Page 98 of 394

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2
OPERATION No MA.IE. 144-00 : Chtiractcristics o/ the e 1,-Jc,tror,ic H clcctroltic
fire1 injc ctiwt systettt.
((L-JETRONIC,,
The H L-Jetronic 1) system is’an intermittent low-pressure injection system which injects petrol into the inlet
manifold.
The system measures the quantity of air drawn in by the engine. which is the main parameter for calculating
the amount of fuel. to be injected. The metering of the fuel is carried out by electro-magnetically triggered
injectors. These are under constant fuel pressure. The quantity of fuel injected is proportional to the duration
of injection. which in turn is optimally determined for any given engin& operating condition by an electronic
control unit ( E.C.U. ) from information supplied by several electric sensors.
One of the principal contributions of the H L-Jetronic H system is the reduction in the level of pollution of the
exhaust emissions.
The (( L-Jetronic v system is made up of the following components :
1
: Electric fuel pump
2 : Fuel filter
3 : Thermal switch
4 :, Double relay
5 : Electronic control unit ( E.C.U. )
6 : Supplementary air control
7 : Pressure regulator
8 : Injectors
9 : Cold-start injector
10. Idling speed adjustment screw
11 : Air-flow sensor ( with incorporated air temperature sensor )
12 : Switch on throttle butterfly spindle
13 : Additional resistors for the injectors (8)
Page 101 of 394
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6
OPERATION No MA.IE. 144 - 00 : Churacteristics o/ the H L-Jetronic )) electronic
/uel injectian .system. FUEL CIRCUIT
A multiple roller-valve pump ( 2 ) draws the fuel from tank ( 1) and provides the injection pressure,
A filter (4) is fitted to the system.
In the fuel return pipe, the pressure regulator ( 3) maintains, under fuel load! a relative constant fuel pressure of
2 bars ( 29 ‘psi ).
The pressure regulator is connected to the intake manifold by a flexible pipe0 This allows the difference of
pressure betw.een the fuel and the inlet manifold to remain constant.Thus the necessary quantity of fuel delivered
by the injectors ( 5) depends exclusively on its duration of opening.
Page 108 of 394

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine INJECTORS ( i ) :
Each cylinder is supplied by an electro-magnetically controlled injector which is fitted in the inlet duct;
the injector vaporises the fuel upstream of the inlet valve. In the case of the (( L-Jetronic )) system. all the
injectors operate simultaneously. However, in order to ensure regular fuel supply to the cylinders, there are
two injections for each rotation of the camshaft, each one supplying half the metered quantity of fuel required I
for the complete engine cycle.
The injector consists of a valve housing and an injector needle fitted with a magnetic core. The mobile magnetic
/
core is in one piece with the needle which in turn is compressed against the air-tight injector housing seat by
a helicoidal spring. At the rear end of the injector, there is a solenoid. and at the front a guide for the injector
needle.
Impulses coming from the E.C.U. create a magnetic.field in the solenoid; the magnetic core is attracted, and the
needle lifts off its seat the fuel under pressure is free to pass through, The movement of the magnetic core is
approximately 0.15 mm.
The duration of opening is determined by the E.C.U. as a function of the operating conditions of the engine at the
moment in question{. TEMPERATURE SENSORS t(
When the engine is started, for a temperature of approximately - 20” C, it needs two to three times more fuel than
when it has reached normal operating temperature. The enrichment of the mixture must be reduced as the engine
warms up, and must cease as soon as the engine has reached normal operating temperature. In’order to start off
this regulating procedure, the engine temperature must be communicated to the E.C.U. ( Electronic Control Unit ).
This is the object .of the temperature sensors.
The temperature sensor consists of a hollow threaded rod in which is located an NTC Thermistor made in semi-
conducting material. The letters .NTC, which signify (( negative temperature coefficient )) characterise its specific
property : its electrical resistance decreases as the temperature increases.
The (( L-Jetronic 1) system is fitted with.a water temperature sensor ( 2) and an air temperature sensor, the latter
situated in the air-flow sensor.
Page 114 of 394
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Op. MA.IE. 144.00 19
/
One-way valve
Safety valve
PRESSURE REGULATOR
Id.17
t Return to tank
Page 136 of 394

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5. Air-flow sensor ( DIAGRAM 5 )
- Disconnect the E.C.U.
- Using an ohmmeter check the continuity of circuits (( 6 )a, H 7 )) (( 8 H and (( 9 )) linking the air-flow sensor to
the multiple terminal board. as well as the continuity between each of the terminals
- The air-flow meter does not require any maintenance. It is not necessary to oil the flop. It must work without
high spot or catching
When the air-flow sensor is removed blank off the ducts so OS to protect it from dust
- Check the air circuit for air-tightness.
6. Resistors and injectors :
- A dirty injector may cause o lock of power. or on unstable idling speed.
- It is possible to test the functioning of the injectors with the engine idling by disconnecting each injector
in turn the engine rpm should decrease each time.
- Disconnect the E C U
- The resistance of an injector is 2 to 3 II.
- Each supplementary resistance is 5 to 7 R
- The volume delivered by an injector ( kept constantly open and under the normal operating pressure ) is
approximately 200 cm3 /min ( 12 25 cu in/min )-
- If the rubber pipe on one of the injectors appears wet on the outside, the injector must be replaced.
- Using an ohmmeter, check the continuity of the circuits
Page 145 of 394
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine OPERATION No MA.IE. 144-0 : (,hcrkir~g m/cl nrl;tts/ir/<~ I/W a I.-J~~/m,i~ ~~otectrot,ic Op. MA.IE. 144-O 25 fi~cl irijection systc~rti.
ANNEXE : A - CHECKING THE IGNITION
THE ENGINE TURNS, BUT DOES
NOT FIRE
Page 149 of 394
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 28 OPERATION N” MA.IE. 144-O : Ch <,c ,ng n,,d nlfjusfiup Ihe u I.-~<~tro,,ir i) <~lrr/mr,ir k’
/,,,.I i,,jrr/io,, S~S,W1, ANNEXE : D - ADJUSTING THE IDLING SPEED AND THE EXHAUST EMISSION
CHECKING CONDITIONS
1.
Checking the idling speed must be carried out
on a clean engine on which the ignition and the
valve clearances are properly adjusted and
fitted with a clean air-filter.
2. Check that the throttle butterfly returns correctly
to its stop.
3. Do not load the alternator by switching an any
of the electrical components, except the iqnition
and the electric cooling fan (s) 4.
Run the engine to bring the oil temperature up
to 70 +o 80’ C ( wait for the electric cooling
fan is) to cut in ). IMPORTANT : Use exclusively (I high tension
tachometer ( do not damage the H.T. lead of
the ignition wiring harness ).
ADJUSTMENT
1. Check that the butterfly is not jammed in position
when it is resting against its stop.
2. Wait for the electric cooling fan (s) to cut in.
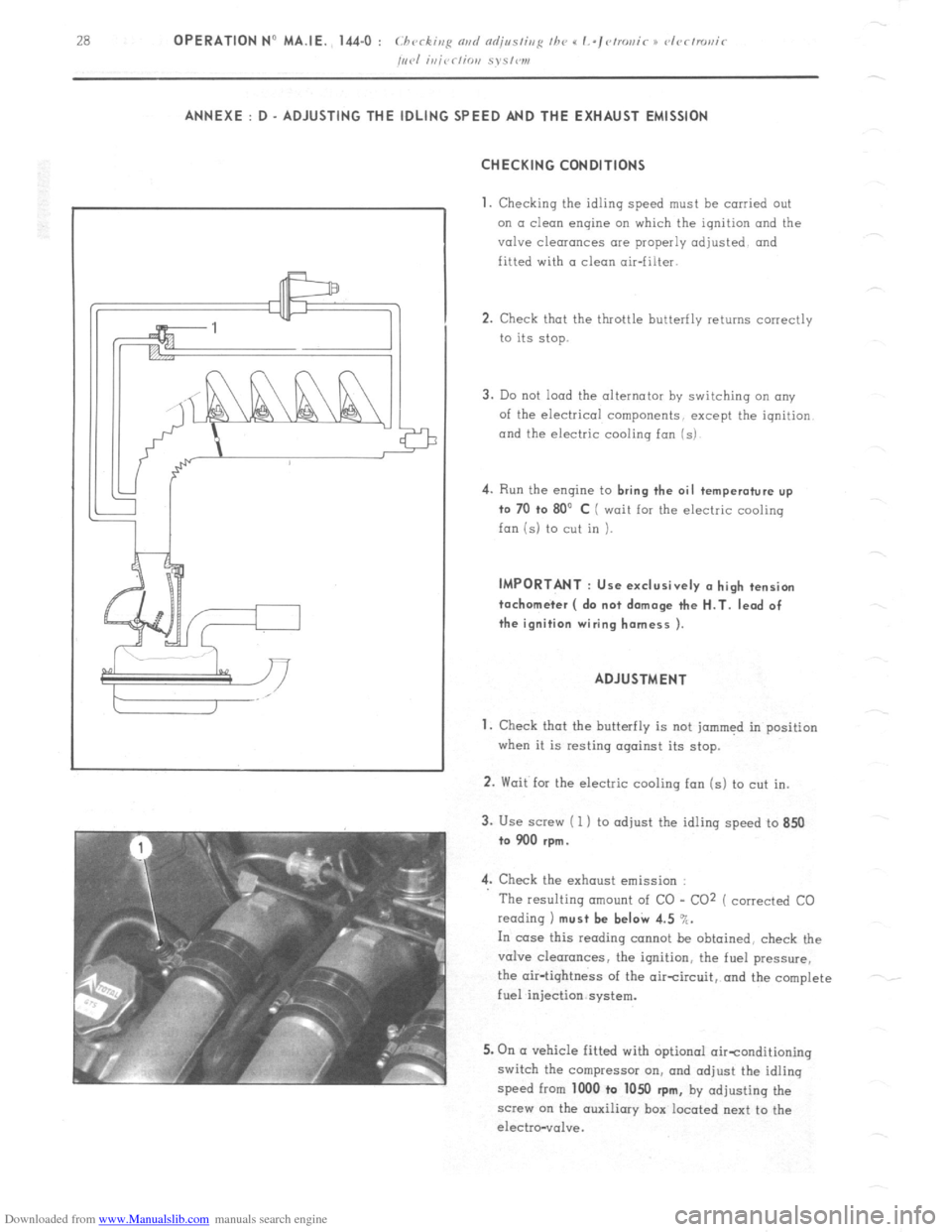
3. Use screw ( 1 ) to adjust the idling speed to 850
to 900 rpm.
4. Check the exhaust emission :
The resulting amount of CO - CO2 ( corrected CO
reading 1 must be beI& 4.5 %.
In case this reading cannot be obtained, check the
valve clearances, the ignition, the fuel pressure,
the air-tightness of the aircircuit, and the complete
fuel injection system.
5. On (I vehicle fitted with optional oirtonditioning
switch the compressor on, and adjust the idling
speed from 1000 to 1050
rpm, by adjusting the
screw on the auxiliary box located next to the
electro-vol”e.
Page 150 of 394
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine OPERATION No MA. 173-O : Chrrkivp fhr prmd s,,pp/> Op. MA. 173.0 1
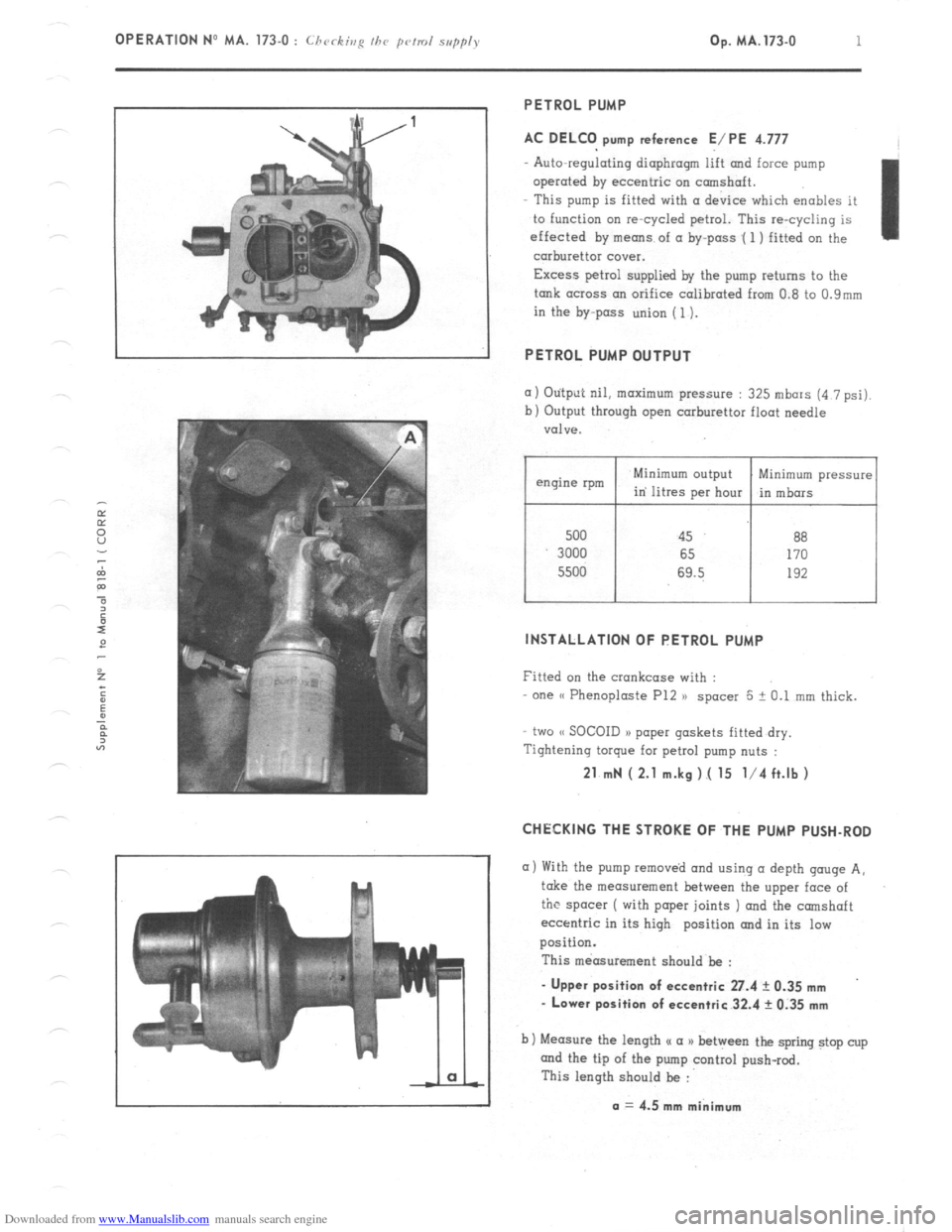
PETROL PUMP
AC DELCO pump reference E/PE 4.777
Auto-regulating diaphragm lift and force pump
operated by eccentric on camshaft.
This pump is fitted with (I device which enables it
to function on re-cycled petrol. This re-cycling is
effected by means of a by-pass .( 1 ) fitted on the
carburettor cover.
Excess petrol supplied by the pump returns to the
tank across an orifice calibrated from 0.8 to 0.9mm
in the by-pass union (1).
PETROL PUMP OUTPUT
(I) Otitput nil, maximum pressure : 325 mbars (4 7 psi).
b) Output through open carburettor float needle
valve.
500 45 88
3000 65 170
5500 69.5 192
I I
Minimum pressure
in mbors
INSTALLATION OF PETROL PUMP
Fitted on the crankcase with :
one (( Phenoploste P12 )) spacer 5 + 0.1 mm thick.
two (< SOCOID a> paper gaskets fitted dry.
Tightening torque for petrol pump nuts :
21 mN ( 2.1 m.kg ).( 15 l/4 ft.lb )
CHECKING THE STROKE OF THE PUMP PUSH-ROD
a) With the pump removed and using (I depth gouge A,
take the measurement between the upper face of
the spacer ( with paper joints ) and the camshaft
eccentric in its high position and in its low
position.
This measurement should be :
- Upper position of eccentric 27.4 ? 0.35 mm
- Lower position of eccentric 32.4 rk 0.35 mm
b) Measure the length u a a) between the spring stop cup
and the tip of the pump control push-rod.
This length should be :
a = 4.5 mm minimum