1977 DATSUN PICK-UP fuel cap
[x] Cancel search: fuel capPage 66 of 537

PRECAUTIONS
CYLINDER
HEAD
PRECAUTIONS
I
Use
thoroughly
cleaned
parts
Especially
make
sure
that
oil
holes
are
clear
of
foreign
matter
2
When
installing
sliding
parts
such
as
bearings
be
s
uIe
to
apply
engine
oil
to
them
3
Use
new
packing
and
oil
seals
4
Do
not
reuse
lock
washers
5
Keep
tools
and
work
benches
clean
6
Keep
necessary
parts
and
tools
near
at
hand
7
Be
sure
to
follow
specified
tight
ening
torque
and
order
8
Applying
sealant
Use
sealant
to
eliminate
water
and
oil
leaks
Parts
requiring
sealant
are
I
Front
cover
and
corners
of
cyl
inder
block
See
Figure
EM
78
EM153
Fig
EM
78
Applying
alant
Front
cover
and
cylinder
block
2
Main
bearing
cap
and
cylinder
block
Each
side
of
rear
main
bearing
cap
and
each
corner
of
cylinder
block
See
Figure
EM
79
Engine
Mechanical
ENGINE
ASSEMBLY
CONTENTS
EM
21
EM
21
PISTON
AND
CONNECTING
ROD
ENGINE
ASSEMBLY
EM
22
EM
22
Cylinder
block
Rear
main
bearing
cap
20to2Smm
Ill
Points
to
be
applied
sealant
EM151
s
e
00
000
o
Fig
EM
79
Applying
sealanl
Main
bearing
cap
and
cylinder
block
3
Cylinder
block
Step
portions
at
four
mating
surfaces
cylinder
block
to
front
chain
cover
and
cylinder
block
to
rear
main
bearing
cap
See
Figure
EM
80
Note
Do
not
apply
too
much
sealant
J
Apply
sealant
at
hese
points
EM152
Fig
EM
80
Applying
sealant
Cylinder
block
CYLINDER
HEAD
Valve
assembly
and
valve
spring
Using
Valve
Lifter
STl2070000
set
valve
pring
seat
in
position
and
fit
valve
guide
with
oil
seaL
Assemble
valve
in
the
order
shown
below
valve
inner
and
outer
valve
springs
spring
retainer
valve
collet
and
valve
rocker
guide
EM
21
Fig
EM
81
Installing
valves
Notes
a
Ensure
that
valve
face
is
free
from
foreign
matter
b
The
L20B
engine
uses
double
type
valve
springs
2
Valve
rocker
pivot
assembly
Screw
valve
rocker
pivots
joined
with
lock
nuts
into
pivot
hushing
3
Camshaft
assembly
Set
locating
plate
and
carefully
install
camshaft
in
cylinder
head
Do
not
damage
the
bearing
inside
Oblong
groove
of
locating
plate
must
be
directed
toward
front
side
of
engine
Camshaft
bracket
tightening
torque
1
8
to
2
0
kg
in
13
to
15
ft
lb
4
Install
camshaft
sprocket
on
earn
shaft
and
tighten
it
together
with
fuel
pump
drive
cam
to
specified
torque
Tightening
torque
12
tol6
kg
m
87
to
116
ft
lb
this
time
check
camshaft
end
Fig
EM
82
Installing
camshaft
sprocket
Page 75 of 537

Engine
Mechanical
g
Piston
ring
Ring
height
Top
and
second
Side
clearance
Top
Second
Ring
gap
Top
Second
Oil
mm
in
mrn
in
mm
in
h
Cylinder
block
Cylinder
bore
inner
diameter
mm
in
Wear
limit
of
dittoed
inner
diameter
Cylinder
bore
taper
and
out
of
round
Difference
in
cylind
bore
Surface
flatness
mm
in
mm
in
mm
in
mm
in
i
Cylinder
head
Surface
flatness
mm
in
TIGHTENING
TORQUE
Cylinder
head
bolts
kg
m
fl
lb
Connecting
rod
big
end
nuts
kg
m
ft
Ib
Flywheel
fixing
bolts
kg
m
ft
Ib
Main
bearing
cap
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
Camshaft
bracket
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
Camshaft
sprocket
bolt
kg
m
ft
lb
Oil
pan
bolts
kg
m
ft
1b
Oil
pump
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
Oil
strainer
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
Oil
pan
drain
plug
kg
m
ft
lb
Rocker
pivot
lock
nuts
kg
m
ft
Ib
Camshaft
locating
plate
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
Carburetor
nuts
kg
m
ft
lb
Manifold
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
Fuel
pump
nuts
kg
m
ft
lb
Crank
pulley
bolt
kg
m
ft
lb
Water
pump
bolts
kg
m
ft
Ib
Front
cover
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
EM
30
1
977
to
1
990
0
0778
to
0
0783
0
040
to
0
073
0
0016
to
0
0029
0
030
to
0
070
0
0012
to
0
0028
0
25
to
0
40
0
0098
to
0
0157
0
30
to
0
50
0
0118
to
0
0197
0
30
to
0
90
0
0118
to
0
0354
85
000
to
85
050
3
3465
to
3
3484
0
2
0
0079
om
5
0
0006
0
05
0
0020
less
than
0
05
0
0020
less
than
0
05
0
0020
6
5
to
8
5
47
to
61
4
5
to
5
5
33
to
40
14
to
16
101
to
116
4
5
to
5
5
33
to
40
1
8
to
2
0
13
to
15
12
to
16
87
to
116
0
6
to
0
9
4
3
to
6
5
I
J
to
1
5
8
0
to
10
8
0
8
to
1
1
5
8
to
8
0
2
0
to
3
0
14
to
22
5
0
to
6
0
36
to
43
0
6
to
0
9
4
3
to
6
5
0
5
to
1
0
3
6
to
7
2
1
2
to
1
6
8
7
to
11
6
1
2
to
1
8
8
7
to
13
0
12
to
16
87
to
116
0
4
to
0
5
2
9
to
3
6
8
mm
0
315
in
dia
6
mm
0
236
in
dia
1
0
to
1
3
7
2
to
9
4
0
4
to
0
6
2
9
to
4
3
Page 105 of 537
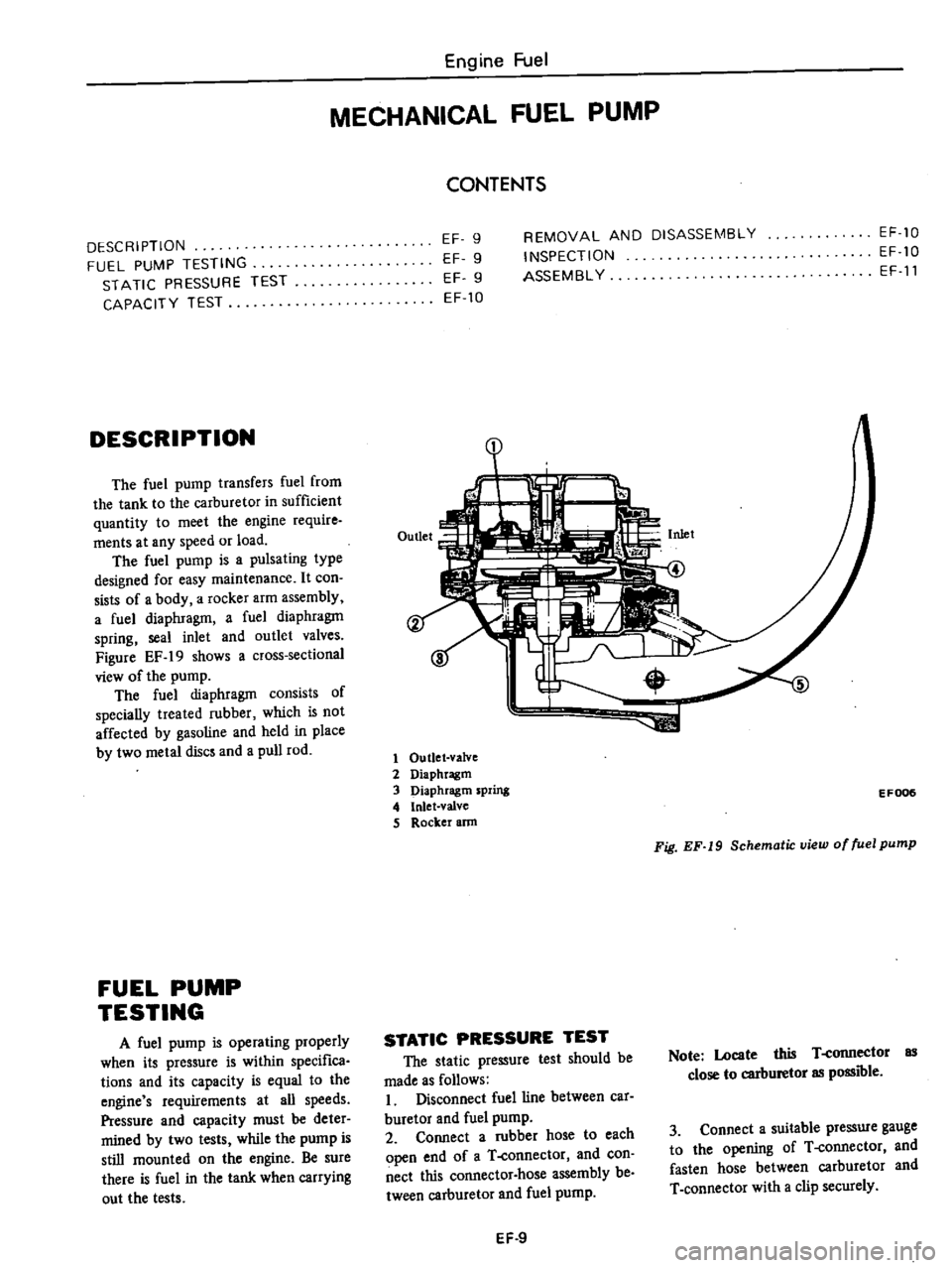
DESCRIPTION
FUEL
PUMP
TESTING
STATIC
PRESSURE
TEST
CAPACITY
TEST
DESCRIPTION
The
fuel
pump
transfers
fuel
from
the
tank
to
the
carburetor
in
sufficient
quantity
to
meet
the
engine
require
ments
at
any
speed
or
load
The
fuel
pump
is
a
pulsating
type
designed
for
easy
maintenance
It
con
sists
of
a
body
a
rocker
arm
assembly
a
fuel
diaphragm
a
fuel
diaphragm
spring
seal
inlet
and
outlet
valves
Figure
EF
19
shows
a
cross
sectional
view
of
the
pump
The
fuel
diaphragm
consists
of
specially
treated
rubber
which
is
not
affected
by
gasoline
and
held
in
place
by
two
metal
discs
and
a
pull
rod
FUEL
PUMP
TESTING
A
fuel
pump
is
operating
properly
when
its
pressure
is
within
specifica
tions
and
its
capacity
is
equal
to
the
engine
s
requirements
at
all
speeds
Pressure
and
capacity
must
be
deter
mined
by
two
tests
while
the
pump
is
still
mounted
on
the
engine
Be
sure
there
is
fuel
in
the
tank
when
carrying
out
the
tests
Engine
Fuel
MECHANICAL
FUEL
PUMP
CONTENTS
EF
9
EF
9
EF
9
EF
10
REMOVAL
AND
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
ASSEMBL
Y
EF
10
EF
10
EF
11
1
1
Outlet
valve
2
Diaphragm
3
Diaphragm
spring
4
Inlet
valve
S
Rocker
ann
EF006
Fig
EF
19
Schematic
view
of
fuel
pump
STATIC
PRESSURE
TEST
The
static
pressure
test
should
be
made
as
follows
I
Disconnect
fuel
line
between
car
buretor
and
fuel
pump
2
Connect
a
rubber
hose
to
each
open
end
of
a
T
connector
and
con
nect
this
connector
hose
assembly
be
tween
carburetor
and
fuel
pump
Note
Locate
this
T
connector
as
close
to
carburetor
as
possible
3
Connect
a
suitable
pressure
gauge
to
the
opening
of
T
connector
and
fasten
hose
between
carburetor
and
T
connector
with
a
clip
securely
EF
9
Page 106 of 537

4
Run
the
engine
at
varying
speeds
5
The
pressure
gauge
indicates
static
fuel
pressure
in
the
line
The
gauge
reading
should
be
within
the
following
range
0
21
to
0
27
kg
em2
3
0
to
3
8
psi
Note
If
the
fuel
in
carburetor
float
chamber
has
run
out
and
engine
has
stopped
clip
and
pour
fuel
into
carburetor
Fasten
clip
secure
ly
and
repe
1
static
pressure
test
Pressure
below
the
lower
limit
indi
cates
extreme
wear
on
one
part
or
a
small
amount
of
wear
on
each
working
part
It
also
indicates
ruptured
dia
phragm
worn
warped
dirty
or
gum
ming
valves
and
seats
or
a
weak
diaphragm
return
spring
Pressure
above
the
upper
limit
indicates
an
excessively
strong
tension
of
dia
phragm
return
spring
or
a
diaphragm
that
is
too
tight
Both
of
these
condi
tions
require
the
removal
of
pump
assembly
for
replacement
or
repair
CAPACITY
TEST
The
capacity
test
is
made
only
when
static
pressure
is
within
the
specifications
To
make
this
test
pro
ceed
as
follows
1
Disconnect
pressure
gauge
from
T
connector
and
in
its
vacant
place
install
a
suitable
container
as
a
fuel
sump
2
Run
engine
at
1
000
rpm
3
The
pump
should
deliver
1
000
cc
2
11
US
pt
of
fuel
in
one
minute
or
less
If
little
or
no
fuel
flows
from
the
open
end
of
pipe
it
is
an
indication
that
fuel
line
is
clogged
or
pump
is
malfunctioning
REMOVAL
AND
DISASSEMBLY
Remove
fuel
pump
assembly
by
unscrewing
two
mounting
nuts
and
disassemble
in
the
following
order
1
Separate
upper
body
and
lower
body
by
unscrewing
body
set
screws
Engine
Fuel
2
Take
off
cap
and
cap
gasket
by
removing
cap
screws
3
Unscrew
elbow
and
connector
4
Take
off
valve
retainer
by
un
screwing
two
retainer
screws
and
re
move
two
valves
5
To
remove
diaphragm
press
down
its
center
against
spring
force
With
diaphragm
pressed
down
tilt
it
until
the
end
of
pull
rod
touches
the
inne
wall
of
body
Then
release
diaphragm
to
unhook
push
rod
Be
careful
during
this
operation
not
to
damage
diaphragm
or
oil
se
L
i
J
EFOO7
Fig
EF
20
Remouing
pull
rod
6
Drive
rocker
arm
pin
out
with
a
press
or
hammer
8
o
6
7
8
@
INSPECTION
I
Check
upper
body
and
lower
body
for
cracks
EF
10
I
fuel
pump
cap
2
Cap
gasket
3
Valve
packing
4
fuel
pump
val
e
assembly
S
Valve
retainer
6
Diaphragm
assembly
7
Diaphragm
spring
8
PuRro
9
Lower
body
seal
washer
10
Lower
body
seal
11
Inkl
connector
12
Outlet
connector
13
Rocker
arm
spring
14
Rocker
arm
I
S
Rocker
artyl
side
pin
16
Fuel
pump
packing
17
Spacer
fuel
pump
fo
cylinder
block
EF510
Fig
EF
21
Slruc
ure
of
fuel
pump
2
Check
valve
assembly
for
wear
on
valve
and
valve
spring
Blow
valve
assembly
with
brea
th
to
examine
its
function
Page 107 of 537

3
Check
diaphragm
for
small
holes
carcks
or
wear
4
Check
rocker
arm
for
wear
at
the
mating
portion
with
camshaft
5
Check
rocker
arm
pin
for
wear
A
worn
pin
may
cause
oil
leakage
6
Check
all
other
components
for
any
abnormalities
and
replace
if
neces
sary
DESCRIPTION
INSPECTION
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
DESCRIPTION
The
electric
fuel
pump
is
adopted
on
air
conditioner
equipped
models
Engine
Fuel
ASSEMBLY
Reverse
the
order
of
disassembly
Closely
observe
the
following
instruc
tions
L
Use
new
gaskets
2
Lubricate
rocker
ann
rocker
arm
link
and
rocker
arm
pin
before
installa
tion
3
To
test
the
function
proceed
as
follows
Position
fuel
pump
assembly
about
I
meter
3
3
ft
above
fuel
level
of
fuel
strainer
and
connect
a
pipe
from
strainer
to
fuel
pump
Operate
rocker
arm
by
hand
If
fuel
is
drawn
up
soon
after
rocker
arm
is
released
fuel
pump
is
functioning
properly
ELECTRIC
FUEL
PUMP
CONTENTS
EF
11
EF
11
EF
12
DISASSEMBL
Y
ASSEMBL
Y
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
EF
12
EF
12
The
silicon
transistor
type
fuel
pump
consists
of
a
transistor
diodes
a
sole
I
Tr
lOsistor
6
Ou
tIet
valve
2
Plunger
7
Return
spring
3
Diaphragm
8
Filter
4
Diode
9
Magnet
5
Magnet
coil
10
Inlet
valve
INSPECTION
I
Disconnect
fuel
hose
at
pump
outlet
2
Connect
a
suitable
hose
approxi
mately
6
mm
0
24
in
inner
dia
meter
to
pump
outlet
ev
J
J
Note
If
diameter
is
too
small
the
following
proper
delivery
capacity
cannot
be
obtained
even
if
pump
functions
properly
EF
11
EF
13
noid
a
pump
mechanism
and
filter
parts
I
T
nsistor
2
Re
ist
f
I
3
Dinde
4
Signal
coil
5
Main
coil
6
Resistor
3
7
Zener
dlOdl
8
Resistor
2
EF719
Fig
EF
22
Construction
of
electric
fuel
pump
3
With
hose
outlet
in
a
higher
posi
tion
than
pump
operate
pump
and
check
delivery
capacity
for
more
than
15
seconds
4
The
capacity
should
be
I
400
cc
Page 117 of 537

Notes
a
The
idle
rpm
and
CO
vary
accord
ing
to
the
altitude
Therefore
they
should
be
properly
adjusted
when
the
position
of
the
H
L
lever
is
changed
EF729
ADJUSTMENT
AND
INSPECTION
CARBURETOR
IDLE
R
P
M
AND
MIXTURE
RATIO
Cautions
3
On
automatic
transmission
equi
ped
models
check
should
be
per
formed
in
the
0
position
Be
sure
to
engage
parking
brake
and
to
lock
both
front
and
rear
wheels
with
wheel
chocks
b
Keep
your
foot
down
on
the
brake
pedal
while
depressing
the
accelera
tor
pedal
Otherwise
vehicle
surges
forward
dangerously
Notes
a
00
not
attempt
to
screw
the
idle
adjusting
screw
down
completely
Ooing
so
could
cause
damage
to
tip
which
in
turn
will
tend
to
cause
malfunctio11ll
b
If
idle
limiter
cap
obstructs
proper
adjustment
remove
it
To
install
idle
limiter
cap
refer
to
Idle
Limiter
Cap
c
After
idle
adjustment
has
been
made
shift
the
lever
to
the
N
or
P
position
for
automatic
trans
mission
d
When
measuring
CO
percentage
in
Engine
Fuel
b
Counties
1
219
m
4
000
ft
or
more
above
sea
level
have
been
designated
by
law
as
High
Altitude
Counties
For
further
details
refer
to
1977
OATSUN
PICK
UP
Service
Bulletin
Pub
No
257
0
I
Air
cleaner
rID
mOl
If
Low
altitude
Ll
n
n
L
n
Fig
EF
34
sert
probe
into
tail
pipe
more
than
40
em
15
7
in
CO
Idle
adjustment
with
CO
meter
Idle
mixture
adjustment
requires
the
use
of
a
CO
meter
especially
for
California
models
When
preparing
to
adjust
idle
mixture
it
is
essential
to
have
the
meter
thoroughly
warmed
up
and
calibrated
I
Check
carburetor
pipes
for
proper
connection
2
Warm
up
engine
until
water
tem
perature
indicator
points
to
the
middle
of
gauge
The
procedure
to
warm
up
engine
is
not
specifically
recom
mended
Either
driving
vehicle
or
oper
ating
engine
at
no
load
will
be
good
3
Make
sure
that
water
tempera
ture
indicator
points
to
the
middle
Further
keep
engine
running
at
about
2
000
rpm
for
about
5
minutes
with
out
applying
load
to
engine
in
order
to
stabilize
engine
condition
Engine
hood
should
be
open
4
Run
engine
for
about
10
minutes
at
idling
speed
Ouring
this
10
minutes
proceed
as
described
in
steps
5
to
9
below
5
Remove
air
hose
between
3
way
connector
5
way
connector
for
Cali
fornia
models
and
air
check
valve
as
EF
21
shown
in
Figure
EF
35
Plug
the
dis
connected
hose
to
prevent
dust
from
entering
0
o
EF259
Fig
EF
35
Disconnecting
air
hose
from
air
check
valve
6
Race
engine
I
500
to
2
000
rpm
two
or
three
times
under
no
load
then
run
engine
for
one
minute
at
idling
speed
7
Adjust
throttle
adjusting
screw
until
engine
is
at
specified
speed
Engine
speed
Manual
transmission
750
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
0
position
650
rpm
8
Check
ignition
timing
If
neces
sary
adjust
it
to
specifications
This
operation
need
not
be
carried
out
at
1
600
Ian
1
000
miles
service
Ignition
timing
Manual
transmission
120
750
rpm
Non
California
100
750
rpm
California
Automatic
transmission
in
0
position
120
650
rpm
9
At
about
10
minutes
after
engine
is
run
at
idling
speed
adjust
idle
adjusting
screw
so
that
CO
percentage
is
at
specified
level
CO
percentage
Manual
transmission
2
t
l
at
750
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
0
position
2
t
I
at
650
rpm
10
Repeat
procedures
as
described
in
steps
6
7
and
9
above
so
that
CO
percentage
is
at
specified
level
Check
ing
idle
CO
in
step
9
can
be
carried
out
right
after
step
7
II
Race
engine
1
500
to
2
000
Page 118 of 537

rpm
two
or
three
iimes
under
no
load
and
make
sure
that
specified
CO
per
centage
is
obtained
12
Connect
air
hose
to
air
check
valve
If
engine
speed
increases
readjust
it
to
the
specified
speed
with
throttle
adjustingsqew
CO
idle
edJustment
without
CO
meter
If
CO
meter
is
not
available
the
following
procedures
may
be
used
L
Check
carburetor
pipes
for
proper
connection
2
Warm
up
engine
until
water
tem
perature
indicator
points
to
the
middle
of
gauge
The
procedure
to
warm
up
engine
is
not
specifically
recom
mended
Either
driving
vehicle
or
oper
ating
engine
at
no
load
will
be
good
3
Make
sure
that
water
temperature
indicator
points
to
the
middle
Further
keep
engine
running
at
about
2
000
rpm
for
about
5
minutes
without
applying
load
to
engine
in
order
to
stabilize
engine
condition
Engine
hood
should
be
open
4
Run
engine
for
about
10
minutes
at
idling
speed
During
this
10
minutes
proceed
as
described
in
steps
5
to
9
below
5
Remove
air
hose
between
3
way
connector
5
way
connector
for
Cali
fornia
models
and
air
check
valve
shown
in
Figure
EF
35
Plug
the
dis
connected
hose
19
prevent
dust
from
entering
6
Race
engine
1
500
to
2
000
rpm
two
or
three
times
under
no
load
then
run
engine
for
one
minute
at
idling
speed
7
Adjust
throttle
adjusting
screw
so
that
engine
speeds
are
as
indicated
below
Engine
speed
Manual
transmission
815
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
670
rpm
8
Check
ignition
timing
if
neces
sary
adjust
it
to
the
value
required
by
specifications
This
operation
need
not
be
carried
out
at
1
600
km
1
000
miles
service
9
At
about
10
minutes
after
engine
Engine
Fuel
is
run
at
idling
speed
adjust
idle
adjusting
screw
until
maximum
rpm
is
obtained
10
Repeat
procedures
as
described
in
steps
6
7
and
9
above
until
engine
speed
at
best
idle
mixture
is
815
rpm
for
manual
transmission
models
and
670
rpm
for
automatic
transmission
models
in
D
position
Adjustment
in
step
9
can
be
carried
out
right
after
step
7
11
Turn
the
idle
adjusting
screw
clockwise
until
engine
speed
drops
off
below
specified
rpm
Engine
speed
drops
off
Manual
transmission
60
to
70
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
15
to
25
rpm
12
Connect
air
hose
to
air
check
valve
If
engine
speed
increases
readjust
it
to
the
specified
speed
with
throttle
adjusting
screw
Idle
limiter
cep
Do
not
remove
this
idle
limiter
cap
unless
necessary
If
this
unit
is
re
moved
it
must
be
readjusted
at
lime
of
installation
To
adjust
proceed
as
follows
I
After
adjusting
throttle
or
idle
speed
adjusting
screw
check
to
be
sure
that
the
amount
of
CO
contained
in
exhaust
gases
meets
the
established
standard
2
Install
idle
limiter
cap
in
position
making
sure
that
the
adjusting
screw
can
rotate
another
1
8
turn
in
the
CO
RICH
direction
Carbo
to
per
CO
rich
450
lIS
rotation
t
CO
lean
J
SQ
dl
lim
ET031
1
e
Iter
cap
Fig
EF
36
Setting
idle
limiter
cap
FUEL
LEVEL
1
Turn
down
float
chamber
to
al
low
float
to
come
into
contact
with
needle
valve
and
measure
Hu
shown
EF
22
in
Figu
re
EF
37
When
H
is
approximalely
7
mill
0
283
in
lOp
float
position
is
correct
The
top
float
position
can
be
ad
justed
by
bending
float
seat
Upon
completion
of
the
adjust
ment
check
fuel
level
wi
th
attached
level
gauge
p
j
i
I
it
I
Float
seat
2
Float
3
Float
chamber
4
Needle
valve
t
I
IIf
ET032
Fig
EF
37
Adjusting
float
level
2
Adjust
bottom
float
position
so
that
clearance
h
between
float
seat
and
needle
valve
stemis
I
3
to
L
7
mm
0
051
to
0
067
in
when
Iloat
is
fully
rals
n
Jloa
t
goppe
q
re
3
After
adjustments
in
steps
I
and
2
above
have
been
made
make
sure
that
when
fuel
is
delivered
to
the
float
chamber
the
fuel
level
is
maintained
within
the
range
of23
mm
0
91
in
as
shown
in
FigureEF
38
H
23
mm
0
91
in
EF260
Fig
EF
38
Checking
ruellevel
FAST
IDLE
I
With
carburetor
assembly
reo
moved
from
engine
measure
throttle
valve
clearance
A
with
a
wire
gauge
placing
the
upper
side
of
fast
idling
screw
on
the
first
step
on
fast
idling
cam
Page 126 of 537

Engine
Fuel
DISASSEMBLY
AND
ASSEMBLY
ff
C
oI
Q
f
@
ID
J
@
tJ
@
1
Lock
lever
2
Filter
set
screw
3
Fuel
filter
4
Fuel
nipple
5
Needle
valve
body
6
Needle
valve
7
Fuel
chamber
parts
8
Accelerating
pump
parts
9
Altitude
compensator
pipe
California
models
tng
ail
bleed
adJ
@
@1
@
A
Choke
chamber
B
Center
body
C
Throttle
chamber
I
J
@
EF725
EF30
11
High
speed
enricher
air
bleed
12
Choke
valve
13
Accelerating
pump
lever
14
Throttle
return
spring
15
Accelerating
pump
rod
16
Automatic
choke
cover
17
Automatic
choke
body
and
diaphragm
chamber
18
Richer
jet
19
Coasting
air
bleed
I
20
Primary
main
jet
21
Secondary
main
jet
22
Secondary
slow
air
bleed
23
Secondary
slow
jet
24
Plug
25
Air
bleed
26
Coasting
jet
27
Secondary
main
air
bleed
28
Power
valve
29
Primary
main
air
bleed
30
Plug
31
Primary
slow
jet
32
No
2
primary
slow
air
bleed
33
Primary
and
secondary
small
venturi
34
Venturi
stopper
screw
35
Choke
connecting
rod
36
Anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
37
Fast
idle
cam
38
Diaphragm
chamber
parts
39
Idle
limiter
cap
40
Idle
adjust
screw
41
Idle
adjust
screw
spring
42
Throttle
adjust
screw
3
Thr9ttle
dj
t
5Crew
spring
44
Primary
and
secondary
throttle
valve
45
B
C
D
D
California
models
46
Vacuum
control
solenoid
valve
47
B
C
D
D
Non
Califomia
models
Note
Do
not
remove
the
parts
marked
with
an
asterisk
Ill
@ff
Fig
EF
62
Carburetor
part