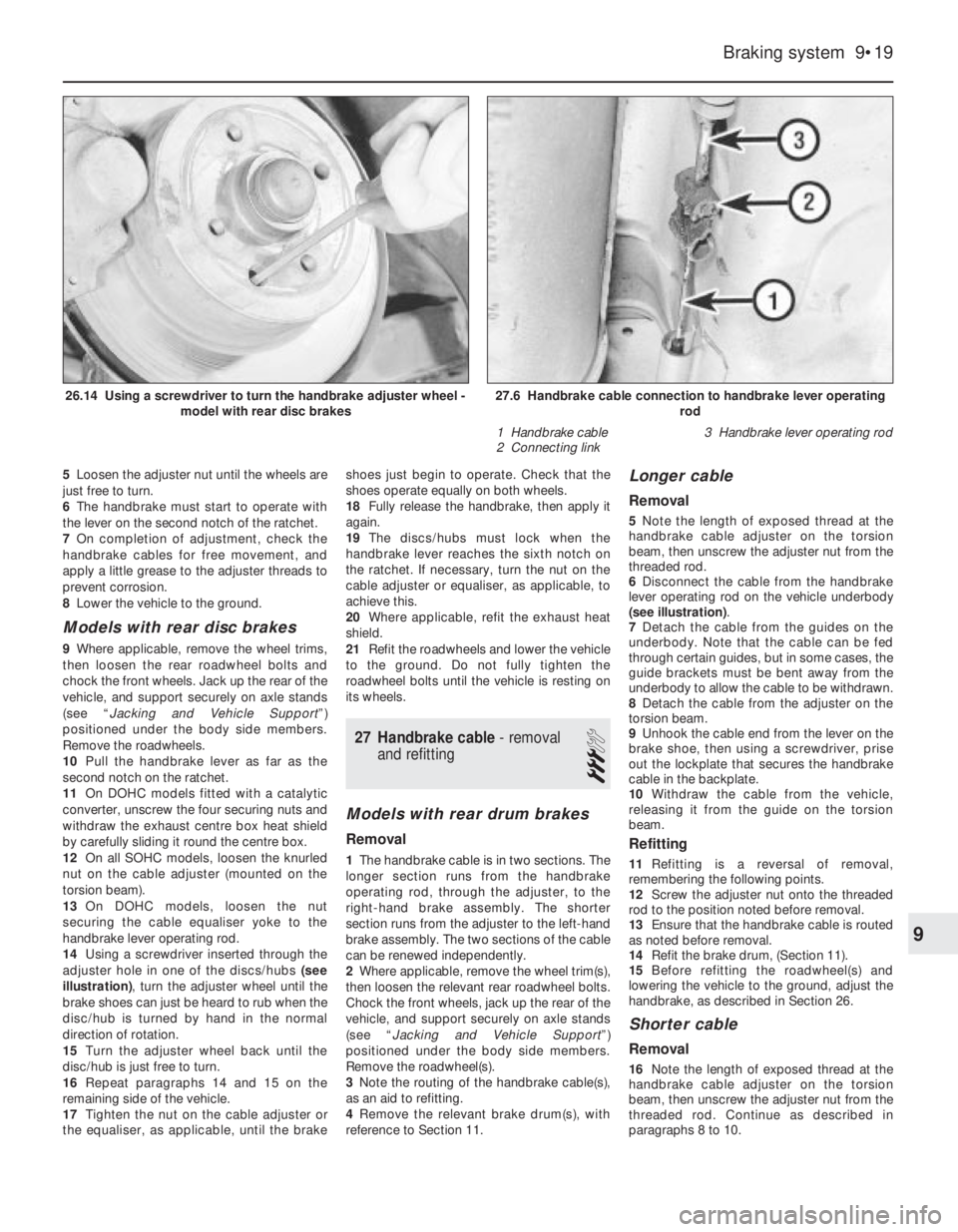
5Loosen the adjuster nut until the wheels are
just free to turn.
6The handbrake must start to operate with
the lever on the second notch of the ratchet.
7On completion of adjustment, check the
handbrake cables for free movement, and
apply a little grease to the adjuster threads to
prevent corrosion.
8Lower the vehicle to the ground.
Models with rear disc brakes
9Where applicable, remove the wheel trims,
then loosen the rear roadwheel bolts and
chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear of the
vehicle, and support securely on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheels.
10Pull the handbrake lever as far as the
second notch on the ratchet.
11On DOHC models fitted with a catalytic
converter, unscrew the four securing nuts and
withdraw the exhaust centre box heat shield
by carefully sliding it round the centre box.
12On all SOHC models, loosen the knurled
nut on the cable adjuster (mounted on the
torsion beam).
13On DOHC models, loosen the nut
securing the cable equaliser yoke to the
handbrake lever operating rod.
14Using a screwdriver inserted through the
adjuster hole in one of the discs/hubs (see
illustration), turn the adjuster wheel until the
brake shoes can just be heard to rub when the
disc/hub is turned by hand in the normal
direction of rotation.
15Turn the adjuster wheel back until the
disc/hub is just free to turn.
16Repeat paragraphs 14 and 15 on the
remaining side of the vehicle.
17Tighten the nut on the cable adjuster or
the equaliser, as applicable, until the brakeshoes just begin to operate. Check that the
shoes operate equally on both wheels.
18Fully release the handbrake, then apply it
again.
19The discs/hubs must lock when the
handbrake lever reaches the sixth notch on
the ratchet. If necessary, turn the nut on the
cable adjuster or equaliser, as applicable, to
achieve this.
20Where applicable, refit the exhaust heat
shield.
21Refit the roadwheels and lower the vehicle
to the ground. Do not fully tighten the
roadwheel bolts until the vehicle is resting on
its wheels.
27Handbrake cable - removal
and refitting
3
Models with rear drum brakes
Removal
1The handbrake cable is in two sections. The
longer section runs from the handbrake
operating rod, through the adjuster, to the
right-hand brake assembly. The shorter
section runs from the adjuster to the left-hand
brake assembly. The two sections of the cable
can be renewed independently.
2Where applicable, remove the wheel trim(s),
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts.
Chock the front wheels, jack up the rear of the
vehicle, and support securely on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheel(s).
3Note the routing of the handbrake cable(s),
as an aid to refitting.
4Remove the relevant brake drum(s), with
reference to Section 11.
Longer cable
Removal
5Note the length of exposed thread at the
handbrake cable adjuster on the torsion
beam, then unscrew the adjuster nut from the
threaded rod.
6Disconnect the cable from the handbrake
lever operating rod on the vehicle underbody
(see illustration).
7Detach the cable from the guides on the
underbody. Note that the cable can be fed
through certain guides, but in some cases, the
guide brackets must be bent away from the
underbody to allow the cable to be withdrawn.
8Detach the cable from the adjuster on the
torsion beam.
9Unhook the cable end from the lever on the
brake shoe, then using a screwdriver, prise
out the lockplate that secures the handbrake
cable in the backplate.
10Withdraw the cable from the vehicle,
releasing it from the guide on the torsion
beam.
Refitting
11Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
12Screw the adjuster nut onto the threaded
rod to the position noted before removal.
13Ensure that the handbrake cable is routed
as noted before removal.
14Refit the brake drum, (Section 11).
15Before refitting the roadwheel(s) and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, adjust the
handbrake, as described in Section 26.
Shorter cable
Removal
16Note the length of exposed thread at the
handbrake cable adjuster on the torsion
beam, then unscrew the adjuster nut from the
threaded rod. Continue as described in
paragraphs 8 to 10.
Braking system 9•19
27.6 Handbrake cable connection to handbrake lever operating
rod
1 Handbrake cable
2 Connecting link3 Handbrake lever operating rod26.14 Using a screwdriver to turn the handbrake adjuster wheel -
model with rear disc brakes
9
Page 151 of 525

Refitting
17Proceed as described in paragraphs 11
to 15 inclusive.
Models with rear disc brakes
(SOHC)
General
18The procedure is as described for models
with rear drum brakes, remembering the
following points.
19Ignore the references to removal and
refitting of the brake drum.
20Note that there is no lockplate securing
the handbrake cable to the brake backplate,
but the return spring must be unhooked from
the cable end.
21On models with a catalytic converter,
when removing the longer cable, unscrew the
four securing nuts and withdraw the exhaust
centre box heat shield by carefully sliding it
round the centre box.
DOHC models
Removal
22The left and right-hand handbrake cables,
and the equaliser yoke, are removed as an
assembly on DOHC models.
23Loosen the rear roadwheel bolts, then
chock the front wheels, jack up the rear of the
vehicle, and support securely on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheels.
24Note the routing of the handbrake cables,
as an aid to refitting.
25On models with a catalytic converter,
unscrew the four securing nuts and withdraw
the exhaust centre box heat shield by
carefully sliding it round the centre box.
26Note the length of exposed thread at the
cable equaliser yoke, then unscrew the
securing nut and disconnect the equaliser
yoke from the handbrake lever operating rod.
27Unhook the cable ends from the brake
shoe operating levers and the return springs
(see illustration).
28Detach the cable from the guides on the
underbody and the semi-trailing arms. Note
that the cables can be fed through certainguides, but in some cases, the guide brackets
may have to be bent away from the
underbody to allow the cables to be
withdrawn.
29Withdraw the cables and equaliser
assembly from the vehicle.
Refitting
30Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
31Use a new self-locking nut to secure the
equaliser yoke to the handbrake lever
operating rod, and screw the nut onto the rod
to the position noted before removal.
32Ensure that the cables are routed as
noted before removal.
33Before refitting the roadwheels and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, adjust the
handbrake, as described in Section 26.
28Handbrake lever - removal
and refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Jack up the vehicle, and support on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned securely under the body side
members.
3On models with a catalytic converter,
unscrew the four securing nuts and withdraw
the exhaust centre box heat shield by
carefully sliding it round the centre box.
4On all SOHC models, note the length of
exposed thread at the handbrake cable adjuster
on the torsion beam, then slacken the adjuster
to enable the cable to be disconnected from the
handbrake lever operating rod. Disconnect the
cable from the operating rod and slide the
rubber sealing grommet from the underbody
and operating rod.
5On DOHC models, note the length of
exposed thread at the handbrake cable
equaliser yoke, then unscrew the securing nut
and disconnect the equaliser yoke from the
handbrake lever operating rod. Slide the
rubber sealing grommet from the underbody
and operating rod.
6Remove the front passenger seat, as
described in Chapter 11.7Remove the rear section of the centre
console, as described in Chapter 11.
8Access to the handbrake lever-to-floor
mounting bolts is provided by slits in the
carpet. If no slits are provided, either carefully
cut some, or release and fold back the carpet.
9Unscrew the mounting bolts, and withdraw
the handbrake lever sufficiently to disconnect
the handbrake “on” warning lamp switch
wiring (see illustration).
10Disconnect the wiring and withdraw the
handbrake lever and operating rod from the
vehicle.
11A worn ratchet segment can be renewed
by driving the securing sleeve from the
handbrake lever, using a metal rod or a bolt of
similar diameter (see illustration).
12Drive the new sleeve supplied with the
new segment into the lever to permit a little
play between the segment and lever.
13If desired, a new pawl can be fitted if the
original pivot rivet is drilled out (see
illustration).
14Rivet the new pawl so that the pawl is still
free to move.
15The handbrake “on” warning lamp switch
can be removed from the lever assembly after
unscrewing the securing bolt.
Refitting
16Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
17Refit the rear section of the centre
console, as described in Chapter 11.
18Refit the front passenger seat, as
described in Chapter 11.
9•20Braking system
28.13 Drilling out the handbrake lever pawl
pivot pin
28.11 Driving out the handbrake lever
ratchet segment securing sleeve28.9 Handbrake lever securing bolts
(arrowed)27.27 Handbrake cable end fitting at brake
shoe - DOHC model
1 Operating lever
2 Cable bracket on semi-trailing arm
Page 174 of 525

Idle mixture CO content:
All carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.5 to 1.5%
20 NE and 20 SEH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.0 max.
20 XEJ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.7 to 1.2%
All other injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.3 % (at 2800 to 3200 rpm)
Air filter element:
1.4 and 1.6 litre ‘round type’ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion W103
1.6 and 1.8 litre ‘square type’ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion U512
1.8 litre ‘round type’ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion type not available
2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion U554
Fuel filter:
1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 litre ‘in-line’ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion L201
Ignition system:
Ignition timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Refer to Chapter 5
Spark plugs
SOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RN9YCC or RN9YC
DOHC models:
except C20 XE and X20 XEV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RC9MCC *
C20 XE and X20 XEV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Vauxhall P/N 90444724 (FR8LDC)
Plug gap:
RN9YCC and RC9MCC * . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.8 mm
RN9YC * . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.7 mm
FR8LDC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.7 to 0.8 mm
* Information on spark plug types and electrode gaps is as recommended by Champion Spark Plug. Where alternative types are used, refer to the
manufacturer’s recommendations
Brakes
Minimum pad friction material thickness (including backing plate):
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7.0 mm
Minimum shoe friction material thickness:
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.5 mm above rivet heads
Tyres
Tyre size:
51/2 J x 13 wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .165 R13-82T
51/2 J x 14 wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175/70 R14-82T, 195/60 R14-85H, or 195/60 R14-85V
6J x 15 wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .195/60 R15-87V or 205/55 R15-87V
PressuresSee “Weekly checks”
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Automatic transmission drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Roadwheel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11081
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Engine oil (sump) drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5541
Servicing Specifications 1•3
1
The maintenance intervals in this manual
are provided with the assumption that you,
not the dealer, will be carrying out the work.
These are the minimum maintenance intervals
recommended by the manufacturer for
vehicles driven daily. If you wish to keep your
vehicle in peak condition at all times, you may
wish to perform some of these procedures
more often. We encourage frequent
maintenance, because it enhances the
efficiency, performance and resale value of
your vehicle.
If the vehicle is driven in dusty areas, used
to tow a trailer, or driven frequently at slow
speeds (idling in traffic) or on short journeys,more frequent maintenance intervals are
recommended. Vauxhall recommend that the
service intervals are halved for vehicles that
are used under these conditions.
When the vehicle is new, it should be
serviced by a factory-authorised dealer
service department, to preserve the factory
warranty.
Maintenance is essential for ensuring safety
and for getting the best in terms of
performance and economy from your vehicle.
Over the years, the need for periodic
lubrication -oiling, greasing, and so on -has
been drastically reduced, if not eliminated.
This has unfortunately tended to lead someowners to think that because no action is
required, components either no longer exist,
or will last for ever. This is certainly not the
case; it is essential to carry out regular visual
examination comprehensively to spot any
possible defects at an early stage before they
develop into major expensive repairs.
The following service schedules are a list of
the maintenance requirements, and the
intervals at which they should be carried out,
as recommended by the manufacturers.
Where applicable, these procedures are
covered in greater detail near the beginning of
each relevant Chapter.
Maintenance schedule
Page 240 of 525

REF
Overall length: *
Saloon models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4432 mm
Hatchback models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4352 mm
Overall width: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1876 mm
Overall height (unladen): *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1400 mm
Wheelbase: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2600 mm
Track:
Front: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1426 mm
Rear: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1423 mm
Ground clearance (minimum): *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120 mm
Weights
Kerb weight: *
Dependent on model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1098 ± 101 kg
Maximum gross vehicle weight: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Refer to VIN plate
Maximum roof rack load: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100 kg
Maximum towing hitch downward load: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75 kg
Maximum towing weight: *
Trailer with brakes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1175 ± 175 kg
Trailer without brakes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .550 ± 50 kg
* Exact details depend upon model and specification.
Refer to owners handbook.
Dimensions and Weights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•1
Conversion Factors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•2
Buying Spare Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•3
Vehicle Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•3
General Repair Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•4
Jacking and Vehicle Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•5Radio/cassette unit Anti-theft System . . . . . . . .REF•5
Tools and Working Facilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•6
MOT Test Checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•8
Fault Finding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•12
Glossary of Technical Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•20
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•25
Reference REF•1
Dimensions and Weights
Page 251 of 525

Engine
m mEngine fails to rotate when attempting to start
m mEngine rotates, but will not start
m mEngine difficult to start when cold
m mEngine difficult to start when hot
m mStarter motor noisy or excessively rough in engagement
m mEngine starts, but stops immediately
m mEngine idles erratically
m mEngine misfires at idle speed
m mEngine misfires throughout the driving speed range
m mEngine hesitates on acceleration
m mEngine stalls
m mEngine lacks power
m mEngine backfires
m mOil pressure warning light illuminated with engine running
m mEngine runs-on after switching off
m mEngine noises
Cooling system
m
mOverheating
m mOvercooling
m mExternal coolant leakage
m mInternal coolant leakage
m mCorrosion
Fuel and exhaust systems
m
mExcessive fuel consumption
m mFuel leakage and/or fuel odour
m mExcessive noise or fumes from exhaust system
Clutch
m
mPedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little resistance
m mClutch fails to disengage (unable to select gears)
m mClutch slips (engine speed increases, with no increase in vehicle
speed)
m mJudder as clutch is engaged
m mNoise when depressing or releasing clutch pedal
Manual transmission
m
mNoisy in neutral with engine running
m mNoisy in one particular gear
m mDifficulty engaging gears
m mJumps out of gear
m mVibration
m mLubricant leaks
Automatic transmission
m
mFluid leakage
m mTransmission fluid brown, or has burned smell
m mGeneral gear selection problems
m mTransmission will not downshift (kickdown) with accelerator fully
depressed
m mEngine will not start in any gear, or starts in gears other than Park
or Neutral
m mTransmission slips, shifts roughly, is noisy, or has no drive in
forward or reverse gears
Driveshafts
m mClicking or knocking noise on turns (at slow speed on full-lock)
m mVibration when accelerating or decelerating
Braking system
m
mVehicle pulls to one side under braking
m mNoise (grinding or high-pitched squeal) when brakes applied
m mExcessive brake pedal travel
m mBrake pedal feels spongy when depressed
m mExcessive brake pedal effort required to stop vehicle
m mJudder felt through brake pedal or steering wheel when braking
m mBrakes binding
m mRear wheels locking under normal braking
Suspension and steering systems
m
mVehicle pulls to one side
m mWheel wobble and vibration
m mExcessive pitching and/or rolling around corners, or during
braking
m mWandering or general instability
m mExcessively stiff steering
m mExcessive play in steering
m mLack of power assistance
m mTyre wear excessive
Electrical system
m
mBattery will not hold a charge for more than a few days
m mIgnition/no-charge warning light remains illuminated with engine
running
m mIgnition/no-charge warning light fails to come on
m mLights inoperative
m mInstrument readings inaccurate or erratic
m mHorn inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
m mWindscreen/tailgate wipers inoperative, or unsatisfactory in
operation
m mWindscreen/tailgate washers inoperative, or unsatisfactory in
operation
m mElectric windows inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
m mCentral locking system inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
The vehicle owner who does his or her own maintenance according to
the recommended service schedules should not have to use this section
of the manual very often. Modern component reliability is such that,
provided those items subject to wear or deterioration are inspected or
renewed at the specified intervals, sudden failure is comparatively rare.
Faults do not usually just happen as a result of sudden failure, but
develop over a period of time. Major mechanical failures in particular are
usually preceded by characteristic symptoms over hundreds or even
thousands of miles. Those components that do occasionally fail without
warning are often small and easily carried in the vehicle.
With any fault-finding, the first step is to decide where to begininvestigations. Sometimes this is obvious, but on other occasions, a
little detective work will be necessary. The owner who makes half a
dozen haphazard adjustments or replacements may be successful in
curing a fault (or its symptoms). However, will be none the wiser if the
fault recurs, and ultimately may have spent more time and money than
was necessary. A calm and logical approach will be found to be more
satisfactory in the long run. Always take into account any warning
signs or abnormalities that may have been noticed in the period
preceding the fault - power loss, high or low gauge readings, unusual
smells, etc. - and remember that failure of components such as fuses
or spark plugs may only be pointers to some underlying fault.
REF•12Fault Finding
Introduction
Page 253 of 525

MFaulty ignition coil (Chapter 5).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2A).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
Engine hesitates on acceleration
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the carburettor/throttle body, inlet manifold or
associated hoses (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
Engine stalls
MVacuum leak at the carburettor/throttle body, inlet manifold or
associated hoses (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
MFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MFuel tank vent blocked, or fuel pipes restricted (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
Engine lacks power
MTiming belt incorrectly fitted or tensioned (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
MFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2A).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the carburettor/throttle body, inlet manifold or
associated hoses (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
MBrakes binding (Chapters 1 and 9).
MClutch slipping (Chapter 6).
Engine backfires
MTiming belt incorrectly fitted or tensioned (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MVacuum leak at the carburettor/throttle body, inlet manifold or
associated hoses (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
Oil pressure warning light illuminated with engine
running
MLow oil level, or incorrect oil grade (Chapter 1).
MFaulty oil pressure warning light switch (Chapter 12).
MWorn engine bearings and/or oil pump (Chapter 2A).
MHigh engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
MOil pressure relief valve defective (Chapter 2A).
MOil pick-up strainer clogged (Chapter 2A).
Engine runs-on after switching off
MExcessive carbon build-up in engine (Chapter 2A).
MHigh engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
MFaulty fuel cut-off solenoid - carburettor models (Chapter 4A).
MFuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models (Chapter 4B).
Engine noises
Pre-ignition (pinking) or knocking during acceleration or
under load
MIgnition timing incorrect/ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MIncorrect grade of spark plug (Chapter 1).
MIncorrect grade of fuel (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the carburettor/throttle body, inlet manifold or
associated hoses (Chapter 4A or 4B).
MExcessive carbon build-up in engine (Chapter 2A).
MBlocked carburettor jet(s) or internal passages - carburettor
models (Chapter 4A).
MBlocked injector/fuel injection system fault - fuel-injected models
(Chapter 4B).
Whistling or wheezing noises
MLeaking inlet manifold or carburettor/throttle body gasket
(Chapter 4A or 4B).
MLeaking exhaust manifold gasket or pipe-to-manifold joint
(Chapter 4C).
MLeaking vacuum hose (Chapters 4A, 4B, 4C, 5, 9 and 12).
MBlowing cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2A or 2B).
Tapping or rattling noises
MWorn valve gear or camshaft (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MAncillary component fault (coolant pump, alternator, etc.)
(Chapters 3, 5, etc.).
Knocking or thumping noises
MWorn big-end bearings (regular heavy knocking, perhaps less
under load), (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MWorn main bearings (rumbling and knocking, perhaps worsening
under load), (Chapter 2A or 2B).
MPiston slap (most noticeable when cold), (Chapter 2A).
MAncillary component fault (coolant pump, alternator, etc.)
(Chapters 3, 5, etc.).
REF•14Fault Finding
Engine (continued)
Page 256 of 525

Note:Before diagnosing suspension or steering faults, be sure that the
trouble is not due to incorrect tyre pressures, mixtures of tyre types, or
binding brakes.
Vehicle pulls to one side
MDefective tyre (Chapter 1).
MExcessive wear in suspension or steering components (Chapters 1
and 10).
MIncorrect front wheel alignment (Chapter 10).
MAccident damage to steering or suspension components
(Chapter 1).
Wheel wobble and vibration
MFront roadwheels out of balance (vibration felt mainly through the
steering wheel), (Chapters 1 and 10).
MRear roadwheels out of balance (vibration felt throughout the
vehicle), (Chapters 1 and 10).
MRoadwheels damaged or distorted (Chapters 1 and 10).
MFaulty or damaged tyre (Chapter 1).
MWorn steering or suspension joints, bushes or components
(Chapters 1 and 10).
MWheel bolts loose (Chapters 1 and 10).
Excessive pitching and/or rolling around corners,
or during braking
MDefective shock absorbers (Chapters 1 and 10).
MBroken or weak spring and/or suspension component (Chapters 1
and 10).
MWorn or damaged anti-roll bar or mountings (Chapter 10).
Wandering or general instability
MIncorrect front wheel alignment (Chapter 10).
MWorn steering or suspension joints, bushes or components
(Chapters 1 and 10).
MRoadwheels out of balance (Chapters 1 and 10).
MFaulty or damaged tyre (Chapter 1).
MWheel bolts loose (Chapters 1 and 10).
MDefective shock absorbers (Chapters 1 and 10).
Excessively stiff steering
MLack of steering gear lubricant (Chapter 10).
MSeized track rod end balljoint or suspension balljoint (Chapters 1
and 10).
MBroken or incorrectly adjusted auxiliary drivebelt - power steering
(Chapter 1).
Fault Finding REF•17
REF
Note:Before assuming that a brake problem exists, make sure that the
tyres are in good condition and correctly inflated, that the front wheel
alignment is correct, and that the vehicle is not loaded with weight in an
unequal manner. Apart from checking the condition of all pipe and
hose connections, any faults occurring on the anti-lock braking system
should be referred to a Peugeot dealer for diagnosis.
Vehicle pulls to one side under braking
MWorn, defective, damaged or contaminated brake pads/shoes on
one side (Chapters 1 and 9).
MSeized or partially seized front brake caliper/wheel cylinder piston
(Chapters 1 and 9).
MA mixture of brake pad/shoe lining materials fitted between sides
(Chapters 1 and 9).
MBrake caliper or backplate mounting bolts loose (Chapter 9).
MWorn or damaged steering or suspension components
(Chapters 1 and 10).
Noise (grinding or high-pitched squeal) when
brakes applied
MBrake pad or shoe friction lining material worn down to metal
backing (Chapters 1 and 9).
MExcessive corrosion of brake disc or drum. This may be apparent
after the vehicle has been standing for some time (Chapters 1 and 9).
MForeign object (stone chipping, etc.) trapped between brake disc
and shield (Chapters 1 and 9).
Excessive brake pedal travel
MInoperative rear brake self-adjust mechanism - drum brakes
(Chapters 1 and 9).
MFaulty master cylinder (Chapter 9).
MAir in hydraulic system (Chapters 1 and 9).
MFaulty vacuum servo unit (Chapter 9).
Brake pedal feels spongy when depressed
MAir in hydraulic system (Chapters 1 and 9).
MDeteriorated flexible rubber brake hoses (Chapters 1 and 9).
MMaster cylinder mounting nuts loose (Chapter 9).
MFaulty master cylinder (Chapter 9).
Excessive brake pedal effort required to stop
vehicle
MFaulty vacuum servo unit (Chapter 9).
MDisconnected, damaged or insecure brake servo vacuum hose
(Chapter 9).
MPrimary or secondary hydraulic circuit failure (Chapter 9).
MSeized brake caliper or wheel cylinder piston(s) (Chapter 9).
MBrake pads or brake shoes incorrectly fitted (Chapters 1 and 9).
MIncorrect grade of brake pads or brake shoes fitted (Chapters 1
and 9).
MBrake pads or brake shoe linings contaminated (Chapters 1 and 9).
Judder felt through brake pedal or steering wheel
when braking
MExcessive run-out or distortion of discs/drums (Chapters 1 and 9).
MBrake pad or brake shoe linings worn (Chapters 1 and 9).
MBrake caliper or brake backplate mounting bolts loose (Chapter 9).
MWear in suspension or steering components or mountings
(Chapters 1 and 10).
Brakes binding
MSeized brake caliper or wheel cylinder piston(s) (Chapter 9).
MIncorrectly adjusted handbrake mechanism (Chapter 9).
MFaulty master cylinder (Chapter 9).
Rear wheels locking under normal braking
MRear brake shoe linings contaminated (Chapters 1 and 9).
MFaulty brake pressure regulator (Chapter 9).
Braking system
Suspension and steering