1977 DATSUN PICK-UP height
[x] Cancel search: heightPage 333 of 537

PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
Condition
Probable
cause
Knocking
sound
during
starting
or
noise
during
coasting
on
propeller
shaft
Worn
damaged
universal
joint
Worn
sleeve
yoke
and
main
shaft
spline
Loose
propeller
shaft
installation
Loose
joint
installation
Damaged
center
bearing
or
insulator
Loose
or
missing
bolts
at
center
bearing
bracket
to
body
Scraping
noise
Dust
cover
on
sleeve
yoke
rubbing
on
transmission
rear
extension
Dust
c
ver
on
companion
flange
rubbing
on
differ
mtial
carrier
Whine
or
whistle
Damaged
center
bearing
Corrective
action
Replace
Replace
Retighten
Adjust
snap
ring
Replace
Replace
or
tighten
bolts
Straighten
out
dust
cover
to
remove
inter
ference
Replace
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
TYPE
H190
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
REMOVAL
PRE
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
ASSEMBLY
AND
ADJUSTMENT
PRECAUTIONS
IN
REASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLY
OF
DIFFERENTIAL
CASE
PD
5
PD
7
PD
7
PD
7
PD
8
PD
PD
8
PD
8
DESCRIPTION
The
differential
carrier
on
the
620
series
has
a
gear
ratio
of
4
37S
The
drive
pinion
is
rnounted
in
two
tapered
roUer
bearings
which
are
pre
loaded
by
pinion
bearing
adjusting
spacer
and
washer
during
assembly
The
drive
pinion
is
positioned
by
a
washer
located
between
a
shoulder
of
ASSEMBl
Y
OF
DIFFERENT
Al
CASE
ADJUSTMENT
OF
DRIVE
PINION
HEIGHT
ADJUSTME
NT
OF
DRIVE
PINION
PRELOAD
t
ADJUST
ENT
OF
SIDE
8EARING
SHIMS
INSTAllATION
REPLACEME
NTOF
FRONT
Oil
SEAL
the
drive
pinion
and
the
rear
bearing
The
differential
case
is
supported
in
the
carrier
by
two
tapered
roller
side
bearings
These
are
preloaded
by
in
serting
shims
between
the
bearings
and
the
differential
case
The
differential
case
assembly
is
positioned
for
proper
ring
gear
and
drive
pinion
backlash
by
PO
5
PD
8
PD
9
PD
lO
PD
11
PD
13
PD
13
varying
these
shims
The
ring
gear
is
bolted
to
the
differential
case
The
case
houses
two
side
gears
in
mesh
with
two
pinion
mates
mounted
on
a
pinion
shaft
The
pinion
shaft
an
chored
in
the
case
by
lock
pin
The
pinion
mates
and
side
gears
are
backed
by
thrust
washers
The
carrier
is
of
malleable
cast
iron
Page 337 of 537
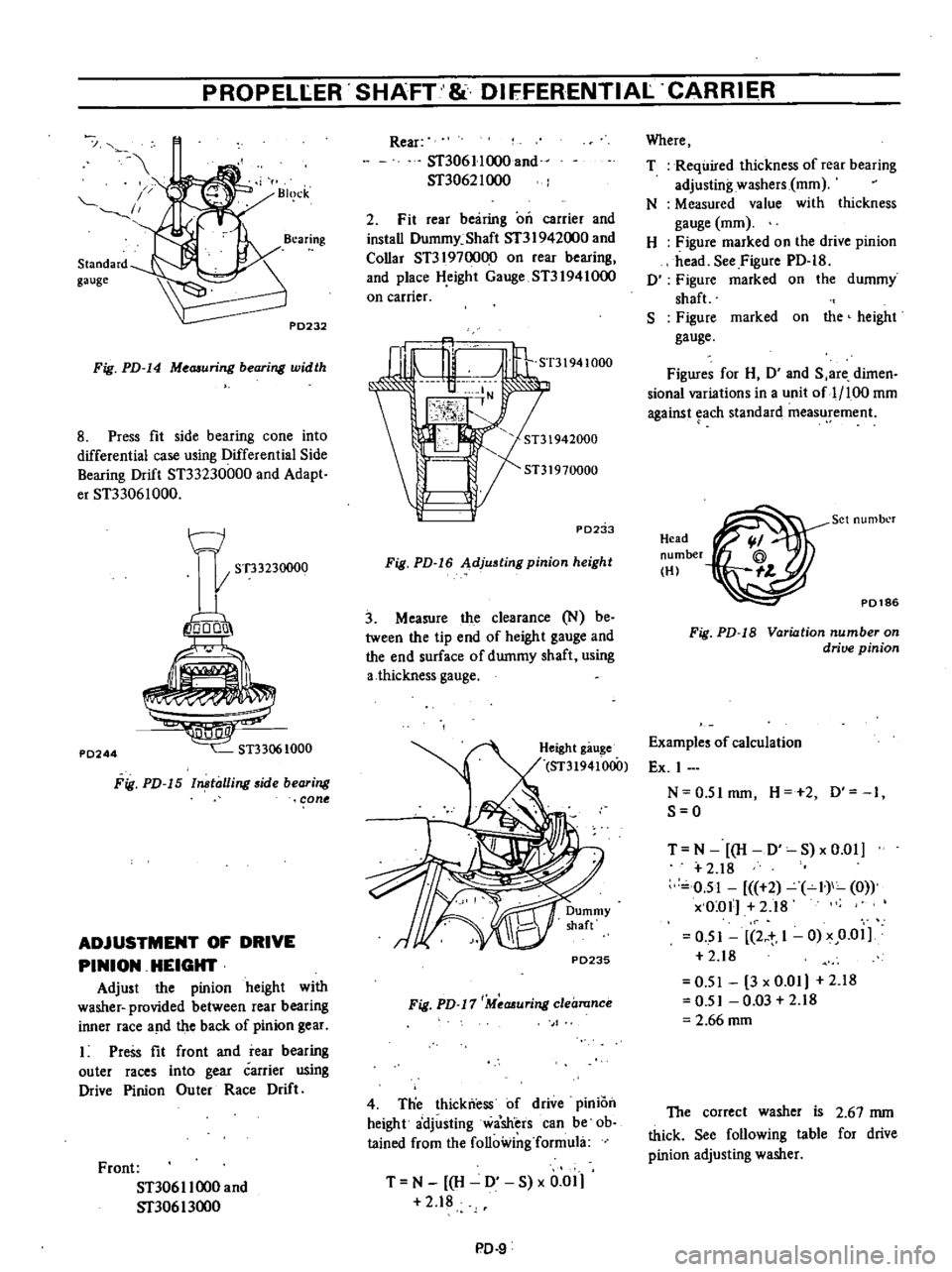
PROPELLER
SHAFT
DifFERENTIAL
CARRIER
Standard
gauge
I
1
Fig
PD
14
Me
uring
bearing
width
8
Press
fit
side
bearing
cone
into
differential
case
using
Differential
Side
Bearing
Drift
ST33230000
and
Adapt
er
ST33061000
t
J
I
ST33230000
io
o1
P0244
Fig
PD
15
ln
talling
side
bearing
cone
ADJUSTMENT
OF
DRIVE
PINION
HEIGHT
Adjust
the
pinion
height
with
washer
provided
between
rear
bearing
inner
race
a
ld
the
back
of
pinion
gear
Press
fit
front
and
rear
bearing
outer
races
into
gear
carrier
using
Drive
Pinion
Ou
ter
Race
Drift
Front
ST306
I
1000
and
Sf30613oo0
Rear
ST306
II
000
and
ST3062I
000
2
Fit
rear
bearing
on
carrier
and
install
Dummy
Shaft
Sf3
I
942000
and
Collar
ST3197oo00
on
rear
bearing
and
place
H
eight
Gauge
ST31941000
on
carrier
ST31941000
PD2
b
Fig
PD
16
Adjusting
pinion
height
3
Measure
the
clearance
N
be
tween
the
tip
end
of
height
gauge
and
the
end
surface
of
dummy
shaft
using
a
thickness
gauge
P0235
Fig
PD
17
Measuring
clearance
4
Tlie
thickness
of
drive
pInIOn
height
adjusting
wa
sh
ers
can
be
ob
tained
from
the
following
formula
T
N
H
0
S
x
0
01
2
18
PD
9
Where
T
Required
thickness
of
rear
bearing
adjusting
washers
mOl
N
Measured
value
with
thickness
gauge
mOl
H
Figure
marked
on
the
drive
pinion
head
See
Figure
PD
18
0
Figure
marked
on
the
dummy
shaft
S
Figure
marked
on
the
height
gauge
Figures
for
H
0
and
S
are
dimen
sional
variations
in
a
unit
of
1
100
mOl
against
each
standard
measurement
Head
number
HI
P0186
Set
numbl
r
Fig
PD
18
Variation
number
on
drive
pinion
Examples
of
calculation
Ex
I
N
0
5Imm
H
2
0
1
S
O
T
N
H
D
S
xO
01
2
18
0
51
2
I
0
x
O
ol
2
18
O
SI
2
t
1
0
x
0
01
2
18
0
51
3
x
0
01
2
18
0
51
0
03
2
18
2
66
mOl
The
correct
washer
is
2
67
mm
thick
See
following
table
for
drive
pinion
adjusting
washer
Page 340 of 537

PROPELLER
SHAFf
DIFFERENTIAL
CARR
IER
Ex
2
A
0
B
3
C
I
0
0
E
0
20
mOl
F
0
17
mOl
H
2
Left
side
T
I
A
C
D
H
x
om
0
17S
E
0
I
0
2
x
0
01
0
I7S
0
20
0
I
0
2
x
0
01
0
17S
0
20
3
Om
0
17S
0
20
0
03
0
17S
0
20
O
34S
mrn
The
correct
shinjs
are
O
OS
plus
0
10
plus
0
20
mrn
thick
Right
side
T2
B
D
H
xO
0l
O
ISO
F
3
0
2
x
om
O
ISO
0
17
3
0
2
x
om
0
150
0
17
S
x
0
01
0
ISO
0
I7
O
OS
0
1S0
0
17
0
37
mrn
The
correct
shims
are
0
07
plus
0
1
0
plus
0
20
mm
thick
Note
If
w1ues
signifying
A
B
C
0
and
H
are
not
given
regard
them
as
zero
and
compute
Aft
assembly
check
to
see
that
preload
and
backlash
are
correct
If
not
readjust
Side
bearing
adjusting
shim
Thickness
mm
in
O
OS
0
0020
0
07
0
0028
0
1
0
0
0039
0
20
0
0079
0
50
0
0197
2
Fit
determined
side
bearing
adjusting
shim
on
differential
case
and
press
fit
left
and
right
side
bearing
inner
races
on
it
using
Side
Bearing
Drift
ST33230000
and
Adapter
ST33061000
3
Install
differential
case
assembly
into
gear
carrie
tapping
with
a
rubber
mallet
4
Align
mark
on
bearing
cap
with
that
on
gear
carrier
and
install
bearing
cap
on
carrier
And
tight
n
bolts
to
specified
torque
Tightening
torque
4
0
to
S
O
kg
m
29
to
36
fHb
S
Measure
ring
gear
to
drive
pinion
backlash
If
backlash
is
too
small
remove
shims
from
left
side
and
add
them
to
right
side
To
reduce
backlash
remove
shims
from
right
side
and
add
them
to
left
side
Backlash
O
1S
to
0
20
mrn
0
00S9
to
0
0079
in
Fig
PD
22
Mccuuring
back1aah
6
At
the
same
time
check
side
bearing
preload
Bearing
preload
should
read
12
0
to
20
0
kg
cm
10
to
17
in
lb
of
rotating
torque
3
S
to
S
8
kg
7
7
to
12
8
Ib
at
ring
gear
bolt
hole
PD
12
If
preload
does
not
accord
with
this
specification
adjust
it
with
side
bear
ing
shims
7
Check
and
adjust
the
tooth
con
tact
pattern
of
ring
gear
and
drive
pinion
I
Thoroughly
clean
ring
and
drive
pinion
gear
teeth
2
Paint
ring
gear
teeth
lightly
and
evenly
with
a
mixture
of
ferric
oxide
and
gear
oil
to
produce
a
contact
pattern
3
Rotate
pinion
through
several
revolutions
in
the
forward
and
reverse
directions
until
a
defmite
contact
pat
tern
is
developed
on
ring
gear
4
When
contact
pattern
is
incor
rect
readjust
thickness
of
adjusting
washer
S
Incorrect
contact
pattern
of
teeth
can
be
adjusted
in
the
following
manner
a
Heel
contact
To
correct
increase
thickness
of
pinion
height
adjusting
washer
in
order
to
bring
drive
pinio
close
to
ring
gear
P0193
Fig
PD
23
Hul
contact
b
Toe
contact
To
correct
reduce
thickness
of
pinion
height
adjusting
washer
in
order
to
make
drive
pinion
go
away
from
ring
gear
P0194
1
Fig
PD
24
To
contact
Page 347 of 537
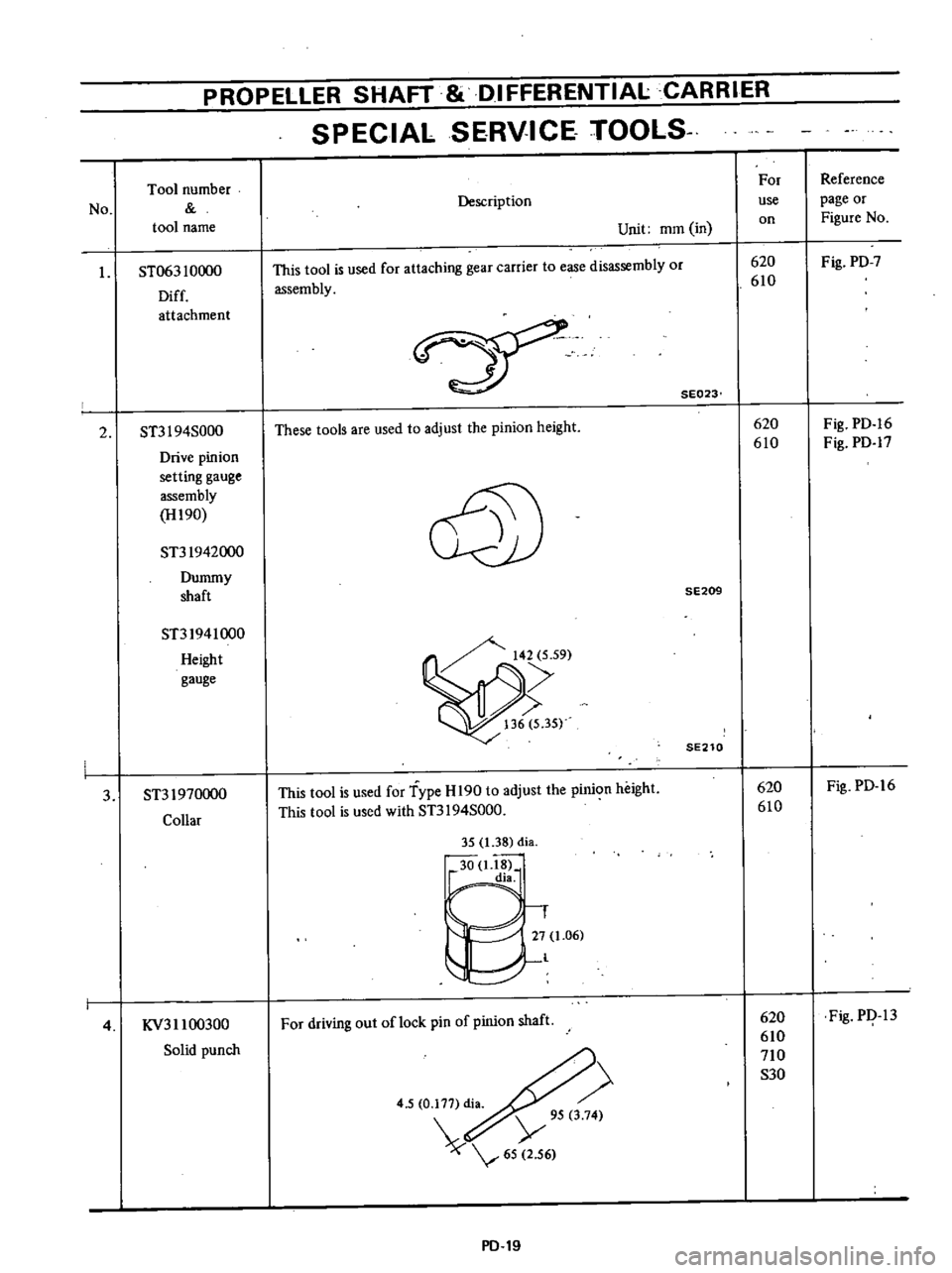
PROPELLER
SHAFT
8i
DIFFERENTIALCARRIER
SPECIAL
SERVICE
TOOlS
No
Tool
number
tool
name
I
ST063
10000
Diff
attachment
2
ST3I
94S000
Drive
pinion
setting
gauge
assembly
H190
ST31942000
Dummy
shaft
ST31941000
Height
gauge
3
ST31970000
Collar
4
KV311
00300
Solid
punch
Description
Unit
mOl
in
This
tool
is
used
for
attaching
gear
carrier
to
ease
disassembly
or
assembly
SE023
These
tools
are
used
to
adjust
the
pinion
height
@
SE209
SE210
This
tool
is
used
for
Type
H
190
to
adjust
the
pinion
height
This
tool
is
used
with
ST3I
94S000
35
1
38
di
30
1
18
dia
1
27
1
06
l
For
driving
out
oflock
pin
of
pinion
shaft
4
5
0
177
di
Y
95
3
74
65
2
56
PD
19
For
use
on
620
610
620
610
620
610
620
610
710
S30
Reference
page
or
Figure
No
Fig
PD
7
Fig
PD
16
Fig
PD
17
Fig
PD
16
Fig
PI
13
Page 358 of 537

s
Install
tension
rod
at
rear
end
tighten
nut
to
make
the
distance
of
rubber
bushing
to
be
33
4
mm
1
315
in
and
torque
lock
nut
to
1
6
to
2
2
kg
m
12
to
16
ft
lb
6
Install
tension
rod
bracket
to
chassis
frame
bracket
and
torque
nut
to
1
6
to
2
2
kg
m
12
to
16
ft
lb
When
two
rubber
bushings
are
dif
ferent
in
size
arrange
adjusting
nut
Standard
dimension
is
11
0
mOl
0
433
in
as
shown
in
Figure
FA
16
Torque
lock
nut
to
1
6
to
2
2
kg
m
12
to
16
ft
lb
Il
0
11
0
0
433
t
lP
33
4
1
315
I
11
0
0
433
1
0
11
0
0
433
Adjusting
nut
Y
i
w
36
6
l
441
Unit
mm
in
FA235
Fig
FA
16
Tension
rod
detail
INSPECTION
I
Check
tension
rod
for
bend
and
the
thread
for
faulty
condition
Repair
or
replace
as
required
2
Check
bushing
rubber
for
wear
and
deterioration
Replace
if
neces
sary
TORSION
BAR
SPRING
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Removal
1
Raise
vehicle
on
a
hoist
or
stands
2
Remove
wheel
3
Loosen
nuts
at
spring
anchor
bolt
Front
Axle
Front
Suspension
4
Remove
dust
cover
at
the
rear
end
of
torsion
bar
spring
and
detach
snap
ring
S
Withdraw
torsion
bar
spring
rear
ward
after
pulling
ou
t
anchor
arm
realWard
I
nstallalation
Install
torsion
bar
spring
in
the
reverse
sequence
of
removal
noting
the
following
instructions
I
Coat
grease
on
the
serrations
of
torsion
bar
spring
and
install
it
to
torque
arm
Note
Be
sure
to
install
right
and
left
torsion
bar
springs
correctly
They
can
be
identified
with
R
Right
and
L
Left
marked
on
the
end
surface
2
Install
anchor
arm
and
tighten
adjusting
nut
to
obtain
A
dimen
sion
See
Figure
F
A
17
When
anchor
arm
is
properly
adjusted
to
A
specification
upper
link
should
be
in
contact
with
rebound
bumper
rubber
See
Figure
FA
18
Install
snap
ring
and
dust
cover
Temporarily
tighten
adjust
ing
nut
until
B
specification
is
reached
I
I
I
FA236
Fig
FA
17
Installing
anchor
arm
Specifications
for
torsion
bar
spring
Diameter
x
length
mOl
in
Torsional
rigidity
kg
m
deg
ft
lb
deg
FA
9
Anchor
arm
setting
post
ion
A
ISt02Smm
0
59
to
0
98
in
Temporary
tightening
distance
B
60
to
70
mOl
2
36
to
2
76
in
UjPPje
Rebound
bumper
rubber
j
4W
Fig
FA
18
Setting
procedure
Notes
3
A
and
8
specifications
are
only
the
preliminary
rough
settings
directions
for
performing
the
final
adjustment
that
determines
the
ride
height
are
found
on
page
F
A
II
under
Adjustment
b
Discard
old
snap
ring
after
re
moving
it
Replace
with
new
one
during
reinstallation
3
Install
wheel
and
lower
vehicle
Adjust
vehicle
posture
at
curb
weight
full
fuel
tank
no
passengers
refer
ring
to
Adjustment
4
Torque
lock
nut
to
3
1
to
4
1
kg
m
22
to
30
ft
lb
INSPECTION
Check
torsion
bar
spring
for
wear
twist
etc
When
adjusting
vehicle
posture
replace
torsion
bar
spring
with
a
new
one
if
the
specified
height
can
not
be
obtained
All
models
21
9
x
830
0
862
x
32
68
3
74
27
I
Page 363 of 537

Front
Axle
Front
Suspension
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Condition
Vibration
shock
and
shimmy
ing
of
steering
wheeL
Vehicle
pulls
to
right
or
left
Probable
cause
Vibration
Too
much
backlash
of
steering
gear
wear
of
each
part
of
linkage
and
vibration
of
front
wheels
are
in
many
cases
transmitted
to
the
steering
wheel
This
is
Very
much
noticeable
when
traveJling
over
bad
roads
and
at
higher
speeds
Shock
When
the
front
wheels
are
travelling
over
bumpy
roads
the
play
of
the
steering
linkage
is
transmitted
to
the
steering
wheel
This
is
especially
noticeable
when
travelling
rough
road
Shimmy
Abnormal
vibrations
of
the
front
suspen
sion
group
and
the
whole
steering
linkage
which
occur
when
a
specific
speed
is
attained
Improper
air
pressure
of
tire
Unbalance
and
deformation
of
roadwheel
Unevenly
worn
tire
or
insufficient
tightening
Improperly
adjusted
or
worn
front
wheel
bearing
Faulty
wheel
alignment
Worn
or
loose
suspension
link
screw
bushing
Damaged
idler
arm
Insufficiently
tightened
steering
gear
housing
Worn
steering
linkage
Improper
steering
gear
adjustment
insufficient
back
lash
Faulty
shock
absorber
or
loose
installation
Unbalanced
vehicle
posture
When
driving
with
hands
off
the
steering
wheel
on
a
fiat
road
the
vehicle
gently
swerves
to
right
or
left
Note
A
faulty
rear
suspension
may
also
be
the
cause
of
this
condition
and
therefore
see
also
the
chapter
dealing
with
the
rear
suspension
Improper
air
pressure
of
tire
or
insufficient
tightening
of
wheel
nu
ts
Difference
in
height
of
right
and
left
tire
treads
Incorrect
adjustment
or
abrasion
of
front
wheel
bearing
Weakened
front
torsion
spring
or
deviation
from
standard
specification
Improper
wheel
alignment
Worn
or
loose
suspension
link
screw
bushing
FA
14
Corrective
action
Adjust
Correct
the
unbalance
or
re
place
Replace
or
tighten
Adjust
or
replace
Adjust
Replace
Replace
TIghten
Replace
ball
joint
Adjust
Replace
or
tighten
Adjust
Adjust
or
tighten
Replace
tires
Adjust
or
replace
Replace
Readjust
Replace
Page 377 of 537

The
620
series
vehicles
are
equip
ped
with
hydraulic
brakes
on
the
four
wheels
and
mechanical
hand
brakes
on
the
rear
wheels
The
front
brake
is
the
uni
servo
type
and
the
rear
the
duo
servo
with
the
built
in
hand
BRAKE
PEDAL
FRONT
BRAKE
REAR
BRAKE
BRAKE
PEDAL
Qi
f
l
II
t
Unit
mm
in
I
Under
the
condition
that
the
push
rod
of
brake
lamp
swi
tch
is
pushed
in
position
the
height
of
brake
pedal
from
toeboard
to
148
mm
5
83
in
operating
the
switch
adjusting
nuts
Then
tighten
nuts
securely
Tightening
torque
1
2
to
1
5
kg
m
9
to
I
I
ft
Ib
2
Adjust
the
length
of
push
rod
Brake
System
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION
brake
The
mechanical
hand
brake
is
controlled
by
a
hand
brake
lever
locat
ed
in
the
driver
s
compartment
For
added
safety
the
tandem
I
1lI3ter
cylinder
Master
Vac
and
Nissan
Load
Sensing
Valve
N
L
S
V
ADJUSTMENT
CONTENTS
are
standard
equipment
on
all
models
The
Master
Vac
is
installed
to
increase
braking
force
The
N
L
S
V
ensures
greater
safety
and
reliability
BR
2
BR
2
BR
3
HAND
BRAKE
Parking
brake
BLEEDING
HYDRAULIC
SYSTEM
BR
3
BR
3
Free
height
Full
stroke
at
pedal
pad
A
148
5
83
B
134
10
140
5
28
to
5
51
C
43
to
49
1
69
to
1
93
Depressed
height
1
Push
rod
adjusting
nut
2
Switch
adjusting
nuts
3
BraKe
lamp
switch
BA765
Fig
BR
l
Adjusting
brake
pedal
with
its
adjusting
nut
so
as
to
become
0
6
to
1
2
mOl
0
024
to
0
047
in
in
play
Then
tigh1en
nut
securely
Tightening
torque
1
6
to
2
2
kg
m
12
to
16
ft
lb
Note
Take
care
not
to
allow
the
push
rod
to
get
into
master
cylinder
in
free
condition
BR
2
3
After
completing
adjustment
operate
brake
pedal
several
times
to
ensure
that
it
travels
over
its
entire
stroke
of
137
mm
5
39
in
smoothly
without
showing
squeak
noise
twist
ing
or
interference
FRONT
BRAKE
1
Raise
vehicle
until
wheel
clear
floor
2
Remove
rubber
boot
from
brake
disc
3
Ughtly
tap
adjuster
housing
and
move
it
forward
Turn
down
adjuster
wheel
with
a
screwdriver
and
spread
brake
shoes
Stop
turning
adjuster
wheel
when
a
considerable
drag
is
Jelt
and
lock
up
brake
drum
Note
For
both
right
and
left
brakes
brake
shoes
spread
when
adjuster
wheel
is
turned
downward
4
Return
adjuster
wheel
12
ratches
to
obtain
correct
clearance
between
brake
drum
and
brake
shoes
Turn
brake
drum
and
make
sure
that
brake
drum
turns
without
dragging
when
brake
shoes
interfere
with
brake
drum
then
readjust
clearance
5
Install
rubber
boot
Page 395 of 537

Brake
System
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Brake
pedal
Free
height
Free
play
at
pedal
pad
Full
stroke
at
pedal
pad
Depressed
height
mOl
in
mOl
in
mOl
in
mm
in
148
S
83
I
to
3
0
04
to
0
12
134
to
140
5
28
to
S
51
43
to
49
169
to
193
Brake
adjustment
notches
Front
Rear
12
12
Master
cylinder
Inner
diameter
Piston
to
cylinder
deaJance
mm
in
mm
in
19
0S
Yo
O
IS
0
OOS9
Master
Vac
Diaphragm
diameter
mOl
in
Maximum
vacuum
leakage
after
15
sec
mmHg
inHg
Shell
seal
depth
A
mOl
in
Push
rod
length
B
mOl
in
152
4
6
2S
0
98
6
7
to
7
0
0
264
to
0
276
10
0
to
10
5
0
394
to
0
413
Front
drum
brake
Type
Wheel
cylinder
inner
diameter
Lining
Width
x
Thickness
x
Length
Lining
wear
limit
Uni
servo
mm
in
I9
0S
Yo
45
x
4
5
x
244
1
77
x
0
177
x
9
61
1
0
0
039
mm
in
mOl
in
Rear
drum
brake
Type
Wheel
cylinder
inner
diameter
Duo
servo
mOl
in
19
0S
Yo
Brake
drum
Inner
diameter
Repair
limit
of
thickness
Inside
runout
mm
in
mOl
in
mOl
in
254
0
10
2SS
S
10
06
0
02
0
0008
maximum
PaJking
brake
Type
Stroke
Adjuster
sliding
resistance
mm
in
kg
lb
Stick
type
80
to
100
3
lS
to
3
94
S
to
12
11
to
26
BR
20