1977 DATSUN PICK-UP oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: oil pressurePage 291 of 537

Automatic
Transmission
I
M
nual
f4fL
J
0
I
1
r
PR
0
range
kickdown
Shift
valves
In
2nd
gear
position
To
queeO
t
Front
Clutch
Low
a
A
8
8
e
e
a
o
14
0
Oil
COO
R
L
ubrication
n
0
Drain
1
4
j
v
I
Front
Lub
icet
p
n
o
I
Thron
p
ain
V
I
j
R
gu
ato
V
I
Not
Ma
ked
X
r
p
n
Li
pr
IGo
no
f
d
p
l
Governor
p
c
Torque
CO
I
1
p
ThrOWepr
VK
Th
o
V
lv
7
1
iftV
8
Throttle
BKk
up
V
hl
ID
So
e
COw
P
Ifk
Check
V
I
1
24
5
Mod
Yo
I
@2nCl
3rdSl
lilr
V
12
3
ht
2nd
Shih
V
5
L
I
X
S
COnd
Primary
G
rw
Va
Gov
nor
Valve
AT
27
Fig
AT
39
Oil
pressure
circuit
diagram
D
ronge
kickdown
shift
values
in
2nd
gear
position
Page 293 of 537

Automatic
Transmission
2
range
2nd
gear
Torqu
Con
Fron
Clutch
l
ow
A
B
ke
Br
I
12
011
Cool
i
IL
12
ID
v
Th
ot
Valve
7
T
onl
Beck
up
V
ID
So
0
Id
1ft
v
Front
Lubric
t
Orltic
Check
Va
Or
lnVal
e
Throttle
Dr
in
V
l
P
Modif
Va
15
BJl
@
2nct
3rd
Tim
If
Ve
12
3
1
2nd
Stolt
21
Se
onc
l
Lock
Va
3
I
PR
02
1
s
I
Jl
J
I
r
A
ul
Gr
v
2
w
Valve
Note
Merltedl
D
a
n
I
G
v
Line
p
IOo
nOf
f
d
pr
G
no
p
r
c
o
Torque
con
pr
Thron
p
re
ond
a
nor
v
Fig
A
T
42
Oil
pressure
circuit
diagram
2
range
2nd
gear
AT
29
Page 294 of 537

1
RANGE
LOW
GEAR
Automatic
Transmission
f
Wilen
slJrting
in
I
range
the
drlvlIlg
gear
is
IOl
ked
to
the
low
gear
fJIIIJ
In
H
range
the
rear
clutch
is
engJged
and
the
low
and
reverse
brake
hulds
he
onnecting
drum
and
feac
planet
carrier
from
rotating
The
power
tlow
lakes
place
through
the
input
shaft
and
into
lhe
rear
clutch
ROlalion
of
the
rear
clutch
drives
lhe
rear
dutch
hub
and
front
internal
gear
The
front
internal
gear
rotates
the
front
planetary
gears
clockwise
to
cause
the
sun
gear
to
rotate
counter
clockwise
Counterclockwise
rotation
of
the
sun
gear
turns
the
rear
planetary
gear
clockwise
The
rear
planet
carrier
splined
to
the
connecting
drum
is
held
from
rotating
by
the
low
and
reverse
brake
The
clockwise
rotation
of
the
rear
planetary
gears
therefore
rotates
the
rear
internal
gear
and
internal
drive
tlange
The
internal
drive
tlange
is
splined
to
the
output
shaft
and
rotates
the
uutput
shaft
clockwise
However
the
output
shaft
rotates
at
a
lower
speed
compared
to
that
of
the
input
shaft
This
is
caused
by
the
fact
Ihat
the
front
planet
carrier
rotates
at
the
same
speed
as
Ihe
OUlput
shaft
in
the
same
direction
since
the
carrier
is
splined
to
the
output
shaft
The
front
internal
gear
and
planetary
gear
assem
bly
are
rotating
in
the
same
direction
but
the
planet
carrier
is
rotating
at
a
speed
slower
than
the
ring
gear
So
the
gear
ralio
of
this
speed
range
is
a
combination
of
the
ratios
provided
by
the
front
and
rear
planetary
gear
as
semblies
When
the
manual
valve
Vis
posi
tioned
at
I
the
line
pressure
7
is
applied
into
the
line
pressure
circuits
I
4
and
5
The
oil
pressure
in
5
actuates
the
luw
and
reverse
brake
after
being
introduced
into
the
circuit
12
through
Ihe
1st
2nd
shift
valve
ID
and
the
line
pressure
I
acts
on
C
A
T076
Fig
AT
43
Power
transmission
during
1
J
range
Fai1
A
TOn
Fig
AT
44
Operation
of
each
mechanism
during
JJ
range
Clutch
Low
Band
servo
On
Parking
Gm
Range
reverse
w
pawl
ratIO
Front
Rur
brake
Operatlon
Release
clulCh
Park
on
on
Reverse
2
182
on
on
on
Neutral
01
low
2
458
on
on
Drive
02
Second
1
458
on
on
03
Top
1000
on
on
on
on
2
Second
1
458
on
on
2
Second
IAS8
on
on
I
1
low
2
458
on
on
the
rear
clutch
and
governor
The
line
pressure
4
acts
in
the
same
manner
as
in
2
range
Similar
to
that
of
the
D
range
the
line
pressure
inr
reases
with
the
degree
of
accelerator
pedal
depression
and
the
line
pressure
decreases
with
the
increase
of
car
speed
The
governor
pressure
15
which
acts
on
the
I
st
2nd
shift
valve
does
not
increase
until
it
overcomes
the
combined
force
of
the
line
pressure
12
and
the
spring
causing
no
st
2nd
speed
cha
nge
AT
30
Page 295 of 537

Automatic
Transmission
1
range
Low
gear
14
Down
ift
llll
Oid
VK
@50
I
10
Th
o
D
IttV
v
il
Dr
in
14
I
Front
Lubrlc
t
Oritlc
O
mV
I
i
ChKk
V
Th
on
P
Modif
t
0
11
1
IS
V
g
M
nu
V
l
PR
NOI
M
keel
X
Ir
0
11
1
1
1
P
IOov
nOt
tMod
P
O
no
p
Torqul
con
pr
Tn
ont
pr
AT
31
1M
2nd
hlf
23
6
J
s
ond
O
V
i
I
I
V
Oov
1
Of
v
Fig
A
T
45
Oil
pressure
circuit
diagram
II
II
range
Low
gear
Page 307 of 537

Automatic
Transmission
i
r
11
I
@
@
j
A
T290
Assembly
I
Prior
to
assembly
dip
all
parts
in
clean
automatic
transmission
fluid
Reverse
disassembly
procedure
to
assemble
brake
2
Use
extreme
care
to
avoid
dam
aging
rubber
ring
when
installing
seal
lace
3
Blow
compressed
air
from
apply
side
of
piston
to
test
for
definite
piston
operation
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
93
7
i
8
ror
1
1
r
c
f
f
A
J
II
1
0
c
r
1
1
I
@
L
O
j
0
n
iJ
fl
IV
I
AT160
Fig
AT
93
Testing
piston
Apply
side
4
With
apply
side
of
piston
plugged
with
thumb
blow
compressed
air
into
cylinder
from
release
side
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
94
If
retainer
is
raised
a
little
it
is
an
indication
that
attaching
bolts
are
loose
calling
for
retightening
1
Anchor
end
pin
2
Band
strut
3
Apply
4
Release
5
Return
spring
6
Band
servo
piston
stem
7
Band
servo
piston
8
Servo
retainer
9
Brake
band
assembly
10
Transmission
case
Fig
AT
92
Sectional
view
ofseruo
piston
7
o
i
J
1S
I
z
1
Y
i
1
t
9
c
fa
AT161
Fig
AT
94
Testing
piston
Release
side
GOVERNOR
Disassembly
I
Separate
governor
from
oil
dis
tributor
by
unscrewing
attaching
bolts
2
To
disassemble
secondary
gover
nor
remove
spring
seat
spring
and
secondary
governor
valve
from
valve
body
in
that
order
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
95
To
control
val
i
1
3
5MI
n
ID
r
Ii
I
4
From
control
valve
Line
pre
sure
I
I
A
TOgO
4
Oil
distributor
5
Output
shaft
I
Primary
governor
2
Secondary
governor
3
Governor
valve
body
Fig
AT
95
Testing
secondary
govemor
AT
43
3
If
primary
governor
is
to
be
dis
assembled
for
any
purpose
remove
spring
seat
primary
governor
valve
spring
and
spring
seat
Inspection
I
Check
valve
for
faulty
condition
Replace
spring
if
found
weakened
beyond
use
Faulty
piston
should
also
be
replaced
with
a
new
one
2
Examine
to
see
if
primary
gover
nor
slides
freely
without
binding
3
To
determine
if
secondary
gaver
nor
is
in
good
condition
blow
air
under
light
pressure
into
hole
at
A
and
listen
for
noise
like
that
of
a
model
plane
Assembly
Reverse
disassembly
procedure
to
assemble
governor
Note
Do
not
confuse
primary
gover
nor
with
secondary
governor
After
installation
check
that
spring
is
not
deflected
OIL
PUMP
Disassembly
I
Free
pump
cover
from
pump
housing
by
removing
attaching
bolts
2
Take
out
inner
and
outer
gears
from
pump
housing
Inspection
I
Inspect
for
wear
or
damage
to
gear
teeth
Replace
rubber
ring
if
found
damaged
beyond
use
2
Using
a
straight
edge
and
feelers
measure
pump
and
gear
clearances
as
follows
Clearance
between
inner
or
outer
gear
and
pump
cover
See
Figure
AT
96
Standard
clearance
0
02
to
0
04
mm
0
0008100
0016
in
Replace
if
over
0
08
mm
0
00
11
in
Page 309 of 537
I
F
1
D
t
l
a
J
n
f
19l1
Ull
IU
P
C
o
J
CJ
IODrR
CC
t
LL6
SJQIl2J
lhl
fB
rt
AT169
Fig
AT
102
Removing
separate
pllJte
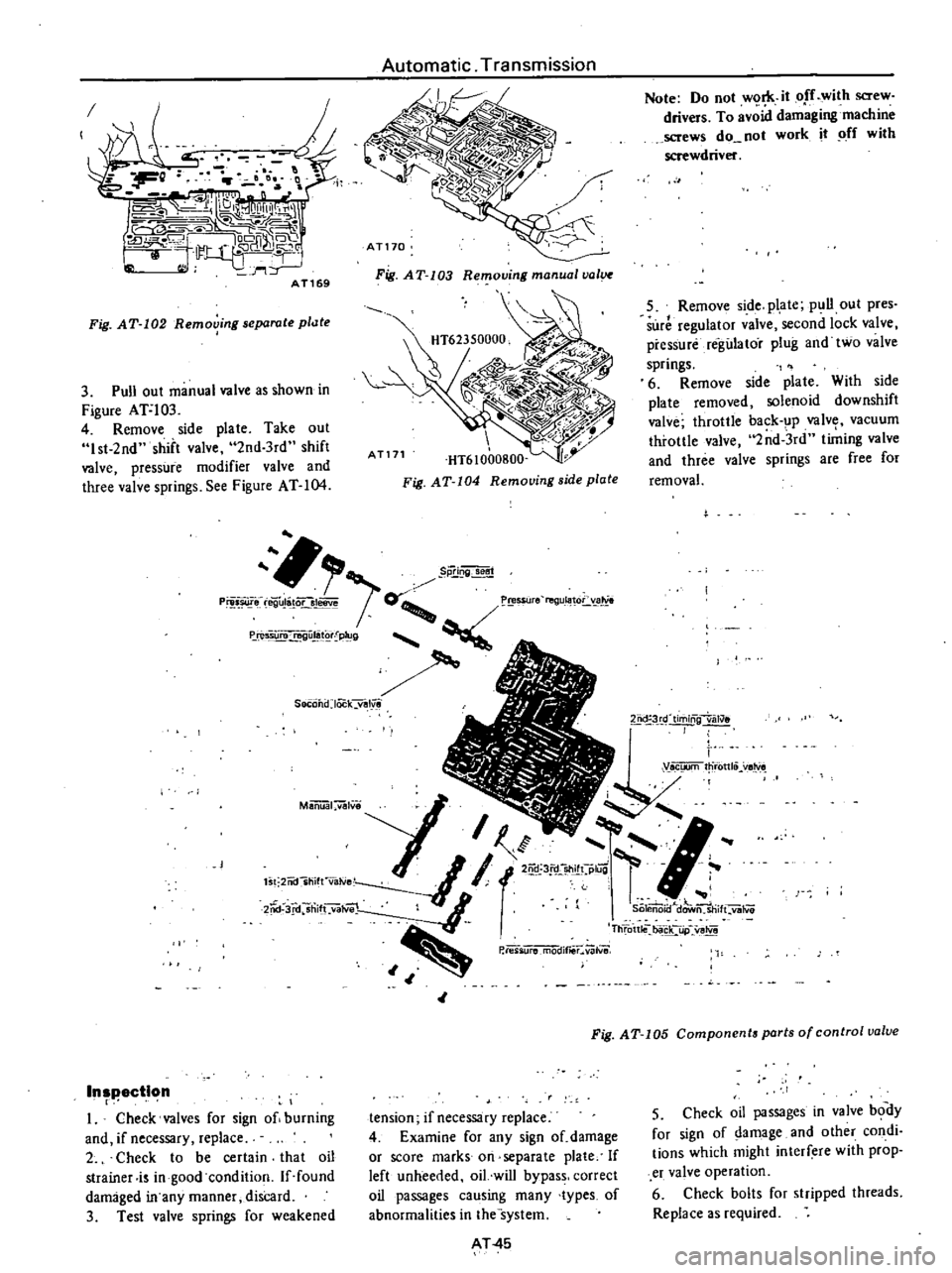
3
Pull
out
manual
valve
as
shown
in
Figure
Ar103
4
Remove
side
plate
Take
out
1st
2nd
shift
valve
2nd
3rd
shift
valve
pressure
modifier
valve
and
three
valve
springs
See
Figure
AT
104
Automatic
Transmission
Fig
AT
103
Removing
manual
val
AT1
1
HT61000800
Fig
AT
104
Removing
side
plate
g
p
e
eguJa
Of
le6Ve
or
r
essure
reguJl
oL
@iO
I
f
g
SecOni
J
lOCltvalYi
y
h
l
l
2I
r
JI
Io
J
l
j
t
1
i
S
r
0
x
t
i
3
1
Note
Do
not
w
it
off
with
screw
drivers
To
avoid
darnagingmachine
screws
do
not
work
it
ff
with
screwdriver
5
Remove
side
plate
pull
out
pres
sure
regulator
valve
second
lock
valve
pressure
regi1lator
plug
and
two
valve
springs
6
Remove
side
plate
With
side
plate
removed
solenoid
downshift
valve
throttle
back
up
valve
vacuum
throttle
valve
2
d
3rd
t
ing
valve
and
three
valve
springs
are
free
for
removal
2nd
3rd
timing
talve
r
en
i
C1iJrilth
rottle
lI
lY
e
M
a
alVSY
I
j1
f
I
1
f
Iv
I
f
2i
3
CP
g
f
st
2nd
S
t
a
el
2i1d
3
d
St1itLvalv
so
iit
a
stiift
V81v
i
hrottle
f
iicnjp
VB
y
i
P
ie
mo
i
Inspection
r
I
Check
valves
for
sign
of
burning
and
if
necessary
replace
2
Check
to
be
certain
that
oil
strainer
is
in
good
condition
If
found
damaged
in
any
manner
disCard
3
Test
valve
springs
for
weakened
Fig
AT
105
Components
ports
of
control
uolue
tension
if
necessary
replace
4
Examine
for
any
sign
oLdamage
or
score
marks
on
separate
plate
If
left
unheedcd
oiL
will
bypass
correct
oil
passages
causing
many
types
of
abnormalities
in
thesystem
AT45
5
Check
oil
passages
in
valve
b
dy
for
sign
of
damage
and
other
condi
tions
which
might
interfere
with
prop
er
valve
operation
6
Check
bolts
for
stripped
threads
Replace
as
required
Page 310 of 537

Automatic
Transmission
Valve
spring
chart
Mean
coil
Installed
Valve
spring
Wiredia
dia
No
of
free
length
mm
in
mm
in
active
coil
mm
in
Length
Load
mm
in
kg
lb
Manual
detent
1
3
6
0
15
0
32
4
26
5
5
5
0
051
0
236
1
276
1
043
12
1
Pressure
regulator
1
2
10
5
13
0
43
0
23
5
2
8
0
047
0
413
1
693
0
925
6
2
Pressure
modifier
0
4
8
0
5
0
18
5
9
0
0
1
0
016
0
315
0
728
0
354
0
2
1st
2nd
shift
0
6
6
0
6
0
32
0
16
0
0
625
0
024
0
236
1
260
0
630
1
378
2nd
3rd
shifl
0
7
6
2
8
0
41
0
17
0
1
40
0
028
0
244
1
614
0
669
3
09
2nd
3rd
timing
0
7
5
5
15
0
32
5
27
0
0
55
0
028
0
217
1
280
1
063
1
21
Throule
back
lIP
0
8
6
5
14
0
36
0
18
8
1
92
0
031
0
256
1417
0
740
4
23
Solenoid
downshift
0
55
5
0
12
0
22
0
12
5
0
60
0
0217
0
197
0
866
0
492
1
32
Second
lock
0
55
5
0
16
0
33
5
21
0
0
60
0
0217
0
197
1
319
0
827
1
32
Throule
relief
0
9
5
6
14
0
26
8
19
0
2
9
0
035
0
220
1
055
0
748
4
83
Orifice
check
0
23
4
77
12
0
J5
5
11
5
0
01
0
0091
0
1878
0
610
0
453
0
02
Primary
governor
0
45
8
3
5
0
21
8
7
5
0
215
0
0177
0
327
0
858
0
295
0
474
Secondary
governor
0
7
8
5
5
5
25
1
10
5
I
10
0
028
0
335
0
988
0
413
2
43
Free
lenglhm
A
installed
f
n
ri
DO
n
i
Wire
dia
AT172
Assembly
Assemble
in
reverse
order
of
disas
sembly
However
observe
the
follow
ing
assembly
noles
Refer
to
Valve
Spring
Chart
and
illustralion
in
as
sembling
valve
springs
Dip
all
parts
in
clean
automatic
transmission
fluid
before
assembly
Tighten
parts
to
spec
ifications
when
designated
I
Slide
valve
into
valve
body
arid
be
particularly
careful
that
they
are
not
forced
in
any
way
2
Install
side
plates
using
Torque
Driver
ST25160000
and
Hexagon
Wrench
HT6
I
000800
See
Figure
AT
l
07
Fig
AT
106
Value
spring
AT
46
Page 312 of 537

Automatic
Transmission
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSIS
AND
ADJUSTMENT
INSPECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
BEFORE
TRQUBLE
DIAGNOSIS
TESTING
INSTRUMENT
FOR
INSPECTION
CHECKING
OIL
LEVEL
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
OF
OIL
EAKAGE
CHECKING
ENGINE
IDLING
REVOLUTION
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTING
KICKDOWN
SWITCH
AND
DqWNSHIFT
SOLENOID
N
J
J
CII
Q
t
L
8li
p
JYSTMs
T
OF
MANUAL
LINKAGE
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTING
INHIBITOR
SWITCH
STALL
TEST
STALL
TEST
PROCEDURES
JUDGEMENT
Since
most
automatic
transmission
troubles
can
be
repaired
by
simple
adjustment
do
not
disassemble
im
mediately
Firstly
inspect
and
adjust
the
auto
matic
transmission
in
place
utilizing
the
Trouble
Shooting
Chart
If
the
trouble
can
not
be
solved
by
this
procedure
remove
and
disas
semble
the
automatic
transmission
It
is
advisable
to
check
overhaul
and
repair
each
part
in
the
order
listed
in
the
Trouble
Shooting
Chart
I
In
the
Trouble
Shooting
Chart
the
diagnosis
items
are
arranged
ac
cording
to
difficulty
from
easy
to
difficult
therefore
please
follow
these
items
The
transmission
should
not
be
removed
unless
necessary
2
Tests
and
adjustments
should
be
made
on
the
basis
of
standard
values
and
the
data
should
be
recorded
INSPECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
BEFORE
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSIS
TESTING
INSTRUMENT
FOR
INSPECTION
I
Engine
tachometer
2
Vacuum
gauge
ROAD
TEST
VEHICLE
SPEED
AT
GEAR
SHIFT
CHECKING
SPEED
CHANGING
CONDITION
CHECKING
ITEMS
DURING
SPEED
CHANGE
SHIFT
SCHEDULE
LINE
PRESSURE
TEST
LINE
PRESSURE
governor
feed
pressure
JUDGEMENT
IN
MEASURING
LINE
PRESSURE
At
49
TR6
uBLE
SHOOTINC
CHART
INSPECTING
ITEMS
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
CHART
FOR
3N71B
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
GUIDE
FOR
3N71B
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
CONTENTS
AT
4B
AT
48
AT
4B
AT
49
AT
49
AT
49
AT
49
AT
50
AT
50
AT
50
3
Oil
pressure
gauge
It
is
convenient
to
install
these
instruments
in
a
way
that
allows
meas
urements
to
be
made
from
the
driver
s
seat
CHECKING
OIL
LEVEL
In
checking
the
automatic
transmis
sion
the
o
illevel
and
the
condition
of
oil
around
the
oil
level
gauge
should
be
examined
This
is
an
easy
and
effective
trouble
shooting
procedure
since
some
changes
in
oil
condition
are
often
linked
with
developed
troubles
For
instance
Lack
of
oil
causes
faulty
operation
by
making
the
clutches
and
brakes
slip
resulting
in
severe
wear
This
is
because
the
oil
pump
sucks
air
causing
oil
foaming
thus
rapidly
deteriorating
the
oil
quality
and
pro
ducing
sludge
and
varnish
Excessive
oil
is
also
bad
because
of
oil
foaming
caused
by
the
gears
stirring
up
the
oil
During
high
speed
driving
excessive
oil
in
the
transmission
often
blows
out
from
the
breather
Measuring
011
level
To
check
the
fluid
level
start
the
engine
and
run
it
until
normal
operat
T
AO
AT
51
AT
51
AT
52
AT
52
AT
52
AT
52
AT
53
AT
3
AT
53
AT
53
AT
54
AT
57
ing
temperatures
o
temperature
SO
to
800C
122
to
l760F
Approxi
mately
ten
minute
of
operation
will
raise
the
temperature
to
this
range
and
engine
idling
conditions
are
stabi
lized
Then
apply
the
brakes
and
move
the
transmission
shift
lever
through
all
drive
positions
and
place
it
in
park
P
position
In
this
inspec
tion
the
car
must
be
placed
on
a
level
surface
The
amount
of
the
oil
varies
with
the
temperature
As
a
rule
the
oil
level
must
be
measured
after
its
temper
ture
becomes
sufficiently
high
1
Fill
the
oil
to
the
line
H
The
difference
of
capacities
between
both
H
and
L
is
approximately
0
4
liter
Ji
V
S
p
Y
Imp
pl
and
therefore
do
not
to
fill
beyond
the
line
H
2
When
topping
up
and
changing
oil
care
should
be
taken
to
prevent
mixing
the
oil
with
dust
and
water
InspectIng
011
condition
The
condition
of
oil
sticking
to
the
level
gauge
indicates
whether
to
over
haul
and
repair
the
transmission
or
look
for
the
faulty
part
If
the
oil
has
deteriorated
to
a
varnish
ike
quality
it
causes
the
con
trol
valve
to
stick
Blackened
oil
indi
cates
a
burned
clutch
brake
band
etc